索-梁组合结构的面内外模态分析
沈忠伟
(国家电网湖南省电力公司检修公司,长沙 410014)
索-梁组合结构的面内外模态分析
沈忠伟
(国家电网湖南省电力公司检修公司,长沙 410014)
利用哈密顿变分原理以及结构动静态构型的影响,建立了索-梁组合结构的约化运动学控制方程.根据求解得到的面内面外特征值方程,并通过分段函数的引入,研究了结构的模态函数的几种形式.随后,根据索-梁组合结构中索的模态函数,分析了面内外运动“局部模态”和“模态局部化”现象的产生.研究表明,在面内运动,在不考虑内共振情况下,面内运动索的大幅振动是由于“模态局部化”现象的产生,而根据特征值方程,“局部模态”只能出现在索-梁组合结构索的面外运动.
哈密顿变分原理;索-梁组合结构;局部模态
拉索在工程中应用广泛,是一种主要只能承受拉力不能承受压力的构件,拉索具有强度较高、松弛较低、质量较轻等特点,使得其能而较好地应用于各种建筑工程结构中,对于向大跨度方向发展的桥梁结构如斜拉桥,拉索是结构必用的构件.众所周知,拉索的自然特性突出,如具有小质量、大柔度及较低的阻尼特性,在风、雨、地震及车辆等荷载作用下,使得斜拉索产生的大幅振动,可能会使得桥梁发生破坏,对桥梁结构的安全性和行车安全产生严重威胁.因此,斜拉索的非线性动力学问题一直以来都受到科研工作者的重视,是力学领域的研究热点[1].
近年来,Fujino[2]等、Gattulli[3]和赵跃宇等[4]建立了索-梁模型(主梁一端固定一端与斜拉索连接),分别应用多尺度法研究了拉索的面外模态与梁的2个方向的弯曲模态之间的满足1:1和2:1内共振模式.以往的文献局限在将索的模态函数仅仅简化为单索情况下的模态函数形式,使得对拉索在桥面和桥塔的运动研究较为简单,从而根据可能的“局部模态”去分析斜拉索可能会产生的大幅振动.“局部模态”是指在结构振动中,只有索的振动.但是结构不同使得单索的模态函数与索-梁结构的模态函数也会有较大的差异[3-4].这极有可能在理论上使得研究失去合理性,因此很难对拉索大幅振动及桥梁的破坏机理进行合理解释,很难满足未来超大跨度桥梁建设的工程需要[5-6].目前较少有文献根据索-梁组合结构的特性去分析可能的面内面外运动索的大幅振动,即从索的模态函数去分析可能出现的“局部模态”及“模态局部化”现象,而“模态局部化”是指在结构振动中,索的振动起主导作用,从而进一步揭示大幅振动产生的机理[7-8].
基于上述原因,严格根据特征值方程,确定索的模态函数可以更好地理解局部模态,模态局部化现象,进一步揭示索的大幅振动产生原因[9].
1 索-梁运动方程
索-梁模型如图1所示.

图1 索-梁组合结构的动静态构型
索和梁的轴向位移可以忽略.因此,索-梁组合结构运动方程可以由哈密顿变分原理得出[10]:

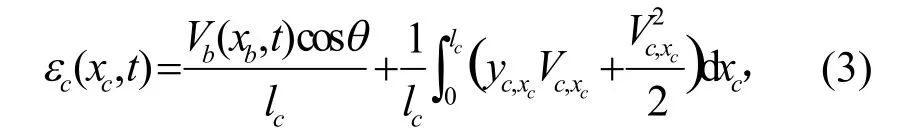
为了更好理解索-梁组合结构的动力学行为,对上述方程进行无量纲化,无量纲化参数如下:
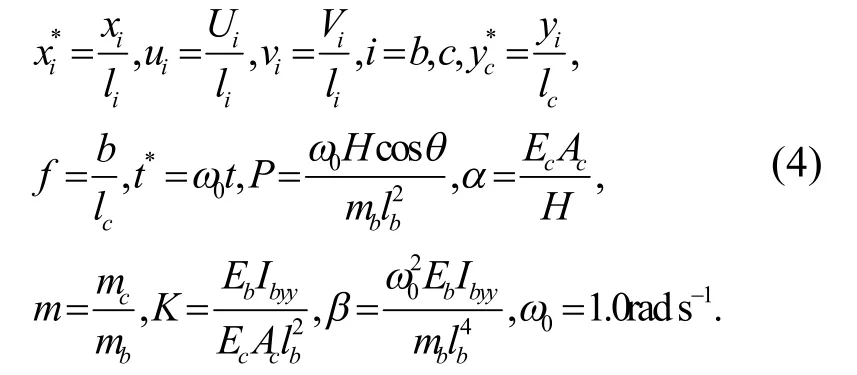
将式(4)代入索-梁运动方程以及边界和连接条件,可以得到:
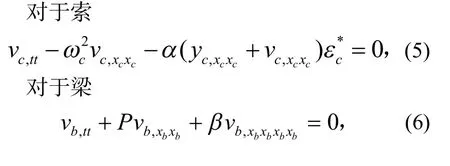
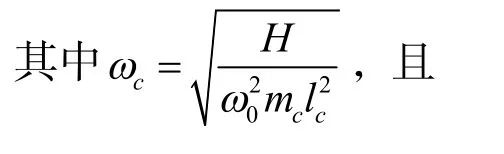
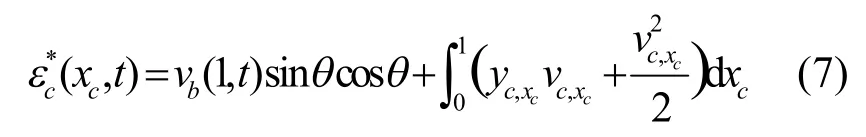
利用分离变量法可以得到整体系统的固有频率以及索和梁的模态函数.对索和梁的位移函数进行分离变量
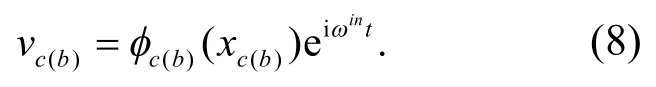
将式(8)代入索,梁运动方程以及边界和连接条件中.
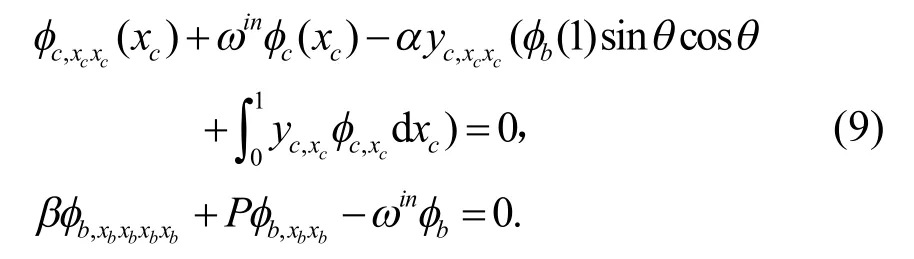
为了求解式(9),引入索的辅助条件,假设
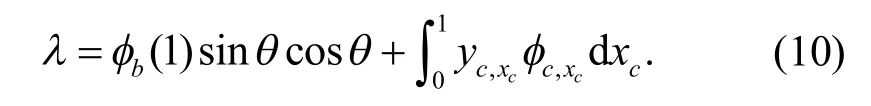
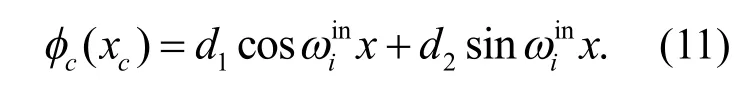
同样地,考虑到l=0,在结构的连接点处力平衡条件可以表示成

这意味着该情况下的剪力为零.类似地索的模态函数可以表示成

梁的边界和连接条件为:
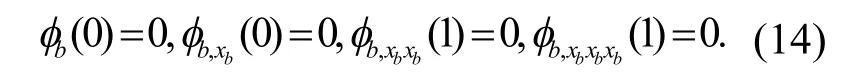
在l=0这种情况下,索-梁结构特征值方程可以通过式(14) 单独的求得.同样地,将式(13)代入式(10),可以得到整体结构特征值方程:

借助于软件Mathematica,式(13)和式(15)可以分别得到求解,但是通过计算,2个方程得到的解答并不是相等的(见图2).因此,l=0这种情况是不存在的[3-6].

