无穷区间上p-Laplacian积微分方程极值解的存在性
方玉萍,王颖
(临沂大学数学与统计学院,山东 临沂 276000)
无穷区间上p-Laplacian积微分方程极值解的存在性
方玉萍,王颖
(临沂大学数学与统计学院,山东 临沂 276000)
带有p-Laplacian算子的积微分方程在应用力学、天体物理和经典电学中有着广泛的应用。非线性微分方程边值问题是微分方程研究领域的一个重要分支。因此,p-Laplacian积微分方程边值问题的研究有着巨大的理论和实际意义。系统地研究无穷区间上, 较为复杂边值条件下的一类p-Laplacian 积微分方程。利用单调迭代方法,在适当的条件下,不仅得到了方程极值解的存在性, 而且得到了方程解的迭代序列。最后,通过一个例子说明了结果的实用性。
p-Laplacian 算子;积微分方程;单调迭代方法;极值解;无穷区间
多孔介质中的湍流问题是一个基本的力学问题,为研究此类问题Leibenson[1]引入了下面p-Laplacian方程
(φp(x′(t)))′+f(t,x(t),x′(t))=0

Kim[11]研究了下面的一维p-Laplacian边值问题(BVP):
(1)

应用不动点指数理论,文[11]得到BVP (1)正解的存在性和解的迭代序列。
文[12]考虑了方程
(φp(u′(t)))′+φ(t)f(t,u(t),u′(t))=0,
t∈J′
(2)
方程(2)的边值条件同BVP(1),这里f∈C(J×J×J,J),φ∈C(J,J)。借助于Avery-Peterson不动点理论,文[12]获得了方程三个正解的存在性。受以上文章的启发,我们主要研究下面的p-Laplacian方程:
(3)



(4)
这里K∈C(D,J),D={(t,s)∈J×J:t≥s},H∈C(J×J,J),f∈C(J′×J×J×J×J,J),f在t=0点奇异。
本文主要利用单调迭代方法讨论BVP(3)的极值解。主要特色如下:首先, 若p=2,g(t)=0,β=a=b=0,α=1并且f中不含有Tu,Su,则BVP(3)可以转化为下面的两点边值问题:
(5)
文[13]研究了BVP(5)正解的存在性,而且许多学者对于二阶微分方程做了系统的研究,如文[14-15]。其次, BVP(3)中,所研究的非线性项f是更为一般的情况,不仅含有导数项,而且含有Tu,Su。最后,研究的边值条件也更为复杂,即两点,三点,多点边值问题是BVP(3)的特殊情况。因此,在一定程度上推广了文[11-13,16-17]的结果。
1 预备知识和引理
定义1 若α是Banach空间E中锥P上的连续凹函数,则有α:P→ [0 ,+∞)是连续的,并且
α(tu+(1-t)v)≥tα(u)+(1-t)α(ν),
u,v∈P,t∈[0,1]
引理1[20]

定义本文所使用的空间E:
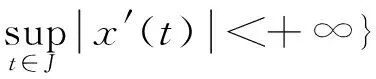
(6)
范数

P={x∈E:x在[0,+∞)是凹的,非减的,
x(t)≥0,x′(t)≥0,t∈J}
本文的主要条件:
(H1)
令
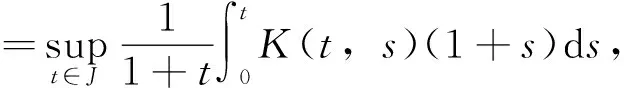

(H2)
f∈C(J′J×J×J×J,J),f(t,0,0,0,0)≡0,t∈J,
f(t,u0,u1,u2,u3)≤q(t)h(t,u0,u1,u2,u3),
h(t,u0,u1,u2,u3)∈C(J×J×J×J×J,J),
h(t,0,0,0,0)≡0,
h(t,(1+t)u0,u1,(1+t)u2,(1+t)u3)有界,
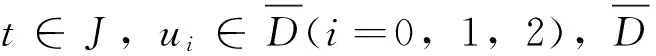
q∈L(J,J),q(t)≡0,t∈J,

