卵巢癌组织细胞黏附分子1的表达变化及意义
夏芬,胡燕玲,李莉
(华中科技大学同济医学院附属武汉中心医院,武汉430014)
卵巢癌组织细胞黏附分子1的表达变化及意义
夏芬,胡燕玲,李莉
(华中科技大学同济医学院附属武汉中心医院,武汉430014)
目的探讨细胞黏附分子1(CADM1)在卵巢癌组织中的表达变化及其临床意义。方法 收集卵巢癌患者59例,取其癌组织及癌旁正常组织,采用qRT-PCR、Western blotting和免疫组化法分别检测CADM1 mRNA和蛋白在卵巢癌及对应癌旁正常组织中的表达。χ2检验及Kaplan-Meier生存曲线分析CADM1的表达水平与卵巢癌患者临床病理参数、预后的相关性。结果卵巢癌组织中CADM1 mRNA和蛋白表达水平分别为0.28±0.12、1.32±0.23,癌旁正常组织分别为1.52±0.14、2.93±0.42,癌组织与癌旁正常组织比较,P均<0.05。癌旁正常组织中CADM1阳性细胞百分比(90%±5%)显著高于癌组织(10%±2%)(P<0.05)。CADM1表达水平与卵巢癌患者FIGO分期、远处转移及淋巴结转移显著相关(P均<0.05)。CADM1低表达(mRNA表达量<0.57)患者中位生存期显著低于CADM1高表达患者(13.2比24.5个月,P<0.05)。结论 卵巢癌组织中CADM1呈低表达状态,低水平的CADM1促进卵巢癌的发生发展,且与其不良预后相关。
卵巢肿瘤;细胞黏附分子1;临床病理参数;预后
卵巢癌是全世界最常见的女性恶性肿瘤[1]。其在确诊时大多已到肿瘤晚期,尽管近年来针对卵巢癌研究鉴定出一些用于早期诊断的标志物,但临床上可用于卵巢癌筛查的只有CA125,其特异性和灵敏度均较低[2,3]。细胞黏附分子1(CADM1)属于免疫球蛋白超家族黏附分子,其功能涉及细胞之间的相互作用,在肺腺癌中具有肿瘤抑制作用[4]。近年来研究发现,CADM1在多种肿瘤如结肠癌[5]、非小细胞肺癌[6]、乳腺癌[7]及食管鳞癌[8]中低表达,并且与肿瘤患者恶性病理参数和不良预后显著相关。但CADM1在卵巢癌中的表达变化及临床意义尚不清楚,本研究进行了相关探讨。现报告如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1临床资料收集2008年1月~2012年12月于本院行手术治疗的卵巢癌患者49例,均经病理检查确诊,年龄(51.2±3.9)岁。入选标准:手术前未接受过放化疗,并具有完整病理资料和随访资料的卵巢癌患者。其卵巢癌组织及对应癌旁正常组织标本经手术切除后迅速分块取材,置于液氮冻存或4%多聚甲醛固定并石蜡包埋保存备用。
1.2组织CADM1 mRNA测定采用RT-PCR法。按TRIzol试剂说明书RNA提取步骤提取冻存组织中总RNA,取1 μg总RNA反转录成cDNA。CADM1引物序列:上游引物:5′-GAATCCCAACAGGCAGACC-3′,下游引物:5′-TTTGCCAGCTCTATACCGATC-3′;GAPDH上游引物:5′-TCATACTCCTGCTTGCTGAT-3′,下游引物:5′-GGGACCTGACTGACTACCTC-3′。按qRT-PCR说明书要求配制反应体系进行PCR扩增反应。以GAPDH基因为内参,采用2-ΔΔCt法计算CADM1基因在组织中相对表达量。计算所有卵巢癌组织中CADM1表达量的平均值,将样本分为高表达组(ADM1 mRNA>0.57)和低表达组(ADM1 mRNA<0.57)。
