Research progress on anti-tumor properties of Marsdenia tenacissima
Yan-Lan Hu, Shao-Hui Wang, Cui-Wei He, Tong-Xiang Liu,*
1Key Laboratory of Ethnomedicine, Minzu University of China, Beijing, China.
Background
Tongguanteng (Marsdenia tenacissima) belongs to the family Asclepiadaceae mainly distributed in the Guizhou,Yunnan, Sichuan, and Guangxi provinces of China and other areas in Southeast Asia [1]. It was first recorded in the ancient book ofDiannanbencaoby Lan Mao of the Ming dynasty of China (1436 A.D.) as bitter, light astringent, sub-cold, homing to the lung meridian,clearing heat and detoxifying, relieving cough and asthma,and eliminating stagnation and pain [2], which is consistent with the description in theYunnan Zhongcaoyao Xuan(1970 edition) andQuanguo Zhongcaoyao Huibian(1975 edition). Additionally, theYunnansheng Yaopin Biaozhun(1977 edition) stated that Tongguanteng (Marsdeniatenacissima)decreased inflammation and had anti-cancer effects [2].Tongguanteng (Marsdenia tenacissima) contains C21steroidal saponins, which are considered to exert anti-tumor effects; it also contains polysaccharides,alkaloids, and resins [3]. This plant has long been used as a traditional medicine to treat various types of cancer and shows potential curative effects, mild side effects, and good value for development by targeting multiple components of different signaling pathways [1] based on studies conducted since the early 1970s [4, 5].
Clinically, Tongguanteng (Marsdenia tenacissima)is the main raw material of compound preparations applied for anti-tumor treatment, and Xiaoaiping injection(Approval number: Z20025869) is a prescribed total water extract preparation of Tongguanteng (Marsdenia tenacissima)used to treat cancer. Based on clinical research conducted in the Henan province, Tongguanteng(Marsdenia tenacissima) was prepared as tablets and injections by the Henan Xinxiang Qianwei Pharmaceutical Factory [4, 5]. Since then, in combination with other anti-cancer drugs, it has been widely used to treat lung cancer, colon cancer, esophageal cancer, and other cancers and has been shown to increase progression-free survival and reduce the incidence of adverse reactions in patients [6 - 10]. Here, we review the research progress related to the treatment of different tumors with Tongguanteng (Marsdenia tenacissima),its extract, and Xiaoaiping injection to provide a scientific basis for the further development and utilization of Tongguanteng (Marsdenia tenacissima).
Hematological neoplasms
Yeet al[11] studied the role and related mechanisms of the ethanolic extract of Tongguanteng (Marsdenia tenacissima)on the human Burkitt’s lymphoma cell line Raji, human acute promyelocytic leukemia cell line NB4,and human erythroleukemia cell line K562, and found that Tongguanteng (Marsdenia tenacissima)inhibited the proliferation of all three tumor cell lines. However, it showed no effects on normal peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Flow cytometry analysis revealed that Tongguanteng (Marsdeniatenacissima) induced significant K562 cells apoptosis, increased the number of cells in the G0/G1 phase, decreased the number of cells in the S phase, arrested cells in the G0/G1 phase, and inhibited colony formation in a dose-dependent manner.The expression of BCL-2-associated x protein (Bax),Caspase-3, and Caspase-9 was up-regulated, while that of B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) and Cyclin D1 was down-regulated. Thus, Tongguanteng (Marsdenia tenacissima)wasdemonstrated to exert good inhibitory effects on K562 tumor cells.
Tenacissoside C, a C21steroidal saponin, was extracted from the air-dried stems of Tongguanteng (Marsdenia tenacissima)and was found to arrest cells in the G0/G1 phase, decrease Cyclin D1 expression, and inhibit cell proliferation [12]. Analysis of apoptosis-related proteins,including Caspase-3, Caspase-8, Caspase-9, Bax, Bcl-2,Bcl-2 antagonist killer, and Bcl-xl (B-cell lymphoma-extra large), revealed no change in Caspase-8 expression, while Caspase-3 and Caspase-9 were up-regulated, indicating that tenacissoside C promoted cell apoptosis through a mitochondrial pathway. The Raji,NB4, and K562 cell lines were also studied by Xue [13]who found that tenacissoside C among the four C21steroid saponin monomers had the strongest proliferation inhibition and apoptosis induction effects in Raji cells strains.
In addition to tenacissoside C, medium and high doses of Tongguanteng (Marsdenia tenacissima)extract (MTE)and two derivatives (tenacissimoside A and 11α-O-benzoyl-12β-O-acetyltenacigenin B) of tenacigenin B, a type of C21steroidal aglycone, from Tongguanteng (Marsdenia tenacissima)significantly inhibited Raji cells proliferation [14]. Wanget al[15]showed that MTE reduces the viability of the human T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell line Jurkat and arrests these cells in the S phase in a dose-dependent manner. Mechanistic studies indicated that MTE induces cell apoptosis by promoting the expression of phosphatases and tensin homolog to inhibit the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. However, human multiple myeloma cells RPMI8226 were not sensitive to MTE [16]. Ceng [17] found that aTongguanteng(Marsdenia tenacissima)water extract, containing dextran and heteropolysaccharides as the main components, affected the proliferation rate of K562 cells and altered cell morphology. After 24 h of culturing the cells with 10, 30, and 50 µL/mL of the water extract, the growth inhibition rates were 45%, 73%, and 84%,respectively, with an IC50value of 11 µL/mL. Total aglycones of Tongguanteng (Marsdenia tenacissima)Caulis improved the sensitivity of K562 cells to paclitaxel,showing anti-tumor effects [18]. However, the inhibitory effects of high, medium, and low doses of total saponins from Tongguanteng (Marsdenia tenacissima)on the mouse lymphocytic leukemia cell line p388 were weaker than those of cyclophosphamide, these results are not ideal [19].
Xiaoaiping injection reduces the mitochondrial trans-membrane potential of the human leukemia cell strains U937, HL60, and K562 and promotes apoptosis[20, 21]. Using a gene chip to detect the gene expression spectrum in U937 cells, it was found that Tongguanteng(Marsdeniatenacissima)up-regulates multiple apoptosis-inducing genes, including the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) ligand and receptor family, Caspase family,Caspase recruitment domain family, and p53 family of genes [22]. However, it does not induce apoptosis in human erythroleukemia cells [23]. Table 1 summarizes data on the four major hematological tumor cell lines mentioned above.
In a clinical trial of 131 patients with non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, the use of a standard CHOP regimen[Cyclophosphamide 750 mg/m2, intravenous injection(i.v.), day 1; Epirubicin 40 mg/m2, i.v., day 1; Vinblastine 1.4 mg/m2, i.v., day 1; Pred 100 mg/m2, taken orally, days 1 to 4, 21 days/cycle] combined with Xiaoaiping injection had an efficacy rate of 71.00%, which was higher than that (58.00%) observed in the control group. Thus, this treatment can improve the quality of life of patients and reduce adverse reactions to chemotherapy [24].
