稽留流产采用舌下含服、阴道给药及口服给予米索前列醇终止妊娠的优劣差异
黎小红 黎绮红 阮翠梨

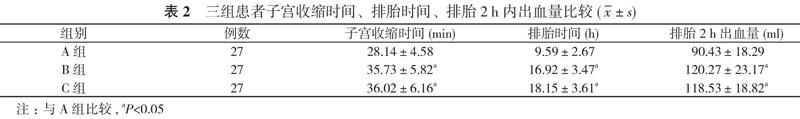
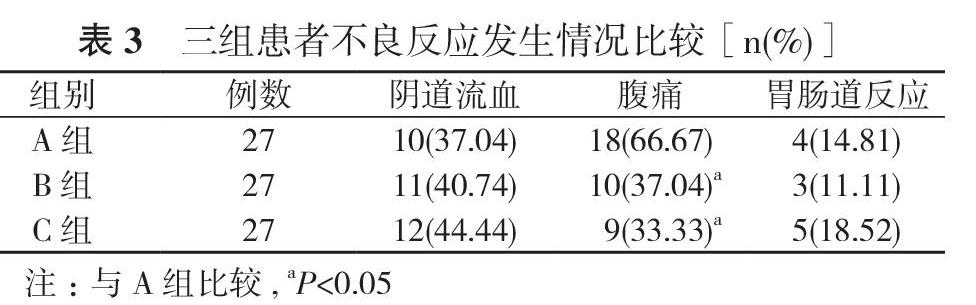
【摘要】 目的 比較稽留流产采用舌下含服、阴道给药及口服米索前列醇终止妊娠的效果。方法 81例稽留流产患者, 按照随机数字表法分为A组、B组和C组, 各27例。A采用舌下含服米索前列醇, B组采用阴道给予米索前列醇, C组采用口服米索前列醇。比较三组的临床效果、子宫收缩时间、排胎时间、排胎2 h内出血量及不良反应发生情况。结果 A组有效率为92.59%, B组有效率为70.37%, C组有效率为40.74%;A组有效率高于B组和C组, B组高于C组, 差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。A组患者的子宫收缩时间(28.14±4.58)min、排胎时间(9.59±2.67)h明显短于B组患者的(35.73±5.82)min、(16.92±3.47)h和C组患者的(36.02±6.16)min、(18.15±3.61)h, 排胎2 h出血量(90.43±18.29)ml明显少于B组患者的(120.27±23.17)ml和C组患者的(118.53±18.82)ml, 差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。A组患者腹痛发生率明显高于B、C组患者, 差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);三组患者阴道流血、胃肠道反应发生率比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。结论 稽留流产采用舌下含服米索前列醇治疗的临床疗效明显优于阴道及口服给药, 但腹痛现象明显, 临床上应合理选择治疗方式。
【关键词】 稽留流产;舌下含服;阴道给药;米索前列醇;终止妊娠
【Abstract】 Objective To compare the effect of sublingual administration, vaginal administration and oral administration of misoprostol for termination of pregnancy in missed abortion. Methods A total of 81 patients with missed abortion were divided by random number table into group A, B and C, with 27 cases in each group. Group A received sublingual administration of misoprostol, group B received vaginal administration of misoprostol, and group C received oral administration of misoprostol. Comparison were made on clinical effect, uterine contraction time, abortion time, bleeding volume within 2 h of abortion and occurrence of adverse reactions in three groups. Results Group A had effective rate as 92.59%, which was 70.37% in group B and 40.74% in group C. Group A had higher effective rate than group B and C, group B was higher than group C. Their difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Group A had obviously shorter uterine contraction time as (28.14±4.58) min, abortion time as (9.59±2.67) h than (35.73±5.82) min, (16.92±3.47) h in group B, and (36.02±6.16) min, (18.15±3.61) h in group C, and obviously less bleeding volume within 2 h of abortion as (90.43±18.29) ml than (120.27±23.17) ml in group B and (118.53±18.82) ml in group C. Their difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Group A had obviously higher incidence of abdominal pain than group B and C, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Three groups had no statistically significant in incidence of vaginal bleeding and gastrointestinal reactions (P>0.05). Conclusion Sublingual administration of misoprostol shows obviously better clinical efficacy than viginal and oral administration, but the abdominal pain is obvious. So the treatment method should be rationally selectod in clinic.