1.3组织CADM1蛋白的测定采用Western blotting法。采用RIPA裂解液提取组织样本总蛋白本并进行浓度测定,取相同质量的蛋白样品进行聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳,浓缩胶80 V电泳40 min,分离胶120 V电泳2 h后转印至NC膜,用5% BSA室温封闭1~2 h,4 ℃孵育一抗(CADM1,1∶600;GAPDH,1∶1 000)过夜,0.5% TBST洗膜3遍,加入辣根过氧化物酶标记的二抗(1∶1 000)室温孵育1 h,0.5% TBST洗膜3遍后用ECL化学发光法检测结果,凝胶成像系统显影。用Quantity One分析软件对Western blotting条带进行定量。以目的蛋白测定值与GAPDH的比值作为目标蛋白的相对表达量。
1.4组织CADM1阳性细胞率的测算采用免疫组化法。组织标本制作4 μm厚度石蜡切片,具体步骤包括脱蜡、水化、抗原修复、内源性过氧化物酶阻断以及血清封闭后,CADM1一抗单克隆抗体(1∶600)4 ℃孵育过夜。PBS洗涤3遍后,加入生物素标记的二抗(1∶1 000),37 ℃孵育1 h,DAB显色,显微镜下观察到棕色即停止显色,经苏木素复染,盐酸乙醇分化、脱水、透明、中性树胶封片。于光学显微镜下进行观察并采集图像。高倍视野下计数阳性细胞数和细胞总数,分别选取6个视野,阳性细胞率=阳性细胞/总细胞数×100%,计算平均值。

2 结果
2.1不同组织CADM1的表达卵巢癌组织中CADM1 mRNA表达水平(0.28±0.12)较癌旁正常组织(1.52±0.14)降低(P<0.05)。卵巢癌组织中CADM1蛋白相对表达量(1.32±0.23)低于对应癌旁正常组织(2.93±0.42)(P<0.05)。卵巢癌组织中CADM1染色强度低于对应癌旁正常组织,并且CADM1主要表达于细胞膜和细胞质,癌组织中CADM1阳性细胞率(10%±2%)低于癌组织中阳性细胞率(90%±5%)(P<0.05)。
2.2卵巢癌组织CADM1表达水平与患者临床病理参数的关系见表1。
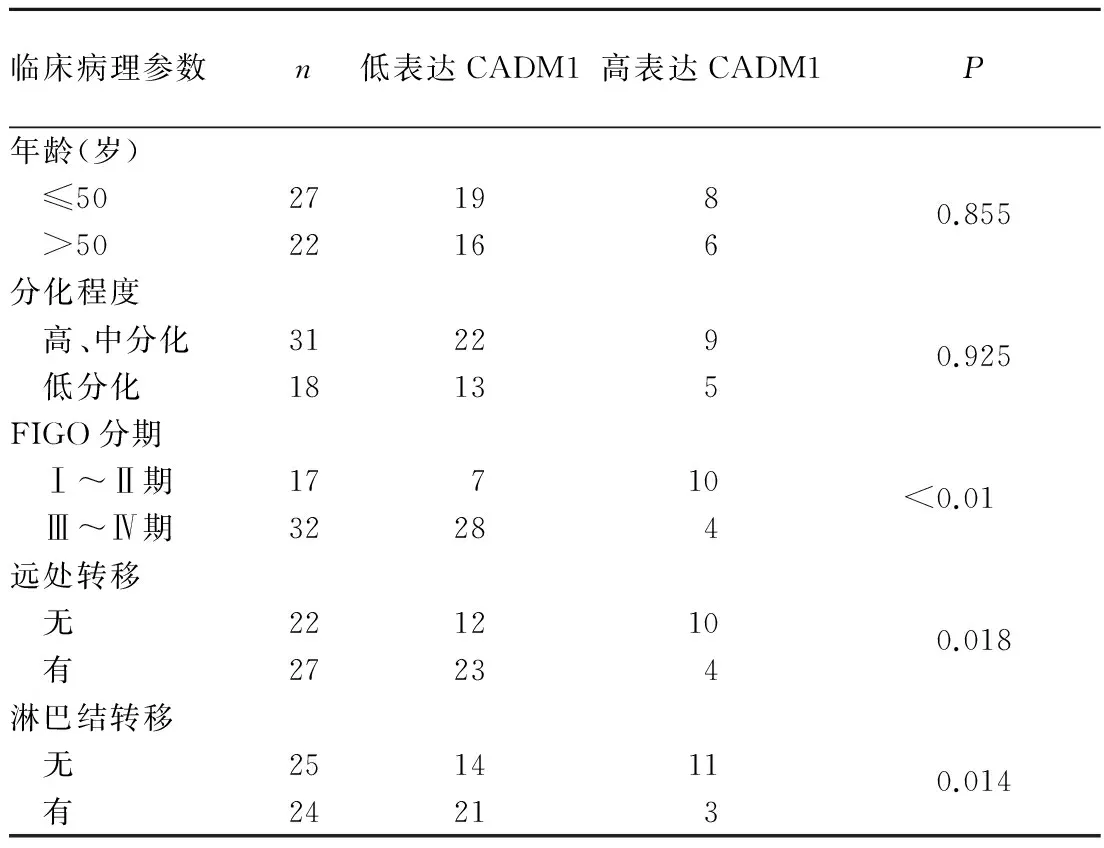
表1 卵巢癌组织CADM1的表达与临床病理参数的关系(例)
2.3卵巢癌组织CADM1表达水平与预后的关系Log-rank检验结果表明,CADM1低表达组中位生存期(13.2个月)显著低于CADM1高表达组(24.5个月)(P<0.05)。见图1。
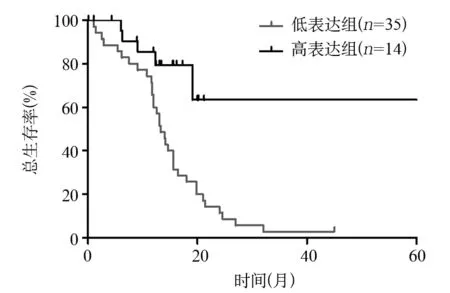
图1 CADM1高表达组与低表达组的生存曲线
3 讨论
肿瘤转移是肿瘤细胞脱离原发部位播散到远处器官形成转移灶的过程,是肿瘤致死性的重要原因,卵巢癌转移与患者不良预后密切相关。
以前的研究发现CADM1在多种肿瘤中缺失或低表达[9]。在本研究中,笔者通过qRT-PCR、Western blotting以及免疫组化染色等方法,从转录水平和蛋白水平上均证实CADM1在卵巢癌组织中呈低表达,并且发现CADM1主要表达于细胞膜和细胞质。这与之前报道CADM1在其他肿瘤中的表达状态一致。CADM1的表达水平与卵巢癌患者的临床分期、淋巴结转移以及远处转移等恶性病理特征显著相关,并且低表达CADM1组总生存时间显著短于CADM1高表达组。以上结果与在其他肿瘤中的报道一致,如食管癌、皮肤癌、喉癌、乳腺癌、结肠癌等[5, 10~12]。提示CADM1在卵巢癌的恶性进展中发挥重要作用。