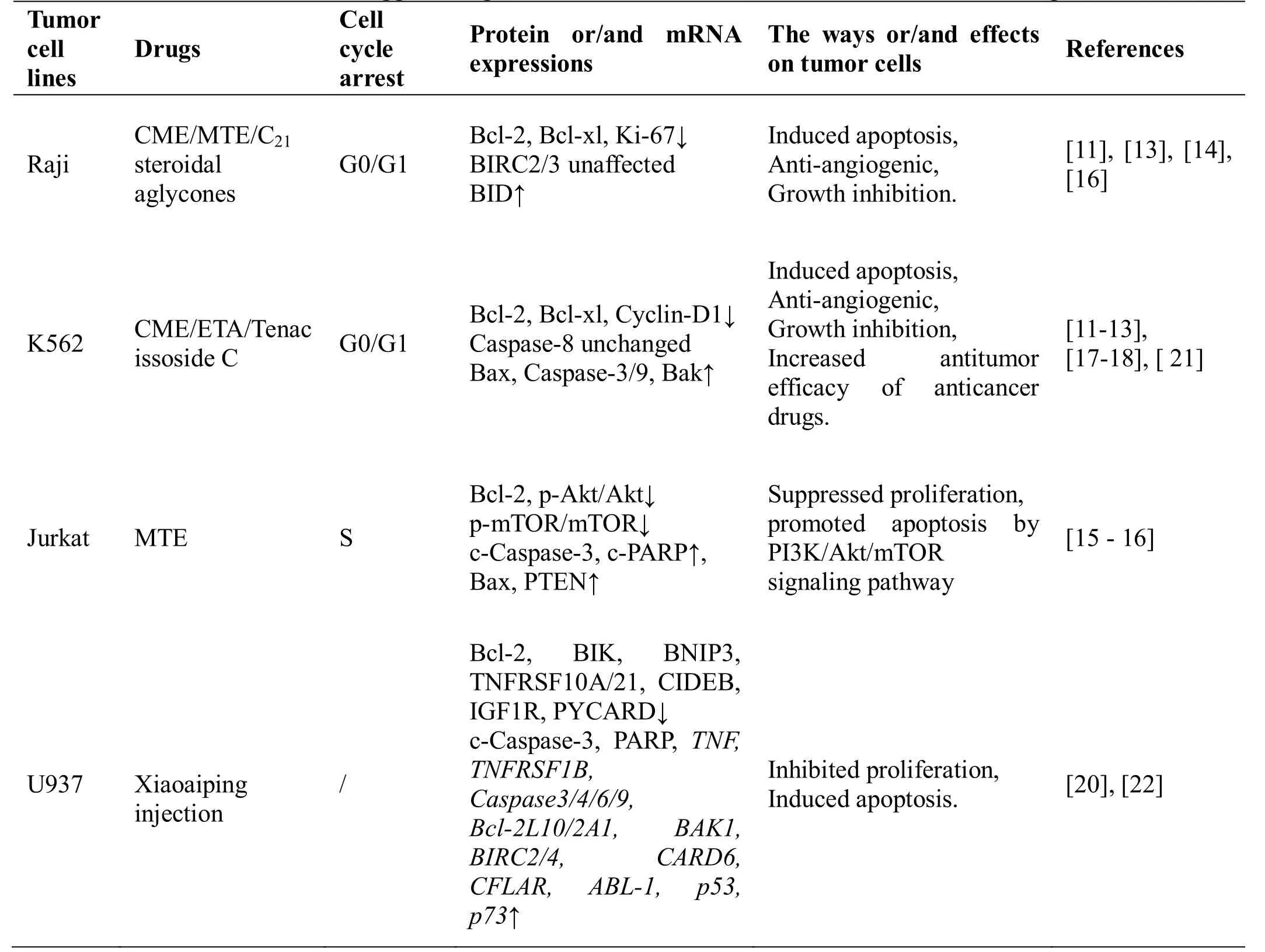
Table 1 Anti-cancer effect of Tongguanteng (Marsdenia tenacissima) on four kinds of hematological tumor cell
Lung cancer
Hanet al[25] showed that combining low-dose MTE (8 mg/mL) with gefitinib had synergistic effects in the human non-small-cell lung cancer cell line HCC827 harboring the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)mutation and in wild-type human non-small-cell lung cancer H292 cells. Comparing three different methods of drug administration, MTE addition to the medium and incubating the cells for 12 h followed by gefitinib addition and incubation for another 72 h (MTE → MTE +gefitinib) was the most potent method of inhibiting tumor cell growth. MTE enhanced gefitinib-induced G2/M cell cycle arrest in H292 cells, and HCC827 cells were arrested in the S phase. At the molecular level, MTE →MTE + gefitinib further enhanced the effects on the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)1/2 and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway, indicating cross-activation of EGFR and a hepatic growth factor receptor (c-Met). The combination suppressed the phosphorylation of components downstream of EGFR and suppressed c-Met and tyrosine-protein kinase receptor activation in human lung adenocarcinoma HCC827/ER cells [26]. A similar approach [27] also showed that MTE reverses gefitinib resistance in the human non-small-cell lung cancer cell lines H460 and H1975 and exerts anti-tumor effects. In a study evaluating whether Tongguanteng (Marsdenia tenacissima)can be used to overcome drug resistance in lung cancer cell lines,Yaoet al[28] found that tenacigenin D, a polyoxypregnane aglycone isolated from Tongguanteng(Marsdenia tenacissima), suppressed P-glycoprotein(P-gp) transportation of drugs out of cancer cells and circumvented the multidrug resistance mediated by P-gp.Analysis of tenacigenin D treatment combined with erlotinib and gefitinib treatment in H292, H460, and H460/Vbl cells revealed that tenacigenin D potentiates the activity of erlotinib and gefitinib in drug-resistant cells.
Furthermore, from the perspective of the immune system, tenacissoside H, a C21steroidal saponin extracted and purified fromTongguanteng (Marsdenia tenacissima),inhibited the growth of Lewis lung tumor xenografts,decreased lung metastases, increased interleukin (IL)-2 levels, attenuated IL-10 levels, restored the T helper 1/T helper 2 balance, and enhanced the immune function in mice to achieve an anti-tumor effect [29]. Additionally,Linet al[30] conducted an MTT assay, a wound healing assay, and a cell invasion assay and found that at increasing injection doses of Xiaoaiping, fewer human lung cancer cells (A549 cells) showed metastasis, growth inhibition increased, the chemokine receptor (CCR) 5 protein levels and C-C chemokine ligand 5 (CCL5)secretion decreased, and CCR9 and CCR4 protein levels were unchanged. Accordingly, the phosphorylation levels of focal adhesion kinase (FAK), activator of transcription 3, ERK, p38, and Ras homolog (Rho) in the CCR5-CCL5 biological axis were decreased. These results indicate that Xiaoaiping attenuated the migration and invasion of A549 cells by down-regulating the Rho C, FAK, and CCR5-CCL5 biological axis. In the human lung adenocarcinoma ASTC-a-1 cells, Xiaoaiping treatment for 72 h decreased cell proliferation and increased Caspase-3 levels, but Caspase-3 level was not significantly changed after culturing with Xiaoaiping for 24 h; inhibitory effects were not evident [31].
