Discovery of Potential Novel TRPC 4 Inhibitor by Combination of Virtual Screening and 3D-QSAR Modeling
, , , , , *,
(1 Ethnic Drug Screening & Pharmacology Center,Key Laboratory of Chemistry in Ethnic Medicinal Resources,State Ethnic Affairs Commission & Ministry of Education,Yunnan Minzu University,Kunming 650500,China;2 State Key Laboratory of Phytochemistry and Plant Resources in West China,Kunming Institute of Botany,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Kunming 650201,China;3 School of Chemical Engineering,Sichuan University of Science & Engineering,Zigong 643000,China; 4 Hospital, Yunnan Minzu University,Kunming 650500,China)
Abstract The modulation of canonical transient receptor potential 4 (TRPC4) may be pivotal in diverse physiological and physiopathological functions in human. To investigate the potential therapeutical roles of novel TRPC4 ligands in diabetes mellitus, a series of compounds with the top rank of Hiphop pharmacophore model and with good fitness were chosen through computer-aided drug design and a series of virtual screening methods. Then, the effects of these compounds were evaluated by bioassay studies on the growth of rat islet cells. The novel compound 7 amoung these compounds promoted the growth of rat islet cells with an EC50 value at 3.58 μmol/L. However, compound 7 failed to show any effect on rat islet cells with TRPC4 knocked down. Meanwhile, the expressions of TRPC4 in mRNA level were significantly decreased after the administration of compound 7 in rat islet cells. Therefore, the therapeutical potential of compound 7 in diabetes mellitus may function through inhibiting TRPC4.
Keywords computer-aided drug design;canonical transient receptor potential;inhibitor;virtual screening;iabetes mellitus
Canonical transient receptor potential 4 (TRPC4) can regulate Ca2+influx and Ca2+store-operated mechanisms,and involve in diverse physiological processes[1,2]. In recent years,increasing studies have indicated the relationship between TRPC4 and diabetes mellitus. For example,the down-regulation of TRPC4 can restore the erectile function of diabetic rats[3]. Another study found that dexamethasone,Rasd1 and TRPC4 may be related to the secretion of insulin in pancreatic β cells[4]. All these findings may provide a new research direction for the treatment of diabetes through inhibiting TRPC4.
It′s publicly known TRPC4 inhibitors can be a tool for further study of TRPC4 function. Although many TRPC4 inhibitors such as SKF96365,2-APB,Fenamic acid and its analogues,ML204 and Benzimidazole derivatives have been discovered[5-7],there arehithertono known specific inhibitors for this channel. Meanwhile,other TRP channel antagonists and their analogs,including compound groups such as ureas,cinnamides,carboxamides,and imidazoles,are reasonable candidates for inhibiting the function of the TRPC4 protein. For example,several studies have shown that TRPC5 inhibitors are likely to show more potent inhibition of TRPC4[8].To find more effective and specific TRPC4 inhibitors, candidate molecules from large databases were screened by computer-aided drug design (CADD).The screening results were ultimately validated through bioassays.The related workflow is shown in Fig.1.

Fig.1 Flowchart for screening of TRPC4 ligand图1 筛选TRPC4抑制剂的流程图
1 Material and Methods
1.1 Chemicals
MTT and glibenclamid were obtained from Solarbio (Beijing,China),DMSO and other commonly used chemicals were purchased from Xilong Scientific (Guangdong,China).
1.2 Data-set preparation
Twenty-five TRPC4 inhibitors were collected from publications[7],as shown in Tab. 1. The training set contained 18 active molecules and 7 was selected as test set to build 3D-QSAR model. In addition,the specification data from Specs Database were screened by our laboratory through drug-five rules and Veber rules.
