严寒地区大型燃气锅炉排烟加热空气方式的优化与应用
肖慧鹏王随林穆连波翟慧星程冬冬马兆康
吴亚东2寿德2张 伟3陈玉平4张彤4王守金5
(1北京建筑大学环境与能源工程学院 北京 100044;2乌鲁木齐市供热行业管理办公室 乌鲁木齐 830000;3新疆维泰热力股份有限公司 乌鲁木齐 830000;4新疆骑马山热力有限公司 乌鲁木齐 830000;5北京华远意通热力科技股份有限公司 北京 100160)
严寒地区大型燃气锅炉排烟加热空气方式的优化与应用
肖慧鹏1王随林1穆连波1翟慧星1程冬冬1马兆康1
吴亚东2寿德2张 伟3陈玉平4张彤4王守金5
(1北京建筑大学环境与能源工程学院 北京 100044;2乌鲁木齐市供热行业管理办公室 乌鲁木齐 830000;3新疆维泰热力股份有限公司 乌鲁木齐 830000;4新疆骑马山热力有限公司 乌鲁木齐 830000;5北京华远意通热力科技股份有限公司 北京 100160)
由于严寒地区冬季室外空气的温度低,助燃的空气进入锅炉会产生爆燃和震动、燃烧效率降低。同时大型供热系统回水温度高,燃气锅炉排烟温度较高,排烟余热深度利用中,烟温降低程度受到回水温度条件限制。本文提出了新的烟气加热空气方式,与常规烟气加热空气方式相比,减少了设备耗材、体积及阻力,应用于大型燃气供热锅炉烟气余热深度梯级利用的节能改造。工程实测表明:烟气余热回收和助燃空气加热系统,可将烟气温度降到锅炉回水温度及以下,锅炉燃气利用热效率提高了13.2%,烟气余热回收率为66.7%,实现了排烟余热深度利用,并解决了助燃空气进入锅炉产生爆燃和震动的问题,为严寒地区燃气锅炉烟气余热深度利用与助燃空气加热提供了参考。
严寒地区;大型燃气锅炉;排烟余热利用;空气加热;工程实测
我国严寒地区和寒冷地区室外温度低,如乌鲁木齐市的供暖室外计算温度为-19.7℃,供暖季平均温度为 -7.1℃,累年最冷月平均温度为 -12.7℃[1],累年最冷日平均温度为-29.3℃[2];哈尔滨市的供暖室外计算温度为-24.2℃,供暖季平均温度为-9.4℃,累年最冷月平均温度为-18.4℃,累年最冷日平均温度为-32.0℃。在这些地区,由于室外空气温度低,作为助燃空气进入锅炉易产生爆燃和振动,使得锅炉燃烧效率降低,对空气进行加热是减少锅炉振动和噪声、提高燃烧效率的重要途径。常规空气加热设备采用烟气加热空气,由于空气和烟气均为气体,与液体相比,对流换热系数低,换热设备传热系数小[3],需要的换热面积大,体积大,耗材多,设备阻力大[4],烟气冷凝水还会对设备造成腐蚀[5-8]。
本文提出的基于空气-水-烟气换热的空气加热方式,与常规空气-烟气换热的空气加热方式相比,大幅度减小体积和耗材,降低了空气和烟气阻力,同时可将排烟温度降到回水温度以下,深度回收烟气显热和水蒸气冷凝潜热[9-16],实现烟气余热深度利用。将该空气加热方式应用于乌鲁木齐市某70 MW大型燃气供热锅炉排烟余热深度利用节能改造工程,进行跟踪检测与数据分析后发现:在空间小、投资低的条件下,显著改善了助燃空气进入锅炉产生爆燃、振动及燃烧效率降低的现象,同时实现排烟余热深度利用,提高锅炉系统效率,为严寒地区燃气锅炉烟气余热深度利用与助燃空气加热系统优化提供参考。

