顺铂致大鼠急性肾损伤肾组织细胞凋亡及NGAL的相关性研究
孟晓燕 黄雯静 阳延松 舒婷婷 杨浩强

【摘要】 目的:研究顺铂(Cisplatin,CDDP)致大鼠急性肾损伤(AKI)模型中肾组织细胞凋亡及肾组织中性粒细胞明胶酶相关脂质运载蛋白(NGAL)变化及相关性。方法:将36只健康雄性Wistar大鼠随机分为盐水对照组(CN组)与顺铂模型组(CP组),CP组为腹腔单次注射顺铂10 mg/kg,CN组腹腔注射同顺铂组等容量生理盐水,观察应用顺铂后12、24、48、96、144 h各组大鼠血清肌酐(Scr),肾组织细胞凋亡及NGAL变化。结果:与CN组相比,CP组48 Scr开始升高,144 h达峰值;CP组12 h肾组织凋亡细胞开始增多,48 h增加最明显;CP组12 h NGAL在肾小管上皮细胞中表达增强(P<0.05),48 h表达最明显。肾组织细胞凋亡同NGAL表达显著相关(r=0.925,P<0.01)。结论:细胞凋亡可能是CDDP致大鼠AKI早期致病机制之一,NGAL不仅是早期肾损伤的标记物,还可能参与AKI发病机制。
【关键词】 顺铂; 急性肾损伤; 中性粒细胞明胶酶相关脂质运载蛋白; 细胞凋亡
Relationship between Apoptosis of Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells and NGAL in the Rodent Model of Cisplatin Induced Acute Kidney Injury/MENG Xiao-yan,HUANG Wen-jing,YANG Yan-song,et al.//Medical Innovation of China,2017,14(05):049-052
【Abstract】 Objective:To observe the relationship between apoptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells and NGAL in the rodent model of Cisplatin induced acute kidney injury.Method:A total of 36 male wistar rats were randomly assigned to different groups.The rats of CP group were injected once intraperitoneal with Cisplatin at
10 mg/kg,the rats of CN group were injected intraperitoneal with same volume of normal saline vehicle.Rats were euthanized at 12,24,48,96 and 144 hours(n=6 in the CP group at each time point).The blood and renal tissue specimens were analyzed at each time point.Result:Significant elevations of creatnine in serum were noted by 48 hours in the CP group versus CN group,peak levels were seen on 144 hours(P<0.05).A significant increased expression of NGAL in renal tissue sections was noted by 12 hours in the CP group versus CN group,the most obvious expression of NGAL was seen on 48 hours(P<0.05).In addition,renal epithelial cells apoptosis was noted by 12 hours in the CP group versus CN group,peak level was seen on 48 