肝癌组织miR- 148a表达变化及其与患者临床病理参数和术后早期复发的关系
周兴芹,陈钟,常仁安
(南通大学附属医院,江苏南通226001)
肝癌组织miR- 148a表达变化及其与患者临床病理参数和术后早期复发的关系
周兴芹,陈钟,常仁安
(南通大学附属医院,江苏南通226001)
目的观察原发性肝癌(HCC)组织微小RNA- 148a(miR- 148a) mRNA表达变化,并分析其与患者临床病理参数和术后早期复发的关系。方法选择HCC组织及其配对的癌旁正常组织各142例份,采用qRT- PCR法检测miR- 148a mRNA表达。分析HCC组织miR- 148a mRNA表达与患者临床病理参数及术后早期复发的关系。结果HCC组织miR- 148a mRNA相对表达量明显低于癌旁正常组织(P<0.05)。以142例HCC患者miR- 148a mRNA相对表达量的均数为截断值,将患者分为miR- 148a mRNA高表达者65例和miR- 148a mRNA低表达者77例。miR- 148a mRNA表达与肿瘤大小、微血管侵犯及TNM分期有关(P均<0.05),而与年龄、性别、肝硬化、血清AFP水平、HBV感染、组织分化程度及肿瘤数目无关(P均>0.05)。142例HCC患者中,早期复发88例、未复发54例。早期复发者miR- 148a mRNA相对表达量明显低于未复发者(P<0.05)。88例早期复发者中,miR- 148a mRNA低表达者55例、miR- 148a mRNA高表达者33例,miR- 148a mRNA低表达者早期复发率明显高于miR- 148a mRNA高表达者(P<0.05)。采用受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线评价miR- 148a mRNA预测HCC术后早期复发的价值,结果显示,miR- 148a mRNA预测HCC术后早期复发的ROC曲线下面积为0.710(95%CI:0.660~0.769,P<0.01),其cut off值为0.31,此时miR- 148a mRNA预测HCC术后早期复发的敏感性、特异性分别77.1%、71.8%。结论HCC组织中miR- 148a mRNA低表达,其表达变化与肿瘤进展有关。miR- 148a mRNA可作为HCC患者术后早期复发的预测因子之一。
原发性肝癌;微小RNA- 148a;临床病理参数;复发
全球范围内每年因肝癌死亡的患者约70万,其中我国约占50%[1]。目前,原发性肝癌(HCC)的治疗方法有多种。手术治疗仍是HCC的首选治疗方法,但术后易复发,术后2年内复发率为62.4%~77.8%,5年生存率较低[2~5]。因此,探讨HCC术后早期复发的分子机制,寻找准确预测HCC术后早期复发的肿瘤分子生物学标志物意义重大。微小RNA(miRNA)是一类由19~25个核苷酸组成的、高度保守的内源性非编码小分子RNA,可通过与目标基因mRNA的3′非翻译区结合,调控下游靶基因表达,继而发挥相应的生物学功能[6,7]。近年研究发现,miRNA与肿瘤的发生、发展密切相关[8,9]。miR- 148a是miRNA家族的成员之一,研究发现,其在胃癌、结肠癌及非小细胞肺癌等多种恶性肿瘤组织中低表达,具有抑癌基因作用[10~12]。但目前关于miR- 148a mRNA在HCC组织中表达的报道甚少,且其与患者临床病理参数及术后早期复发的关系尚不完全明确。2011年1月~2014年7月,本研究观察了HCC组织中miR- 148a mRNA表达变化,现分析其与患者临床病理参数及术后早期复发的关系。
1 临床资料

1.2 HCC组织及其配对癌旁正常组织miR- 148a mRNA表达比较 将手术切除的HCC组织及其配对的癌旁正常组织(距癌组织边缘≥2 cm)离体30 min内置于液氮中,再转入- 80 ℃低温冰箱中冻存。取部分HCC组织及癌旁正常组织,采用TRIzol法提取组织总RNA,紫外分光光度计检测总RNA纯度,OD260/OD280为1.8~2.0,琼脂糖凝胶电泳鉴定总RNA完整,符合实验要求。取总RNA 1 μg,按RNA逆转录试剂盒说明逆转录为cDNA,然后按qRT- PCR试剂盒说明进行PCR扩增。