图1 空气⁃水⁃烟气换热的空气加热方式用于排烟余热深度利用系统原理图Fig.1 The principle diagram of the gas boiler smoke waste heat deep utilization system based on the air⁃water⁃flue gas pattern to heat the air
1 空气加热方式分析
1.1 空气⁃水⁃烟气换热的空气加热方式
结合空气-水-烟气换热的空气加热方式的燃气供热锅炉排烟余热深度利用系统原理见图1。
由图1可知,烟气用于加热一次网回水和二次网回水,锅炉助燃空气的加热方式,采用空气-水-烟气换热的方式,即由空气-水间壁式换热设备和烟气-水间壁式换热设备组成。一次网回水在空气预热器中加热助燃空气后,再进入烟气冷凝热能回收装置吸收烟气余热,当温度先回升到一次网回水温度ts1后,进一步被烟气加热升温,最后进入锅炉;锅炉出口烟气加热一次网回水后温度降到ty2,进一步加热二次网回水,烟温最终降到ty3。
1.2 空气⁃水⁃烟气换热与空气⁃烟气换热的空气加热方式比较
常规空气加热方式为空气与烟气通过间壁式换热设备进行热量交换,为提高单位体积换热能力,通常采用板式换热方式,如图2所示。
空气-水-烟气换热的空气加热方式(如图3所示),即由空气-水间壁式换热设备和烟气-水间壁式换热设备组成,可通过在气侧加肋的方式强化传热[3,17-18],大幅度减小设备体积和耗材,并通过优化降低阻力,便于在空间小、投资低的条件下实施。
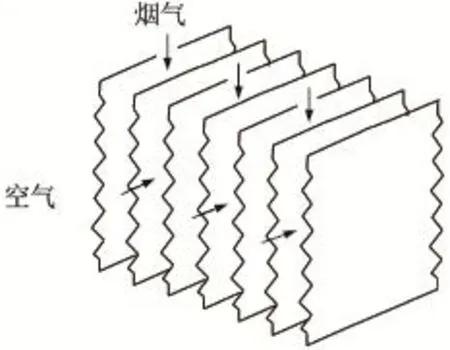
图2 空气⁃烟气换热原理示意图Fig.2 The schematic diagram of heat transfer of air and flue gas

图3 空气(或烟气)⁃水换热示意图Fig.3 The schematic diagram of heat transfer of air or flue gas⁃water
以某70 MW大型燃气供热锅炉烟气余热深度利用节能改造为例,设计条件为:锅炉回水温度53℃,在烟气加热空气系统中,在供暖季室外空气平均温度-7.1℃条件下,空气被加热到30℃,烟气温度从55.3℃降到53℃,空气与烟气总阻力为200 Pa。对其分别采用空气-水-烟气换热的空气加热方式与空气-烟气换热的空气加热方式,且空气-水-烟气换热设备采用自主研发的防腐高效低阻换热设备,进行设备选型,比较结果见表1。
由表1可知,在相同换热量及设计参数下,空气-水-烟气换热的空气加热方式采用自主研发的防腐高效低阻换热设备,其设备的换热面积与空气-烟气换热的空气加热方式相当。空气-烟气换热的空气加热方式的设备体积为空气-水-烟气换热设备体积的6.8倍,其设备净质量是空气-水-烟气换热设备的2.8倍。原因是气-气换热虽然传热温差较大,但两侧流体均为气体,传热系数小,空气-水-烟气换热的空气加热方式传热系数较大,且可通过气侧加肋的方式强化传热,大幅度减小设备体积和耗材。因此,气-气换热设备耗材多、体积大,若减小体积,则会造成设备烟风阻力大,影响锅炉等设备的正常运行。

表1 两种烟气加热空气方式设备选型比较Tab.1 The equipment selection of two types of flue gas heating the air
2 燃气供热锅炉烟气余热深度利用节能改造工程实测
