糖胶树叶挥发油化学成分研究
孔杜林,林 强
(1.海南医学院 药学院,海南 海口 571199; 2.海南师范大学 化学与化工学院,海南 海口 571158)
糖胶树叶挥发油化学成分研究
孔杜林1,林 强2*
(1.海南医学院 药学院,海南 海口 571199; 2.海南师范大学 化学与化工学院,海南 海口 571158)
采用水蒸气蒸馏法提取糖胶树叶的挥发油. 运用气质谱联用(GC-MS)技术研究海南糖胶树叶的挥发油化学成分. 并采用峰面积归一化法确定各成分的相对质量分数. 结果共鉴定出36种成分,占总离子流出峰面积的94.83%. 糖胶树叶挥发油主要有α-蒎烯(16.62%),2-丙烯酸丁酯(15.86%)和大根香叶烯 D(13.37%). 本研究可为糖胶树的进一步研究开发和利用提供基础研究数据.
糖胶树;挥发油;水蒸气蒸馏法;GC-MS
糖胶树(Alstoniascholaris(L.)R.Br.)又称橡皮树、灯架树、黑板树、乳木、魔神树等,属于夹竹桃科 鸡骨常山属(Alstonia). 木材的材质松软细致,全株乳汁丰富,可提取口香糖原料,故名“糖胶树”. 糖胶树生于海拔650米以下的低丘陵山地疏林中,喜湿润肥沃土壤. 为次生阔叶林主要树种. 原产于高温多湿的南亚,广西南部、西部和云南南部野生,广东、湖南和台湾有栽培. 糖胶树它的根、皮、叶均可药用. 外用治外伤出血、消肿,接骨、并可用于配制杀虫剂[1-3]. 糖胶树其根、皮可治痧气、 肺炎、头痛、 伤风、百日咳、慢性支气管炎等;为进一步研究糖胶树叶药用价值,本实验对糖胶树叶挥发油化学成分进行研究.
1 实验部分
1.1 材料与仪器
糖胶树叶采自海南省海口市,经海南师范大学钟琼芯教授鉴定为糖胶树(Alstoniascholaris(L.)R.Br.),属于夹竹桃科 鸡骨常山属(Alstonia).
无水乙醚,氯化钠,无水硫酸钠均为国产分析纯.
气质联用仪(6890-5973型,美国Agilent公司),挥发油提取器,索氏提取器,电热套等.
1.2 挥发油的提取
取新鲜糖胶树叶200 g, 洗净捣碎,采用水蒸气蒸馏收集馏出液300 mL,加入氯化钠至饱和,用乙醚多次萃取,无水硫酸钠干燥,低温分离回收乙醚得淡黄色、有愉快香气的透明油状物51 mg,即为糖胶树叶挥发油.
1.3 检测条件
气相色谱条件:Agilent6890-5973气质联用仪,HP-5msi 毛细管色谱柱 (30 m×0.25 mm,0.25 μm);进样口温度260 ℃,升温程序:初温40 ℃,保留时间3 min,以5 ℃/min升到120 ℃,并保持2 min,再以8 ℃/min升至260 ℃,保持15 min. 载气为高纯核气,流量1.0 μL/min进样量1 μL,不分流进样.
质谱条件:EI电离源;电离电压70 eV,离子源温度230 ℃,柱前压9.8 psi,扫描范围45~550.
2 结果与讨论
按上述1.3实验条件,对海南糖胶树叶的挥发油成分进行GC-MS分析,得糖胶树叶挥发油总离子流图,对总离子流图中各峰经质谱扫描后得到的成分色谱图经质谱工作站NIST05标准质谱数据库对化合物进行检索,鉴定各种化学成分,采用色谱数据处理系统,按峰面积归一化法计算各峰在挥发油中的相对质量分数,结果见表1.
