多角度、多层次解读阅读语篇
曹寅珺
摘 要:为了有效地开展试卷讲评课,教师在讲评课上可采用支架式教学和合作学习的方式,帮助学生多角度、多层次地解读语篇的语言和文脉。本文结合高三英语模拟考试中的完形填空题型,探讨如何开展高效、深入的试卷讲评教学。
关键词:核心素养;试卷讲评;学习支架;合作学习
前言
试卷讲评课是教师经过批卷、数据分析、错误研究后进行的纠错以及巩固知识的课型。不同于听说课和读写课,试卷讲评课上极易出现“教师一言堂,学生被动听”的现象,或者出现教师蜻蜓点水地指出学生在考试中的错误,讲解正确答案,对所考语篇挖掘深度不够等问题。
《普通高中英语课程标准(2017年版)》(以下简称《课标》)指出,完整的教学活动包括教、学、评三方面,教师应处理好教和学之间的关系,推动教、学、评一体化实施(中华人民共和国教育部,2018)。这里的“评”,不仅仅指测试这样的教学评价,也包括测试过后的评讲和反馈。《课标》还指出,在评价活动中,教师的提问和反馈也是重要的评价手段,教师应深度挖掘语篇意义和文脉,同时“反馈要关注师生、生生有意义的互动,促进学生高层次思维和文化意识的发展。”(中华人民共和国教育部,2018)由此可见,试卷讲评课不是对标准答案的复读和解释,不是对知识点讲解的集合, 更不应是教师单方面的展示和灌输。
在本课例中,教师在评价反馈中采用“小老师”教学方法,根据学情邀请有特长的学生担任“小老师”,分享背景知识和相关词汇,采用合作教学的方式帮助学生理解语篇中的词块搭配、指代关系及句子信息展开方式等语篇微组织结构;并采用支架式教学,帮助学生掌握语篇的文脉,再进一步进行主题拓展阅读。整个反馈过程以评促学,有较多师生、生生互动,有利于培养学生的学习策略,形成思维深度。
下面笔者结合高三英语模拟考试中的一篇完形填空题目,探讨如何在试卷讲评课上指导学生多角度、多层次地解读语篇。
背景分析
1. 语篇分析
该文本的测试题型为完形填空,语篇的语言和内容难度都较大,主要講述了月尘的特征、危害以及形成原因。此文对学生的知识面、语篇结构分析能力、上下文信息整合能力、长难句理解能力,乃至词义理解能力都提出了较高要求。
2. 学情分析
经过试卷批改和数据分析可知,学生出错较多的题目为:3、4、5、7、9、10、11、14,错误原因主要集中在逻辑和理解层面,大致可归为三类:(1)词义理解偏差(3、4、10);(2)单句理解偏差,未能有效联系上下文(5、9、14);(3)知识或文脉逻辑理解偏差(7、11、14)。基于以上对语篇和学情的分析,教师设定了本课的活动目标和活动内容。
3. 课前学习活动
课前,教师选定天文学知识丰富的学生A分享与本课相关的天文学知识,教师在A准备的过程中给予个别指导,以便其合理地处理相关词汇和背景知识。课上,学生通过A的分享,了解了有关月尘的基础知识,并习得了天文学中的常见词汇及短语,例如:月尘(lunar dust)、太空舱(capsule)、航天飞机(space shuttle)、近地轨道(low Earth orbit)、绕地球飞行(orbit the earth)、太阳能电池板(solar panel)、月球车(lunar rover)、碰撞(collide)和探测器(probe)等。
活动目标
通过课堂学习和课后完成作业,学生能够:
1. 借助思维导图提取语篇中的重要信息,理解段落逻辑和文脉结构。
2. 借助多元任务单强化对长难句的分析,并获得定位关键信息的学习经验。
3. 借助思维导图完成给本语篇写梗概的任务。
活动过程
本案例包含一堂试卷讲评课的课堂活动和课后作业,教师基于对文本和学情的细致分析确定了活动目标,并基于目标设计了学生课堂任务和小组活动,包括关注文本结构,梳理语篇文脉;关注阅读难点,学习阅读技巧;关注同主题题材的输入和输出,完成梗概写作和延伸阅读。由于任务设计明确,支架搭建合理,本案例的教学设计为学生课上的主动参与、积极思考、互相合作和多元交流提供了保障。教师设计的一系列教学活动既培养了学生良好的学习策略和阅读习惯,也提升了学生自主学习、合作学习的意识。
Task 1:语篇文脉梳理
