躯干控制测量量表在脑性瘫痪中的应用进展
谭朱江,张丹婷,赵秋旭,曹建国
深圳市儿童医院康复科,广东深圳市518038
Chae等[1]认为,复杂躯体活动是完成高级运动技能的先决条件,躯干控制则是进行复杂躯体活动的先决条件。躯干作为身体的中心,是支持肢体活动、重心调节和其他一切活动的基础,对人体姿势平衡、运动功能活动及日常生活能力具有重要作用[2-6]。脑瘫是一组由于发育中胎儿或婴幼儿脑部非进行性损伤所致的持续存在的中枢性运动和姿势发育障碍、活动受限症候群,常表现为躯干控制不良和平衡反应欠佳,从而造成姿势控制不良,日常生活活动和功能由此受到显著限制[7-10]。目前,有许多临床工具用于评估脑瘫患者坐位躯干控制能力,但这些工具只适合评估脑瘫患者坐位躯干控制的静动态平衡能力[11]。
为了准确、有效地评估脑瘫患者坐位躯干控制下所有的功能和活动,并评估基于功能活动的躯干控制的基本要素,Heyrman等[12]开发了躯干控制测量量表(Trunk Control Measurement Scale,TCMS),它是目前评估脑瘫患者躯干控制较全面、准确的测量量表[13]。随着研究发展深入,研究人员还进行TCMS与其他功能性量表的关联性研究,如躯干控制能力与上肢功能、下肢功能、粗大运动功能等之间的关系[14-16]。TCMS具有高信度和高效度,是评估脑瘫患者坐位躯干控制能力的合适且可靠的量表[17]。目前国内尚未引进TCMS,在脑瘫患者的评估和治疗中,对躯干控制没有足够准确、全面的测量方法,临床上躯干控制训练的针对性和有效性较差。
本文详细介绍TCMS的评估方法及其在国外的应用现状,期待将来能够引进国内,用于指导临床。
1 TCMS评估方法与内容
1.1 评估方法
①受试者脱掉矫形器、鞋子或者躯干绷带。
②每一项目的起始姿势均相同。受试者坐在治疗床的边缘,背部、手臂和脚不能支撑,大腿紧贴桌子。
③双手贴着身体并放松地置于腿上。受试者在开始每个项目之前都会被要求坐直,在完成任务的表现过程中需要维持直立姿势。“直立”是指的是受试者能够执行的最直坐姿,因人而异,是识别患者是否畸形或者代偿的参考姿势。每个项目重复执行3次,选择最好的表现得分计入总分。
④受试者在完成分量表的任务时,若静态平衡需要单手支撑,仅允许将手平放于桌面,不允许紧抓。
1.2 评估内容
①静态坐位平衡:测试受试者在没有支持的情况下保持静态稳定姿势的能力。
②选择性运动控制:主动的或预期的平衡调整,检查受试者的动态平衡能力。
③动态可达性:即反应性平衡,检查受试者在短暂的扰动后保持或恢复平衡的能力。
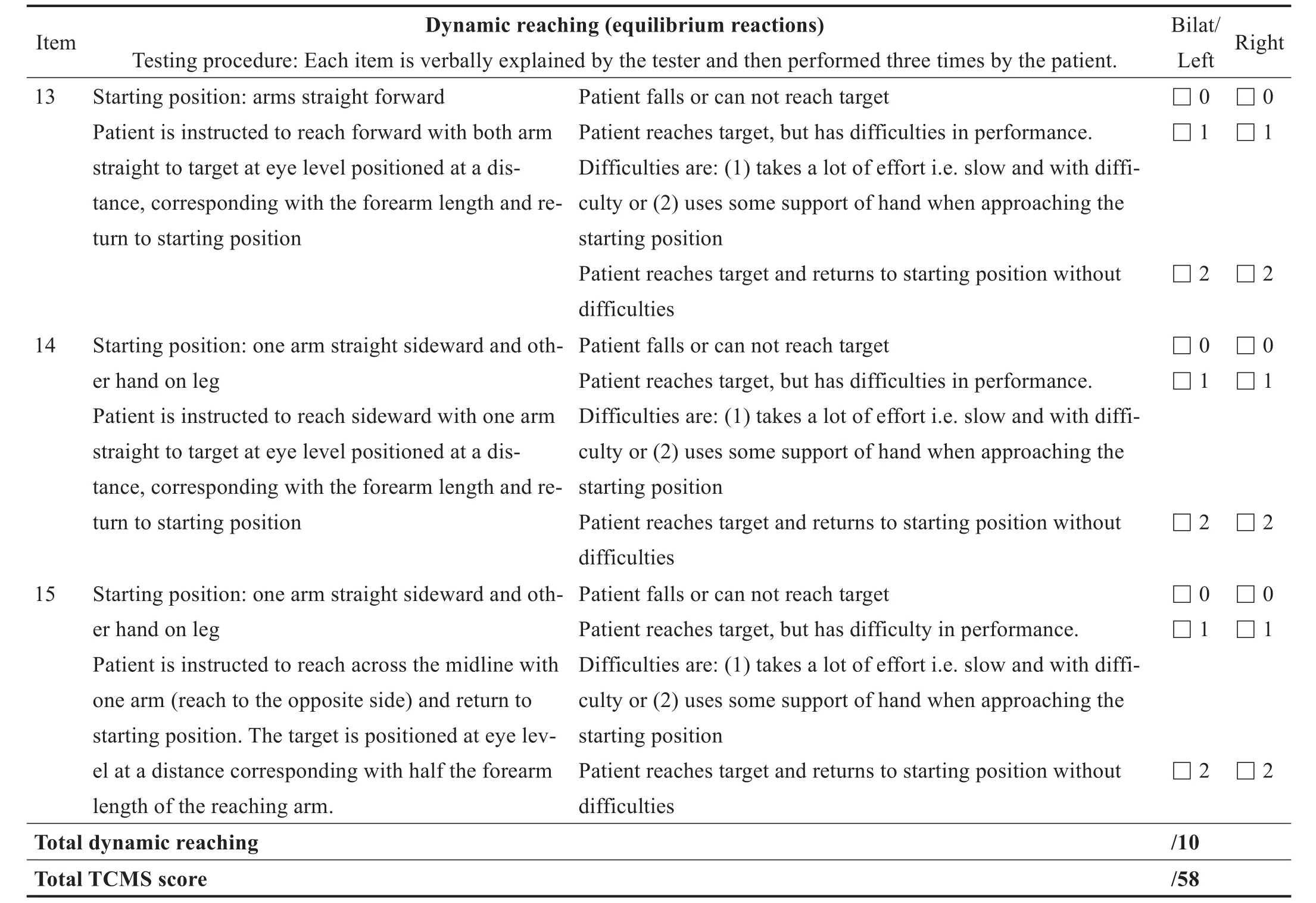
对TCMS总分及3个子量表进行评价,总分的最大值为58分,包括静态坐位平衡测试(5项,20分)和动态坐位平衡测试(10项),后者包括选择性运动控制(7项,28分)和动态可达性测试(3项,10分)[11-12,18]。见附表。
2 TCMS适用范围
TCMS适用于评估5岁及以上神经运动功能障碍患者,包括脑瘫、获得性脑损伤、脊髓损伤、脊髓脊膜膨出、皮质网状束损伤等[19-21],其中在脑瘫患者功能评估中应用最为广泛。
3 TCMS信度和效度
Heo等[17]、Heyrman等[12,22]和Jeon等[18]对痉挛型脑瘫患者进行研究,结果均表明TCMS在评估痉挛型脑瘫患者时具有高的信度和效度,以及较高重测信度和评分者间信度。此外,TCMS是评估痉挛型脑瘫患者躯干控制能力合适、可靠的工具,且该量表可反映脑瘫患者躯干控制的优势和劣势,可有效判断脑瘫患者躯干损害程度,并为改善患者整体功能水平的治疗干预方案提供具体线索。
Marsico等[20]调查TCMS及其子量表在脑瘫、获得性脑损伤和脊髓损伤等神经运动障碍患者中的信度和效度;其中,90例神经运动障碍患者(年龄5~18岁,平均11岁)参加信度研究,50例神经运动障碍患者(年龄5~18岁,平均11岁)参与效度研究;结果表明TCMS在5岁以上神经运动障碍患者中具有良好的信度和效度。此外,他们通过对患者的TCMS评分和功能独立性量表(Functional Independence Measure,FIM)评分进行比较来判别TCMS的有效性,结果显示,若静态平衡评分小于80%、动态可达性评分小于55%或选择性运动控制评分小于35%左右的患者,在日常生活活动中需要辅助。
TCMS评估脑瘫患者具有较高的信度与效度,以及较高重测信度和评估者间信度,且TCMS评估其他神经运动障碍患者也具有良好的信度和效度。
4 TCMS与同类量表比较
坐姿量表(Level of Sitting Scale,LSS)、坐姿姿势控制量表(Seated Postural Control Measure,SPCM)以及脊柱校准和运动范围量表(Spinal Alignment and Range of Motion Measure,SAROMM)已在临床实践中用于评估脑瘫患者的躯干控制能力[23-25],但它们只适用于评估患者的静态坐位平衡和动态坐位平衡,不能检测出患者的反应性平衡。TCMS总评分能够准确有效评估脑瘫患者的静态坐位平衡、动态坐位平衡和反应性平衡的能力。TCMS评估内容范围较为全面,具有较高的可靠性和有效性[26]。
Bañas等[27]通过研究后得出,TCMS评分与粗大运动功能测量(Gross Motor Function Measure,GMFM)评分之间相关程度高于儿童伸手测试(Pediatric Reach Test,PRT)评分,表明TCMS较PRT可以更准确地评估脑瘫患者运动功能水平;且SPCM、神经运动功能障碍儿童坐位评估(Sitting Assessment for Children with Neuromotor Dysfunction,SACND)和躯干控制的分段评估(Segmental Assessment of Trunk Control,SATCo)评估前均需要准备具有规定尺寸的特定材料,而TCMS不涉及任何设备和材料,只需患者能够遵循口头指示,即可进行评估,可节约大量成本。
