基于流形正则化和核方法的最小二乘算法
汪宝彬,彭超权,李学锋
(中南民族大学 数学与统计学学院,武汉 430074)
基于流形正则化和核方法的最小二乘算法
汪宝彬,彭超权,李学锋
(中南民族大学 数学与统计学学院,武汉 430074)
研究了再生核希尔伯特空间中流形正则化下的最小二乘算法的学习能力和收敛速度.该算法能够充分利用输入空间的几何特点以及半监督学习中无标记样本的信息,提高算法的有效性和学习效率.另外,讨论了该算法中正则参数的选取,这对算法实现具有现实的意义.
流形学习;正则化;最小二乘算法;核方法;再生核希尔伯特空间
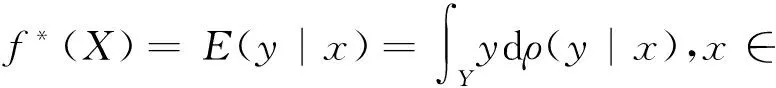
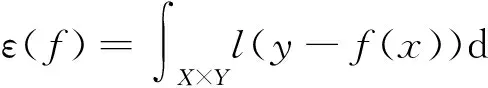
对应的经验泛化误差为:
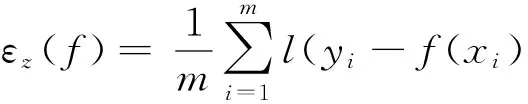
给定假设函数空间H,最小二乘算法定义为:
fz:=arg minf∈Hεz(f).
(1)
在本文中,把再生核希尔伯特空间(RKHS)HK[1]作为假设空间,这里K(·,·):X×X→R是Mercer核,即连续、对称、半正定且:
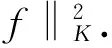
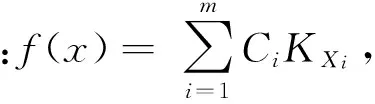
1 建立算法
近年来,多罚研究[8]引起统计学界的广泛关注,其在病态问题中构造稳健解的优势被工业界看重.它能够结合条件概率中的先验测度信息和罚函数项,进行合适的正则参数选择,达到学习的最优效果.在学习理论的背景下,Berklin等人[9]提出多罚正则化方法,对条件概率中的几何结构进行分析,从理论和实验对该方法进行分析;石等人[10]通过积分算子理论,在分布式学习背景中对多罚方法的数学理论有更进一步的研究.本文主要考虑如下算法:
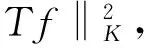
(2)
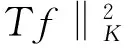
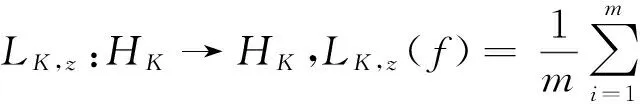
性质1 对于任意μ>0,算法(2)有唯一解如下:
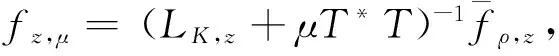
自然地,定义算法(2)的积分形式:
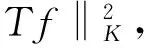
(3)
显然,fμ=(LK+μT*T)-1LK(f*). 这里,积分算子LK:HK→HK定义为:
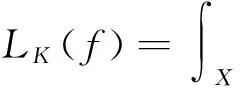
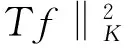
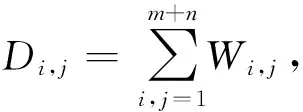
2 主要结果及证明
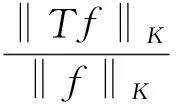
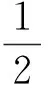
‖fμ-f*‖=O(μr).
证明根据表达式(3),有:
fμ-f*=(LK+μT*T)-1LKf*-f*=
-μT*T(LK+μT*T)-1f*.
因此:
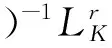
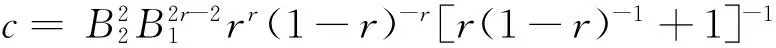
现在估计的重点在于抽样误差fz,μ-fμ,首先要用到以下引理1.
引理1 假设ζi,i=1,…,m是定义在希尔伯特空间(H,‖·‖)上一列独立同分布的随机变量,并且存在常数S>0,使得‖ζi‖≤S,i=1,…,m,则对任意0<δ<1,有:
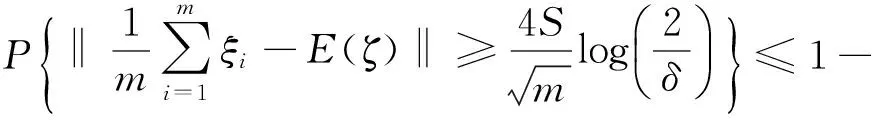
于是,有定理2.