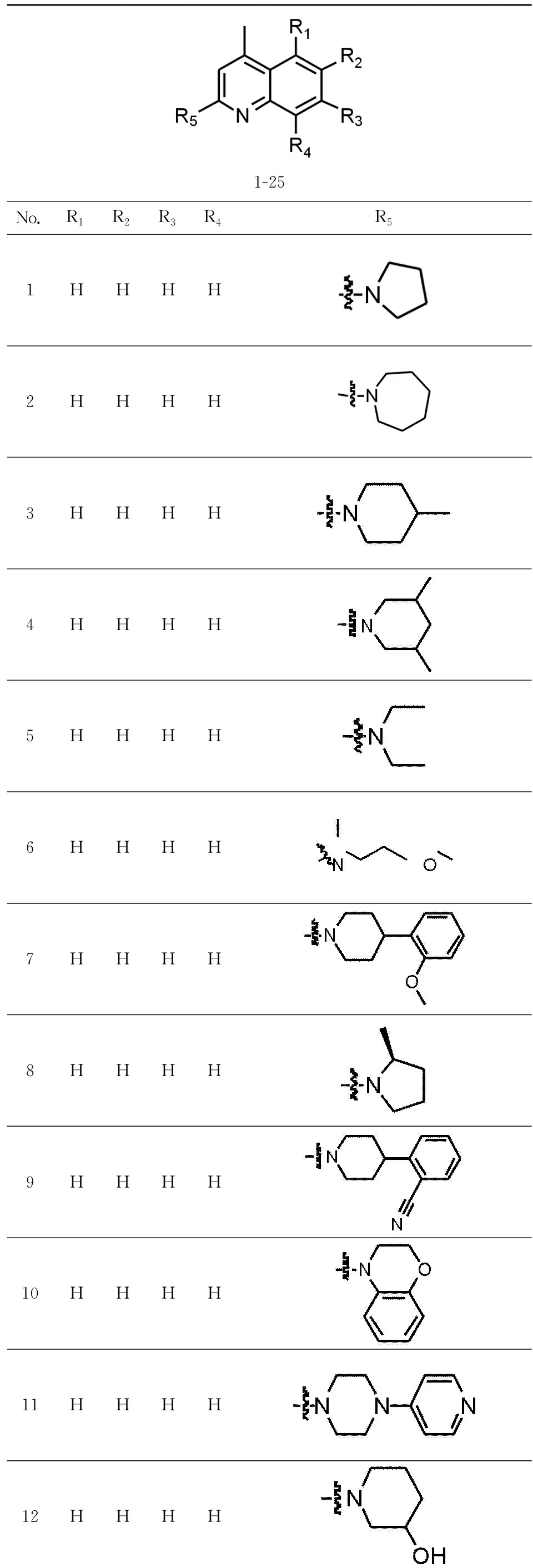
Tab.1 Prublished TRPC4 inhibitors表1 已报导的TRPC4抑制剂的活性分子
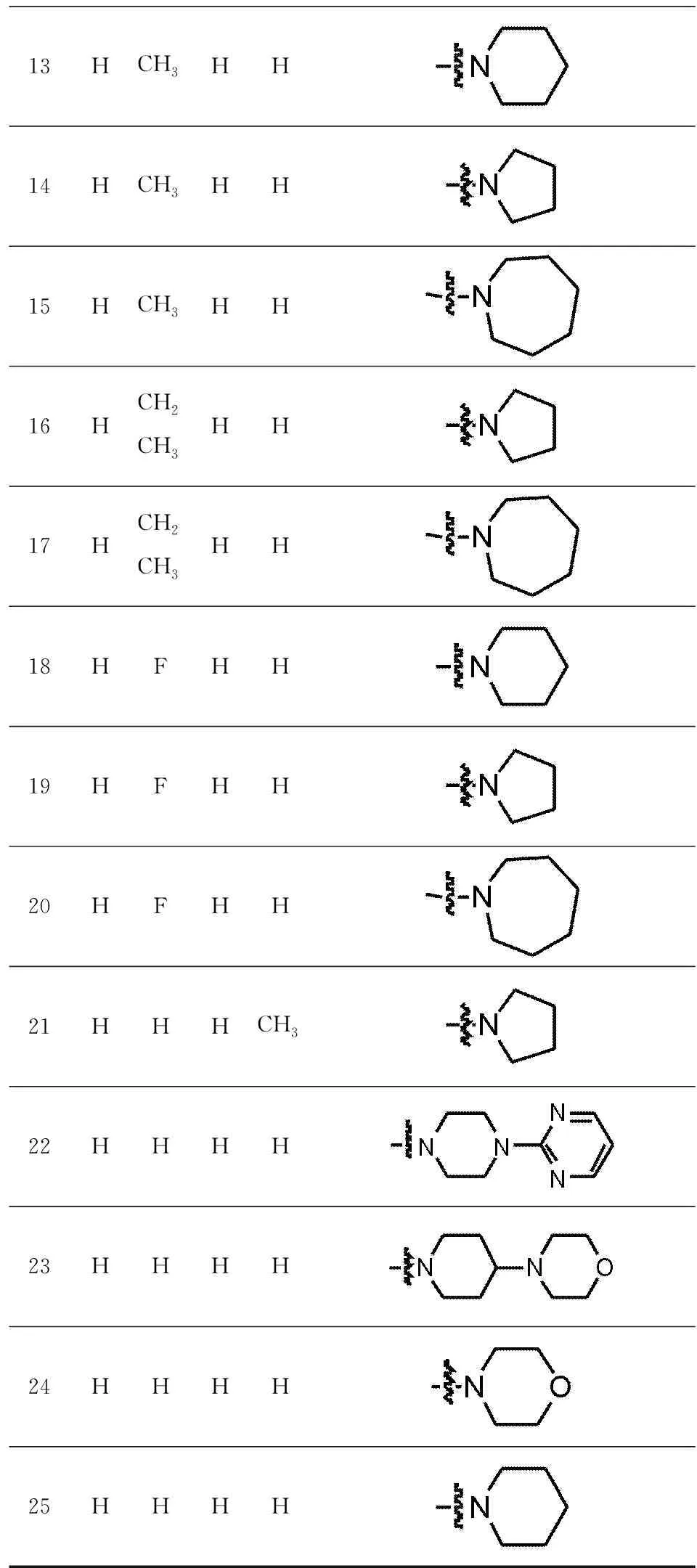
13HCH3HH14HCH3HH15HCH3HH16HCH2CH3HH17HCH2CH3HH18HFHH19HFHH20HFHH21HHHCH322HHHH23HHHH24HHHH25HHHH
1.3 3D-QSAR modeling
The CoMFA model as constructed by using the molecular alignment method[9](Fig.2). In this study,the grid spacing was set to 2 Å in the X,Y,and Z directions and automatically generated as a three-dimensional cubic lattice in the grid area. Lennard-Jones potential and Coulomb potential were employed to calculate steric and electrostatic energies of each molecule,respectively,and asp3-hybridized carbon atom with a+1 charge was used as the probe atom to determine the magnitude of the field values[10]. To improve the signal-to-noise ratio,the column filtration and cut-off values were set at 2.0 kcal/mol and 30 kcal/mol,respectively,and the domination was reduced by the large steric and electrostatic energies. Finally,regression analysis was performed by partial least squares (PLS),and the final model was obtained. A satisfactory result of CoMFA model was obtained as shown in Tab. 2.
Toxic hazard of carcinogenicity and genotoxicity was predicted by Toxtree(version, v2.6.13).