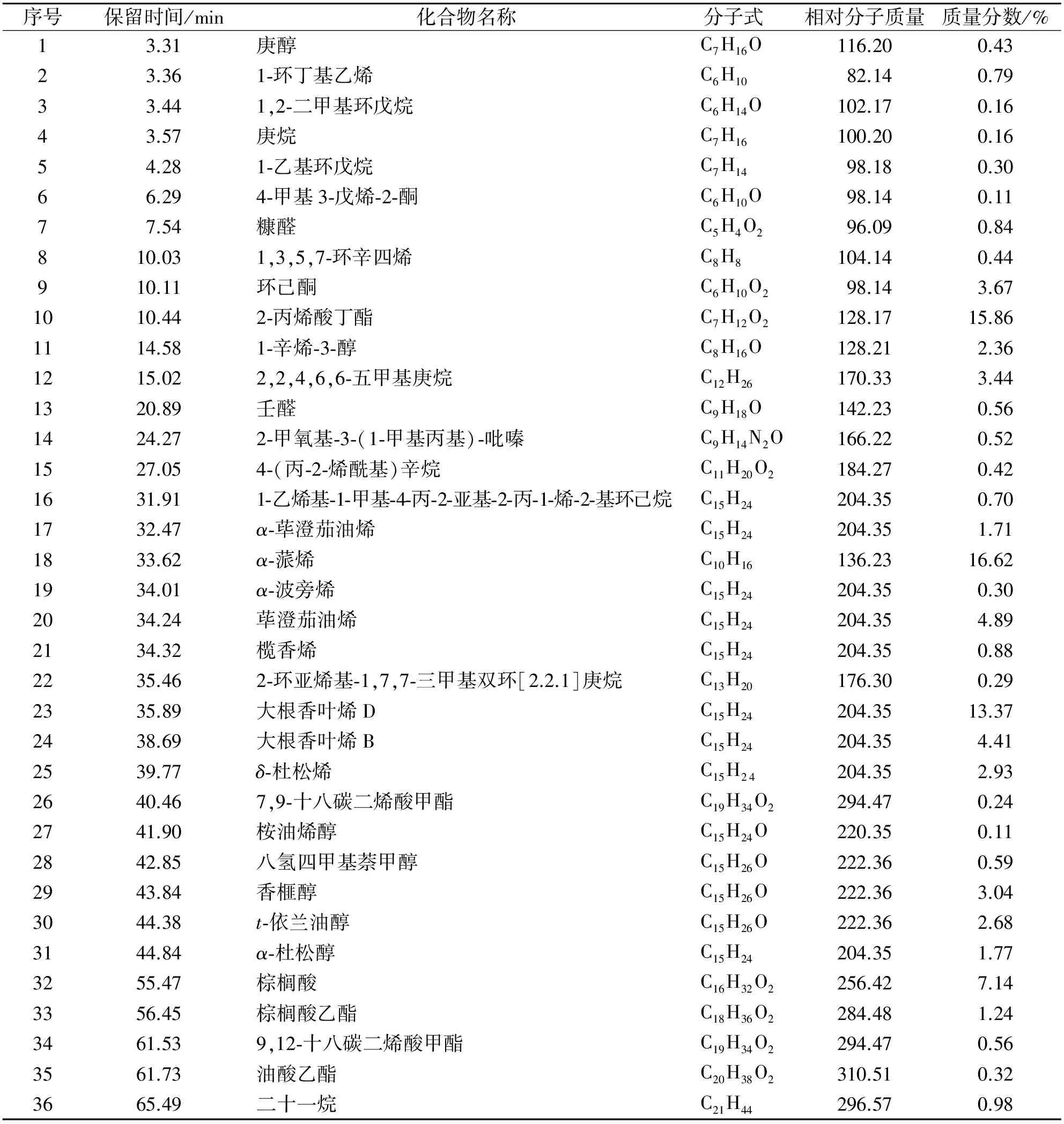
表1 海南糖胶树叶挥发油的化学成分
从糖胶树叶中检测出36种挥发油成分,总含量占挥发油总量的94.83%,主要有醇类、烯烃类和酯类化合物[4-6],其中主要有α-蒎烯(16.62%)、2-丙烯酸丁酯(15.86%)和大根香叶烯D(13.37%).α-蒎烯具有较好的生物学活性及独特的反应多样性.α-蒎烯在化工等领域是合成樟脑、树脂等化工产品的重要原料之一. 近年来,经研究发现α-蒎烯具有抗肿瘤、抗真菌、抗过敏及改善溃疡的作用[7]. 2-丙烯酸丁酯可以用作有机合成中间体,是合成乳化剂、粘合剂、涂料的常用原料[8]. 大根香叶烯D具有抗菌抗病毒的功效[9]. 本研究可为糖胶树的进一步研究、开发和利用提供基础研究数据.
[1] 中国科学院昆明植物研究所. 云南植物志[M]. 北京:科学出版社, 1983.
Kunming institute of botany, Chinese academy of sciences. Journal of Plant Resources [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1983.
[2] 周劲松. 糖胶树育苗造林技术[J]. 中国野生植物资源, 2008, 27(1): 63-66.
