色散对双晶交叉偏振滤波输出特性的影响∗
耿易星 李荣凤 赵研英王大辉 卢海洋 颜学庆
(北京大学物理学院,核物理与核技术国家重点实验室,北京 100871)
色散对双晶交叉偏振滤波输出特性的影响∗
耿易星 李荣凤 赵研英†王大辉 卢海洋 颜学庆
(北京大学物理学院,核物理与核技术国家重点实验室,北京 100871)
(2016年9月13日收到;2016年10月7日收到修改稿)
在北京大学超小型激光等离子体加速器系统上,通过压缩器对激光脉冲引入色散,研究了色散对双晶交叉偏振滤波(XPW)输出特性的影响.结果显示,随着正负色散的引入,XPW功率会减小、输出光谱带宽也会变窄、输出光谱中心波长会发生蓝移和红移.与此同时,正负色散对于三者的影响具有不对称性,负色散相对于正色散会更快减小XPW功率和输出光谱带宽.因此,对双晶XPW输出特性而言,正色散的影响要小于负色散.该结果对双晶XPW技术在高对比度超强激光中的应用提供了重要的实验数据.
啁啾脉冲放大,交叉偏振滤波,光谱,色散
1 引 言
随着超短超强激光的不断发展,尤其是采用啁啾脉冲放大(chirp pulse amplification,CPA)技术后[1],飞秒激光聚焦的功率密度不断提高,当前可以达到的功率密度为1020W·cm-2,为研究强场物理提供新的技术手段[2-4],在如此高的功率密度下,激光的时域对比度在强场物理实验中扮演着重要的角色.
但是,在高功率激光装置中,由于选单元件消光比的限制以及放大过程中的自发放大辐射效应等因素的影响,不可避免地会存在时域背景噪声,从而导致激光脉冲时域对比度下降[5].当超强激光与固体靶相互作用时,如果飞秒激光的自发放大辐射或者预脉冲的功率密度超过1012W·cm-2,靶体会先被预脉冲离化形成预等离子体,进而影响主脉冲与固体靶的相互作用以及最终的实验结果[6-8].为了得到高对比度的激光脉冲,目前发展了多种提高对比度的方法,如可饱和吸收体[9]、光学参量啁啾脉冲放大[10]、交叉偏振滤波(crosspolarized wave,XPW)[11,12]、等离子体镜等[13,14].其中XPW技术结构相对简单,转化效率高,提高对比度明显,尤其是双晶XPW技术的发展,可以有效地避免单晶带来的饱和问题,获得更高的转化效率,更有益于该技术在超强激光中应用[15].在双啁啾脉冲放大激光系统中,双晶XPW技术可有效地提高太瓦(TW)甚至拍瓦(PW)量级的激光对比度[16,17].
XPW技术不但可以有效地提高飞秒激光时域对比度,而且具有良好的光谱展宽和时域压缩效应.在CPA系统中,由于增益窄化效应会导致光谱带宽越来越窄,可压缩的脉冲宽度越来越宽,从而降低激光的功率密度.而XPW输出光谱带宽在特定条件下可以获得倍的展宽,极大地扩展了CPA系统的光谱带宽,使PW激光脉宽可压缩到30 fs[18].目前已有色散对单晶XPW输出特性的理论和实验研究[19-22],还没有对双晶XPW输出特性的相关研究.因此我们在北京大学超小型激光等离子体加速器(compact laser plasma acceler-ator,CLAPA)系统上[23,24],通过改变压缩光栅间距的方法为激光脉冲引入色散,研究了不同色散对双晶XPW效率、输出光谱带宽以及输出光谱中心波长的影响.研究表明,正负色散对双晶XPW上述特征具有不对称的影响,负色散更加快速地降低XPW效率和输出光谱带宽,并且对输出光谱中心波长的影响也更加显著.
2 XPW技术的原理
XPW过程是由晶体三阶非线性张量χ3的实部各向异性所决定的三阶非线性简并四波混频过程,输出波的偏振方向垂直于入射波偏振方向.当激光功率密度达到一定强度时,线偏振激光经过非线性晶体后,其波矢会发生一定角度的旋转,产生与原来偏振方向垂直的交叉偏振波.由于对激光强度存在依赖效应,产生XPW所要求的功率密度一般要大于1012W·cm-2,这样才能保证有较高的转换效率.如果在光路中放置一对偏振正交的偏振片,主脉冲的功率密度较高,经过非线性晶体后偏振方向发生旋转,其正交偏振分量会透过正交的偏振片,而脉冲中的预脉冲和自发放大辐射由于功率密度达不到产生XPW的阈值,不能发生三阶非线性效应,偏振方向不发生偏转,不能透过正交偏振片,从而被滤掉,因此,XPW技术可以有效地提高超强激光脉冲的时域信噪比.