In clinical trials, patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer were treated with NP chemotherapy regimen(vinorelbine and cisplatin) [32], TP chemotherapy regimen (paclitaxel and cisplatin) [33], and docetaxel [34].After combined treatment with Xiaoaiping injection,higher scores for the quality of life were observed than those after treatment without Xiaoaiping [35].Furthermore, myelosuppression and gastrointestinal reactions were alleviated; however, individual patients experienced discomforts, such as low fever, excessive sweating, migratory muscles, and joint pain, during the injection of Xiaoaiping.
Gastrointestinal tumor
Esophageal cancer
Fanet al[36] conductedMTT and BrdU incorporation immunofluorescence assays and found that MTE inhibits the growth and proliferation of human esophageal cancer cells KYSE150 and Eca-109 in a time- and dose-dependent manner and arrests cells in the G0/G1 phase. Expression of cell cycle regulatory proteins Cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK)2/4/6, Cyclin-D1/2/3,Cyclin-E1, and retinoblastoma protein decreased (Table 2), while CDK inhibitors did not affect the expression.After MTE administration, the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway was not affected, while the phosphorylation of proteins involved in the ERK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase,and p38 signaling pathways decreased. In the human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma HKESC-1 cells and its cisplatin-resistant subline HKESC-1cisR, MTE up-regulated p21 expression and restored the effects of cisplatin and caused G2/M phase retardation, thereby reversing chemotherapeutic drug resistance in cancer cells [37] (Table 2).
Numerous clinical trials have shown that Xiaoaiping injection with irinotecan [38, 39], paclitaxel [40, 41],cisplatin [40 - 42], tegafur [43], oxaliplatin [43],docetaxel, or raltitrexed [42] significantly improves the clinical efficacy and progression-free survival as well as reduces diarrhea, oral mucositis, hand-foot syndrome,nausea, leukopenia, and neutropenia in late esophageal carcinoma patients.
Gastric cancer
Liet al[44]showed that Tongguanteng (Marsdenia tenacissima) down-regulates Bcl-2 and Bcl-xl in the human gastric adenocarcinoma cell line BGC-823 in a concentration-dependent manner, but observed no obvious changes in Bax and Bcl-2 antagonist of cell death protein levels. The metadherin gene is a new specific marker of gastric cancer and target for clinical treatment;since Tongguanteng (Marsdenia tenacissima) also significantly reduced its mRNA expression, it could be considered as a new therapeutic strategy for gastric cancer.Additionally, treatment with the water extract of Tongguanteng (Marsdenia tenacissima) prevented body weight loss and reduce tumor size in nude mice xenografted with MKN-45 human gastric cancer cells.[45]. Compared to the celecoxib group, liver and mesenteric node metastasis in Tongguanteng (Marsdenia tenacissima) group was obviously reduced and cyclooxygenase 2 protein expression decreased in the gastric mucosa [46] (Table 2). Kaempferol [47], a flavonol-like substanceand total saponins [19] identified and isolated from Tongguanteng (Marsdenia tenacissima),presented the same inhibitory effects on the growth of the human gastric cancer cell line SGC-7901. Moreover,kaempferol showed stronger effects in the MKN-45 cell line with an IC50of 48.87 μg/mL, which differed from the previous studies in which the main anti-tumor substances in Tongguanteng (Marsdenia tenacissima)were C21steroidal saponins [47]. The studies described above suggest that Tongguanteng (Marsdenia tenacissima)has good therapeutic effects on gastric cancer. Randomized controlled trials indicated that Xiaoaiping injection +XELOX regimen [Capecitabine 1000 mg/m2, po, twice per day (b.i.d), days 1-14; Oxaliplatin 130 mg/m2, i.v, day 1, 21 days/cycle] obviously relieved leukopenia compared to the XELOX regimen alone [48], while a meta-analysis [49] indicated that Xiaoaiping injection +FOLFOX (Oxaliplatin + Calcium folinate +5-fluorouracil) regimen was less effective in relieving leucopenia and gastrointestinal reactions.
Other gastrointestinal tumors
Yaoet al[37] treated the SW620 human colon cancer cells and its P-gp-overexpressing subline SW620 Ad300 with polyoxypregnane steroids with an open-chain sugar moiety ofTongguanteng (Marsdenia tenacissima)and MTE coupled with chemotherapy drugs. The IC50value of combined therapy was remarkably reduced compared with each compound tested alone, drug transporter activity was suppressed, anti-cancer drug concentration in cancer cells was increased, and tumor suppression effect was more apparent. When administered alone, MTE directly inhibited the growth and proliferation of the human colorectal cancer cells line Lovo in a concentration-dependent manner [50]. Wanget al[51]selected the human adenoid cystic carcinoma cell line SACC83 as a target to study the anti-tumor effect and relative mechanisms of Xiaoaiping injection and 17-β-tenacigenin B, which is a C21steroidal glycoside extracted from Tongguanteng (Marsdenia tenacissima).They found that 17-β-tenacigenin B had no prominent effects on SACC83 cells, whereas Xiaoaiping repressed SACC83 cell growth by down-regulating Bcl-2 and up-regulating Bax expression (Table 2).
Hepatic carcinoma
Zhang [52] studied the cytotoxicity of liposoluble constituents extracted from Tongguanteng (Marsdenia tenacissima)on the human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line HepG2 in an MTT assay. After 72 h of liposolublecomponent administration, cell proliferation was decreased to different degrees in a time- and dose-dependent manner with good inhibitory effects observed at concentrations of 50-200 mg/L. Huanget al[53] incubated HepG2 cells with MTE for 24 h and found that the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor(VEGF)-2 and VEGF-A was decreased according to RT-PCR and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay results.VEGF is closely related to the formation of tumor microvasculature, indicating that MTE exerts its anti-tumor effects by inhibiting tumor angiogenesis(Table 3). Furthermore, total aglycones of Tongguanteng(Marsdenia tenacissima) caulis decreased the growth of SMMC-7721 human hepatocellular carcinoma cells,increased the thymus index of H22-bearing mice [54], and enhanced the sensitivity of HepG2 cells to paclitaxel.