ZHOU J S. Culture and seedling technology of Alstonia scholaris (L.)R.Br[J]. Chinese Wild Plant Resources, 2008, 27(1): 63-66.
[3] 张宏意, 方思琪, 彭维, 等. 糖胶树花挥发油GC-MS分析[J]. 中药材, 2010, 33(8): 1273-1274.
ZHANG H Y, FANG S Q, PENG W, et al. GC-MS analysis of the volatile oil from flower s of Alstonia scholaris (L.)R.Br[J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials, 2010, 33(8): 1273-1274.
[4] 孔杜林, 陈亮文, 王忠先, 等. 朱蕉叶挥发油的GC-MS 分析[J]. 应用化工, 2014, 43(4): 759-762.
KONG D L, CHEN L W, WANG Z X, et al. GC-MS Analysis of the volatile oil from leaves of Cordvline fruticosa [J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2014, 43(4): 759-762.
[5] 孔杜林, 陈衍成, 范超军, 等. 大花紫薇叶挥发油化学成分研究[J]. 海南师范大学学报, 2013, 26(1): 36-39.
KONG D L, CHEN Y C, FAN C J, et al. Studies on the Chemical Constituent of Volatile Oil from the Leaves of L. Speciosa (Linn.) Pers [J]. Journal of Hainan Normal University (Natural Science), 2013, 26(1): 36-39.
[6] 孔杜林, 李永辉, 范超军, 等. 美人蕉叶挥发油的 GC-MS 分析[J]. 中国现代中药, 2013, 15(6): 445-447.
KONG D L, LI Y H, FAN C J, et al. GC-MS Analysis of the Volatile Oil from Leaves of Canna indicaL[J]. Modern Chinese Medicine, 2013, 15(6): 445-447.
[7] 廖圣良, 商士斌, 沈明贵, 等. 蒎烯及其衍生化合物药物活性的研究进展[J]. 化学试剂, 2016, 38(3): 219-213.
LIAO S L, SHANG S B, SHEN M G, et al. Progress on medicinal activities of pinenes and pinene-based derivatives [J]. Chemical Reagents, 2016, 38(3): 219-213.
[8] 贾振宇. 分散剂丙烯酸丁酯/丙烯酸共聚物的制备和应用[J]. 精细石油化工进展, 2006, 7(4): 1-4.
JIA Z Y. Synthesis and Application of Poly(butyl acrylate-co-acrylic acid) as Dispersant [J]. Advances in Fine Petrochemicals, 2006, 7(4): 1-4.
[9] 吴怀恩, 韦志英, 朱小勇, 等. 超临界CO2流体萃取法提取艾叶与五月艾挥发油成分的研究[J]. 广西中医学院学报, 2008, 11(4): 31-34.
WU H E, WEI Z Y, ZHU X Y, et al. Study on the chemical constituents of volatile oil from artemisia indica and Artemisia argyi by supercritical CO2fluid extraction [J]. Journal of Guangxi Traditional Chinese Medical University, 2008, 11(4): 31-34.
[责任编辑:张普玉]
Chemical constituent of volatile oil from the leaves ofAlstoniascholaris(L.)R.Br.
KONG Dulin1, LIN Qiang2*
(1.SchoolofPharmaceuticalSciences,HainanMedicalUniversity,Haikou571199,Hainan,China; 2.CollegeofChemistryandChemicalEngineering,HainanNormalUniversity,Haikou571158,Hainan,China)
To investigate the chemical constituents of the volatile oil from leaves ofAlstoniascholaris(L.)R.Br. in Hainan province, the volatile oil was extracted by water steam distillation and then analyzed by GC-MS. The relative percentage contents of each component were determined by peak area normalization method. 36 compounds from the volatile oil were separated and identified, which occupied for 94.83% of total volatile oils. The main chemical constituents wereα-pinene(16.62%), butyl acrylate (15.86%) and germacrene D (13.37%). The present study of the volatile oil from the leaves ofAlstoniascholaris(L.)R.Br. provides a chemical basis for a medicinal herb.
Alstoniascholaris(L.)R.Br.; volatile oil; water steam distillation; GC-MS
2016-11-22.
海南省自然科学基金(20162033),海南医学院科研培育基金(HY2015-02).
孔杜林(1981-),男,副教授,主要从事药物合成研究.*
, E-mail:linqianggroup@163.com.
R284.1
A
1008-1011(2017)02-0210-03