教师提供未完成的思维导图,引导学生厘清逻辑,提炼要点填空,完成符合文意的思维导图。
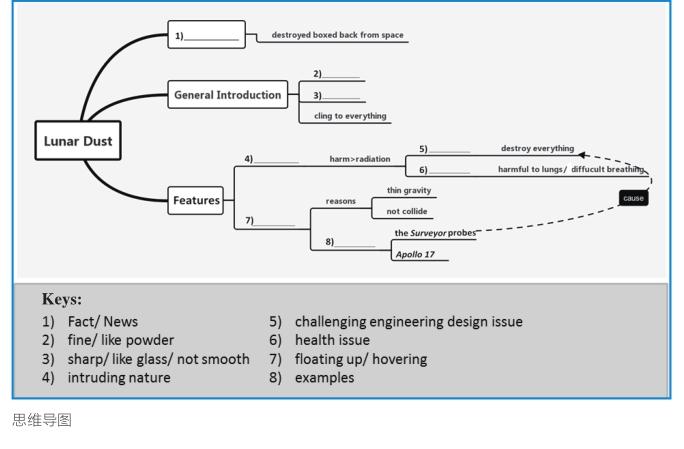
[学生活动过程]
学生深度阅读语篇,厘清段与段、句与句之间的逻辑关系,同时设计思维导图。
[设计思维导图]
本文缺少清晰的主题句,因而文脉较为隐晦,学生独立完成思维导图的设计有一定困难,而提供未完成的思维导图(见图)既可为学生理解语篇的结构指明方向,也方便学生准确把握文脉,为课后活动铺平道路。
Task 2:语篇难点理解
教师提供包含语篇语言理解难点的任务单,组织学生开展合作活动。
任务单按需求分为:
● 锁定题目线索:在学生出错较多的题目方面,帮助学生锁定相关线索。
● 标明指代:在文中的名词和代词的具体指代方面,帮助学生准确定位重点信息。
● 语法填空:在长难句切分和理解方面,帮助学生深入分析长难句中的主从句关系和动词之间的关系。
[学生活动过程]
(1)根据教师的任务单理解文中难点,和同伴合作,互相纠错、释疑,完成任务。
(2)學生完成任务单后,检查原有错误,再二次答题,确认已经解决了所有第一次答题时的存疑和误判。
[设计学习任务单]
学习任务单引导学生在合作中由词到句地精读文本、读懂细节、纠正错误、扫除阅读障碍,为深度理解文脉作好铺垫。
(1)给出重点词汇或词块的英语释义
① Its formed when shooting stars crash on the moons surface, heating its rocks and dirt and reducing them to fine particles. (make them small until they are like powder)
② The dust not only coats the moons surface, but floats up to sixty miles above it... (cover)
(2)锁定答案线索
① Since theres no wind or water to smooth _______ (soft/ hard/ rough/ flat) edges, the tiny grains are sharp and uneven, and cling to nearly everything.(rough对应smooth和uneven)
② In the 1960s, the Surveyor probes filmed a glowing cloud floating just above the lunar surface during sunrise. Later, Apollo 17 astronaut Gene Cernan, while orbiting the moon, recorded a a. _______ (strange/ similar/ common/ different) phenomenon at the sharp line where lunar day meets night. Cernan sketched a series of pictures illustrating the changing scene; streams of particles b. _______ (get under/ lay on /popped off /fell to) the ground and hovered.
a. 两个例证都论证了月尘飘浮在空中,第一个例证中的“floating”对应第二个例证中的“hovered”,都表示飘浮,为类比,答案为“similar”。
b. 同理,因为是从地面“飘起”,所以选择“popped off”。
(3)标明指代
Since theres no wind or water to smooth rough edges, the tiny grains are sharp and uneven, and cling to nearly everything.