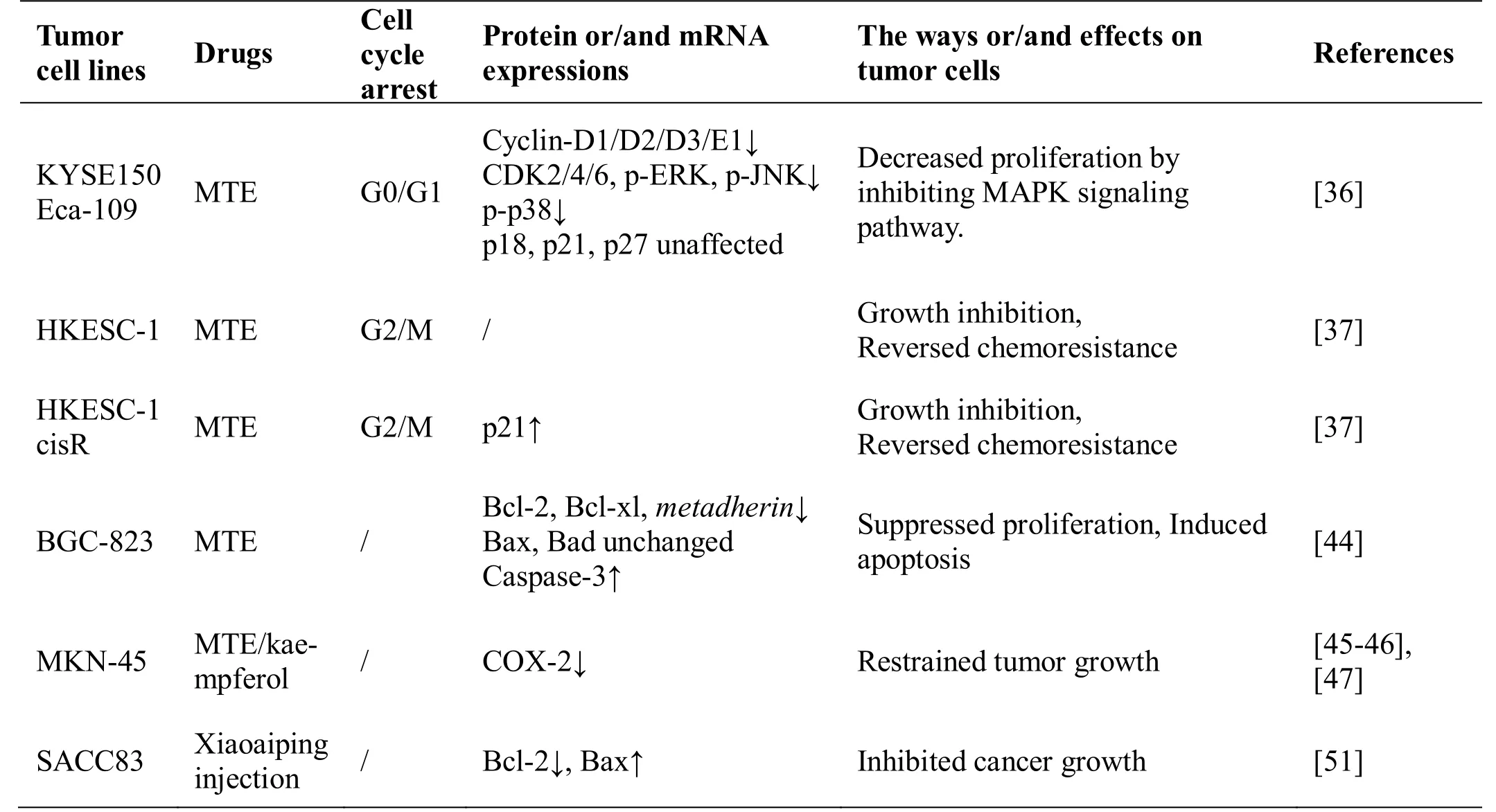
Table 2 Summarized of Tongguanteng (Marsdenia tenacxixssxima) against different gastrointestinal tumor cell stains and relative molecular mechanisms
Huet al[55] studied the effect of a tenacigenin B derivative on reversing the multidrug resistance of human hepatoma HepG2/Dox cell lines overexpressing P-gp and found that doxorubicin, vinblastine, puromycin, and paclitaxel combined with 20 μg/mL tenacigenin B derivatives increased the susceptibility of HepG2/Dox cells by at least six-fold, presumably because the tenacigenin B derivatives interacted with the P-gp substrate site. Hanet al[56] found that MTE inhibited cytochrome P450 (CYP450) activity in the human liver using the cocktail substrate method. The inhibition rates were in the order of 3A4 > 2C9 > 2C19 > 1A2 > 2D6.The regimen of gefitinib combined with MTE reduced the activities of cytochrome P2D6 and cytochrome P3A4in vitroby 2.6- and 4.0-fold, respectively, with little effect xx on other CYP450s. After combined treatment, the mRNA and protein expression levels of cytochrome P2D6 and cytochrome P3A4 in HepG2 cells were clearly decreased.This indicates that MTE inhibited CYP450 activity in HepG2 cells to interfere with the metabolism of gefitinib.
Animal experiments by Jianget al[57] showed that polysaccharides from Tongguanteng (Marsdenia tenacissima)limited tumor growth in H22tumor-bearing mice and increased the spleen index, thymus index, and albumin, TNF-α, and IL-2 levels in the serum, increased the activities of glutathione peroxidase, catalase, and superoxide dismutase (SOD) in the liver, and decreased VEGF and malondialdehyde (MDA) levels (Table 3).These results suggest that the Tongguanteng (Marsdenia tenacissima)polysaccharide regulates the immune function of mice, and its anti-tumor activity may be associated with an antioxidant and immune regulatory response.
Qian [58] used the human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines BEL-7402, SMMC-7721, and HepG2 and H22tumor-bearing mice to determine the inhibitory effect of single and combined administration of Xiaoaiping injection and platinum on the different cell lines.Xiaoaiping injection altered the cell morphology and ultrastructure, decreased cell proliferation rate, arrested the cell cycle in the G0/G1 phase, inhibited Ki-67 protein expression, decreased Bcl-2 expression, and increased Bax expression. These trends were more obvious after combination treatment. VEGF and basic fibroblast growth factor expression also decreased in BEL-7402 cells [59],levels of p53 gene products were decreased [60], and xxxxtumor angiogenesis was inhibited (Table 3). After treatment with Xiaoaiping, mouse hepatocellular carcinoma Hepa1-6 cells showed pseudopod contraction,somatic cells became smaller and round, eosin staining was enhanced, nuclei were smaller and fragmented,chromosomes were stained deep blue or dark black,mouse hepatocellular carcinoma Hepa1-6 cells are adherent cells that were observed suspended in culture medium, and apoptosis was increased according to inverted microscopy results [61]. Xiaoaiping injection directly promoted T and B cell proliferation, regulated immune system function [62], and enhanced the quality of life of patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma,improving their immunity and extending their progression-free survival [63].