注1 由条件(H1),(H2),若x满足BVP(3),则
(φp(x′(t)))′=-f(t,x(t),x′(t),
(Tx)(t),(Sx)(t))≤0,t∈J
即φp(x′(t))在J上非减,也就是说,x′(t)在J上非减。因此,x在J上是凹的。
引理2 假设条件(H1)和(H2)成立, 则x∈P是BVP(3)的解当且仅当x∈C(J)是下面算子方程的不动点:
(Tx)(τ),(Sx)(τ))dτ+φp(b))+
(Sx)(τ))dτ+φp(b))dsdt)+
(Sx)(τ))dτ+φp(b))ds,t∈J
(7)
证明假设x∈P是BVP(3)的解。 对任意的t∈J, 由BVP(3)


即


(Tx)(τ),(Sx)(τ))dτ+φp(b))
(8)
将式(8)由0到t积分可得

(9)

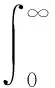


(10)
其中
SR=sup{h(t,(1+t)u0,u1,(1+t)u2,(1+t)u3):
(t,u0,u1,u2,u3)∈J×[0,R]×[0,R]×
[0,k*R]×[0,h*R]}
因此,由式(10)和引理1,有
(11)
由式(10)和式(11)可得,式(9)是有定义的。下面证明x是由式(7)定义的算子A的不动点。
假设x是由式(7)定义的算子A的不动点,对式(7)直接求导数可得
(φp(x′(t)))′=
-f(t,x(t),x′(t),(Tx)(t),(Sx)(t))″
容易证明


证明完毕。
引理3[21-22]空间E由式(6)定义,M是E中的有界集。若
在J上的任一有界子集上等度连续,且对任意给定的ε>0,存在N>0,t1,t2>N,使得
对x∈M一致成立, 则M在E中是相对紧的。
引理4 假设条件(H1),(H2)成立, 则A:P→P是全连续算子。
证明
(i)A:P→P是有定义的。
通过常规的方法可以得到A:P→E是有定义的。下面证明A(P)⊆P。对任意的x∈P, 由式(7)可得
φp((Ax)′(t))=

(12)
(φp((Ax)′(t)))′=
-f(t,x(t),x′(t),(Tx)(t),(Sx)(t))
(13)
由式(7),式(12),式(13)和条件(H2),可知(Ax)(t)>0,(Ax)′(t)≥b≥0,(Ax)′′(t)≤0,即A(P)⊆P。
(ii)A:P→P连续。

