右美托咪定、咪达唑仑对急性左心衰竭机械通气患者的镇静作用
张裕生
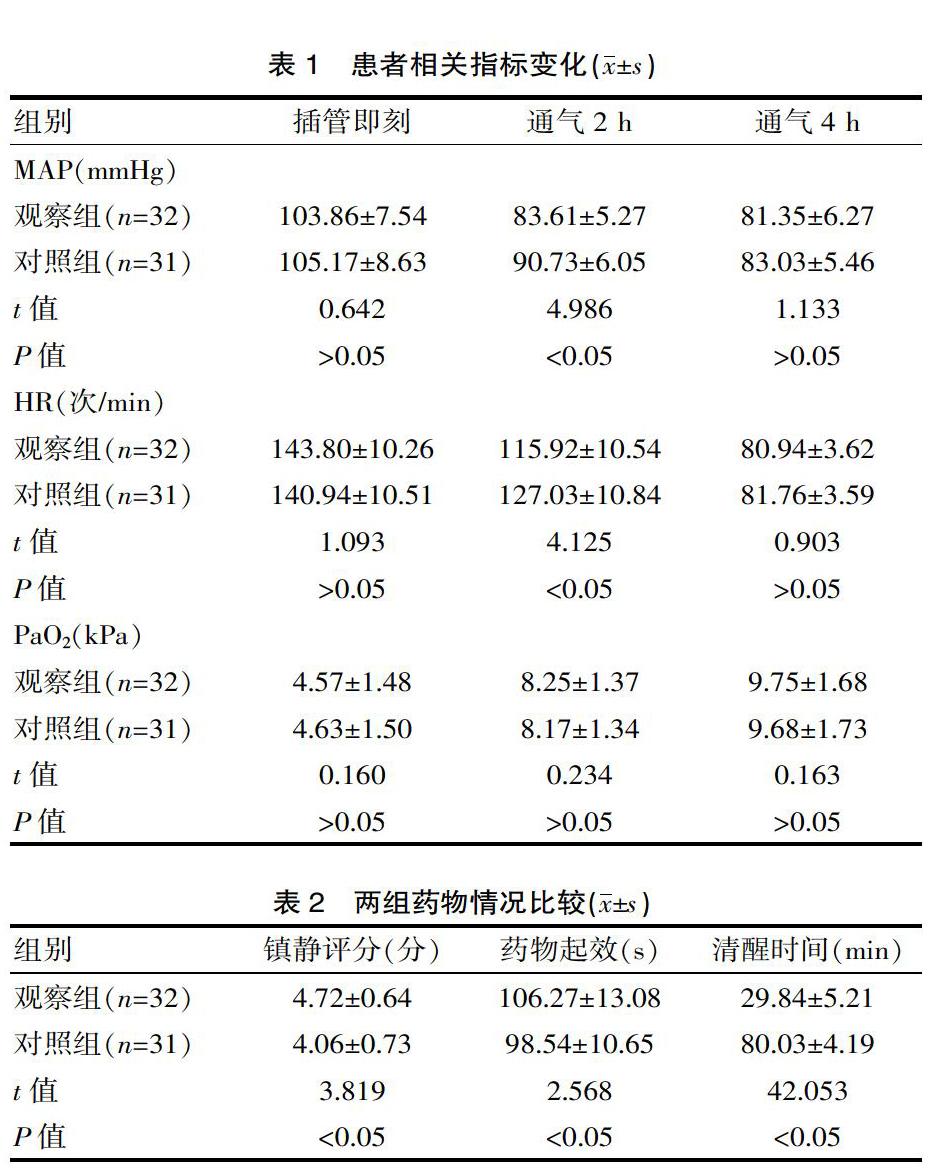
[摘要] 目的 分析急性左心衰竭(ALHF)者行機械通气时分别应用右美托咪定、咪达唑仑临床镇静效果差异。方法 方便选取2018年1—10月期间63例ALHF行机械通气者为研究对象,按治疗小组不同分组,对照组患者应用咪达唑仑镇静(共31例)、观察组以右美托咪定镇静(共32例),对不同时间段两组循环、呼吸指标变化情况进行观察,比较患者药物起效、清醒时间、镇静评分差异,统计治疗期间不良反应发生情况。 结果 两组插管即刻、通气4 h相关循环呼吸指标水平比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),通气2 h时对照组MAP、HR为(90.73±6.05)mmHg、(127.03±10.84)次/min高于观察组(83.61±5.27)mmHg、(115.92±10.54)次/min,(t=4.986,4.125,P<0.05);观察组镇静评分、药物起效、清醒时间依次为(4.72±0.64)分、(106.27±13.08)s、(29.84±5.21)min,对照组为(4.06±0.73)分、(98.54±10.65)s、(80.03±4.19)min,组间比较观察组镇静好、药物起效慢、清醒用时短(t=3.819,2.568,42.053,P<0.05);同时两组不良反应比较,观察组发生率6.25%低于对照组16.13%(χ2=4.911,P<0.05)。 结论 对ALHF行机械通气者以右美托咪定进行镇静诱导、通气镇静维持,通气期间患者循环、呼吸功能影响小,镇静效果良,清醒用时短,不良反应发生少,安全性高。
[关键词] 镇静;咪达唑仑;机械通气;右美托咪定;急性左心衰竭
[中图分类号] R614 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1674-0742(2019)05(c)-0125-03
[Abstract] Objective To analyze the clinical sedative effects of dexmedetomidine and midazolam in patients with acute left heart failure (ALHF). Methods Convenient select sixty-three patients with ALHF mechanical ventilation were enrolled in the study from January to October 2018. The patients were divided into different groups according to the treatment methods. The patients in the control group were treated with midazolam (31 cases) and the observation group was sedated with dexmedetomidine (32 total). For example, the changes of the circulation and respiratory indexes of the two groups were observed at different time periods, and the differences in drug onset, waking time and sedation score were compared, and the adverse reactions occurred during the treatment. Results There was no difference in the levels of circulatory respiration between the two groups immediately after intubation and ventilation for 4 h(P>0.05). The MAP and HR of the control group were (90.73±6.05) mmHg and (127.03±10.84) times/min higher than the observation group of (83.61±5.27) mmHg, (115.92±10.54) times/min(t=4.986, 4.125, P<0.05); observation group of sedation score, drug onset, awake time were (4.72±0.64) points, (106.27±13.08) s, (29.84±5.21) min, the control group was (4.06±0.73)points, (98.54±10.65) s, (80.03±4.19) min. The sedation was good and the drug started slowly. The time of awake was short (t=3.819, 2.568,42.053, P<0.05). At the same time, the incidence of 6.25% in the observation group was 16.13% lower than that in the control group (χ2=4.911, P<0.05). Conclusion In patients with mechanical ventilation of ALHF, dexmedetomidine is used for sedation induction and sedation. During ventilating, with little influence on circulation and respiratory function, good sedation effect, short awake time, less adverse reactions and high safety.

