血液学指标在评估心肺复苏成功患者预后中的临床价值
邓磊,杨鹏,常莉
(四川省医学科学院·四川省人民医院急诊ICU,四川 成都 610072)
血液学指标在评估心肺复苏成功患者预后中的临床价值
邓磊,杨鹏,常莉
(四川省医学科学院·四川省人民医院急诊ICU,四川 成都 610072)
目的:探索血液学指标在评估心肺复苏(cardiopulmonary resuscitation,CPR)成功患者预后的诊断价值。方法:分析我院成功获得CPR的84例老年心脏骤停患者的临床资料,依据患者在CPR成功后是否发生复苏后综合征(post resuscitation syndrome,PRS)分为观察组(发生,n=43)及对照组(未发生,n=41)。检测两组患者CPR成功后24~48 h外周血白介素-6(IL-6)、B型钠尿肽(BNP)与肌钙蛋白Ⅰ(TNI)水平,并分析以上指标对CPR后综合征发生的预测诊断价值。结果:观察组患者血清IL-6、BNP及TNI水平均显著高于对照组,均具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。ROC曲线分析显示,以35.96 ng/L为截点值,IL-6对CPR发生的预测诊断敏感性为83.72%,特异性为82.93%,曲线下面积为0.83,优于BNP及TNI。观察组患者外周血IL-6水平与BNP(r=0.493,P<0.01)及TNI(r=0.484,P<0.01)均呈现显著正相关关系,均具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论:IL-6水平对获得CPR成功患者的预后具有一定预测诊断价值,值得临床推广。
心肺复苏;复苏后综合征;白介素-6;B型钠尿肽;肌钙蛋白Ⅰ
心肺复苏(cardiopulmonary resuscitation,CPR)是急救过程中挽救心跳呼吸骤停患者生命的基本方法。随着我国急救机制的不断完善和急救知识的普及,越来越多的呼吸心跳骤停患者得到了有效的CPR。但这不意味着患者彻底脱离了生命危险,CPR成功后不可避免地会产生器官缺血-再灌注损伤,并在此基础上发展为多器官功能障碍,甚至导致患者死亡,临床上将这一系列表现称为复苏后综合征(post resuscitation syndrome,PRS)[1]。及早发现PRS迹象并及时有效治疗是提高患者预后的关键[2]。影响患者预后的因素可能包括心功能及系统性炎症反应[3],因而本研究以炎症介质-白介素-6(interleukin-6,IL-6)、心功能相关的指标B型钠尿肽(B-type natriuretic peptide,BNP)与肌钙蛋白Ⅰ(troponin Ⅰ,TNI)为分析重点,并分析这些指标在对患者预后评估中的价值,以期为临床诊疗提供参考。
1 资料与方法
1.1 研究对象
分析2015年1月至2017年1月在四川省人民医院接受诊疗且成功获得CPR的84例患者临床资料。所有患者均因心脏呼吸骤停而接受了有效CPR,且在复苏成功后1 h内住院观察。排除以下情况的患者:合并恶性肿瘤等终末期疾病;合并活动性感染;合并严重自身免疫性疾病;合并严重代谢性疾病;既往心脏器质性病变病史。依据患者CPR成功后是否发生PRS将患者分为观察组(发生,n=43)及对照组(未发生,n=41)。研究获得医院伦理委员会批准,所有患者均履行知情同意。
1.2 相关定义及检测指标
所有患者均在同一组医师指导下接受治疗。PRS定为:心跳呼吸骤停获得有效CPR后发生多器官功能障碍。在患者CPR后24~48 h采集静脉血5 mL,离心后取血清冻存(-80 ℃)待测,检测如下指标:IL-6、BNP与TNI,检测采用商品化酶联免疫吸附法检测试剂盒(R&D公司,USA)。
1.3 观察指标
比较两组患者一般临床资料;检测并对比两组患者外周血IL-6、BNP及TNI水平;分析各血液指标对患者是否发生PRS的预测诊断价值;分析观察组患者外周血IL-6水平与BNP及TNI间的相关性。
1.4 统计学分析
2 结果
2.1 一般资料
两组患者一般资料比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),见表1。观察组患者发生CPR后综合征的平均时间为(3.1±0.5) d,均为多器官功能障碍综合征。
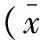
表1 两组患者一般临床资料的比较±s)
2.2 两组患者外周血指标检测结果比较
两组患者CPR成功后24~48 h外周血相关检测指标比较见表2。观察组患者血清IL-6、BNP及TNI水平均高于对照组,均具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。

表2 两组患者外周血指标检测结果比较
2.3 各项指标对老年患者PRS发生的预测诊断价值分析
如表3及图1,ROC曲线分析显示,以35.96 ng/L为截点值,IL-6对CPR后综合征发生的预测诊断敏感性为83.72%,特异性为82.93%,曲线下面积为0.83,优于BNP及TNI。