此外,Hong[28]等对躯干损伤量表(Trunk Impairment Scale,TIS)和TCMS的结构效度和反应性进行比较,结果显示TCMS是TIS的扩展版本,虽然评估比TIS更耗时,但TCMS有更高的检测躯干功能变化的潜力,因为它包含更多更细化的评估项目。
总之,TCMS是目前衡量功能活动期间躯干控制稳定的基础和躯干控制下的主动运动的唯一量表[29]。它可以更有效、全面地评估脑瘫患者静态和动态下躯干控制能力及变化;鉴于TCMS在临床康复中具有高度可靠性、有效性,建议广泛用于临床实践。
5 TCMS与其他功能量表关联性研究
为研究躯干控制能力与上肢功能之间的关系,Kim等[14]选用上肢技巧质量测试(Quality of Upper Extremity Skills Test,QUEST)评估15例脑瘫患者的上肢操作水平,同时对患者进行TCMS评分,结果显示患者的QUEST得分与TCMS得分呈正相关。考虑到躯干功能与上肢的灵活性、协调性及抓握能力的相关性,可以认为TCMS评分结果对于脑瘫患者的上肢功能具有一定的提示作用。
为研究躯干控制能力与下肢功能之间的关系,Balzer等[15]使用改良Ashworth量表、徒手肌力评定(Manual Muscle Test,MMT)、下肢选择性控制评估(Selective Control Assessment of Lower Extremity,SCAOTLE)和TCMS对52例脑瘫患者分别进行评定,结果显示,在分别以肌肉力量和下肢的选择性控制以及年龄为自变量的回归模型中,躯干控制能力是步态能力的最强预测因子,且患者的下肢肌肉力量、下肢选择性控制与躯干控制能力之间表现出强相关性。
为研究坐位躯干控制能力与粗大运动功能能力之间的关系,Seyyar等[16]使用TCMS、GMFM-88和儿童残疾评估功能性技能领域测试(PEDI-FSD)评估58例痉挛型脑瘫患者,应用Spearman相关分析将TCMS的得分与GMFM-88和PEDI-FSD的得分分别进行关联比较,结果表明TCMS与两者均呈高度正相关。由此得出,TCMS可为痉挛型脑瘫患者的粗大运动功能评估提供有价值的信息。
为研究躯干控制能力与平衡功能之间的关系,Panibatla等[29]使用TCMS和儿童平衡量表(Paediatric Balance Scale,PBS)评估24例痉挛型脑瘫患者,结果显示TCMS评分与PBS评分显著相关,且TCMS评分越高的患者,其PBS评分也越高。由此可见,痉挛型脑瘫患者的躯干控制能力与平衡能力之间呈高度正相关。
为研究伴有尿失禁的痉挛型双瘫脑瘫患者的躯干控制能力与尿失禁之间的关系,Talu[30]使用功能性失调和失禁症状评分问卷(Dysfunctional Voiding and Incontinence Symptoms Score,DVISS)、功能障碍性排尿症状评分(Dysfunctional Voiding Symptom Score,DVSS)、MMT和TCMS对50例痉挛型双瘫脑瘫患者进行评估,结果显示,DVISS和DVSS评分与腹部肌肉力量、TCMS评分之间存在高度负相关关系;此外,研究者发现粗大运动功能分级系统(Gross Motor Function Classification System,GMFCS)和DVISS以及GMFCS和DVSS之间均存在高度正相关关系。GMFCS评级越高,DVISS和DVSS评分越高,TCMS评分越低,提示痉挛型双瘫脑瘫患者的躯干控制能力与尿失禁症状之间呈高度负相关。
6 小结
TCMS是目前评估脑瘫患者躯干控制较全面、准确的测量量表,适于评估坐姿躯干姿势控制下所有功能活动,观察患者躯干姿势控制的优势与劣势,有效区分患者日常生活活动的独立性与依赖性,可为临床治疗提供指导,为通过干预躯干控制来改善患者的功能活动提供依据。此外,TCMS也可与其他功能量表联合检测,为脑瘫患者的功能能力提供更详细更有价值的信息,更全面地评估患者目前的运动功能水平,为改善患者整体功能水平的治疗干预方案提供具体线索,从而提高患者的生活质量。同时,TCMS适用于5岁及以上患有各类神经损伤患者的躯干功能评估,虽然目前相关文献研究报道较少,尚无足够研究证据支持,但相信将来相关研究会越来越多、越来越深入。鉴于TCMS的各种优良特性,我们期待未来能将其引进国内,丰富脑瘫患者功能评估内容,指导治疗,评定治疗效果,造福更多的脑瘫患者。
附录:Trunk Control Measurement Scale
Right Item 1 Static Sitting Balance Testing procedure:Each item is verbally explained to the patient and demonstrated by the tester if needed.Starting position(unsupported sitting,hands on legs)Patient isinstructed to sit upright and hold this position for 10 seconds Bilat/Left□0□1□2 2Starting position Patient lifts both arms at eye height in one second and returns to starting position□0□1 