CADM1的具体功能及其机制在以前的研究中已有报道。在正常的内皮祖细胞中,通过TNFα- NF-κB信号通路上调CADM1的表达促进内皮祖细胞迁移;而在肿瘤中却发挥相反的功能,例如CADM1能够抑制食管癌细胞Eca109从G1期向S期转化诱导凋亡发生,抑制肿瘤细胞增殖从而抑制肿瘤在小鼠体内生长[13]。在Faraji等[14]的研究中发现,CADM1影响肿瘤的转移并不是通过影响肿瘤细胞的增殖或侵袭等特性,而是一种依赖宿主的适应性免疫方式,CADM1发挥肿瘤转移抑制功能是通过促使肿瘤细胞对于免疫监控机制更敏感来实现。目前普遍认为上皮间质转化(EMT)是导致肿瘤转移的重要原因。CADM1作为细胞的黏附分子,笔者推测其表达缺失或降低可能会影响肿瘤细胞的EMT转化,但CADM1影响卵巢癌细胞的迁移侵袭能力是否是通过调控EMT转化仍有待进一步研究。
综上所述,CADM1在卵巢癌组织呈低表达状态,并且其表达水平与患者恶性临床病理参数和生存预后显著相关,CADM1的表达量降低可能在卵巢癌的恶性进展中发挥重要作用。
[1] Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012[J]. Int J Cancer, 2015,136(5):E359-E386.
[2] Bast RC Jr, Badgwell D, Lu Z, et al. New tumor markers: CA125 and beyond[J]. Int J Gynecol Cancer, 2005,15(Suppl 3):274-281.
[3] Goh J, Mohan GR, Ladwa R, et al. Frontline treatment of epithelial ovarian cancer[J]. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol, 2015,11(Suppl 6):1-16.
[4] Watabe K, Ito A, Koma YI , et al. IGSF4: a new intercellular adhesion molecule that is called by three names, TSLC1, SgIGSF and SynCAM, by virtue of its diverse function[J]. Histol Histopathol, 2003,18(4):1321-1329.
[5] Zhang JF, Ning JF, Geng JS, et al. Down-regulation of tumor suppressor in lung cancer 1 (TSLC1) expression correlates with poor prognosis in patients with colon cancer[J]. J Mol Histol, 2012,43(6):715-721.