f(τ,x(τ),x′(τ),(Tx)(τ),(Sx)(τ))|dτ≤

h(τ,x(τ),x′(τ),(Tx)(τ),(Sx)(τ)))dτ≤

其中
SR0=sup{h(t,1+t)u0,u1,(1+t)u2,
(1+t)u3:(t,u0,u1,u2,u3)∈
J×[0,R0]×[0,R0]×[0,k*R0]×[0,h*R0]}
所以,对任意的ε>0, 可以找到一个充分大的H0>0满足
由Lebesgue控制收敛定理和f的连续性可得
f(τ,x(τ),x′(τ),(Tx)(τ),(Sx)(τ))|dτ→0,
m→+∞
因此对上述的ε>0,存在N>0,当n>N0时,有
f(τ,x(τ),x′(τ),(Tx)(τ),(Sx)(τ))|dτ≤
f(τ,x(τ),x′(τ),(Tx)(τ),(Sx)(τ))|dτ+
f(τ,x(τ),x′(τ),(Tx)(τ),(Sx)(τ))|dτ+
f(τ,x(τ),x′(τ),(Tx)(τ),(Sx)(τ))|dτ≤ε
即
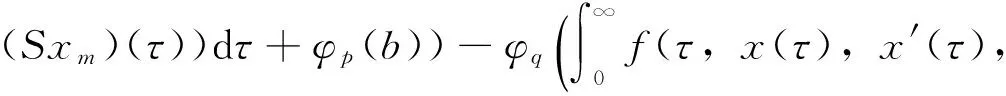
(Tx)(τ),(Sx)(τ))dτ+φp(b))|→0,m→+∞
类似地,对任意的s∈J可得
(Sxm)(τ))dτ+φp(b))-
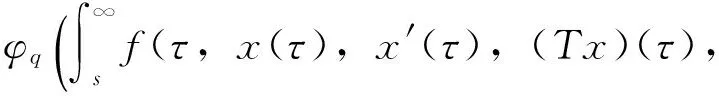
(Sx)(τ))dτ+φp(b))|→0,m→+∞
因此,由Lebesgue控制收敛定理可得
(Sxm)(τ))dτ+φp(b))-
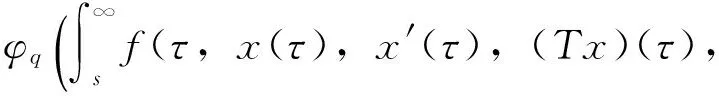
(Sx)(τ))dτ+φp(b))|+
(Txm)(τ),(Sxm)(τ))dτ+φp(b))-

(Sx)(τ))dτ+φp(b))|dsdt)+
(Sxm)(τ))dτ+φp(b))-

(Sx)(τ))dτ+φp(b))|ds→0,m→+∞;
(Axm)′-(Ax)′c=
(Sxm)(τ))dτ+φp(b))-

(Sx)(τ))dτ+φp(b))|→0,m→+∞
故,A:P→P是连续的。
(iii)A:P→P相对紧。

(14)

(15)
其中
SR1=sup{h(t,1+t)u0,u1,(1+t)u2,(1+t)u3:
(t,u0,u1,u2,u3)∈J×[0,R1]×
[0,R1]×[0,k*R1]×[0,h*R1]}
由式(14)-(15)可得
(16)
由式(16)可知AM在E中有界。
(b) 对任意的T>0,t1,t2∈[0,T],x∈M, 不失一般性,假设t1>t2。事实上
(Sx)(τ))dτ+φp(b))+
(Sx)(τ))dτ+φp(b))dsdt)+
(Sx)(τ))dτ+φp(b))ds-

(Tx)(τ),(Sx)(τ))dτ+φp(b))ds|≤
(17)
|φp((Ax)′(t1))-φp((Ax)′(t2))|≤
(18)
由式(17)-(18),对任意的ε>0, 存在δ>0, 对任意的t1,t2∈[0,b],|t1-t2|<δ, 任意的x∈M, 有
|(Ax)′(t1)-(Ax)′(t2)|<ε
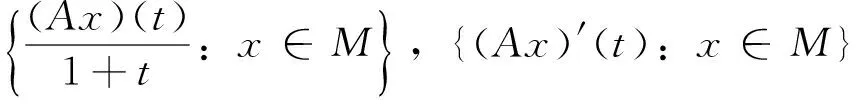
(c) 对任意的x∈M, 由式(7)可得
(Tx)(τ),(Sx)(τ))dτ+φp(b))+
(Sx)(τ))dτ+φp(b))dsdt)+
(Sx)(τ))dτ+φp(b))ds)
(19)
由于
(Tx)(τ),(Sx)(τ))dτ+φp(b))+
(Sx)(τ))dτ+φp(b))dsdt))≤
(20)
(Sx)(τ))dτ+φp(b))ds)=
(Sx)(τ))dτ+φp(b))=b
(21)
根据式(19)-(21)可知
所以,对任意的x∈M,有

(22)
另外,可以得到

所以,对任意的x∈M, 有
|(Ax)′(t)-b|=
(Sx)(τ))dτ+φp(b))-b|≤
t→+∞
(23)
因此,由式(22)-(23),对任意的ε>0, 存在N>0, 对任意的t>N, 任意的x∈M,可得
对任意的t1,t2>N, 任意的x∈M, 有