3Starting position Therapist crosses one leg over the other leg□2□0□0 Patient falls or can only maintain upright sitting with double arm support Patient can only maintain upright sitting with single arm support for 10 seconds Patient can maintain upright sitting without arm support for 10 seconds If score=0,then total score=0 Patient falls or can not lift arms Patient can lift arms without falling but with compensations.Possible compensations are:(1)backward lean,(2)increase of trunk flexion,(3)lateral flexion,and(4)other Patient liftsarms without compensations Patient falls,can not cross legs or can only maintain sitting with double arm support Patient can maintain sitting with single arm support for 10 seconds Patient can maintain sitting without arm support for 10 seconds Patient falls,can not cross legs or can only cross legs with double arm support Patient can only cross legs with single arm support Patient crosses legs without arm support but with clear trunk displacement Patient crosses legs with minimal trunk displacement Patient falls,can not abduct leg or can only abduct leg with double arm support Patient can only abductleg with singlearm support Patient abducts leg without arm support but with clear trunk displacement Patient abducts leg with minimal trunk displacement□1□1□2□2 4Starting position Patient crosses one leg over the other leg(assistance with one hand is allowed)'minimal'=small trunk movements without signs of imbalance of trunk during movement of leg'clear'=clear signs of imbalance i.e.lateral flexion or flexion of trunk□0□0□1□1□2□2□3□3 5Starting position Patient abducts one leg over 10 cm and returns to starting position(10 cm width=width of the knee)'minimal'=small trunk movements without signs of imbalance of trunk during movement of leg'clear'=clear signs of imbalance i.e.lateral flexion or flexion of trunk□0□0□1□1□2□2□3□3 Total static sitting balance /20

Dynamic Sitting Balance Item Bilat/Left Right 6a Selective movement control Testing procedure:Firstly,each item is verbally explained and demonstrated by the tester.Secondly,the item is demonstrated on the patient with manual guidance.Thirdly,the patient is asked to perform the expected movement under manual guidance of the tester.Then,the patient performs the item on its own in three attempts.Starting position:arms crossed over chest Patient is instructed to lean forward with a fixed trunk for approximately 