2.1 工程概况
乌鲁木齐市某70 MW燃气热水锅炉,一次网回水温度为51.8~52.5℃,二次网回水温度为32.6~32.7℃。在安装空间及项目投资均有限的条件下,采用自主研发的防腐高效低阻烟气冷凝热能回收装置和空气-水换热设备,对锅炉进行排烟余热深度利用与助燃空气加热节能改造,加热空气采用空气-水-烟气换热的空气加热方式,原理如图1所示。
2.2 测试原理及数据整理依据
1)节能率Δη
燃气锅炉排烟余热利用提高的燃气利用热效率,即节能率Δη,为回收烟气热量与燃气锅炉燃气燃烧放热量之比:

式中:Q1为回收烟气热量,kW;Qr为燃气锅炉燃气燃烧放热量,kW。
2)排烟余热回收率Δη′
Δ η′为回收烟气热量与锅炉出口烟气携带的总余热量之比:

式中:Qy为锅炉出口烟气携带的总余热量,kW,即烟气从锅炉出口温度降到标准状态(0℃,101.325 kPa)放出的总热量。
2.3 主要测试参数及仪器设备
主要测试参数及仪器设备见表2。
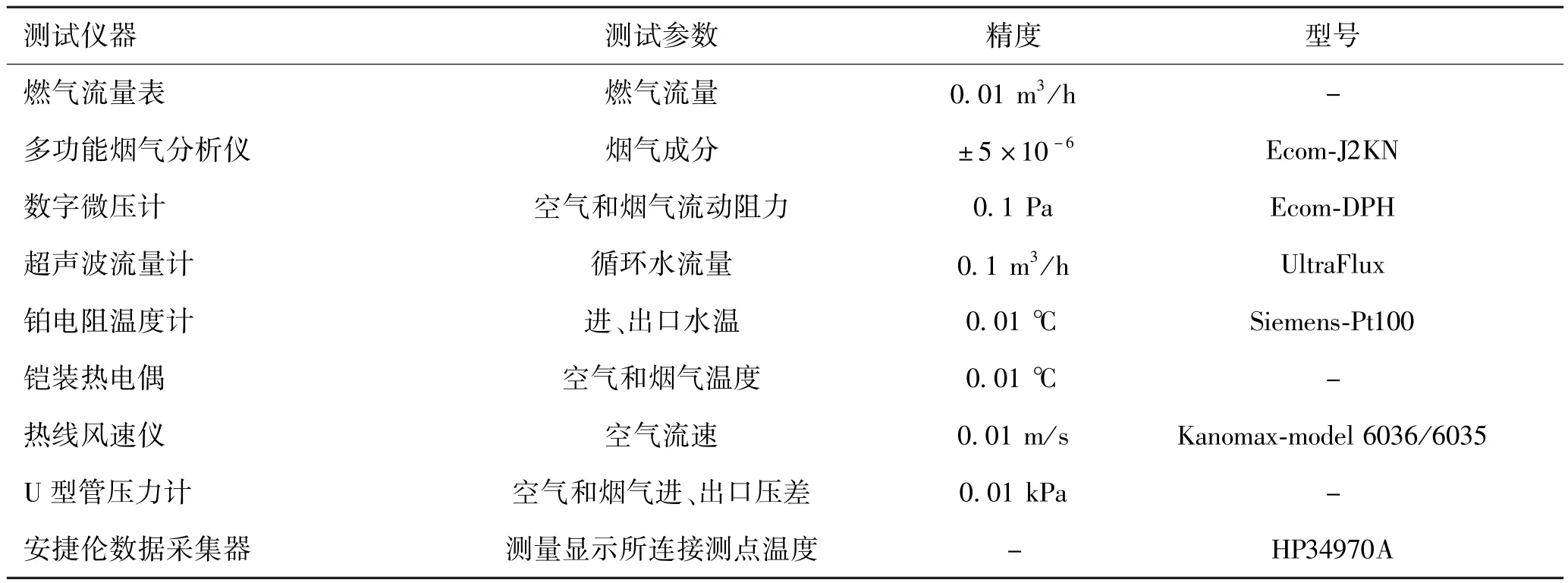
表2 主要测试参数及仪器设备Tab.2 Main test parameters and instruments
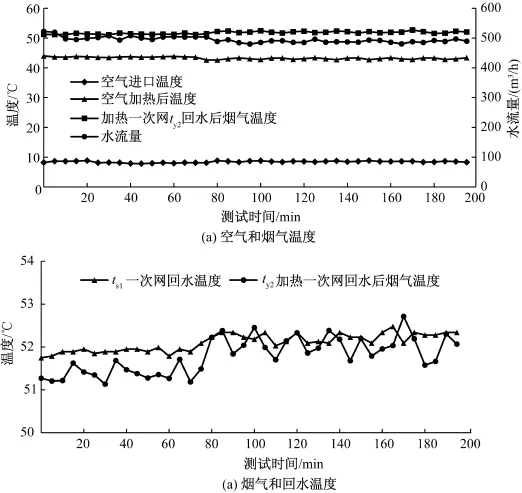
图4 空气⁃水⁃烟气换热过程中空气和烟气及水温变化Fig.4 The temperature change of the air,flue gas and water in the process of heating in the pattern of air⁃water⁃flue gas
3 检测及计算结果与分析
检测时间为2015/2016年供暖季,锅炉负荷率为53.6% ~75.1%,过剩空气系数为1.3~1.4。
3.1 空气⁃水⁃烟气加热过程中温度的变化
采用空气-水-烟气换热的空气加热方式的换热过程中空气、烟气及水温变化见图4(a)和(b)。由图4可知,换热过程中,一次网回水温度为51.8~ 52.5℃,烟气温度由53.3~62.7℃降至51.1~52.7℃,烟气温度降到回水温度及以下。并将7.8~8.9℃的助燃空气加热至42.4~43.4℃。
3.2 空气⁃水⁃烟气加热过程中空气吸热量/烟气放热量
采用空气-水-烟气换热的空气加热方式的换热过程中,空气吸热量/烟气放热量见图5。
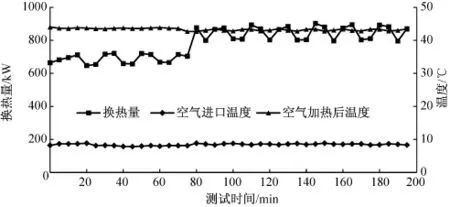
图5 空气吸热量/烟气放热量Fig.5 The variation of the heat transferred from the gas to the air with time
由图5可知,换热过程中,助燃空气温度被加热为42.4~43.4℃,避免严寒地区助燃空气进入锅炉产生爆燃和振动及噪声,此过程空气吸热量或烟气放热量为647~903 kW。

图6 烟气加热一次网回水系统检测结果Fig.6 The testing results of primary network backwater system of flue gas heating
3.4 燃气供热锅炉烟气余热深度利用节能改造工程效果
在燃气供热锅炉排烟余热深度利用节能改造工程中,烟气加热一次网回水,进而加热二次网回水。
