标准大骨瓣减压术治疗大面积脑梗死的效果及对ET、BNP的影响
谢嘉涛
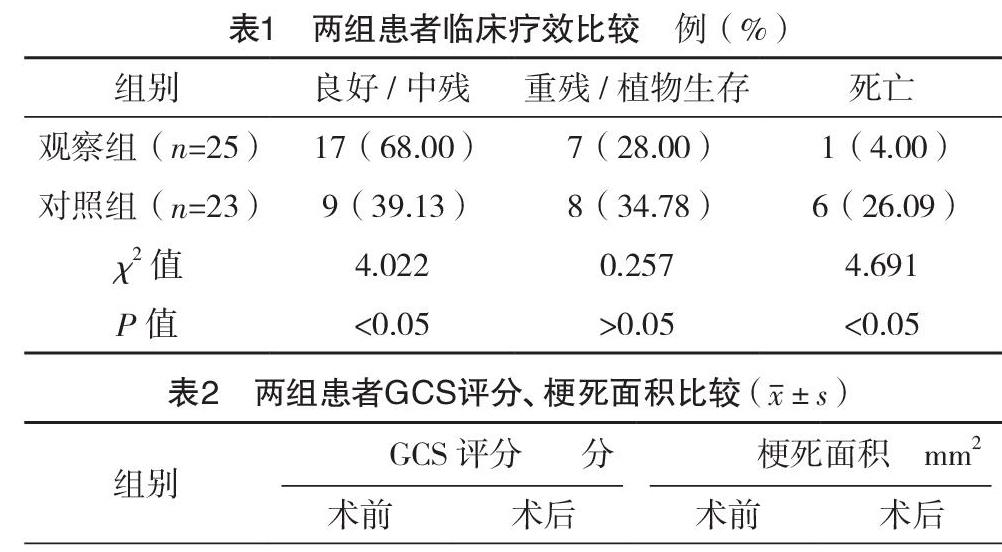
【摘要】 目的:探讨标准大骨瓣减压术治疗大面积脑梗死的效果及对ET、BNP的影响。方法:选取本院于2017年1月-2018年8月收治的大面积脑梗死患者48例,按照手术方法不同分为对照组(23例)和观察组(25例),对照组采用传统去骨瓣减压术治疗,观察组采用标准大骨瓣减压术治疗。比较两组患者手术前后GCS评分、梗死面积、血浆脑钠肽(BNP)和内皮素(ET)水平、临床疗效及不良反应发生情况。结果:观察组良好/中残率为68.00%,显著高于对照组的39.13%(P<0.05);观察组死亡率为4.00%,显著低于对照组的26.09%(P<0.05);观察组的重残/植物生存率与对照组比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。术后,观察组GCS评分明显高于对照组,梗死面积明显小于对照组(P<0.05)。两组患者术后ET、BNP水平均低于术前,且观察组ET、BNP水平均明显低于对照组(P<0.05)。观察组患者不良反应发生率为16.00%,显著低于对照组的47.83%,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论:标准大骨瓣减压术治疗大面积脑梗死可显著提高临床疗效,缩小梗死面积,减少死亡率,降低ET、BNP水平,且不良反應少。
【关键词】 标准大骨瓣减压术; 大面积脑梗死; 脑钠肽; GCS评分
【Abstract】 Objective:To investigate the effect of standard large bone flap decompression in the treatment of massive cerebral infarction and its influence on ET and BNP.Method:48 patients with massive cerebral infarction admitted to our hospital from January 2017 to August 2018 were selected,according to different surgical methods,the patients were divided into control group(23 cases)and observation group(25 cases).The control group was treated with traditional decompressive craniectomy,while the observation group was treated with standard decompressive craniectomy.The GCS score,infarct size,plasma BNP,ET levels,clinical efficacy and adverse reactions were compared between the two groups before and after operation.Result:The good/moderate disability rate in the observation group was 68.00%,significantly higher than 39.13% in the control group(P<0.05),the mortality rate in the observation group was 4.00%,significantly lower than 26.09% in the control group(P<0.05),the rate of heavy residue/plant survival in the observation group was not significantly different from that in the control group(P>0.05).After operation,the GCS score of the observation group was significantly higher than that of the control group,and the infarct area was significantly smaller than that of the control group(P<0.05).After operation,ET and BNP levels in both groups were lower than those before operation,and the ET and BNP levels in the observation group were significantly lower than those in the control group(P<0.05).The incidence of adverse reactions in the observation group was 16.00%,significantly lower than 47.83% in the control group,the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05).Conclusion:Standard large bone flap decompression for the treatment of large cerebral infarction can significantly improve the clinical efficacy,reduce the infarct area,reduce the mortality,reduce the level of ET and BNP,and have fewer adverse reactions.