3 实验装置
实验在北京大学CLAPA系统上进行,该系统的前级为重复频率1 kHz的再生钛宝石放大器.输入XPW的单脉冲能量为150µJ,脉冲宽度为40 fs,输入光谱的中心波长λINI为796.5 nm,输入光谱带宽ΔλINI为35.5 nm.实验中通过改变压缩光栅的间距引入色散,这里仅考虑光栅引入的二阶色散,压缩器引入色散φ2=±2000 fs2.图1所示为双晶XPW技术的实验设置图,其中P1和P2是正交放置的格兰棱镜,消光比优于10-6;F1和F2是聚焦系统.压缩后的飞秒激光脉冲以水平偏振经过一块格兰棱镜P1后进入系统,经过F1聚焦系统聚焦后进入两块BaF2晶体,产生的XPW脉冲由透镜F2准直后,通过第二块偏振正交的格兰棱镜P2输出.
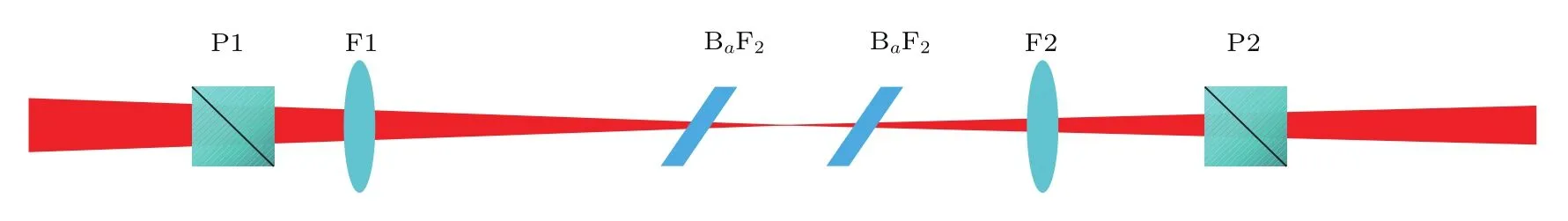
图1 (网刊彩色)双晶XPW技术实验设置 其中P1和P2是一对正交放置的格兰棱镜,F1和F2是聚焦系统Fig.1.(color online)Experimental setup of XPW filter,P1,P2 are orthogonal positioned Glan prisms,F1 and F2 are focus system.
4 实验结果与讨论
4.1 XPW效率
我们首先测量了XPW效率η与色散φ2之间的关系,实验结果如图2所示.当φ2=0时,η为17%.随着φ2不断增大,η不断减小,从初始的17%降至1%.实验中发现,±φ2对双晶XPW效率的影响呈现不对称性.φ2<0时,即引入的色散为负,η随着φ2的增加迅速下降,φ2=-2000 fs2,η=1%.而φ2>0,即引入的色散为正,η随着φ2的增加下降比较缓慢,φ2=2000 fs2,η=5%.当|±φ2|=1120 fs2时,ηφ2=-1120=3%,ηφ2=1120=10%,ηφ2<0明显要小于ηφ2>0.