hours(P<0.05).Apoptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells and NGAL expression was significantly correlated (r=0.925,P<0.01).Conclusion:Apoptosis may be involved in the early pathogenesis of AKI induced by CDDP in rodent modals,NGAL is not only a biomarker of early renal injury,but also may be involved in the pathogenesis of AKI.
【Key words】 Cisplatin; Acute kidney injury; Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin; Cell apoptosis
First-authors address:The Fourth Affiliated Hospital,Guangxi University,Liuzhou 545005,China
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-4985.2017.05.012
急性腎损伤(acute kidney injury,AKI)是常见的内科疾病,也是急危重症常见的合并症,与较高的死亡率和不良预后相关[1]。关于我国AKI的一项横断面研究指出,2013年我国有(140~290)万AKI患者住院,AKI住院死亡率达12.4%,而71.6%的患者在诊断AKI时或之前有肾毒性药物应用[2]。提示药物相关性AKI可能已经成为我国巨大的医疗负担。
顺铂(Cisplatin,CDDP)是一种广泛应用的抗癌药物,剂量相关的肾毒性大大限制了其临床应用,中性粒细胞明胶酶相关脂质运载蛋白(NGAL)是有前景的AKI早期损伤标记物,前期的工作也发现,CDDP致大鼠AKI早期即存在血、尿NGAL升高[3],目前关于NGAL研究主要集中于作为早期诊断,预后评估的生物学标记物及参与疾病发病两方面,在生理情况下或不同的疾病病程中,NGAL扮演着不同甚至截然相反的角色,国内不少研究仅关注于NGAL的早期诊断特性,忽略其生理特性及在疾病发病机制中的角色。本研究通过建立CDDP致大鼠AKI模型,观察肾组织细胞凋亡及肾组织NGAL变化,探讨其相关性,现报道如下。
1 材料与方法
1.1 实验动物 健康雄性Wistar大鼠36只,体重200~220 g,由广西医科大学实验动物中心提供。
1.2 药品与试剂 顺铂注射液(江苏豪森药业,批号120318),TUNEL试剂盒(美国Roche),NGAL试剂盒(武汉博士德生物工程有限公司)。
1.3 方法
1.3.1 动物模型建立 按随机数字法将大鼠分为6组,盐水对照组(CN组),顺铂模型组(CP组),CP组为腹腔单次注射顺铂10 mg/kg,据给药后各时间点不同分为CP 12 h组、CP 24 h组、CP 48 h组、CP 96 h组、CP 144 h组;CN组为腹腔注射同CP组等容量生理盐水。每组6只大鼠,共36只。
1.3.2 标本处理 取各时间点大鼠乙醚吸入麻醉,打开腹腔,门静脉穿刺取血,取血清-80 ℃保存备检,迅速取出双肾,去除被膜,生理盐水冲洗,4%多聚甲醛固定过夜,行肾病理切片。
1.4 观察指标 采用全自动生化仪测定Scr,光镜下观察肾组织切片HE染色形态学改变,应用TUNEL检测肾组织中细胞凋亡情况,免疫组化法检测肾组织中NGAL表达。
1.5 统计学处理 采用SPSS 13.0软件对所得数据进行统计分析,正态分布计量资料用(x±s)表示,比较采用t检验;计数资料以率(%)表示,比较采用 字2检验。相关性分析采用Spearman分析,以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
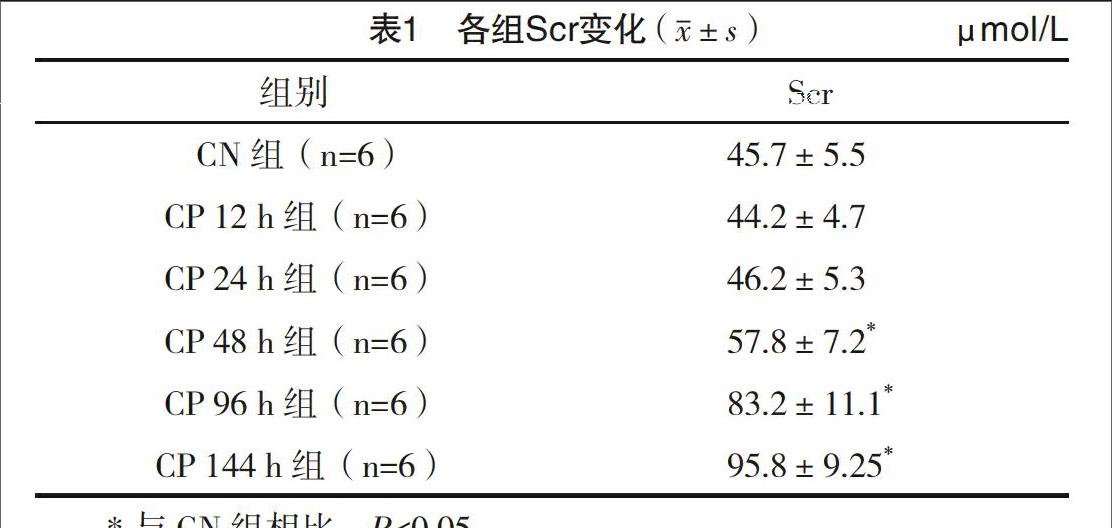
2.1 Scr变化 CP组Scr于48 h开始逐渐升高,144 h达峰值(95.8±9.25)μmol/L,见表1。