对任意的t1,t2>N, 任意的x∈M, 易知
|(Ax)′(t1)-(Ax)′(t2)|≤
|(Ax)′(t1)-b|+|(Ax)′(t2)-b|<ε

由引理3,结合A的连续性可知,A:P→P是全连续的。 证明完毕。
2 主要结果
为方便起见,令
定理1 假设条件(H1),(H2)成立,且存在d>2ρ, 有
(H3)


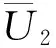
(H4)

(t,u0,u1,u2,u3)∈
J×[0,d]×[0,d]×[0,k*d]×[0,h*d]
则BVP(3)在J上有极大和极小解μ*,ν*,满足
对于
ν0(t)=0,
定义迭代列{μn},{νn}
(Tμn-1)(τ),(Sμn-1)(τ))dτ+φp(b))+
(Tμn-1)(τ),(Sμn-1)(τ))dτ+φp(b))dsdt)+
(Sμn-1)(τ))dτ+φp(b))ds,
(Tνn-1)(τ),(Sνn-1)(τ))dτ+φp(b))+
(Sνn-1)(τ))dτ+φp(b))dsdt)+
(Sνn-1)(τ))dτ+φp(b))ds
并且有

证明由引理4知,A:P→P是全连续的。对任意的x1,x2∈P,x1≤x2, 由A的定义和条件(H3)可知Ax1≤Ax2。记
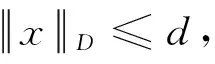
(Tx)(τ),(Sx)(τ))dτ+φp(b))+
(Tx)(τ),(Sx)(τ))dτ+φp(b))dsdt)+
(Sx)(τ))dτ+φp(b))ds|≤
(Sx)(τ))dτ+φp(b))|≤


则有μ0∈Pd。令
μ1=Au0,μ2=Aμ1=A2μ0
由引理4可知μ1∈Pd,μ2∈Pd。定义
μn+1=Aun=An+1μ0,n=0,1,2,…

μ0′(τ),(Tμ0)(τ),(Sμ0)(τ))dτ+φp(b))+
(Sμ0)(τ))dτ+φp(b))dsdt)+
(Sμ0)(τ))dτ+φp(b))ds≤
t∈J
(24)
(Tμ0)(τ),(Sμ0)(τ))dτ+φp(b))≤
(25)
因此,有式(24) -(25)和条件(H4)可知
μ2(t)=(Aμ1)(t)≤(Aμ0)(t)=μ1(t),t∈J;
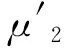
(26)
故
t∈J,n=0,1,2,…
(27)

ν1(t)=(Aν0)(t)=(A0)(t)≥0=ν0(t),t∈J;

t∈J
根据条件(H3),(H4)可得
ν2(t)=(Aν1)(t)=(A0)(t)≥0=ν1(t),t∈J;

t∈J
因此有
t∈J,n=0,1,2,…
(28)
所以存在ν*∈Pd,满足νn→ν*,n→+∞。应用A的连续性和νn+1=Aνn可知Aν*=ν*。
下面证明μ*,ν*是BVP(3)在区间
上的极大和极小解。
令
是BVP(3)的任一解,则有Au=u。由于A是非减的,并且
从而有
ν1(t)=(Aν0)(t)≤u(t)≤(Aμ0)(t)=μ1(t),
t∈J
因此可得
νn(t)≤μ(t)≤μn(t),n=1,2,3,…
(29)

ν0≤ν1≤…≤νn≤…≤ν*≤u≤
μ*≤…≤μn≤…≤μ1≤μ0
(30)
由于f(t,0,0,0,0) ≡0,t∈J, 所以零不是BVP(3)的解。故由式(30)可知结论成立,证明完毕。
注2 定理1中的迭代列分别由一个简单的函数和零函数开始的,这在实际应用中是十分方便的。
类似地可以得到下面的定理2。
定理2 假设条件(H1)-(H3)成立,并且存在dn>dn-1>…>d2>d1>2ρ满足下面的条件:

(t,u0,u1,u2,u3)∈J×[0,dk]×[0,dk]×
[0,k*dk]×[0,k*dk],
k=1,2,…,n
对于
定义迭代列{μkn},{νkn}
(Tμk(n-1))(τ),(Sμk(n-1))(τ))dτ+φp(b))+
(Tμk(n-1))(τ),(Sμk(n-1))(τ))dτ+φp(b))dsdt)+
(Sνk(n-1))(τ))dτ+φp(b))ds,
(Tνk(n-1))(τ),(Sνk(n-1))(τ))dτ+φp(b))+
(Tνk(n-1))(τ),(Sνk(n-1))(τ))dτ+φp(b))dsdt)+
(Tνk(n-1))(τ),(Sνk(n-1))(τ))dτ+φp(b))ds
且
注3 定理1中的解μ*,ν*可能重合,这时BVP(3)在Pd上只有一个解。类似地定理2中的解也可能重合。
3 例 子
考虑BVP
(|x′(t)|x′(t))′+




显然




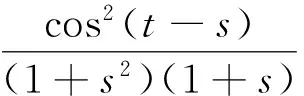
通过计算,可得




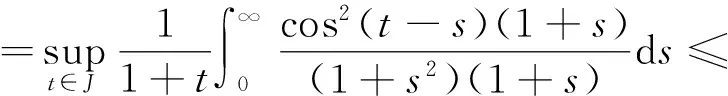
故条件(H1)成立。由
f(t,u0,u1,u2,u3)=
可知q(t)=e-6t,
因此有
即条件(H2)成立。由于