引物序列:miR- 148a上游引物:5′- ACACTCCAGCTGGGACAAA-GTTCTG- 3′,下游引物: 5′- CTCAACTGGTGTCGTGG-AGTCGGCAATTCAGTTGAGTCAGTGCAC- 3′;内参U6上游引物:5′- CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACA- 3′,下游引物:5′- AACGCTTCACGAATTTGCGT- 3′。PCR反应体系共25 μL:SYBR® Premix Ex TaqTMⅡ(2×)12.5 μL,cDNA 2 μL,上下游引物各1 μL,无酶水8.5 μL;反应条件:95 ℃预变性10 min,95 ℃ 15 s、60 ℃ 60 s共40个循环。以U6为内参,采用2-ΔΔCt法计算miR- 148a mRNA相对表达量。实验重复3次,取平均值。结果显示,HCC组织miR- 148a mRNA相对表达量为0.35±0.04,癌旁正常组织为1.00±0.02,二者比较P<0.05。以142例患者miR- 148a mRNA相对表达量的均数为截断值,miR- 148a mRNA高表达者65例,miR- 148a mRNA低表达者77例。
1.2 miR- 148a mRNA表达与HCC患者临床病理参数的关系 miR- 148a mRNA表达与肿瘤大小、微血管侵犯及TNM分期有关(P均<0.05),与年龄、性别、肝硬化、血清AFP水平、HBV感染、组织分化程度及肿瘤数目无关(P均>0.05)。见表1。
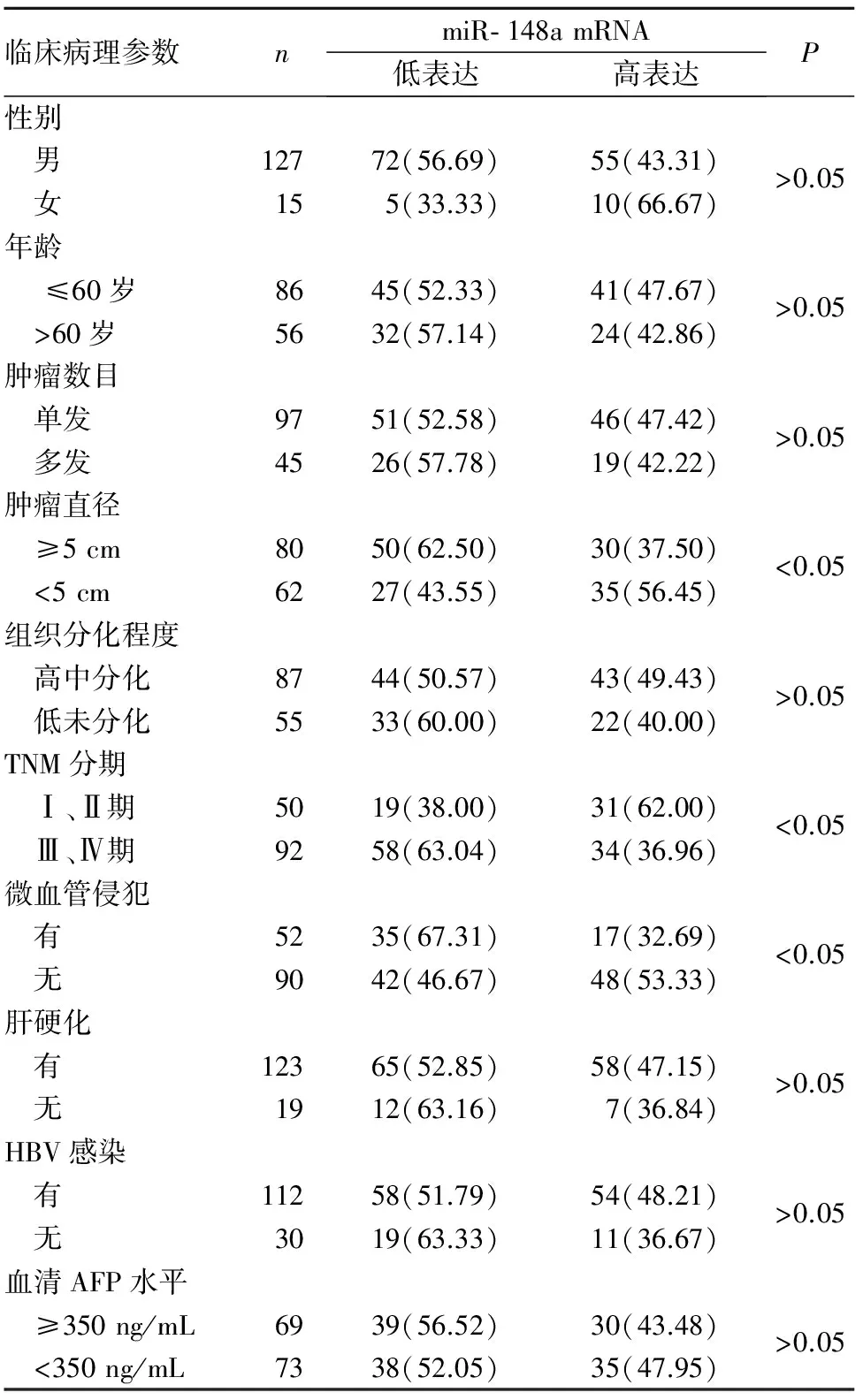
表1 miR- 148a mRNA表达与HCC患者 临床病理参数的关系[例(%)]
1.3 miR- 148a mRNA表达与HCC患者术后早期复发的关系 所有患者术后随访2年。术后1年内每2个月门诊或住院复查1次,术后1~2年每2~3个月复查1次。复查AFP、胸部X线、腹部B超,必要时进行CT、MRI或PET- CT检查。以术后2年内复发定义为早期复发。142例HCC患者中,早期复发88例、未复发54例。早期复发者和未复发者miR- 148a mRNA相对表达量分别为0.20±0.03、0.59±0.06,二者比较P<0.05。88例早期复发者中,miR- 148a mRNA低表达者55例、高表达者33例,miR- 148a低表达者早期复发率明显高于miR- 148a高表达者(P<0.05)。
1.4 miR- 148a mRNA表达预测HCC术后早期复发的价值 ROC曲线分析显示,miR- 148a mRNA表达预测HCC术后早期复发的曲线下面积为0.710(95%CI:0.660~0.769,P<0.01),其cut off值为0.31,此时miR- 148a mRNA预测HCC术后早期复发的敏感性、特异性分别为77.1%、71.8%。见图1。
2 讨论
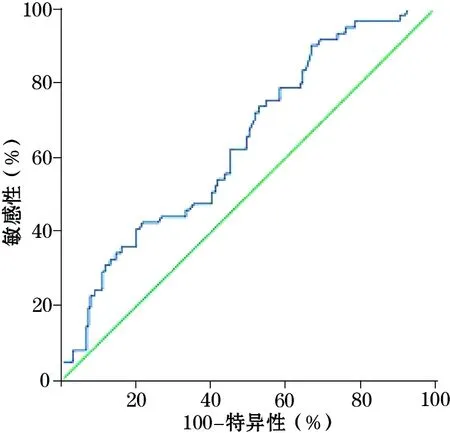
图1 miR- 148a mRNA表达预测HCC患者术后早期复发的ROC曲线
目前关于HCC术后早期复发的分子生物学机制尚不完全明确,临床上缺乏特异性强、敏感性高地预测HCC术后早期复发指标。Budhu等[13]研究发现,Th2- dominant细胞因子与HCC术后早期复发有关;Woo等[14]利用基因芯片技术筛选出了12种与HCC术后早期复发相关的分子生物学标志物,但其预测效果均不令人满意。
miR- 148a是miR- 148a/152家族成员之一,定位于染色体7p15.2,其成熟体由22个核苷酸组成,含有一个包含8个核苷酸区域的种子序列。研究证实,miR- 148a在多种恶性肿瘤组织中表达下调,并可影响肿瘤细胞增殖、侵袭及迁移等生物学行为[10~12];其在胃癌组织中低表达,且在Ⅲ、Ⅳ期胃癌组织中的表达较Ⅰ、Ⅱ期明显降低,提示miR- 148a mRNA低表达与胃癌的恶性进展有关[15]。Szafranska等[16]研究发现,miR- 148a mRNA在胰腺癌组织中表达下调,miR- 148a mRNA低表达可造成其靶基因DNMT1表达升高,从而增加DNMT1对抑癌基因的过度甲基化,继而促进胰腺癌的恶性进展。Tsai等[17]研究发现,复发性结肠癌患者血清miR- 148a mRNA水平降低,并可作为结肠癌根治性切除术后早期复发的分子生物学标志物。