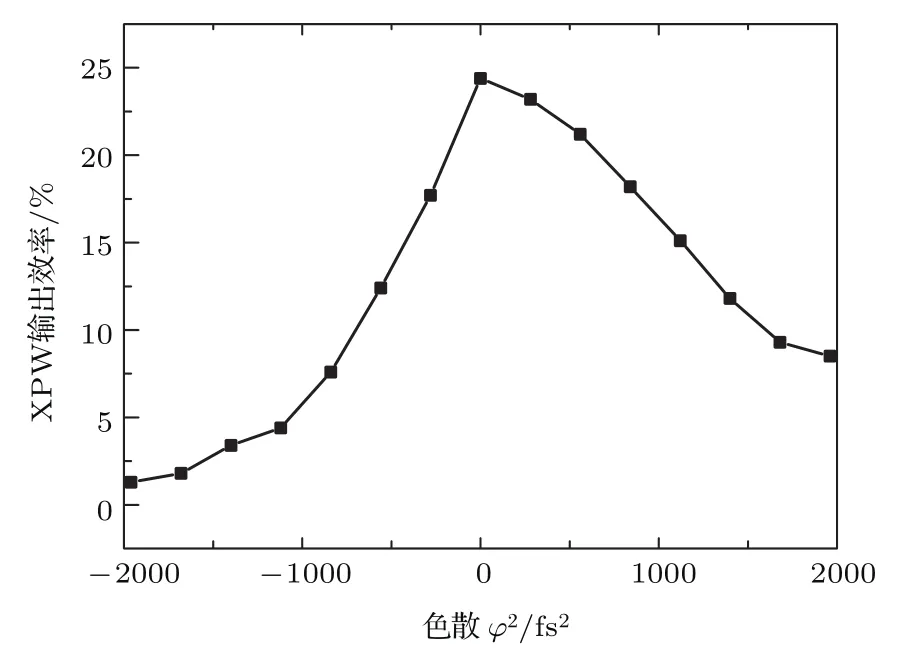
图2 XPW效率与色散φ2的关系Fig.2.Measured XPW efficiency as a function of quadratic spectral phase.
4.2 XPW输出光谱带宽

图3 XPW输出光谱带宽ΔλXPW与色散φ2的关系 实线为测量的XPW输出光谱带宽,虚线为输入光谱带宽Fig.3.Measured spectral width(FWHM)of the XPW pulse as a function of quadratic spectral phase(full line).The dashed line is the spectral width of the initial pulse.
4.3 XPW输出光谱中心波长
色散φ2不但对于XPW输出光谱带宽有影响,而且对于输出光谱中心波长λXPW也有显著的作用,如图4所示,图中实线是实验测量得到的输出光谱中心波长λXPW,虚线是输入光谱的中心波长λINI. 可以看出,φ2=0时,λXPW=775 nm<λINI,存在蓝移.引入色散φ2后,λXPW出现了明显的移动,并且±φ2对λXPW的影响并不对称.φ2<0,λXPW随着φ2的增加开始进行红移,φ2<-350 fs2时,λXPW>λINI,当φ2<-1000 fs2后,λXPW红移的速率开始变缓,维持在806 nm附近.φ2>0时,λXPW随着φ2的增加开始缓慢蓝移,但当φ2>1000 fs2时,λXPW维持在772 nm左右.引入不同色散测量得到的光谱如图5所示.