45°and return to starting position normal righting reaction of the head i.e.limited head extension is not scored as a compensation Patient falls or can not reach target position Patient can lean forward If score=0,then item 6b=0□0□1 6b 7a Starting position:arms crossed over chest Patient is instructed to lean backward with a fixed trunk for approximately 45°and return to starting position normal righting reaction of the head i.e.limited head flexion is not scored as a compensation Patient compensates(1)increased head extension,(2)increased trunk flexion,(3)increased lumbar lordosis,(4)increased knee flexion,and(5)other Patient leans forward without compensations Patient falls or can not reach target position Patient can lean backward If score=0,then item 7b=0□0□1□0□1 7b □0 8a Starting position Patient is instructed to touch the table with the elbow at level of the femoral head(by shortening the ipsilateral side and lengthening the contralateral side)and return Patient compensates(1)increased head flexion,(2)increased trunk flexion,(3)increased knee extension,and(4)other Patient leans backward without compensations Patient falls or does not touch the table with the elbow Patient can touch the table with the elbow If score=0,then item 8b and 8c=0□1□0□1□0□1 8b □0□0 Patient demonstrates(1)no shortening/lengthening or(2)opposite shortening/lengthening Patient demonstrates expected shortening/lengthening If score=0,then item 8c=0 Patient compensates:(1)increased trunk flexion,(2)forwardor backward lean,(3)pelvic lift,and(4)other Patient touches the table without compensations Patient falls or can not lift the pelvis Patient can lift the pelvis If score=0,then item 9b and 9c=0□1□1 8c □0□0 9a Starting position Patient is instructed to lift the pelvis at one side and return to starting position.No lifting of the thigh is allowed.□1□0□1□1□0□1
续表
Dynamic Sitting Balance Item Selective movement control Testing procedure:Firstly,each item is verbally explained and demonstrated by the tester.Secondly,the item is demonstrated on the patient with manual guidance.Thirdly,the patient is asked to perform the expected movement under manual guidance of the tester.Then,the patient performs the item on its own in three attempts.Bilat/Left Right 9b □0□1□0□1 9c□2□0□2□0□1 10a Starting position:arms crossed over chest Patient is instructed to rotate the upper trunk three times with head fixated in starting position.The movement is initiated from the shoulder girdle.