[6] Kikuchi S, Yamada D, Fukami T, et al. Hypermethylation of the TSLC1/IGSF4 promoter is associated with tobacco smoking and a poor prognosis in primary nonsmall cell lung carcinoma[J]. Cancer, 2006,106(8):1751-1758.
[7] Wikman H, Westphal L, Schmid F, et al. Loss of CADM1 expression is associated with poor prognosis and brain metastasis in breast cancer patients[J]. Oncotarget, 2014,5(10):3076-3087.
[8] Zeng D, Wu X, Zheng J, et al. Loss of CADM1/TSLC1 expression is associated with poor clinical outcome in patients with esophageal squamouscell carcinoma[J]. Gastroenterol Res Pract, 2016,2016:6947623.
[9] Murakami Y. Involvement of a cell adhesion molecule, TSLC1/IGSF4, in human oncogenesis[J]. Cancer SCI, 2005,96(9):543-552.
[10] Ito T, Shimada Y, Hashimoto Y, et al. Involvement of TSLC1 in progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Cancer RES, 2003,63(19):6320-6326.
[11] Liu D, Feng X, Wu X, et al. Tumor suppressor in lung cancer 1 (TSLC1), a novel tumor suppressor gene, is implicated in the regulation of proliferation, invasion, cell cycle, apoptosis, and tumorigenicity in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Tumor Biol, 2013,34(6):3773-3783.
[12] Lu B, Di W, Wang H, et al. Tumor suppressor TSLC1 is implicated in cell proliferation, invasion and apoptosis in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma by regulating Akt signaling pathway[J]. Tumor Biol, 2012,33(6):2007-2017.
[13] Liang QL, Chen GQ, Liu QL, et al. Tumor suppressor TSLC1 inhibits growth, proliferation, invasiveness and angiogenesis in nude mice xenografted tumor of Eca109 cells[J]. Int J Clin Exp Med, 2014,7(6):1507-1515.
[14] Faraji F, Pang Y, Walker RC, et al. Cadm1 is a metastasis susceptibility gene that suppresses metastasis by modifying tumor interaction with the cell-mediated immunity[J]. PLoS Genet, 2012,8(9):e1002926.
Expression of CADM1 and its clinical significance in human ovarian carcinoma
XIAFen,HUYanling,LILi
(WuhanCentralHospitalAffiliatedtoHuazhongUniversityofScienceandTechnology,Wuhan430014,China)
Objective To investigate the expression changes of cell adhesion molecule-1 (CADM1) in human ovarian carcinoma and its clinical significance. Methods A total of 59 case of ovarian carcinoma tissues and matched tumor-adjacent tissues were collected. The mRNA and protein expression of CADM1 in the ovarian carcinoma tissues and matched tumor-adjacent tissues was examined by qRT-PCR, immunohistochemistry and Western blotting. The Chi-square test and Kaplan-Meier analysis was used to evaluate the correlation between CADM1 expression and clinicopathological characteristics or overall survival. Results The expression of CADM1 mRNA and protein in the ovarian carcinoma tissues was 0.28±0.12 and 1.32±0.23, respectively, 1.52±0.14 and 2.93±0.42 in the matched tumor-adjacent tissues, and significant difference was found between these two kinds of tissues (all P<0.05). The percentage of positive cells in the adjacent tumor tissues (90%±5%) was significantly higher than that of the cancer tissues (10%±2%),P<0.05. The expression of CADM1 was significantly associated with the FIGO stage, nodal metastasis and distant metastasis (allP<0.05). The median survival time of patients with low expression of CADM1 (mRNA expression <0.57) was higher than that of patients with high expression (13.2 vs. 24.5 months,P<0.05). ConclusionCADM1 is low expressed in the human ovarian cancer tissues. The low expression of CADM1 promotes the occurrence and development of ovarian cancer, and is related to its poor prognosis.
ovarian carcinoma; cell adhesion molecule-1; clinicopathological parameter; prognosis
夏芬(1976-),主治医师,主要研究方向为妇产科疾病的基础与临床。E-mail:wyflw166@163.com
简介:李莉(1979-),主治医师,主要研究方向为妇产科疾病的基础与临床。E-mail:liliwuhan8887@sina.com
10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2016.29.005
R737.14
A
1002-266X(2016)29-0014-03
2016-05-09)