3.4.1 烟气加热一次网回水系统检测结果
在烟气加热一次网回水系统中,结合了空气-水-烟气换热的空气加热方式,将烟气温度进一步降低,深度回收烟气显热和水蒸气冷凝潜热。检测结果见图6。
由图6可知,当回水温度51.8~52.5℃时,空气冷却后回水温度降至50.4~50.7℃,使锅炉排烟温度由124.6~157.8℃降至51.1~52.7℃,将排烟温度降到回水温度及以下,在空间小、投资低的条件下,实现了排烟余热深度利用。
3.4.2 燃气供热锅炉排烟余热深度利用节能改造工程检测结果
在燃气供热锅炉排烟余热深度利用节能改造工程中,烟气加热一次网回水后,继而加热二次网回水,实现余热梯级利用,最终检测结果的平均值,见表3。

表3 燃气供热锅炉排烟余热深度利用节能改造工程检测结果Tab.3 The testing results of energy saving reconstruction project for gas heating boiler flue gas waste heat deep utilization
由表3可知,锅炉平均出口烟温从146℃降至平均排烟温度37.5℃,其中回收的烟气显热和冷凝水潜热基本相当,总节能率 13.2%,总余热回收率66.7%,实现了排烟余热深度回收利用。
4 结论
本文提出了空气-水-烟气换热的空气加热方式,并对采用该空气加热方式的大型燃气供热锅炉烟气余热深度利用节能改造系统的部分及整体进行跟踪实测,得到的结论如下:
1)空气-水-烟气换热的空气加热方式与常规空气-烟气换热的空气加热方式相比,可大幅度减小设备体积和耗材,并可通过结构优化降低烟气和空气侧阻力,在相同换热量及设计参数下,空气-水-烟气换热的空气加热方式采用自主研发的防腐高效低阻换热设备,两种空气加热方式的换热面积相当,空气-烟气换热的空气加热方式设备体积为空气-水-烟气换热的空气加热方式的6.8倍,设备质量是空气-水-烟气换热的空气加热方式的2.8倍,便于在空间小、投资低的条件下应用。
2)空气-水-烟气换热的空气加热方式采用自主研发的防腐高效低阻换热设备的工程实测表明,在被加热介质(一次网回水)温度51.8~52.5℃条件下,将烟气温度降至51.1~52.7℃,即降到了一次网回水温度及以下,助燃空气温度被加热至42.4~43.4℃,避免了助燃空气进入锅炉产生爆燃、振动及噪声。
3)结合空气-水-烟气换热的空气加热方式的燃气供热锅炉烟气冷凝余热深度利用节能改造工程应用表明,在一次网回水温度51.8~52.5℃和二次网回水温度32.6~32.7℃条件下,锅炉烟气温度由124.6~157.8℃降至37.0~38.0℃,提高锅炉燃气利用热效率,总节能率为13.2%,总余热回收率为66.7%,实现了排烟余热深度梯级利用。
本文受北京市教委创新能力提升计划(PXM2016_014210_000016)项目和北京学者计划项目资助。(The project was supported by the Innovation Ability Promoting Project of Municipal Education Commission in Beijing( No.PXM2016_014210_000016)and the Program of Beijing Scholar’s Plan).)