既往研究发现,miR- 148a mRNA在HCC组织中表达下调[18],过表达miR- 148a mRNA能够阻滞细胞周期,抑制HCC细胞增殖[19]。Heo等[20]研究发现,miR- 148a mRNA在HCC组织中表达下调,并与患者预后不良有关。本研究结果显示,HCC组织中miR- 148a mRNA表达降低,且早期复发者miR- 148a mRNA表达较未复发者显著降低,提示miR- 148a mRNA表达降低可能与HCC术后早期复发有关。本研究还发现,miR- 148a mRNA低表达与肿瘤大小、微血管侵犯、TNM分期及淋巴结转移有关,而与年龄、性别、肝硬化、血清AFP水平、HBV感染、组织分化程度及肿瘤数目无关。提示miR- 148a mRNA低表达与HCC患者病情及恶性进展有关。
目前,关于HCC术后早期复发的判定尚无明确标准。有学者将HCC术后2年内复发定义为早期复发[21,22],也有学者选择1年[23]甚至6个月[24]作为术后早期复发的界线。本研究将术后2年内复发定义为早期复发,术后随访发现,142例HCC患者中早期复发88例,且miR- 148a mRNA低表达者早期复发率明显高于miR- 148a mRNA高表达者。ROC曲线分析显示,miR- 148a mRNA表达预测HCC术后早期复发的曲线下面积为0.710,其cut off值为0.31,此时miR- 148a mRNA预测HCC术后早期复发的敏感性、特异性分别为77.1%、71.8%,提示miR- 148a mRNA对预测HCC术后早期复发有一定临床价值。
综上所述,HCC组织中miR- 148a mRNA低表达,其表达变化与肿瘤进展有关;miR- 148a mRNA可作为HCC患者术后早期复发的预测因子之一。
[1] Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, et al. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008[J]. Int J Cancer, 2010,127(12):2893- 2917.
[2] Tang ZY. Hepatoeellular carcinoma- cause, treatment and metastasis[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2001,7(4):445- 454.
[3] Fan ST, Mau Lo C, Poon RT, et al. Continuous improvement of survival outcomes of resection of hepatocellular carcinoma: a 20- year experience[J]. Ann Surg, 2011,253(4):745- 758.
[4] EL- Serag HB. Hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. N Engl J Med, 2011,365(12):1118- 1127.
[5] 周信达,马曾辰,汤钊猷.肝癌复发的临床相关因素//汤钊猷.肝癌转移复发的基础与临床[M].上海:上海科学技术出版社,2003:261- 262.
[6] Shen J, Stass SA, Jiang F. MicroRNAs as potential biomarkers in human solid tumors[J]. Cancer Lett, 2013,329(2):125- 136.
[7] Sorel O, Dewals BG. MicroRNAs in large herpesvirus DNA genomes: recent advances[J]. Biomol Concepts, 2016,7(4):229- 239.
[8] Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, et al. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood- based markers for cancer detection[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2008,105(30):10513- 10518.