图4 XPW输出光谱的中心波长λXPW与色散φ2的关系实线为测量的XPW 输出光谱中心波长λXPW,虚线为输入光谱中心波长λINIFig.4.Measured XPW pulse central-wavelength as a function of quadratic spectral phase(full line).The dashed line is the central-wavelength of the initial pulse.
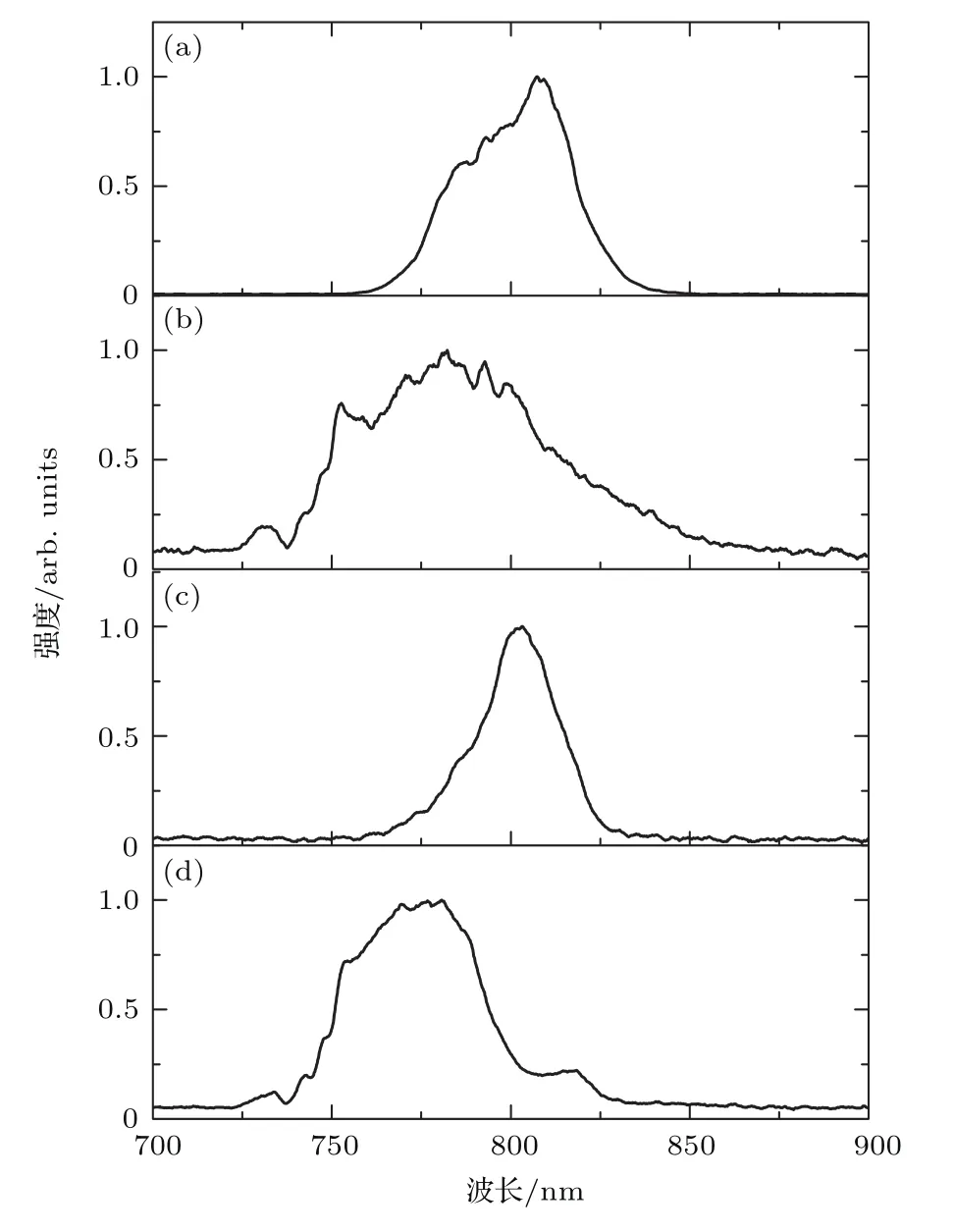
图5 不同色散情况下的XPW输出光谱 (a)输入光谱;(b)当φ2=0 fs2时XPW输出光谱;(c)当φ2=-1960 fs2时XPW输出光谱;(d)当φ2=1960 fs2时XPW输出光谱Fig.5.Experimental XPW pulse spectrum in different quadratic spectral phase:(a)Spectrum of the initial pulse;(b)XPW pulse spectrum measured whenφ2=0 fs2;(c)XPW pulse spectrum measured whenφ2=-1960 fs2;(d)XPW pulse spectrum measured whenφ2=1960 fs2.
5 结 论
在北京大学CLAPA系统上,通过改变压缩光栅间距的方法为激光脉冲引入色散,研究了色散对双晶XPW效率、输出光谱带宽以及输出光谱中心波长的影响.结果显示,正负色散的引入会导致XPW功率减小、输出光谱带宽变窄、输出光谱中心波长出现蓝移和红移,除此之外,正负色散对于三者的影响具有不对称性,负色散相对于正色散会更快减小XPW功率和输出光谱带宽,并且负色散会使输出光谱中心波长快速红移,而正色散对于输出光谱中心波长的影响较小.对双晶XPW输出特性而言,正色散的影响要小于负色散.推测这种不对称性源于双晶XPW技术中的其他非线性效应对XPW效率、输出光谱带宽和输出光谱中心波长的影响.