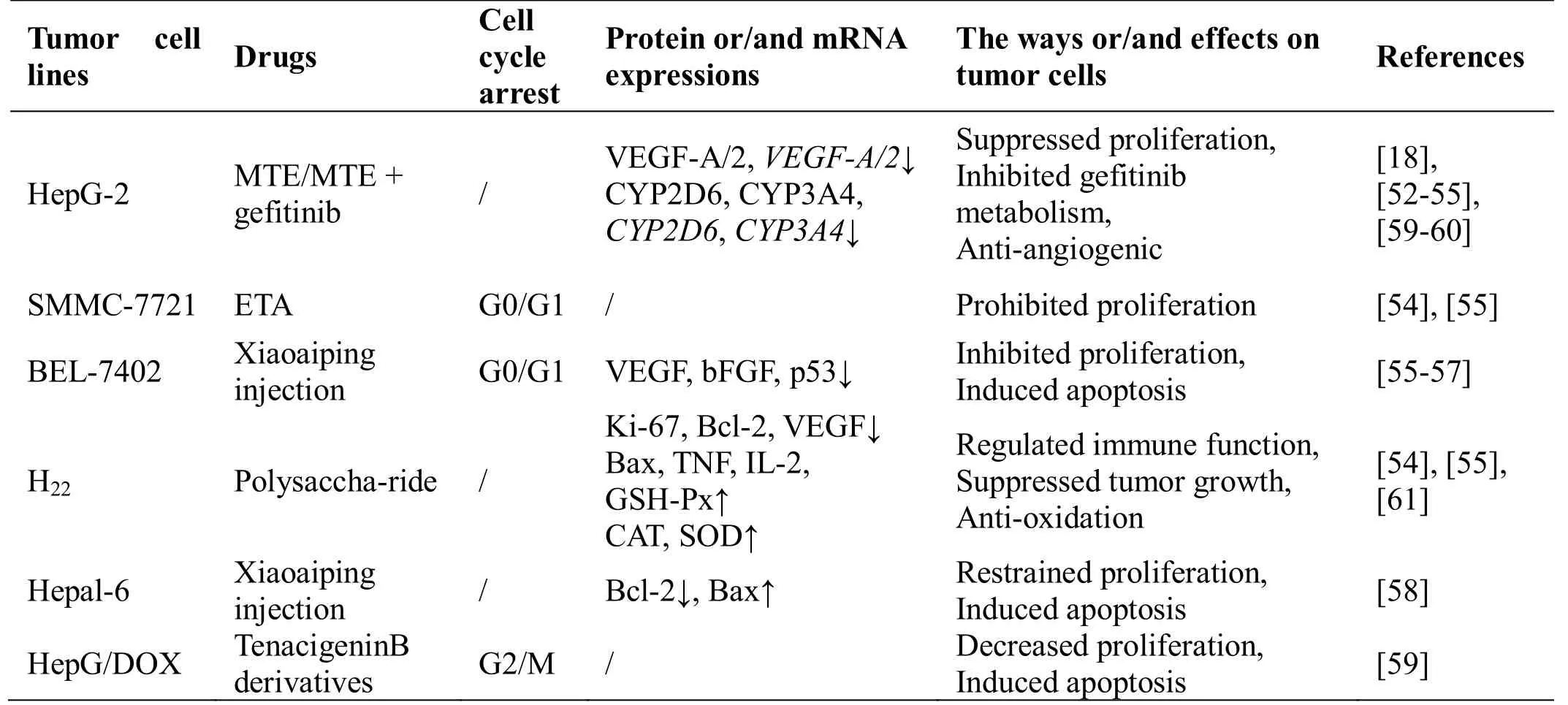
Table 3 Comparison of anticancer molecular mechanisms of Marsdenia tenacissima on different hepatic carcinoma cell lines
Cervical cancer and breast cancer
According to Yao [64], the growth rate of tumors in tumor xenograft nude mice was distinctively slowed by the administration of saponinsfromTongguanteng(Marsdenia tenacissima), which suppressed cervical cancer cell growth in the tumor-bearing mice. The human cervical cancer cell line HeLa and human breast cancer cell line MCF-7 showed increased mortality with an increasing dose of betulinic acid, a pentacyclic triterpenoid present in Tongguanteng (Marsdenia tenacissima).The effects were similar to those of 5-fluorouracil, but the inhibitory effect of betulinic acid on human breast ductal carcinoma cells ZR was not strong [65]. Similarly, total saponins of Tongguanteng(Marsdenia tenacissima)and ETA weakly inhibited the growth of HeLa cells [54], whereas ETA enhanced the anti-cancer activity of taxol in the human papillomavirus-related endocervical adenocarcinoma cell line KB-3-1 and markedly decreased the IC50values than that of taxol alone [18]. Moreover, the combination of Xiaoaiping injection and docetaxel + epirubicin +cyclophosphamide inhibited estrogen receptor ER-α36 expression in breast cancer tissues and improved overall clinical efficacy, three- and five-year disease-free survival,and overall survival in breast cancer patients [66, 67].
Others
Huanget al[68] found that after incubation with the combination of doxorubicin and MTE, the human osteosarcoma cell line MG63 showed decreased survival,increased apoptosis, altered cell morphology, and up-regulated Fas expression, with significant differences compared to the effects of the two drugs alone, indicating that MTE improves the sensitivity of MG63 cells to doxorubicin.
Chenet al[69] studied the effects of different concentrations and incubation times of MTE. MTE exerted anti-angiogenic effects and inhibited the proliferation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells by weakening the interaction of VEGF/VEGFR2 mediated by CCL-2 and promoted apoptosis via the p53-dependent mitochondrial pathway induced by PKCδ. These results verify the effects of MTE on tumor angiogenesis. Daiet al.[70] also found that MTE inhibits tumor growth and angiogenesis in A20 mouse lymphoma and endothelial cells, which play a vital role in the pre-angiogenesis phase. As the MTE concentration was increased,apoptosis also increased. The apoptotic rates in the endothelial cells induced by 0, 6.25, 12.5, and 25 μL/mL MTE were 4.8%, 23.3%, 49.8%, and 92.3%, respectively,based on acridine orange/propidium iodide staining and flow cytometry.Peritumoral neovascularization and microvessel density were clearly decreasedin vivoin A20 solid tumors after administration of 300 μL/d MTE for 14 days in BALB/c mice. The expression levels of VEGF,matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2), and MMP-9 were lower than those in the control group. Additionally,Tongguanteng (Marsdeniatenacissima)showed inhibitory effects toward human subcutaneous glioma U87 cells in nude mice [71] and xenograft mouse sarcoma S180 cells [72].
Discussion
The chemical composition of Tongguanteng (Marsdenia tenacissima)is complex, and studies have focused on its monomer components, derivatives, preparations, and crude extracts. These components showed anti-cancer effects on various tumor cell lines with different mechanisms that varied by cell type. Tongguanteng(Marsdenia tenacissima)exerts its anti-tumor effects mainly in five ways, as shown in Figure 1. First,Tongguanteng (Marsdenia tenacissima)increases the expression of apoptosis-related proteins, such as Caspase-3, Caspase-9, and p53 while decreases those of Bcl-2, Bcl-xl, to promote apoptosis in tumor cells,inhibits Cyclin D1/2/3, Cyclin E1, CDK2/4/6, and other cell cycle proteins, and arrests tumor cells in the G2/M or S phase to inhibit tumor cell proliferation. Second, the expression of VEGF-2, VEGF-A, MMP-2, MMP-9, and basic fibroblast growth factor is down-regulated to suppress the formation of tumor microvasculature. Third,Tongguanteng (Marsdenia tenacissima)increases the expression of IL-2, TNF-α, glutathione peroxidase,catalase, and SOD and down-regulates IL-10 and MDA expression, thereby enhancing the body’s immunity and antioxidant mechanisms. Fourth, the phosphorylation levels of FAK, activator of transcription 3, ERK, p38, and Rho are reduced in the downstream pathway of the CCR5-CCL5 axis to decrease tumor cell migration and invasion. Fifth, EGFR, c-Met, and tyrosine-protein kinase receptor activation is inhibited, which enhances the anti-tumor efficacy of EGFR-TKIs. Additionally,Tongguanteng (Marsdenia tenacissima)inhibits P-gp and CYP450 to enhance the concentration of other anti-tumor drugs in tumor cells, thereby enhancing their anti-tumor effects. Other studies have focused on HIV inhibition [72].Therefore, Tongguanteng (Marsdenia tenacissima) as an anti-neoplastic medicinal plant, either alone or in combination with conventional clinical anti-cancer drugs,has great therapeutic effects.