2.2 肾组织病理变化 与CN组相比,CP组用药后12、24 h肾小管上皮细胞有轻度浊肿,部分刷状缘脱落;用药后48 h,肾小管上皮细胞轻中度浊肿,少量核固缩,见少量蛋白管型形成;至用药后144 h,肾小管上皮细胞扁平,刷状缘脱落,管腔扩张,大片细胞核固缩,部分脱落于肾小管腔内。见图1。
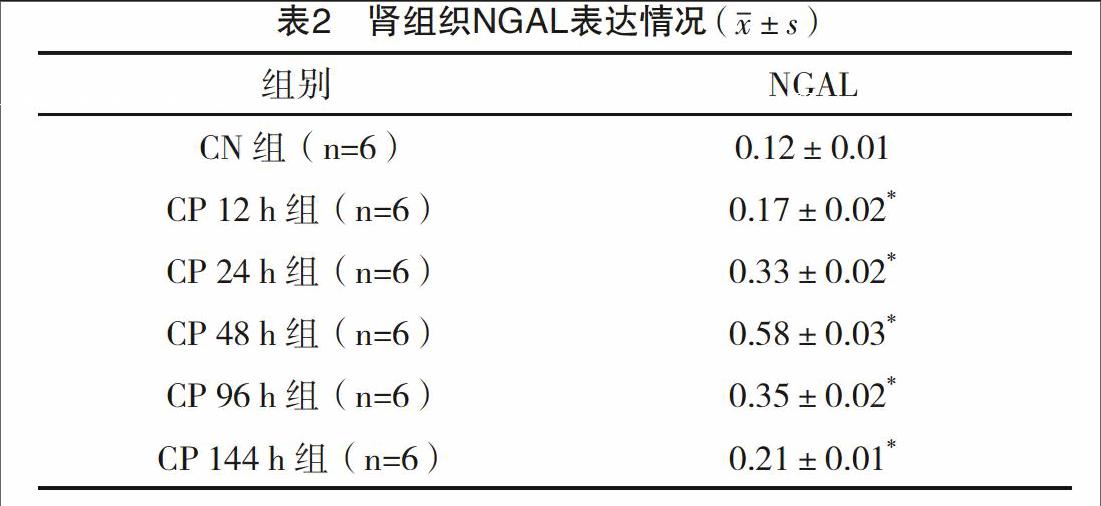
2.3 肾组织NGAL表达情况 每例标本随机地挑选5个400×视野,应用图像分析测定NGAL表达的平均光密度。CN组无明显表达,CP组12 h在皮髓质交界区处肾小管上皮细胞胞浆中表达增强,24、48 h进一步增强(P<0.05),之后表达减弱。见表2和图2。
2.4 肾组织细胞凋亡情况 应用TUNEL法检测细胞凋亡,凋亡细胞的细胞核内DNA特异的3末端被特殊标记,呈棕褐色染色。每例标本随机挑选5个400×视野,计数深棕色细胞核,取平均数计为凋亡细胞数,见表3。肾组织细胞凋亡同NGAL相关性分析提示高度相关,见表4。
3 讨论
順铂是广泛用于多种实体肿瘤的铂类抗瘤药物,肾毒性可出现在约1/3的用药患者中,既往认为顺铂致AKI的机制可能有炎症介质、氧化应激、坏死、凋亡、自噬等,早期诊治可改善患者预后,而传统作为AKI的标记血肌酐,受饮食、肌肉质量影响,且属于“回顾”性指标,敏感性欠佳。近年来关于新的血清及尿液AKI生物标志物的研究逐渐增多,包括NGAL,肾损伤分子1(KIM-1),肝型脂肪酸结合蛋白(L-FABP),白介素18(IL-18),组织型金属蛋白酶抑制物2(TIMP-2),胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白7(IGFBP7),尿外泌体,钙卫蛋白[4](calprotectin),Vanin-1[5]以及最近提出的Wnt信号通路中的Wnt4蛋白[6]等,但目前仍没有足够的证据证实AKI生物标志物在治疗决策中的作用,探讨各生物学标记物在AKI中的生物学特性,有助于进一步理解疾病发病机制及寻找治疗靶标。
NGAL作为诊断及预后评估的研究涉及炎症、感染、代谢、心脑血管、呼吸、泌尿、血液等多系统疾病[7-11]。NGAL已知的主要生物学特性是抑菌和调节细胞内铁贮存,细菌性尿路感染、社区获得性肺炎、脓毒血症患者血清以及细菌性脑膜炎脑脊液,细菌性腹膜炎腹水中均可出现NGAL的升高[12]。有研究提出NGAL参与了固有免疫中抗菌性质的铁耗竭过程[13]。然而,NGAL在一些无菌性疾病中也有表达,提示可能通过结合其他的配体,行使不同功能。
现有研究发现NGAL生物学功能涉及参与炎症反应、氧化应激、促进细胞凋亡等[14-16],但有研究发现外源性NGAL有抗凋亡作用[17],也有关于NGAL抑制未分化甲状腺癌细胞凋亡的报道[18],而关于NGAL在顺铂致AKI中同细胞凋亡的相关性如何,尚未见报道。
本研究在CDDP致大鼠AKI动物实验中观察到,注射CDDP后12 h肾组织NGAL表达增加,至48 h表达最明显;而肾组织细胞凋亡在应用CDDP后12 h开始增多,48 h肾组织细胞凋亡最显著,相关性分析提示肾组织细胞凋亡同NGAL表达高度相关,而Scr在细胞凋亡最显著的48 h才明显升高,在细胞凋亡逐渐减少的情况下仍呈上升趋势,至144 h达峰值,肾脏病理显示有肾小管坏死,提示除损伤早期的细胞凋亡之外,在AKI不同阶段,可能有其他的细胞损伤机制参与AKI的发病。本研究发现肾组织细胞凋亡同NGAL表达高度相关,结合目前已有关于NGAL参与细胞凋亡的报道,在AKI中,NGAL为早期肾损伤标记物之外,是否还参与氧化应激或细胞凋亡,从而在AKI的发病机制中起到一定作用?本研究未对相应的分子机制做深入探讨,有待于后续研究。
綜上,目前国内关于NGAL的研究主要集中于早期诊断的生物学标记物方面,需要有更进一步的研究探讨NGAL在受损组织器官中的生物学特性,可能为AKI的诊治提供更广阔的前景。
参考文献
[1] Lewington A J,Cerda J,Mehta R L.Raising awareness of acute kidney injury:a global perspective of a silent killer[J].Kidney Int,2013,84(3):457-467.