定理2 假设存在S>0, 有|y|≤S,则对任意0<δ<1,有:
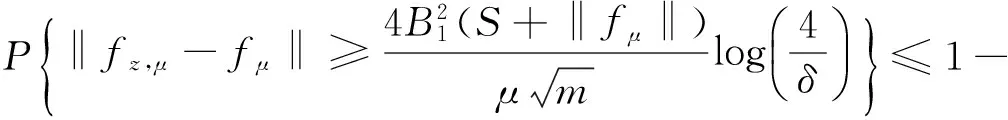
证明从算法(2)的表达式得到:
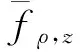
从而,
‖fz,μ-fμ‖≤
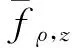
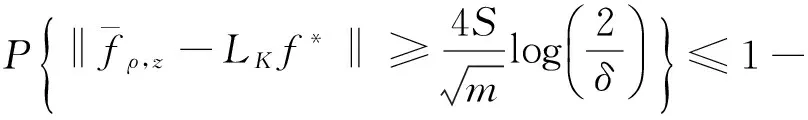
对于第二项‖LK-LK,z‖,令ζi=·,KxiKKxi,则‖·,KxiKKxi‖≤1,i=1,…,m.由引理1有δ.结合第一项和第二项的估计,并将δ替换成δ/2,得到在至少1-δ的概率下,有下式成立:
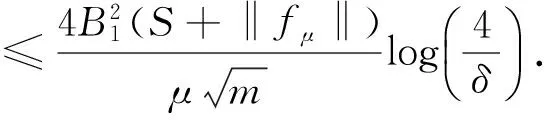
定理2证毕.
现在已有抽样误差和逼近误差两项估计,由算法(2)的学习速率很容易得到定理3.
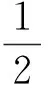
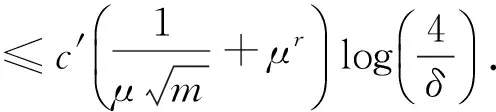
(4)
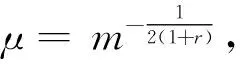
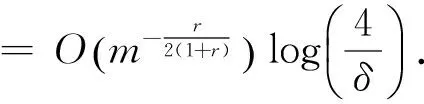
(5)
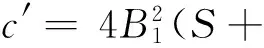
[1] Micchelli C A, Xu Y S, Zhang H Z. Universal kernels[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research,2006,7(4):2651-2667.
[2] Evgeniou T, Pontil M, Poggio T. Regularization networks and support vector machines[J]. Advances in Computational Mathematics,2000,13:1-53.
[3] Bartlett P L, Mendelson S. Rademacher and Gaussian complexities: risk bounds and structural results[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research,2002,3:463-482.
[4] Zhang T. Statistical behavior and consistency of classification methods based on convex risk minimization[J].Annals of Statistics, 2004,32:56-85.
[5] Bartlett P L, Jordan M I, McAuliffe J D. Convexity, classification, and risk bounds[J]. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 2006,101:138-156.
[6] Zhou D X. Capacity of reproducing kernel spaces in learning theory[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory,2003,49:1743-1752.
[7] Shi L, Feng Y L, Zhou D X. Concentration estimates for learning withl1-regularizer and data dependent hypothesis spaces[J]. Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis,2011,31:286-302.
[8] Abhishake, Sivananthan S. Multi-penlty regularization in learning theory[J]. Journal of Complexity,2016,36(C):141-165.
[9] Berklin M, Niyogi P, Sindhwan V. Manifold regularization: A geometric framework for learning from labeled and unlabeled examples[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research,2006,7(1):2399-2434.
[10] Shi L, Guo Z C, Lin S B. Distributed learning with multi-penalty regularization[J]. Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis,DOI: 10.1016/j.acha.2017.06.001.
TheLeastSquareAlgorithmBasedonManifoldRegularizationandKernelMethod
WangBaobin,PengChaoquan,LiXuefeng
(College of Mathematics and Statistics, South-Central University for Nationalities, Wuhan 430074, China)
In this paper, we considered the learning ability and convergence rate of the least square algorithm under the manifold regularization in the Reproducing Kernel Hilbert Space(RKHS). This algorithm can make full use of the geometric construction characteristics of the input space and improve the validity and the learning efficiency of the classical least square algorithm by extracting the information from the unlabeled data. Moreover, we discussed the choice of the regularization parameter, which is meaningful to the design of the algorithm.
manifold learning;regularization; least square algorithm; kernel method; reproducing kernel Hilbert space
2017-09-02
汪宝彬(1976-),男,副教授,博士,研究方向:概率统计,E-mail: wbb1818@126.com
国家自然科学基金资助项目(11671307);湖北省自然科学基金资助项目(2017CFB523)
O211
A
1672-4321(2017)04-0143-03