□1□0□1□2 10b 11a Starting position:arms crossed over chest Patient is instructed to rotate the upper trunk three times with head fixated in starting position.The movement is initiated from the shoulder girdle.□0□1□0□1□2 11b 12a Starting position:arms crossed over chest Patient is instructed to shuffle the pelvis three times in a forward direction and return backwards in three times to the starting position Shuffle movement=combination of lateral flexion and rotation with the pelvis,alternated left and right□1□2□0□1□2 12b Patient demonstrates no shortening/lengthening Patient demonstrates partially expected shortening/lengthening(partial=short and/or small ROM)Patient demonstrates expected shortening/lengthening If score=0,then item 9c=0 Patient compensates:(1)contralateral head flexion,(2)marked lateral trunk displacement,and(3)other Patient lifts the pelvis without compensations Patient(1)falls,(2)can not rotate the upper trunk i.e.patient can not perform the rotation movement,even not with the entire trunk,or(3)demonstrates no selective rotation of the upper trunk(en bloc)Patient demonstrates partial selective rotation of the upper trunk(partial=asymmetrical,small ROM,more shoulders than trunk)Patient demonstrates expected selective rotation of the upper trunk If score=0,then item 10b=0 Patient rotates the upper trunk with head rotation Patient rotates the upper trunk without head rotation Patient(1)falls,(2)can not rotate the lower trunk i.e.patient can not perform the rotation movement,even not with the entire trunk,or(3)demonstrates no selective rotation of the lower trunk(en bloc)Patient demonstrates partial selective rotation of the lower trunk(partial=asymmetrical,small ROM,additional movement of upper trunk)Patient demonstrates expected selective rotation of the lower trunk If score=0,then item 11b=0 Patient compensates with pelvic tilt Patient rotates the lower trunk without compensations Patient falls or can not shuffle the pelvisin forward and backward direction i.e.no displacement of the body in either direction Patient can partially shuffle the pelvis(partial=with mainly lateral flexion and little rotation;small ROM;takes a lot of effort)Patient can shuffle the pelvis by use of both lateral flexion and rotation in one direction and partially in the other direction Patient can shuffle the pelvis by use of both lateral flexion and rotation in both directions If score=0,then item 12b=0 Patient compensates with excessive trunk displacement Patient shuffles pelvis without compensations Total selective movement control□3□1□2/28