图2 索-梁组合结构的特征值方程
2 局部模态与模态局部化
所以,根据特征值分析,我们可以得出结论,对于索梁组合结构面内振动,“局部模态”是不可能发生的,在不考虑内共振情形下,桥梁结构中索的大幅振动是由于发生了“模态局部化”现象.因此,对应着的索的模态函数应表示为
3 结论
本文根据变分原理,得到了索-梁组合结构的运动方程,根据分离变量法得到了结构的特征值方程,研究了索-梁组合结构面内面外振动特性.研究表明,“局部模态”只可能发生在面外运动,即所谓的大幅振动,为索的振动,因此梁的面外受力分力为零,即梁没有任何位移,而完全表现为索的振动位移,即“局部模态”发生了,所以“局部模态”只可能发生在面外运动,“局部振动”不可能发生在面内.面内运动所谓的“局部模态”实际上应为 “模态局部化”现象,其对应着的模态函数应有所不同.
[1]Wgnitchai W, Fujino Y, Susumpow T. A non-linear dynamic model for cables and its application to a cable-structure system[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 1995, 187(4):695-712.
[2]Fujino Y, Wrnitchai W, Pacheco B M. An experimental and analytical study of autoparametric resonance in a 3DOF model of cable-stayed beam[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 1993, 4(4):111-138.
[3]Gattuli V, Lepidi M, John H G, Taylor A C. One-to-two global interaction in a cable-stayed beam observed through analytical finite element and experimental models[J]. International Journal of Non-linear Mechanics, 2005, 40(4): 571-588.
[4]王志搴, 赵珧冰, 孙测试, 等.索-梁组合结构的建模及面内动力特性分析.固体力学学报[J]. 2014, 35(3): 1-5.
[5]Kang Zhan, Xu Kesheng, Luo Zhen. A numerical study on nonlinear vibration of an inclined cable coupled with the deck in Cable-stayed bridges[J]. Journal of Vibration and Control,2012, 18(3): 404-416.
[5]陈水生, 孙炳楠.斜拉桥索一桥耦合非线性参数振动数值研究[J]. 土木工程学报, 2003, 36(4): 70-75.
[6]王志搴, 唐驾时, 罗迎社.索-梁耦合结构的Hopf分岔的反控制[J]. 固体力学学报, 2016, 37(1): 90-96.
[7]Zhqian Wang , Ceshe Sun, Yaobing Zhao,at al.Modeling and nonlinear modal characteristics of the cable-stayed beam[J].European Journal of Mechanics - A/Solids, 2014, 47(C):58-69.[8]Xia Y, Fujino Y. Auto-parametric vibration of a cable-stayed beam structure under random excitation[J]. Journal of Engineering-Mechanics, 2006, 132(3): 279-286.
[9]Gattuli V, Morandini M, Paopolone A. A parametric analytical model for non-linear dynamics in cable-stayed beam[J].Earthquake Engineering and Structural Dynamics, 2002, 31(6):1281-1300.
[10]Gattuli V, Lepedi M. Nonlinear interactions in the planar dynamics of cable-stayed beam[J]. International Journal of Solid of Structures, 2003, 40(18): 4729-4748.
(责任编校:徐赞)
In-out-plane Modal Analysis of the Cable-stayed Beam
SHEN Zhong-wei
(State Grid Hunan Maintenance Company, Changsha, Hunan 410014, China)
Using the Hamilton principle and the effects of the dynamic and static configuration of the cable and beam, the equations of motion of the cable-stayed beam can be obtained. Considering the boundary and continuity conditions, the in-plane eigenvalue problem is investigated. By introducing the piecewise function, the mode shapes can be obtained. It is shown that the curve veering phenomenon can be observed in the natural frequency spectrum of the system. The frequency crossover phenomenon is obvious. Considering the local mode and global mode, the mode shapes of the cable-stayed beam are discussed.
Hamilton’s principle; cable-stayed beam; local modal
O313.3
A
10.3969/j.issn.1672-7304.2017.02.0006
1672–7304(2017)02–0025–03
2016-12-09
湖南省教育厅科研项目(15C1411)
沈忠伟(1968-),男,湖南长沙人,工程师,主要从事电力非线性及分岔控制研究,E-mail: wangzq@hnu.edu.cn.