[9] Paulmurugan R. MicroRNAs- a new generation molecular targets for treating cellular diseases[J]. Theranostics, 2013,3(12):927- 929.
[10] Xia J, Guo X, Yan J, et al. The role of miR- 148a in gastric cancer[J]. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 2014,140(9):1451- 1456.
[11] Li J, Song Y, Wang Y, et al. MicroRNA- 148a suppresses epithelial- to- mesenchymal transition by targetingROCK1 in non- small cell lung cancer cells[J]. Mol Cell Biochem, 2013,380(1- 2):277- 282.
[12] Takahashi M, Cuatrecasas M, Balaguer F, et al. The clinical significance of MiR- 148a as a predictive biomarker in patients with advanced colorectal cancer[J]. PLoS One, 2012,7(10):e46684.
[13] Budhu A, Forgues M, Ye QH, et al. Prediction of venous metastases, recurrence, and prognosis inhepatocellular carcinoma based on a unique immune response signature of theliver microenvironment[J]. Cancer Cell, 2006,10(2):99- 111.
[14] Woo HG, Park ES, Cheon JH, et al. Gene expression- based recurrence prediction of hepatitis B virus- related human hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2008,14(7):2056- 20564.
[15] Zheng B, Liang L, Wang C, et al. MicroRNA- 148a suppresses tumor cell invasion and metastasis by downregulating ROCK1 in gastric cancer[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2011,17(24):7574- 7583.
[16] Szafranska AE, Davison TS, John J, et al. MicroRNA expression alterations are linked to tumorigenesis and non- neoplastic processes in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma[J]. Oncogene, 2007,26(30):4442- 4452.
[17] Tsai HL, Yang IP, Huang CW, et al. Clinical significance of microRNA- 148a in patients with early relapse of stage Ⅱ stage and Ⅲ colorectal cancer after curative resection[J]. Transl Res, 2013,162(4):258- 268.