[1]中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部.GB50736—2012民用建筑供暖通风与空气调节设计规范[S].北京:中国建筑工业出版社,2012:174.(Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Repubic of China.GB50736—2012 Design code for heating ventilation and air conditioning of civil buildings[S].Beijing:China Architecture&Building Press,2012:174.)
[2]中国有色金属工业协会.GB50019—2015工业建筑供暖通风与空气调节设计规范[S].北京:中国建筑工业出版社,2016:192.(China Nonferrous Metals Industry Association.GB50019—2015 Design code for heating ventilation and air conditioning of industrial buildings[S].Beijing:China Architecture&Building Press,2016:192.)
[3]章熙民,任泽霈,梅飞鸣.传热学[M].北京:中国建筑工业出版社,2007.(ZHANG Ximin,REN Zepei,MEI Feiming.Heat transfer[M].Beijing:China Architecture&Building Press,2007.)
[4]陈康,赵岩,王随林,等.热电厂排烟余热深度回收利用模拟试验与节能分析[J].暖通空调,2013,43(3):53-58.(CHEN Kang,ZHAO Yan,WANG Suilin,et al. Simulation test and energy efficiency analysis of flue gas heat deep recovery of thermal power plants[J].Journal of HV&AC,2013,43(3):53-58.)
[5]Damon G H.Acid corrosion of steel effect of carbon content on the corrodibility of steel in sulfuric acid[J].Industrial and Engineering Chemistry,1941,33(1):67-69.
[6]孙传水.12MnCuCr钢耐硫酸露点腐蚀性能的研究[J].材料保护,1998,31(10):10-12.(SUN Chuanshui.The study about sulfuric acid dew point corrosion resistancesteel of 12MnCuCr[J].Material Protection,1998,31(10):10-12.)
[7]曲逵,刘丰.热管换热器尾部受热面腐蚀分析及耐腐材料合理选用研究[J].能源研究与利用,2004(4):9-10.(QU Kui,LIU Feng.The corrosion analysis and corrosion materials reasonable choice of heating surface for heat pipe heat exchanger[J].Energy Research and Utilization,2004(4):9-10.)
[8]Hal T.An update on mechanical plating[J].Plating and Surface Finishing,1987(5):24-27.
[9]Lazzarin R M,Longo G A,Piccininni F,et al.Absorption dehumidification of natural gas exhaust[J].Heat Recovery System&CHP,1992,12(5):385-389.
[10]石书强,王随林,吴佳蕾,等.大型燃气锅炉排烟余热深度利用改造工程实测分析[J].暖通空调,2016,46(2):74-77.(SHI Shuqiang,WANG Suilin,WU Jialei,et al.Measurement analysis of large gas fired boiler flue gas heat deep recovery reconstruction project[J].Journal of HV&AC,2016,46(2):74-77.)
[11]车得福,刘艳华.烟气热能梯级利用[M].北京:化学工业出版社,2006.(CHE Defu,LIU Yanhua.Gradient utilization of flue gas heat[M].Beijing:Chemical Industry Press,2006.)
[12]车得福.冷凝式锅炉及其系统[M].北京:机械工业出版社,2002.(CHE Defu.The condensing boiler and system[M].Beijing:China Machine Press,2002.)