Fig.2 The alignment of small molecules图2 小分子的空间结构排列
Tab.2 The experimental inhibitory activity,the predicted values and residuals
表2 化合物抑制率、预测值和残差值
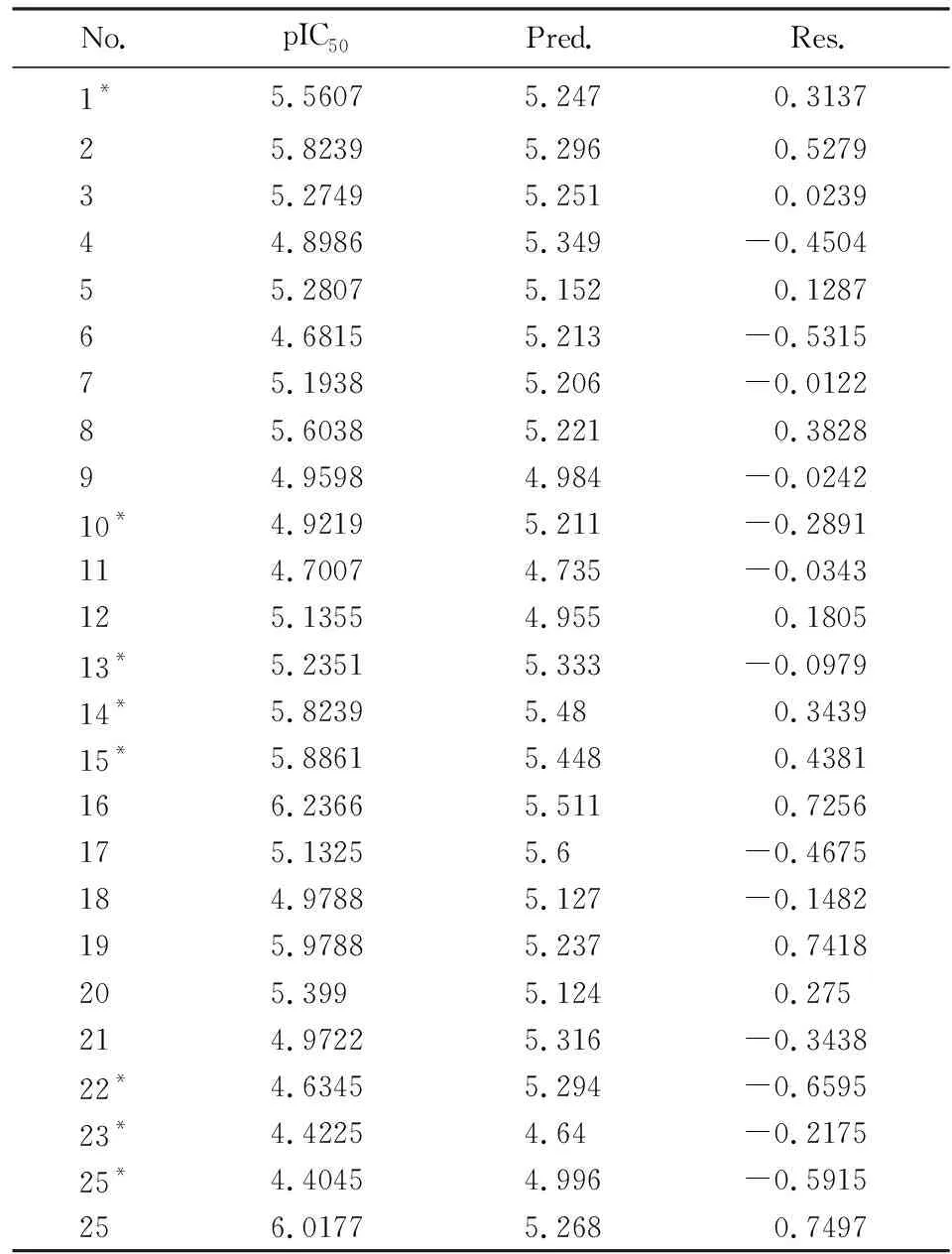
No.pIC50Pred.Res.1*5.56075.2470.313725.82395.2960.527935.27495.2510.023944.89865.349-0.450455.28075.1520.128764.68155.213-0.531575.19385.206-0.012285.60385.2210.382894.95984.984-0.024210*4.92195.211-0.2891114.70074.735-0.0343125.13554.9550.180513*5.23515.333-0.097914*5.82395.480.343915*5.88615.4480.4381166.23665.5110.7256175.13255.6-0.4675184.97885.127-0.1482195.97885.2370.7418205.3995.1240.275214.97225.316-0.343822*4.63455.294-0.659523*4.42254.64-0.217525*4.40454.996-0.5915256.01775.2680.7497
Notes: *Test samples for 3D-QSAR model validation.
Abbreviations: No.,compound number; IC50,half-maximal inhibitory concentration; pIC50,negative logarithm of IC50; Pred.,predicted activity; Res.,residue.