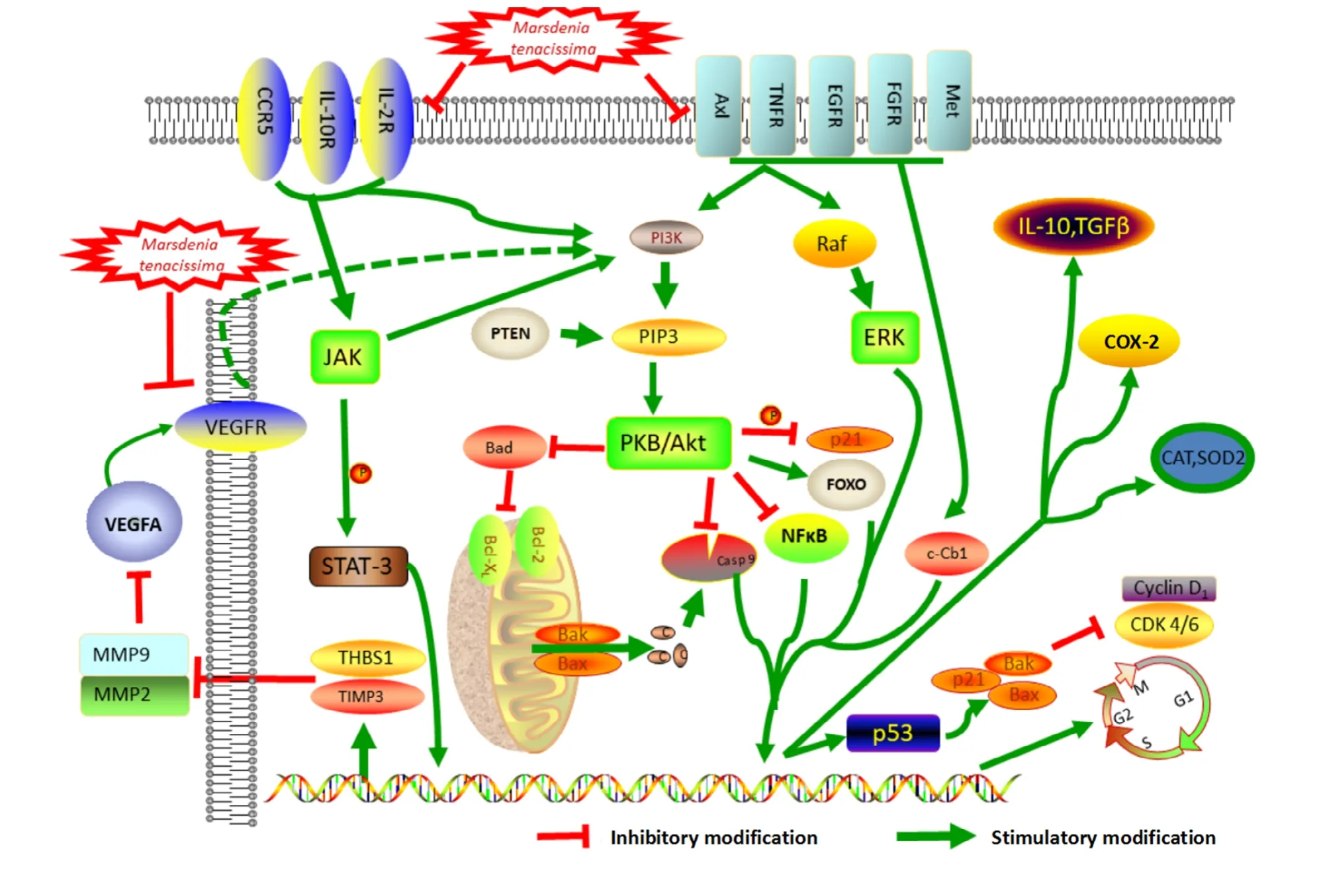
Figure 1 Schematic description of the mechanisms of antitumor for Tongguanteng (Marsdenia tenacissima)
However, the mechanism underlying the anti-tumor activity of Tongguanteng (Marsdenia tenacissima) is not completely understood, and only a few randomized control studies and large multicenter trials have been reported on the clinical efficacy of Xiaoaiping injection for treating tumors. Additionally, its adverse effects and benefits of co-administration with other therapies, for example, co-application with molecular targeted drugs,require further analysis because many reports have documented adverse reactions to Tongguanteng(Marsdenia tenacissima) [73, 74]. Thus, the clinical application of this plant for treating cancer remains limited. Further studies on the anti-cancer mechanism,long-term effect, and toxic components of Tongguanteng(Marsdenia tenacissima) [75] are needed to provide a basis for the development and application of this plant in the clinical treatment of tumors.
1. Xing WX, Chen B, Mi HM,et al. Textual research of Wuguteng. Chin Med Mat 2003: 524-526.
2. Cai F, Chu ZY, Zhang H. Research progress of traditional Chinese medicine Marsdenia tenacissima.J Liaoning Univ Tradit Chin Med 2007: 37-39.
3. Han L, Zhang H, Kang TG,et al. Research progress of Marsdeniae Tenacissimae. Chin Arch Tradit Chin Med 2016: 2329-2331.
4. Ye DS, Luan YG, Li HQ. Symposium on the treatment of malignant tumors by marsdeniae tenacissimae caulis. Bulletin Med Res 1984: 9-10.
5. Ye DS. Anti-tumor effect of Wuguteng preparation through identification. Bulletin Med Res 1985: 193.
6. Zhang GZ, Liu SN. The effect of Xiaoaiping injection in patients with advanced esophageal cancer. Oncol Prog 2017: 670-672.
7. Wang ZL, Fan QX, Fan KS. Clinical study of Xiaoaiping in the treatment of cancer. J Henan Med Univ 1994: 79-80.
8. Zhang J, He W J, Wang JG,et al. Clinical observation on Xiao’aiping injection combined with icotinibin treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. J Hubei Univ Chin Med 2018: 42-45.
9. Bai RL. Effect of Xiaoaiping injection combined with chemotherapy in the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Chin J Misdiagn 2010:5359-5360.