表3 各项指标对老年患者CPR后综合征发生的预测诊断价值分析

观察项目诊断分界点曲线下面积敏感性(%)特异性(%)IL⁃6(ng/L)35.960.8383.7282.93BNP(pg/mL)121.800.6872.0960.98TNI(ng/mL)8.310.7779.0775.61

2.4 观察组患者外周血IL-6水平与BNP及TNI间的相关性分析
如图2,观察组患者外周血IL-6水平与BNP(r=0.493,P<0.01)及TNI(r=0.484,P<0.01)均呈现显著正相关关系,均具有统计学意义。
3 讨论
急救知识的普及急诊抢救医疗制度的完善使得我国呼吸心脏骤停患者的救治率获得了极大提高。

患者在获得有效CPR后有望获得进一步治疗,但这不意味着脱离了生命危险。心脏骤停后会导致各组织器官不同程度缺血缺氧,待恢复血供后缺血-再灌注损伤几乎难以避免[4]。临床上将获得CPR成功后出现多器官功能障碍的情况称为CPR后综合征[5]。事实上,CPR后综合征是导致此类患者最终死亡的主要原因之一。挽救此类患者的主要途径为及早对患者病情做出客观判断,积极防治多器官功能障碍的发生。因而,临床上需要可靠、便捷的预测CPR后综合征发生的指标。基于以上需求,我们尝试分析获得CPR成功患者外周血相关指标的改变,以期探寻到可对患者预后有预测诊断价值的实用指标。
本研究发现观察组患者CPR成功后24~48 h外周血IL-6、BNP及TNI水平均高于对照组。这提示以上指标可能对预测患者预后具有一定价值。IL-6是一种促炎介质,其在感染、损伤及缺血再灌注等病理生理过程中均可显著升高;其具有直接损伤细胞的细胞毒性作用;可通过多条信号通路参与调节急性炎症的级联放大过程[6-8]。事实上,常用临床指标如白细胞计数、中性粒细胞等也对系统性炎症有一定判断价值,但在应激状态下升高的白细胞常为不成熟白细胞,对临床判断有一定影响。而IL-6则主要由成熟的单核巨噬细胞所分泌,对炎症的敏感性更佳,因而本研究采用了该项指标以反映患者系统性炎症的程度[7-8]。BNP是钠尿肽家族的重要成员之一,其在心室壁张力升高的情况下可迅速释放至外周血,因而是临床反映心脏功能的实用指标[9-10]。在CPR后综合征发生的过程中,心功能的降低常在病程早期即出现,可能是心肌受损的结果,同时也可能是与心律失常等因素有关[11-12]。无论何种因素导致患者出现心功能水平降低或障碍,均可能导致BNP水平的升高[10]。TNI是调节心肌兴奋收缩偶联的关键蛋白,心肌细胞破坏后其可释放至外周血,且其在外周血中的水平与心肌受损程度呈现正相关,因而其是临床反映心肌受损的关键指标[13]。在临床工作中,TNI常被用于评估急性心肌梗死的有无及程度,其对心肌细胞破坏的诊断具有较高的可靠性[14-15]。为了明确此3项指标对患者预后的评估价值,采用受试者工作曲线分析显示,以35.96 ng/L为截点值,IL-6对CPR后综合征发生的预测诊断敏感性及特异性均超过80%,优于BNP及TNI。这提示IL-6具有更高的预测诊断价值。同时,本研究采用相关性分析发现IL-6水平与BNP及TNI均呈现显著正相关关系,提示IL-6对此两项指标具有一定代表性。且随着临床检验水平不断提高,检测指标范围在不断扩大,IL-6已经从一项科研常用指标成为了多数医院的常用实验室指标。但IL-6在CPR后患者病理生理改变中的具体机制尚需进一步研究以明确。
综上,IL-6水平对获得CPR成功患者的预后具有一定预测诊断价值,值得临床推广。
[1] Silversides JA,Major E,Ferguson AJ,etal.Conservative fluid management or deresuscitation for patients with sepsis or acute respiratory distress syndrome following the resuscitation phase of critical illness:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J].Intensive Care Med,2017,43(2):155-170.
[2] 谭纪萍,刘瑛,王鑫,等.中国人口老龄化发展趋势与老年健康研究现状[J].中国老年学杂志,2012,32(19):4335-4337.
[3] 薛继可,冷巧云,高玉芝,等.急诊科心搏骤停患者心肺复苏预后的影响因素[J].中华急诊医学杂志,2013,22(1):28-34.
[4] Li J,Li C,Yuan W,etal.Mild hypothermia alleviates brain oedema and blood-brain barrier disruption by attenuating tight junction and adherens junction breakdown in a swine model of cardiopulmonary resuscitation[J].PLoS One,2017,12(3):e0174596.