[18] Zhang SL, Liu L. microRNA- 148a inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell invasion by targeting sphingosine- 1- phosphate receptor 1[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2015,9(2):579- 584.
[19] Long XR, He Y, Huang C, et al. MicroRNA- 148a is silenced by hypermethylation and interacts with DNA methyltransferase 1 in hepatocellular carcinogenesis[J]. Int J Oncol, 2014,44(6):1915- 1922.
[20] Heo MJ, Kim YM, Koo JH, et al. microRNA- 148a dysregulation discriminates poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in association with USP4 overexpression[J]. Oncotarget, 2014,5(9):2792- 2806.
[21] Imamura H, Matsuyama Y, Tanaka E, et al. Risk factors contributing to early and late phase intrahepatic recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after hepateetomy[J]. J Hepatol, 2003,38(2):200- 207.
[22] Wu JC, Huang YH, Chau GY, et al. Risk factors for early and laterecurrence inhepatitis B- related hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Hepatol, 2009,51(5):890- 897.
[23] Poon RT, Fan ST, Ngl O, et al. Different risk factors and pmgnosis for early and late intrahepatic recurrence after resection of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cancer, 2000,89(5):500- 507.
[24] 徐国斌,易广雄,熊斌,等.原发性肝癌术后早期肝内复发转移36例的介入治疗[J].介入放射学,2013,22(4):325- 327.
ExpressionchangesofmiR- 148ainhepaticcarcinomatissuesanditsrelationshipswithclinicopathologicalparametersandearlypost-operativerecurrence
ZHOUXingqin,CHENZhong,CHANGRen′an
(AffiliatedHospitalofNantongUniversity,Nantong226001,China)
To observe the expression changes of microRNA- 148a (miR- 148a) in the primary hepatic carcinoma (HCC) tissues, and further to analyze its relationships with the clinicopathological parameters of patients and their early post- operative recurrence.MethodsQuantitative RT- PCR (qRT- PCR) were used to detect the relative expression of miR- 148a in 142 cases of HCC tissues and 142 cases of paired adjacent normal tissues. The relationships between miR- 148a expression and the clinicopathological parameters as well as early post- operative recurrence in HCC patients were analyzed.ResultsThe relative expression of miR- 148a was significantly lower in HCC tissues than in the adjacent normal tissues (P<0.05). The mean of the relative expression of miR- 148a in HCC tissues from 142 patients was set as cut- off value, thereafter, patients were categorized into the high- expression group (n=65) and low- expression group (n=77). The expression of miR- 148a was significantly associated with tumor size, microvascular invasion, and TNM stages (P<0.05), while was not statistically associated with age, gender, cirrhosis, serum level of AFP, HBV infection, histological differentiation, or tumor numbers (P>0.05). In the 142 HCC patients, 88 of them suffered from early post- operative recurrence, while the other 54 patients did not. The expression of miR- 148a was significantly lower in patients with early post- operative recurrence than that of those without recurrence (P<0.05). In the 88 patients with early post- operative recurrence, there were 55 cases of patients with low expression of miR- 148a and 33 patients with high expression of miR- 148a. The early recurrence rate was significantly higher in patients with low expression of miR- 148a than that of those with high expression of miR- 148a (P<0.05). Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to evaluate the predictive value of miR- 148a in early post- operative recurrence. Consequently, area under the curve was 0.710 (95%CI:0.660- 0.769,P<0.01), and the cut- off value of relative mRNA expression of miR- 148a was 0.31. Therefore, the sensitivity and specificity of miR- 148a expression in predicting early post- operative recurrence of HCC was 77.1% and 71.8%, respectively.ConclusionThe miR- 148a is low expressed in HCC tissues, and the expression change is associated with tumor progression. Moreover, miR- 148a can be taken as an effective predictive indicator for early post- operative recurrence of HCC.
primary hepatic carcinoma; micro RNA- 148a; clinicopathological parameters; recurrence
江苏省临床医学科技专项基金资助项目(BL2014060);江苏省“科教兴卫工程”医学领军人才和创新团队基金资助项目(LJ201134);南通市科技计划项目(MS22016041)。
周兴芹(1978- ),女,主治医师,主要研究方向为恶性肿瘤的分子生物学机制。E- mail: zhouxingqin666@126.com
常仁安(1975- ),男,副主任医师,主要研究方向为肝脏恶性肿瘤的诊治。E- mail: xuluzlk@yeah.net
10.3969/j.issn.1002- 266X.2017.36.003
R735.7
A
1002- 266X(2017)36- 0009- 04
2017- 02- 21)