且对于
(t,u0,u1,u2,u3)∈
J×[0,d]×[0,d]×[0,k*d]×[0,h*d],
h满足
h(t,(1+t)u0,(1+t)u1,(1+t)u2,(1+t)u3)≤
因此,定理1的所有条件都满足。 故定理1的结论成立。
[1] LEIBENSON L S. General problem of the movement of a compressible fluid in a porous medium[J]. Izvestiia Akademii Nauk Kirgizskoi SSSR, 1983, 9: 7-10.
[2] DIAZ J I, THELIN F D. On a nonlinear parabolic problem arising in some models related to turbulent flows [J]. SIAM Journal on Mathematical Analysis, 1994, 25(4): 1085-1111.
[3] RAMASWAMY M, SHIVAJI R. Multiple positive solutions for classes ofp-Laplacian equations [J]. Differential Integral Equations, 2004, 17: 1255-1261.
[4] ORUGANTI S, SHI J, SHIVAJI R. Diffusive logistic equation with constant yield harvesting I: Steady-states [J]. Transactions of the American Mathematical Society, 2002, 354(9): 3601-3619.
[5] ORUGANTI S, SHI J, SHIVAJI R. Logistic equation withp-Laplacian and constant yield harvesting [J]. Abstract and Applied Analysis, 2004, 2004(9): 723-727.
[6] GLOWINSKI R, RAPPAZ J. Approximation of a nonlinear elliptic problem arising in a non-Newtonian fluid flow model in glaciology [J]. Esaim Mathematical Modelling Numerical Analysis, 2003, 37: 175-186.
[7] CIRSTEA F, MOTREANU D, RADULESCU V. Weak solutions of quasilinear problems with nonlinear boundary condition [J]. Nonlinear Analysis, 2001, 43(5): 623-636.
[8] ZHAO X, GE W. Existence of at least three positive solutions for multi-point boundary value problem on infinite intervals withp-Laplacian operator [J].Journal of Applied Mathematics Computing, 2008, 28: 391-403.
[9] SUN J, CHEN H. Multiple positive solutions for multi-point boundary value problems with ap-Laplacian on the half-line [J]. Journal of Applied Mathematics Computing, 2010, 33: 173-191.
[10] LIANG S, ZHANG J. The existence of countably many positive solutions for one-dimensionalp-Laplacian with infinitely many singularities on the half-line [J]. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2008, 201(1): 210-220.
[11] KIM C G. Existence and iteration of positive solutions for multi-point boundary value problems on a half-line [J]. Computers and Mathematics with Applications, 2011, 61(7): 1898-1905.
[12] GUO Y, YU C, WANG J. Existence of three positive solutions form-point boundary value problems on infinite intervals [J]. Nonlinear Analysis, 2009, 71: 717-722.
[13] LIU Y. Existence and unboundedness of positive solutions for singular boundary value problems on half-line [J]. Applied Mathematics and Computation 2003, 144(2): 543-556.
[14] LIU B, LI J, LIU L. Existence and uniqueness for an m-point boundary value problem at resonance on infinite intervals [J]. Computers and Mathematics with Applications, 2012, 64(6): 1677-1690.
[15] LIAN H, GENG F. Multiple unbounded solutions for a boundary value problem on infinite intervals [J]. Boundary Value Problems, 2011, 2011(1):1-8.
[16] LIU Y, WONG P. Unbounded solutions of BVP for second order ODE with p-laplacian on the half line [J]. Applications of Mathematics, 2013, 58(2): 179-204.
[17] LI J, LIU B, LIU L. Solutions for a boundary value problem at resonance on [0,+∞][J]. Mathematical Computer Modelling, 2013, 58: 1769-1776.
[18] 程伟, 徐家发. 一类分数阶哈密顿系统非平凡解的存在性[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 55(5): 21-26.
CHEN W, XU J F. Existence of nontrivial solutions for a class of fractional Hamiltonian systems [J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 2016, 55(5): 21-26.
[19] 王金华, 向红军, 赵育林. 一类分数阶差分方程边值问题解的存在性及Ulam稳定性[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 55(2):1-6.
WANG J H, XIANG H J, ZHAO Y L. Existence and Ulam stability of solutions for a boundary value problem of nonlinear fractional difference equation [J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 2016, 55(2): 1-6.
[20] JIANG J, LIU L, WU Y. Positive solutions for p-Laplacian fourth-order differential system with integral boundary conditions [J]. Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society, 2012, 2012(11): 715-735.
[21] LIU Y. Boundary value problem for second order differential equations on unbounded domain [J]. Acta Analysis Functionalis Applicata, 2002, 4(3): 211-216.
[22] CORDUNEANU C. Integral equations and stability of feedback systems [M]. New York: Academic Press, 1973.
Existenceofextremalsolutionsforthep-Laplacianintegro-differentialequationoninfiniteintervals
FANGYuping,WANGYing
(School of Mathematics and Statistics, Linyi University, Linyi 276000, China)
The integro-differential equation withp-laplacian operator is widely used in applied mechanics, astrophysics and classical electrology. The boundary value problem of nonlinear differential equations is an important branch of differential equations. Therefore, it is a great theoretical and practical significance to study the boundary value problems ofp-Laplacian integro-differential equations. A class ofp-Laplacian integro-differential equations with complex boundary conditions on infinite interval is systematically studied. By using the monotone iterative technique, the existence of extremal solutions as well as iterative schemes under the suitable conditions is established. At last, an example is given to demonstrate the use of the main result.
p-Laplacian operator; integro-differential equations; the monotone iterative technique; extremal solutions; infinite intervals
O175.8
A
0529-6579(2017)05-0041-10
10.13471/j.cnki.acta.snus.2017.05.006
2016-09-28
国家自然科学基金(11626125);山东省自然科学基金(ZR2016AP04);山东省高等学校科技计划项目(J16LI03);临沂大学博士科研启动基金(LYDX2016BS080);大学生创新创业项目(201610452168)
方玉萍 (1996年生),女;研究方向非线性微分方程;E-mail:312838088@qq.com
王颖(1981年生),女;研究方向:非线性微分方程;E-mail: lywy1981@163.com