10. Wu Y. Comparison and analysis of irinotecan alone or combined with Xiaoaiping in the treatment of elderly patients with advanced gastric cancer. Chin Pharm 2016: 657-659.
11. Ye B, Li J, Li Z,et al. Anti-tumor activity and relative mechanism of ethanolic extract of Marsdenia tenacissima (Asclepiadaceae) against human hematologic neoplasm in vitro and in vivo. J Ethnopharmacol 2014, 153: 258-267.
12. Ye B, Yang J, Li J,et al. In vitro and in vivo antitumor activities of tenacissoside C from Marsdenia tenacissima. Planta Med 2014, 80: 29-38.
13. Xue HL, Huang XD, He D,et al. Effect of Marsdenia tenacissima extract on proliferation and apoptosis of hematological neoplasm cell lines. J Sichuan Univ 2012, 43: 174-179.
14. Li D, Li C, Song Y,et al. Marsdenia tenacssima extract and its functional components inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of human Burkitt leukemia/lymphoma cells in vitro and in vivo. Leuk Lymphoma 2015, 1-10.
15. Wang Y, Chen B, Wang Z,et al. Marsdenia tenacissimae extraction (MTE) inhibits the proliferation and induces the apoptosis of human acute T cell leukemia cells through inactivating PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway via PTEN enhancement. Oncotarget 2016, 7: 82851-82863.
16. Chen B, Li CP, Chen JH,et al. Effect of extract from Marsdenia tenacissima on Jurkat, Raji and RPMI8226 cells in vitro. Chin J Biochem Pharm 2009, 30: 174-177.
17. Ceng C, Chen Y, Shan LH,et al. Inhibition effect of Marsdenia tenacissima on K562 cells proliferation.Anti-tumor Pharm 2011, 1: 505-507.
18. Zhu RJ, Shen XL, Dai LL,et al. Total aglycones from Marsdenia tenacissima increases antitumor efficacy of paclitaxel in nude mice. Molecules 2014,19: 13965-13975.
19. Lin YC. The inhibition of total glycosides in glaucescent fissistigma root on SGC-7901, S180 and P388 tumor cells. J Pharm Res 2015, 34: 376-378.
20. Li D, OuYang J, Li CP,et al. Marsdenia tenacissimae Induces apoptosis of human U937,HL60 leukemia cells. Chin J Biochem Pharma 2008:33-37.
21. Chen B, Li CP, Chen JH,et al. Study on the inhibition and apoptosis of leukemia cells induced by Marsdenia tenacissimae extraction. J Nanjing TCM Univ 2009, 25: 233-234.
22. Li D, OuYang J, Li CP,et al. Effect of Marsdenia tenacissimae on the apoptosis-associated gene expression profile of U937 cells. Chin J Biochem Pharm 2008: 240-243.
23. Fang YQ. Research of Xiaoaiping injection on HEL cell line In vitro. Med Inf 2010, 5: 2506-2507.
24. Wang SG, Feng LF, Li D. One hundred and thirty one cases of non hodgkin lymphoma treated with Xiaoaiping injection in combination with chemotherapy. Henan Tradit Chin Med 2017:1488-1490.
25. Han SY, Ding HR, Zhao W,et al. Enhancement of gefitinib-induced growth inhibition by Marsdenia tenacissima extract in non-small cell lung cancer cells expressing wild or mutant EGFR. BMC Complem Altern M 2014, 14:165.
26. Han SY, Zhao W, Han HB,et al. Marsdenia tenacissima extract overcomes Axl- and Met-mediated erlotinib and gefitinib cross-resistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncotarget 2017,8: 56893-56905.
27. Han SY, Zhao MB, Zhuang GB,et al. Marsdenia tenacissima extract restored gefitinib sensitivity in resistant non-small cell lung cancer cells. Lung Cancer 2012, 75: 30-37.
28. Yao S, To KK, Wang YZ,et al. Polyoxypregnane steroids from the stems of Marsdenia tenacissima. J Nat Prod 2014, 77: 2044-2053.
29. Wei WJ, Zhang GQ, Liu SJ,et al. Anti-tumor effect of Tenacissoside H and Influence on immune function of lewis lung cancer mice. Chin J Inf Tradit Chin Med 2014, 2163-66.
30. Lin SS, Li FF, Sun L,et al. Marsdenia tenacissima extract suppresses A549 cell migration through regulation of CCR5-CCL5 axis, Rho C, and phosphorylated FAK. Chin J Nat Med 2016, 14:203-209.
31. Chen TS, Wang XP, Wang ZP,et al. Fluorescence emission analysis of caspase-3 activation induced by Xiaoaiping (XAP) inside living human lung adenocarcinoma cells. Spectrosc Spectr Anal 2008:1327-1331.
32. Bai RL. Effect of Xiaoaiping injection combined with chemotherapy in the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Chin J Misdiagn 2010:5359-5360.
33. Ye L, Fu B. Effect of Xiaoaiping injection on the efficacy of recent TP regimen chemotherapy in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer.Shanxi Med J 2017: 1189-1191.
34. Zhang GH. Effect of Xiaoaiping combined with docetaxel on advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J Huaihai Med 2017: 479-480.
35. Zhang H, Zhang J, Ding H,et al. Clinical value of Tongguanteng (Radix seu Herba Marsdeniae Tenacissimae) extract combined with chemotherapy in the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a Meta-analysis. J Tradit Chin Med 2016, 36:261-270.
36. Fan W, Sun L, Zhou JQ,et al. Marsdenia tenacissima extract induces G0/G1 cell cycle arrest in human esophageal carcinoma cells by inhibiting mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway. Chin J Nat Med 2015, 13: 428-437.
37. Yao S, To KK, Ma L,et al. Polyoxypregnane steroids with an open-chain sugar moiety from Marsdenia tenacissima and their chemoresistance reversal activity. Phytochemistry 2016, 12647-58.
38. Wu Y. Comparison and analysis of irinotecan alone or combined with Xiaoaiping in the treatment of elderly patients with advanced gastric cancer. Chin Pharm 2016: 657-659.
39. Hong HJ, Fang L. Application of Xiaoaiping combined with CPT-11 chemotherapy in elderly patients with advanced gastric cancer. J Med Forum 2017: 129-130.
40. Lv XR. Effect of Xiaoaiping injection combined with chemotherapy on advanced esophageal cancer.World Latest Med Inf 2017: 102.
41. Sheng YL. Therapeutic value of xiaoaiping combined with TP on advanced esophageal cancer.Guide Chin Med 2017: 207-208.
42. Qian XL, Zhou F, Zuo Y,et al. Clinical observation on treating TS by chemotherapy plus the Xiaoaiping.Clin J Chin Med 2017: 56-58.
43. Liu W. Clinical observation and study of Xiaoaiping injection combined with SOX regimen for advanced gastric cancer. Shangdong Univ 2017.
44. Li QH, Wang N, Pan SY,et al. Effect of extract from Marsdenia Tenacissima on the apoptosis of BGC-823 gastric cancer cell and the expression of MTDH gene. Chin Arch Tradit Chin Med 2017, 35:892-896.