[1]Strickland D,Mourou G 1985Opt.Commun.55 447
[2]Macchi A,Borghesi M,Passoni M 2013Rev.Mod.Phys.85 751
[3]Hiroyuki D,Nishiuchi M,Pirozhkov A S 2012Rep.Prog.Phys.75 056401
[4]Corde S,TaPhuoc K,Lambert G,Fitour R,Malka V,Rousse A,Beck A,Lefebvre E 2013Rev.Mod.Phys.85 1
[5]Ivanov V V,Maksimchuk A,Mourou G 2003Appl.Opt.42 7231
[6]Culfa O,Tallents G J,Wagenaars E,Ridgers C P,Dance R J,Rossall A K,Gray R J,McKenna P,Brown C D R,James S F,Hoarty D J,Booth N,Robinson A P L,Lancaster K L,Pikuz S A,Faenov Y A,Kampfer T,Schulze K S,Uschmann I,Woolsey N C 2014Phys.Plasmas21 043106
[7]Timur Z E,James K K,Atsushi S,Toshimasa M,Masaharu N,Kei K,Hideo N,Katsunobu N,Akito S,Hideyuki K,Tatsufumi N,Yuji F,Hajime O,Alexander S P,Akifumi Y,Mamiko N,Hiromitsu K,Kiminori K,Masaki K,Sergei V B 2014Nucl.Instrum.Methods Phys.Res.Sect.A745 150
[8]Yabuuchi T,Mishra R,McGuffey C,Qiao B,Wei M S,Sawada H,Sentoku Y,Ma T,Higginson D P,Akli K U,Batani D,Chen H,Gizzi L A,Key M H,Mackinnon A J,McLean H S,Norreys P A,Patel P K,Stephens R B,Ping Y,Theobald W,Stoeckl C,Beg F N 2013New J.Phys.15 015020
[9]Jeffrey W,Charles G D 2004Opt.Express12 1383
[10]Norihiko N,Atsushi M 2007Opt.Lett.32 3516
[11]Jullien A,Albert O,Burgy F,Hamoniaux G,Rousseau J P,Chambaret J P,Augé-Rochereau F,Chériaux G,Etchepare J 2005Opt.Lett.30 8
[12]Liu C,Wang Z H,Li W C,Liu F,Wei Z Y 2010Acta Phys.Sin.59 7036(in Chinese)[刘成,王兆华,李伟昌,刘峰,魏志义2010物理学报59 7036]
[13]Röde C,Heyer M,Behmke M,Kübel M,Jäckel O,Ziegler W,Ehrt D,Kaluza M C,Paulus G G 2011Appl.Phys.B103 295
[14]Anna L,Tiberio C,Pascal D O,Fabrice R,Michel P,Fabien Q,Pascal M,Michel B,Hervé L,Philippe M 2007Opt.Lett.32 310
[15]Jullien A,Albert O,Chériaux G,Etchepare J,Kourtev S,Minkovski N,Saltiel S M 2006Opt.Express14 7
[16]Chvykov V,Rousseau P,Reed S,Kalinchenko G,Yanovsky V 2006Opt.Lett.31 1456
[17]Xu Y,Leng Y X,Guo X Y,Zou X,Li Y Y,Lu X M,Wang C,Liu Y Q,Liang X Y,Li R X,Xu Z Z 2014Opt.Commun.313 175
[18]Lureau F,Laux S,Casagrande O,Radier C,Chalus O,Caradec F,Simon-Boisson C 2012Proc.SPIE8235 823513
[19]Ricci A,Jullien A,Rousseau J P,Liu Y,Houard A,Ramirez P,Papadopoulos D,Pellegrina A,Georges P,Druon F,Forget N,Lopez-Martens R 2013Rev.Sci.Instrum.84,043106
[20]Lliev M,Meier A K,Greco M,Durfee C G 2015Appl.Opt.54 2
[21]Jullien A,Canova L,Albert O,Boschetto D,Antonucci L,Cha Y H,Rousseau J P,Chaudet P,Chériaux G,Etchepare J,Kourtev S,Minkovski N,Saltiel S M 2007Appl.Phys.B87 595
[22]Li G,Liu H J,Lu F,Wen X L,He Y L,Zhang F Q,Dai Z H 2015Acta Phys.Sin.64 020602(in Chinese)[李纲,刘红杰,卢峰,温贤伦,何颖玲,张发强,戴增海 2015物理学报64 020602]
[23]Shang Y,Zhu K,Lin C,Lu H Y,Zou Y B,Zhao Y Y,Shou Y R,Cao C,Zhao S,Geng Y X,Zhu J,Fu H Z,Wang H Y,Lu Y R,Yuan Z X,Guo Z Y,Chen J E,Yan X Q 2013Sci.Sin.:Phys.Mech.Astron.43 1282(in Chinese)[尚勇,朱昆,林晨,卢海洋,邹宇斌,赵研英,寿寅任,曹超,赵栓,耿易新,祝娇,符合振,王洪勇,陆元荣,袁忠喜,郭之虞,陈佳洱,颜学庆 2013中国科学:物理学 力学天文学43 1282]
[24]Yan X Q,Lin C,Lu H Y,Zhu K,Zou Y B,Wang H Y,Liu B,Zhao S,Zhu J,Geng Y X,Fu H Zh,Shang Y,Cao C,Shou Y R,Song W,Lu Y R,Yuan Z X,Guo Z Y,He X T,Chen J E 2013Front.Phys.8 577
PACS:06.60.Jn,42.65.—k,42.65.Re DOI:10.7498/aps.66.040601
Influences of quadratic spectral phase on characteristics of two crystal cross-polarized generation with femtosecond pulses∗
Geng Yi-XingLi Rong-FengZhao Yan-Ying†Wang Da-HuiLu Hai-YangYan Xue-Qing
(State Key Laboratory of Nuclear Physics and Technology,Peking University,Beijing 100871,China)
13 September 2016;revised manuscript