[5] Bundgaard K,Hansen SM,Mortensen RN,etal.Association between Bystander Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Redeemed Prescriptions for Antidepressants and Anxiolytics in Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Survivors[J].Resuscitation,2017,115:32-38.
[6] Peberdy MA,Andersen LW,Abbate A,etal.Inflammatory markers following resuscitation from out-of-hospital cardiac arrest-A prospective multicenter observational study[J].Resuscitation,2016,103:117-124.
[7] Durukan AB,Gurbuz HA,Salman N,etal.Ventilation during cardiopulmonary bypass did not attenuate inflammatory response or affect postoperative outcomes[J].Cardiovasc J Afr,2013,24(6):224-230.
[8] Qian J,Yang Z,Cahoon J,etal.Post-resuscitation intestinal microcirculation:its relationship with sublingual microcirculation and the severity of post-resuscitation syndrome[J].Resuscitation,2014,85(6):833-839.
[9] Bartus K,Podolec J,Lee RJ,etal.Atrial natriuretic peptide and brain natriuretic peptide changes after epicardial percutaneous left atrial appendage suture ligation using LARIAT device[J].J Physiol Pharmacol,2017,68(1):117-123.
[10]Le S,Xiao J,Li W,etal.Continuous administration of recombinant human B-type natriuretic peptide can improve heart and renal function in patients after cardiopulmonary bypass surgery[J].J Thorac Dis,2017,9(3):692-701.
[11]古丽巴哈尔,熊小伟,周圣华.心肺复苏后综合征72例临床分析[J].中华老年多器官疾病杂志,2017,16(3):217-218.
[12]O’Connor MF,Nunnally ME.Expect the unexpected:clinical trials are key to understanding post-intensive care syndrome[J].Crit Care,2013,17(3):149.
[13]Geri G,Mongardon N,Dumas F,etal.Diagnosis performance of high sensitivity troponin assay in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest patients[J].Int J Cardiol,2013,169(6):449-454.
[14]Pan GZ,Xie J,Tian XF,etal.The Impact of Different Plasma Glucose Levels on Heart Rate in Experimental Rats With Acute Myocardial Infarction[J].Cardiol Res,2016,7(4):146-151.
[15]Lyngbakken MN,Røsjø H,Holmen OL,etal.Gender,High-Sensitivity Troponin I,and the Risk of Cardiovascular Events (from the Nord-Trøndelag Health Study)[J].Am J Cardiol,2016,118(6):816-821.
(学术编辑:杜柯君)
本刊网址:http://www.nsmc.edu.cn
作者投稿系统:http://noth.cbpt.cnki.net
邮箱:xuebao@nsmc.edu.cn
本刊网址:http://www.nsmc.edu.cn
作者投稿系统:http://noth.cbpt.cnki.net
邮箱:xuebao@nsmc.edu.cn
The value of haematological index in estimating prognosisfor of patients after successful cardiopulmonary resuscitation
DENG Lei,YANG Peng,CHANG Li
(DepartmentofEmengencyICU,SichuanPeople’sHospital,Chengdu610072,Sichuan,China)
Objective:To explore the diagnostic value of haematological index in estimating prognosisfor of patients after successful cardiopulmonary resuscitation(CPR).Methods:84 patients undergoing cardiac arrest in our hospital were selected,and divided into the observation group (n=43,yes) and the control group (n=41,no) according to whether suffer from post resuscitation syndrome(PRS).The levels of Interleukin-6(IL-6),B-type natriuretic peptide(BNP),Troponin Ⅰ(TNI) and after successful CPR with 24~48 h in the patients of the two groups were detected,and the diagnostic value of haematological index in estimating CPR was analyzed.Results:The levels of IL-6,BNP and TNI in the observation group were significantly higher than those in the control group,and the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05).ROC analysis showed that the IL-6 cut-off point value of 35.96ng/L,as used for post CPR syndrome,provided a sensitivity of 83.72%,a specificity of 82.93%,an Area under the curve of 0.83,better than these of BNP and TNI.Correlation analysis showed that,for the patients in the observation group,the levels of IL-6 had significant positive correlation with BNP(r=0.493,P<0.01) and TNI (r=0.484,P<0.01),all had statistical significance.Conclusion:IL-6 can be used as a marker to estimating in estimating prognosisfor of patients after successful CPR,be worthy of clinical promotion.
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation;Post resuscitation syndrome;Interleukin-6;B-type natriuretic peptide;Troponin Ⅰ
10.3969/j.issn.1005-3697.2017.04.023
2017-04-05
邓磊(1980-),男,硕士,主治医师。E-mail:Denglei1980@sina.cn
时间:2017-8-15 11∶26 网络出版地址:http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/51.1254.R.20170815.1126.046.html
1005-3697(2017)-04-0564-04
R459.7
A