45. Zhou YY, Li YY, Li L,et al. The experimental study on the extractive of Glaucescent Fissistigma root inhibiting the gastric cancer tumors growth in mouse.Lab Animal Sci 2012, 29: 13-15.
46. Chen Y, Chen YY, Lin CH. Effects of acanthopanax obscurus on growth, metastasis and cyclooxygenase-2 expression in MKN-45 human gastric cancer in situ. Chin J Gerontol 2015, 35:2939-2941.
47. Zhang W, Wang ZF, Wang J,et al. Chemical constituents from Marsdenia tenacissima and their anti-tumor activities. Chin Tradit Patent Med 2017,39: 334-338.
48. Zhang D, Wu J, Wang K,et al. Which are the best Chinese herbal injections combined with XELOX regimen for gastric cancer? A PRISMA-compliant network meta-analysis. Med 2018, 97: e0127.
49. Zhang D, Zheng J, Ni M,et al. Comparative efficacy and safety of Chinese herbal injections combined with the FOLFOX regimen for treating gastric cancer in China: a network meta-analysis.Oncotarget 2017, 8: 68873-68889.
50. Zhu XX, Zhao LH, Yan SH,et al. Study of Glauceacent Fissistigma Root extractive on multiplication of Lovo cells. Chin J Clin Pharm Ther 2007: 1372-1375.
51. Wang Q, Cao J, Wang P,et al. Antitumor effect of C21 steroidal glycosides on adenoid cystic carcinoma cell line SACC83. Clin Lab 2015, 61:1553-1560.
52. Zhang H, Pei ZD, Zhang XY,et al. Antitumor activities of liposoluble components of caulis Marsdeniae tenocissimae and analysis on its chemical constituents. Chin J Chin Mat Med 2010,35: 3325-3328.
53. Huang Z, Lin H, Wang Y,et al. Studies on the anti-angiogenic effect of Marsdenia tenacissima extract in vitro and in vivo. Oncol Lett 2013, 5:917-922.
54. Han L, Leng CY, Li WH,et al. Study on in-vitro and in-vivo antitumor activity of extracts from caulis Marsdeniae Tenacissimae. Tradit Chin Drug Res Clin Pharm 2017, 28: 51-55.
55. Hu YJ, Shen XL, Lu HL,et al. Tenacigenin B derivatives reverse P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance in HepG2/Dox cells. J Nat Prod 2008, 71: 1049-1051.
56. Han SY, Zhao HY, Zhou N,et al. Marsdenia tenacissima extract inhibits gefitinib metabolism in vitro by interfering with human hepatic CYP3A4 and CYP2D6 enzymes. J Ethnopharmacol 2014, 151:210-217.
57. Jiang S, Qiu L, Li Y,et al. Effects of Marsdenia tenacissima polysaccharide on the immune regulation and tumor growth in H22 tumor-bearing mice. Carbohydr Polym 2016, 137: 52-58.
58. Qian J. Experimental study of Marsdenia tenacissima injection combination with platinum in treatment of primary liver cancer. Nanjing Univ Chin Med 2009.
59. Zuo XD, Cui YA, Qin SK,et al. Expressions of VEGF and bFGF in human hepatocarcinoma cell with glaucescent fissistigma root injection. Chin Clin Oncol 2010, 15: 1062-1065.
60. Zhang R, Liu J, Liu YC,et al. Experimental study on effect of glaucescent fissistigma root preparation on Bel-7402 cells apoptosis. Mod Oncol 2013, 21:488-491.
61. Li WJ, Lin CF, Ren YM,et al. Experimental study of Xiaoaiping against hepatoma cells growth in vitro.Chin Remed Clin 2010, 10: 164-165.
62. Chen B, Li CP, OuYang J,et al. Effect of extractive of marsdenia tenacissima on human normal immunocytes and hemopoietic stem cells in vitro.Chin Clin Oncol 2010, 15: 887-890.
63. Huang Z, Wang Y, Chen J,et al. Effect of Xiaoaiping injection on advanced hepatocellular carcinoma in patients. J Tradit Chin Med 2013, 33:34-38.
64. Yao M, Xiao CM, Li Y,et al. Chemical constituents of glycosides from Marsdenia tenaccima and the anticancer activity in vivo. J Nanchang Univ 2015,39: 88-90,
65. Ni CH, Pei ZD, Zhang JX,et al. Study on extraction,isolation and antitumor activity of betulinic acid from caulis Marsdeniae tenocissimae. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Form 2012, 18: 172-175.
66. Ruan LW, Deng YC. Study on effect of Xiaoaiping in enhancing efficacy of neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer and its mechanism. Chin J Chin Mat Med 2015, 40: 749-752.
67. Li XG, Liu BX. Effect of Xiaoaiping combined with neoadjuvant chemotherapy on the pro-proliferation molecule expression and immune function in patients with breast cancer. J Hainan Med Univ 2017:3096-3099.
68. Huang T, Gong WH, Zou CP,et al. Marsdenia tenacissima extract sensitizes MG63 cells to doxorubicin-induced apoptosis. Genet Mol Res 2014,13: 354-362.
69. Chen BY, Chen D, Lyu JX,et al. Marsdeniae tenacissimae extract (MTE) suppresses cell proliferation by attenuating VEGF/VEGFR2 interactions and promotes apoptosis through regulating PKC pathway in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Chin J Nat Med 2016, 14: 922-930.
70. Dai X, Ji Y, Jiang P,et al. Marsdenia tenacissima extract suppresses tumor growth and angiogenesis in A20 mouse lymphoma. Oncol Lett 2017, 13:2897-2902.
71. Zhang ZQ, Han F, Xie HT,et al. Experimental study on the effect of Marsdenia tenacissima on glioma in nude mice. J New Chin Med 2013, 45: 160-161.
72. Pang X, Kang LP, Fang XM,et al. C21 steroid derivatives from the Dai herbal medicine Dai-Bai-Jie, the dried roots of Marsdenia tenacissima, and their screening for anti-HIV activity.J Nat Med 2017, 72:166-180
73. Xu XJ, Li GZ. Xiaoaiping injection caused serious adverse reactions in 1 case. People’s Mil Surg 2017,60: 925-926.
74. Zhang Y. Xiaoaiping injection caused serious adverse reactions in 1 case. Drug Eval Res 2013, 36:488.
75. Porwal M, Khan NA, Maheshwari KK. Evaluation of acute and subacute oral toxicity induced by ethanolic extract of Marsdenia tenacissima leaves in experimental rats. Sci Pharm 2017, 85: pii: E29.
 Traditional Medicine Research2018年4期
Traditional Medicine Research2018年4期
- Traditional Medicine Research的其它文章
- Long-term effect of Chinese herbal medicine Tianqi Capsule on the incidence of diabetes: an 8-year cohort study protocol
- Influence of astragalus polysaccharide on kidney status and fibrosis indices of a rat model of streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy
- Study on alantolactone-induced differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells into vascular cells
- Jianpi Qingchang Decoction-containing serum regulates the autophagy of interstitial cells