[13]Kuck J.Efficiency of vapour-pump-equipped condensing boilers[J].Applied Thermal Engineering,1996,16(3):233-244.
[14]Oskabe M.Themal-hydraulic behavior and prediction of heat exchanger for latent heat recovery of exhaust flue gas[C]//Proceeding of ASME IMechE(Heat Transfer Division-II).U.S.:American Society of Mechanical Engineers,1999:43-50.
[15]Wang S L,Yang D M,Ai X Y.Heat and mass transfer of flue gas in heat exchangers with anticorrosion platings[C]//Heat Transfer Science and Technology.New York:Hemisphere Publishing Corporation,2000:731-736.
[16]刘民科.烟气凝结换热器传热强化与工程应用研究[D].北京:北京建筑工程学院,2012.(LIU Minke. Research on the intensification of transfer in flue gas condensing heat exchanger and engineering application[D]. Beijing:Beijing University of Civil Engineering and Architecture,2012.)
[17]Idem S A,Jocobi A M,Goldschmidt V M.Heat transfer characterization of a finned-tube heat exchanger(with and without condensation)[J].Journal of Heat Transfer,1990,112(1):64-70.
[18]Oskabe M,Itoh T.Themal-hydraulic prediction for wet region of economizer using spirally finned tubes[C]//Proceeding of JSME.U.S.:American Society of Mechanical Engineers,2000:863-870.
Optimization of Air Heating in Large Gas⁃fired Boiler by Flue
Gas Waste Heat in Cold Areas
Xiao Huipeng1Wang Suilin1Mu Lianbo1Zhai Huixing1Cheng Dongdong1Ma Zhaokang1Wu Yadong2Shou De2Zhang Wei3Chen Yuping4Zhang Tong4Wang Shoujin5
(1.School of Environment and Energy Engineering,Bejing University of Civil Engineering and Architecture,Beijing,100044,China;2.The Management Office of Urumqi’s Heating Industry,Urumchi,830000,China;3.Xinjiang Weitai Heating Institute,Urumchi,830000,China;4.Xinjiang Qimashan Heating Institute,Urumchi,830000,China;5.Beijing Huayuanyitong Thermal Technology Institute,Beijing,100160,China)
Because the outdoor air temperature in cold regions is severely low in winter,the combustion-supporting air will cause deflagration and vibration while directly supplied to the boiler and the combustion efficiency is also decreased.At the same time,the temperature of the return water in a large heating system,and the exhaust gas from the gas boiler,are both high.Thus,the exhaust gas could not be cooled down to a relatively low temperature by the return water during the waste heat utilization process.This paper presents a new way to heat the air by using flue gas waste heat,which is smaller,requires less space,and has less resistance compared with conventional heat exchange equipment.The proposed method can be applied to the flue gas waste heat deep-utilization of a large gas heating boiler.Field test results show that the flue gas waste heat deep-utilization and the combustion-supporting air heating system can cool the flue gas temperature near to or even lower than the return water temperature of heating network.The utilization efficiency of gas combustion is increased by 13.2%,and the recovery rate of the flue gas waste heat is 66.7%.Then,flue gas waste heat deep recovery is realized,and the problem in which the combustion-supporting air causes deflagration and vibration while directly supplied to the boiler is solved.The paper provides a reference for flue gas waste heat deep-utilization in cold regions,and for combustion-supporting air heating system optimization.
cold regions;large gas-fired boiler;flue gas waste heat recovery;air heating;engineering test
TK115;TK229.8
:A
0253-4339(2017)03-0101-07
10.3969/j.issn.0253-4339.2017.03.101
王随林,女,教授,北京建筑大学环境与能源工程学院,13911602617,E-mail:suilinwang@bucea.edu.cn。研究方向:供热节能和热能高效利用。
国家“十三五”重点研发计划项目(2016YFB0601100)资助。(The project was supported by State’s Key Project of Research and development Plan in 13th Five-Year(No.2016YFB0601100).)
2016年11月16日
About the corresponding author
Wang Suilin,female,professor,School of Environment and Energy Engineering,Bejing University of Civil Engineering and Architecture,+86 13911602617,E-mail:suilinwang@ bucea.edu.cn. Research fields:heating saving and heat energy utilization efficiently.