“The intruding nature of lunar dust represents a more challenging engineering design issue, as well as a health issue for settlers, ...”
“tiny grains”指代“lunar dust”,“intruding nature”指代上文的“cling to nearly everything”。
(4)语法填空
When Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin returned from the moon, their cargo a. _______ (include) nearly fifty pounds of rock and soil, b. _______ were packed in an aluminum box with seals c. _______ (design) to maintain the lunar surfaces low-pressure environment. d._______ back at Johnson Space Center, in Houston, scientists discovered that the seals e. ________ (destroy)—by moon dust. Lunar dust is fine, like a powder, f.________ it cuts like glass.
a.“included”,在这里是句中的谓语动词。
b.“which”,定语从句修饰“rock and soil”。
c.“designed”,过去分词作后置定语,修饰“seals”。
d. “But”,表示“本来要好好保存,却全部被破坏了”,表转折。
e.“had been destroyed”,宾语从句中的谓语动词。
f.“but”,表示“月尘像粉末,却锋利如玻璃”,表转折。
Task 3:梗概写作和同主题延伸阅读(课后学习活动)
教师根据已完成的思维导图,归纳、总结语篇中的重要内容,并要求学生在课后根据思维导图完成书面的梗概写作任务。同时,教师提供同主题的阅读材料,供学生课后泛读。梗概写作旨在进一步让学生巩固对文章逻辑和框架的理解,并培养他们的书面语言表达能力。同主题延伸阅读旨在增加主题词汇的复现率,让学生对原本感到陌生的主题更加熟悉。
“The intruding ___6___ of lunar dust represents a more challenging engineering design issue, as well as a(n) ___7___ issue for settlers, than does radiation,” wrote Harrison Schmitt, an Apollo 17 astronaut, in his 2006 book, Return to the Moon. The dust damaged spacesuits and ate away layers of moon boots. Over the ___8___ of six Apollo missions, not one rock box ___9___ its vacuum seal. Dust followed the astronauts back into their ships, too. According to Schmitt, it smelled like gunpowder and made breathing difficult. No one knows precisely what the extremely small particles do to human lungs.
The dust not only ___10___ the moons surface, but floats up to sixty miles above it—as an outer part of its atmosphere, where particles are bound to the moon by gravity, but are so thin that they ___11___ collide. In the 1960s, the Surveyor probes filmed a glowing cloud floating just above the lunar surface during sunrise. Later, Apollo 17 astronaut Gene Cernan, while orbiting the moon, recorded a ___12___ phenomenon at the sharp line where lunar day meets night. Cernan sketched a series of pictures___13___ the changing scene; streams of particles ___14___ the ground and hovered, and the resulting cloud came into sharper focus as the astronauts orbiter approached daylight. ___15___ theres no wind to form and sustain the clouds, their origin is something of a mystery. Its presumed that theyre made of dust, but no one fully understands how or why they do their thing.
1. A. solar B. lunar C. dusty D. mysterious
2. A. destroyed B. survived C. changed D. redesigned
3. A. because B. however C. but D. so
4. A. adapting B. reducing C. tailoring D. shaping
5. A. soft B. hard C. rough D. flat
6. A. nature B. speed C. degree D. troops
7. A. intelligence B. health C. fund D. future
8. A. moment B. situation C. course D. program
9. A. installed B. lost C. found D. maintained
10. A. coats B. affects C. protects D. spoils
11. A. frequently B. violently C. gently D. rarely
12. A. strange B. similar C. common D. different
13. A. illustrating B. examining C. leaving D. acting
14. A. get under B. lay on C. popped off D. fell to
15. A. Although B. Wherever C. Unless D. Since