7 October 2016)
The rapid developments of ultra-intense and ultra-short laser offer the possibility to study laser driven ion acceleration with using solid density target.However,the prepulse and amplified spontaneous emission generated in the amplification can create preplasma at the target front by heating,melting and evaporating a portion of a solid density.The main pulse then interacts with the preplasma,which would be harmful to laser ion acceleration.Therefore,many methods have been developed to enhance the temporal contrast of high power laser system,such as saturable absorber,cross polarized wave generation(XPW)and plasma mirror.With many advantages,such as high conversion efficiency,introducing neither spatial nor spectral distortions,and easy setup compared with other mechanisms,XPW has be√en used to clean the femtosecond laser system.Besides that,the spectrum of the XPW pulse could be broadened by3 times under the best condition compared with the initial spectrum.It can solve the spectrum narrowing problem during the laser amplification to obtain ultra-short femtosecond laser pulse.Here,we experimentally investigate the output power,spectrum bandwidth and center wavelength shift of the generated cross-polarized wave according to the input pulse quadratic spectral phase.
The femtosecond laser pulse in compact laser plasma accelerator system at Peking University is used to investigate the role of quadratic spectral phase in characterizing the two crystal cross-polarized generation.The Ti:Sapphire-based laser system has a central wavelength of 798 nm and bandwidth of 35.5 nm which allows the pulse to be compressed down to 40 fs duration(FWHM).Typical the input pulse energy of XPW is 150µJ and the laser system operates well at 1 kHz repetition rate.The quadratic spectral phase can be increased by changing the position of compressor grating.
The conversion efficiency,spectrum bandwidth and the central wavelength shift by changing the quadratic spectral phase are measured.The conversion efficiency is 17%when quadratic spectral phaseφ2=0,and decreases as quadratic spectral phase increases.The rapid decrease is caused by negative quadratic spectral phase.The spectrum bandwidth is 62 nm under the optimum condition,and the broadening effect exists when quadratic spectral phase is in a range of-280 fs2<φ2<1400 fs2.It is slowly blue-shifted whenφ2>0 and stays at 772 nm whenφ2>1000 fs2.It starts to be red-shifted whenφ2<0 and stays at 806 nm finally.
In conclusion,with the increase of quadratic spectral phase,we observe the effects of conversion efficiency and spectrum bandwidth and the shift of central wavelength.Moreover,the influences of positive and negative quadratic spectral phase on characteristics of XPW are different.Our result shows that the negative quadratic spectral phaseis more effective at reducing the conversion efficiency and spectrum bandwidth than the positive one.
chirp pulse amplification,cross-polarized generation,spectrum,quadratic spectral phase
:06.60.Jn,42.65.—k,42.65.Re
10.7498/aps.66.040601
∗国家自然科学基金(批准号:11504009)和国家重大科学仪器设备开发专项(专项号:2012YQ030142)资助的课题.
†通信作者.E-mail:zhaoyanying@pku.edu.cn
*Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(Grant No.11504009)and the National Grand Instrument Project,China(Grant No.2012YQ030142).
†Corresponding author.E-mail:zhaoyanying@pku.edu.cn