注:TCMS英文版已获原作者Lieve Heyrman许可:(Iam very pleased with your interest in the TCMSand your initiative to translate it into Chinese.Therefore,Igive you the permission to use the TCMSand to start up the translation process of the TCMS.Iwish you the best with your work on this.)
Item 13 Dynamic reaching(equilibrium reactions)Testing procedure:Each item is verbally explained by the tester and then performed three times by the patient.Starting position:arms straight forward Patient isinstructed to reach forward with both arm straight to target at eye level positioned at a distance,corresponding with the forearm length and return to starting position Bilat/Left□0□1 Right□0□1 Patient falls or can not reach target Patient reaches target,but has difficulties in performance.Difficulties are:(1)takes a lot of effort i.e.slow and with difficulty or(2)usessome support of hand when approaching the starting position Patient reaches target and returns to starting position without difficulties Patient falls or can not reach target Patient reaches target,but has difficulties in performance.Difficulties are:(1)takes a lot of effort i.e.slow and with difficulty or(2)usessome support of hand when approaching the starting position Patient reaches target and returns to starting position without difficulties Patient falls or can not reach target Patient reaches target,but has difficulty in performance.Difficulties are:(1)takes a lot of effort i.e.slow and with difficulty or(2)usessome support of hand when approaching the starting position Patient reaches target and returns to starting position without difficulties□2□2 14Starting position:one arm straight sideward and other hand on leg Patient isinstructed to reach sideward with one arm straight to target at eye level positioned at a distance,corresponding with the forearm length and return to starting position□0□1□0□1□2□2 15Starting position:one arm straight sideward and other hand on leg Patient isinstructed to reach across the midline with one arm(reach to the opposite side)and return to starting position.The target ispositioned at eye level at a distance corresponding with half the forearm length of the reaching arm.□0□1□0□1□2□2 Total dynamic reaching Total TCMSscore/10/58