1.4 Cells culture
Rat pancreatic islet cell line (INS-1) was purchased from China infrastructure of cells line resources in Kunming. Cells were routinely cultured in RPMI 1640 supplied with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS),100 U/mL G-penicillin and 100 μg/mL streptomycin in a humidified environment of 5% CO2and air at 37℃. Cells were passaged every 3-4 days.
1.5 MTT assay
MTT assays were used for determining cell viability and proliferation.MTT stock solution was prepared by solving MTT at a concentration of 5 mg/mL in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS),sterilized with a 0.2 μm filter and then stored in a capped lightproof container at 4 ℃. For this study,islet cells were plated onto 96-well plates. After being cultured for 24 h,the culture medium was removed. Then compound 7 was added into the medium at three different concentrations (3.14 μmol/L,0.314 μmol/L,0.0314 μmol/L). RPMI 1640 medium with 10% FBS was used for control group. Glibenclamide was used as the positive control group at the concentration of 1 μg/L. After another 24 h,MTT was added 100 μL each well and incubated for 4 h. Next,DMSO was added 200 μL each well. After mixed on a shaking table for 10 min,absorbance was detected at 490 nm with a Multimode Reader (Thermo Fisher).
1.6 RNA interference
Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) for rat TRPC4 and TRPC5 were obtained from Qiagen (Valencia,USA). The cultured islet cells were seeded onto six well plates (2×105cells per well) in complete medium. After 24 h,the cells were serum-deprived and 10 μL of 20 μmol·L-1siRNA mixture,or siRNA control was transfected into the cells using HiPerFect transfection reagent (Qiagen). After 72 h of transfection,RT-PCR was carried out to confirm that the mRNA expressions of TRPC4 or TRPC5 had been knocked down in the cells.
1.7 RNA isolation and real-time quantitative PCR
Total RNA was extracted from MAECs using TRIzol reagent (CWbio. Beijing) following the manufacturer′s protocol. Equal amounts of RNA were reverse-transcribed into cDNA. Primers for TRPC4 (sense: 5′- ACCATCGTGGAGTGGATGA-3′; antisense: 5′-TGTCGCCAGATACAAGGAGT-3′) and β-actin (sense: 5′-CGGCCATCACGCCACAGGCTT-3′; antisense: 5′-CGTCTTCACCACCATGGAGA-3′) were used to generate a 147 bp and a 197 bp product,respectively. Quantitative real-time PCR was performed using the UltraSYBR (with ROX,CWbio). The PCR amplification included an initial denaturation at 95 ℃ for 3 min,40 cycles of denaturation at 94 ℃ for 40 s,annealing at 60 ℃ for 2 min,and extension for 30 s,at 72 ℃. Results of the log-linear phase of the growth curve were analyzed and relative quantification was performed using the 2-ΔΔCTmethod with β-actin as a house-keeping gene.
1.8 Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS22.0. Data were presented as means ± S.E.M. Comparison between two groups was analyzed using Student′st-test.
2 Results
2.1 Analysis of 3D-QSAR modeling
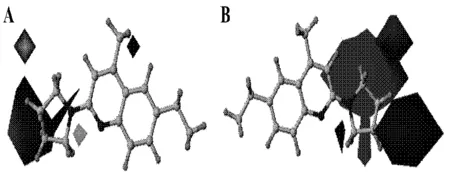
1)Steric fields; B) Electrostatic fieldsFig.3 The 3D contour maps of CoMFA model图3 CoMFA模型的三维轮廓图
According to the results of activity prediction by 3D-QSAR model,the activity of candidate molecules at themicro mole level remained (Tab. 3). However,there were several new skeletons appearing in the hit molecules,which were different from quinoline compounds. It deserves further study to discover more effective and novel skeleton TRPC4 inhibitors. Furthermore,the effectiveness of these hit molecules would be tested by bioassay.