[2] Yang L,Xing G,Wang L,et al.Acute kidney injury in China:a cross-sectional survey[J].Lancet,2015,386(10 002):1465-1471.
[3]孟晓燕,郑妮,张敏,等.顺铂致大鼠急性肾损伤血、尿NGAL变化及还原型谷胱甘肽干预的研究[J].中国现代医学杂志,2014,24(33):15-18.
[4] Westhoff J H,Fichtner A,Waldherr S,et al.Urinary biomarkers for the differentiation of prerenal and intrinsic pediatric acute kidney injury[J].Pediatr Nephrol,2016,31(12):2353-2363.
[5] Hosohata K,Ando H,Fujimura A.Urinary vanin-1 as a novel biomarker for early detection of drug-induced acute kidney injury[J].J Pharmacol Exp Ther,2012,341(3):656-662.
[6] Zhao S L,Wei S Y,Wang Y X,et al.Wnt4 is a novel biomarker for the early detection of kidney tubular injury after ischemia/reperfusion injury[J].Sci Rep,2016,6:32 610.
[7] Chakraborty S,Kaur S,Guha S,et al.The multifaceted roles of neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin(NGAL) in inflammation and cancer[J].Biochim Biophys Acta,2012,1826(1):129-169.
[8] Mishra J,Dent C,Tarabishi R,et al.Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin(NGAL) as a biomarker for acute renal injury after cardiac surgery[J].Lancet,2005,365(9466):1231-1238.
[9] Parikh C R,Coca S G,Thiessen-Philbrook H,et al.
Postoperative biomarkers predict acute kidney injury and poor outcomes after adult cardiac surgery[J].J Am Soc Nephrol,2011,22(9):1748-1757.
[10] Parikh C R,Devarajan P,Zappitelli M,et al.Postoperative biomarkers predict acute kidney injury and poor outcomes after pediatric cardiac surgery[J].J Am Soc Nephrol,2011,22(9):1737-1747.
[11] Torres-Salido M T,Cortes-Hernandez J,Vidal X,et al.
Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a biomarker for lupus nephritis[J].Nephrol Dial Transplant,2014,29(9):1740-1749.
[12] Nasioudis D,Witkin S S.Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin and innate immune responses to bacterial infections[J].Med Microbiol Immunol,2015,204(4):471-479.
[13] Goetz D H,Holmes M A,Borregaard N,et al.The neutrophil lipocalin NGAL is a bacteriostatic agent that interferes with siderophore-mediated iron acquisition[J].Mol Cell,2002,10(5):1033-1043.
[12] Cowland J B,Sorensen O E,Sehested M,et al.Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin is up-regulated in human epithelial cells by IL-1 beta,but not by TNF-alpha[J].J Immunol,2003,171(12):6630-6639.
[13] Aigner F,Maier H T,Schwelberger H G,et al.Lipocalin-2 regulates the inflammatory response during ischemia and reperfusion of the transplanted heart[J].Am J Transplant,2007,7(4):779-788.
[14] Bahmani P,Halabian R,Rouhbakhsh M,et al.Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin induces the expression of heme oxygenase-1 and superoxide dismutase 1,2[J].Cell Stress Chaperones,2010,15(4):395-403.
[15] Nelson A M,Zhao W,Gilliland K L,et al.Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin mediates 13-cis retinoic acid-induced apoptosis of human sebaceous gland cells[J].J Clin Invest,2008,118(4):1468-1478.
[16] Pawar R D,Pitashny M,Gindea S,et al.Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin is instrumental in the pathogenesis of antibody-mediated nephritis in mice[J].Arthritis Rheum,2012,64(5):1620-1631.
[17] Mishra J,Mori K,Ma Q,et al.Amelioration of ischemic acute renal injury by neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin[J].J Am Soc Nephrol,2004,15(12):3073-3082.
[18] Iannetti A,Pacifico F,Acquaviva R,et al.The neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin(NGAL),a NF-kappaB-regulated gene,is a survival factor for thyroid neoplastic cells[J].Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2008,105(37):14 058-14 063.
(收稿日期:2016-12-22) (本文編辑:程旭然)