Tab.3 The results of PLS analysis for the CoMFA表3 CoMFA模型的偏最小二乘法的分析结果

12AM-879-420007574.85513AN-153-430929585.25114AE-641-150861995.21115AF-399-344640495.207
Abbreviations: No.,compound number; Pred CoMFA,predicted activity by CoMFA model
2.2 Effects of compound 7 on viability of rat islet cells (INS-1 cell line)
The EC50values of this compound and glibenclamide were shown in Tab.4. As demonstrated in Fig.4,the administration of compound 7 significantly decreased the expressions of TRPC4 in INS-1 cell line. The inhibitory effect of compound 7 was similar to that of ML204[7]. Glibenclamide showed no effect on the expression of TRPC4 in INS-1 cells.

Tab.4 EC50 values of compound 7 and glibenclamide obtained by MTT表4 MTT法测得的化合物7与格列本脲的EC50值
Values are means ± SEM. Data were obtained from five separate experiments (n=5). Signicance of the difference between groups is indicated as follows:*P< 0.05,compared with Compound 7 group.
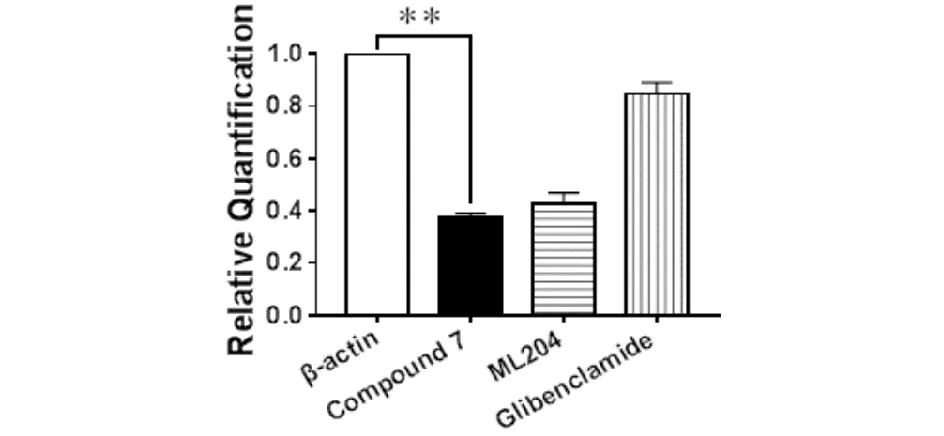
Values are means ± SEM; data were obtained from five separate experiments (n=5); signicance of the difference between groups was indicated as follows:**P < 0.01Fig.4 Effect of the Compound 7 on the expressions of TRPC4 in INS-1 (relative to β-actin)图4 化合物7对INS-1中TRPC4表达的影响(相对于β-actin).
3 Discussion
Diabetes is a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycemia resulting from defects in insulin secretion,insulin action or both[11]. Therefore,chemicals with stimulative function on the growth of islet cells may show potential therapeutic effect on diabetes mellitus. Studies have shown that the expressions of various TRPC subtypes (such as TRPC1 and TRPC4) are significantly changed in type 1 and 2 diabetes patients and diabetic animal tissues (such as kidney,blood vessels,and inflammatory cells)[12]. By performing MTT assay in the present study,EC50value of compound 7 was not significantly different from that of glibenclamide. As type I diabetes has the feature of low secretion of insulin,increasing the amount of islet cells may be helpful for increasing the release of insulin in patients with type I diabetes. Moreover,compound 7 shows significant inhibitory effect on the expression of TRPC4 in islet cells. The results suggested that the inhibitor of TRPC4,compound 7,may have the potential positive effect on type 1 diabetes and related diseases. More importantly,since the close homology of TRPC4 and TRPC5 is particularly evident in the N-terminus and the transmembrane domains with about 80% identity in primary sequence[13],it is imperative to distinguish effects of compound 7 on TRPC4 and TRPC5. By performing RNA interference,compound 7 still markedly influenced the growth of INS-1 with TRPC5 knocked down but did not show effect on that of INS-1 with TRPC4 knocked down. This finding indicates compound 7 may play selective role between TRPC4 and TRPC5. Of course,further studies such as patch clamp analysis and compound affinity detection should be performed to verify the specificity and potency of the inhibitory effect of compound 7 on TRPC4,especially in islet cells.
——评《多中心城市空间结构:概念、案例与优化策略》

