砂土中单桩基础冲刷的修正应变楔计算①
杨晓峰,张陈蓉,黄茂松,袁聚云,高博雷
(1.同济大学土木工程学院地下建筑与工程系,上海 200092; 2.同济大学岩土及地下工程教育部重点实验室,上海 200092)
砂土中单桩基础冲刷的修正应变楔计算①
杨晓峰1,2,张陈蓉1,2,黄茂松1,2,袁聚云1,2,高博雷1,2
(1.同济大学土木工程学院地下建筑与工程系,上海 200092; 2.同济大学岩土及地下工程教育部重点实验室,上海 200092)
由冲刷引起的深水结构物桩基础周围土体损失致使基础水平承载性能下降的问题越发受到重视。应变楔方法假设桩前土体抵抗为三维楔形体,其尺寸发展与楔形体区域土体发挥的内摩擦角有关,从而得到水平受荷桩的p-y曲线。本文对应变楔方法进行修正和拓展,建立非线性位移假设以考虑桩前楔形体区域土体应变沿深度的非均匀分布,将冲刷坑底以上土体的有效自重作用等效为竖向荷载,对楔形体的深度进行修正,以解决楔形体方法只适用于地表水平的情况,得到砂土中单桩基础冲刷的修正应变楔计算方法;并通过与模型试验及三维有限元分析的对比来验证该方法的合理性。分析结果表明:冲刷深度增加会显著降低桩基水平承载性能,冲刷深度3.2D和6.4D情况下的桩顶位移比平均值分别趋近于1.8和3.0;相比有限元方法,本文修正SW方法计算的p-y曲线结果与实测结果更为接近。
冲刷; 水平受荷桩; 修正应变楔方法;砂土; p-y曲线
0 引言
桥梁基础和海上风电因水流冲刷会造成桩基周围土体的损失,引起水平承载性能下降,甚至上部结构的破坏,因此对冲刷条件下桩基础水平承载性能的评估越来越受重视[1-5]。Ni等[2]将冲刷简单地模拟为整个土层的剥离,分析了砂土中不同冲刷深度对单桩水平承载力的损失。Achmus等[4]的有限元分析表明,冲刷深度对海上大直径桩的水平位移和转角有重大影响。Li等[5]研究了局部冲刷尺寸(冲刷深度、宽度和坡角)对海洋软黏土中水平受荷单桩承载力的影响,认为冲刷深度达到5倍桩径时单桩水平承载力下降40%左右。Lin等[6]令冲刷条件下与Reese地表水平条件下的桩前楔形体土体极限抗力值相等,对Reese极限平衡方法[7]进行修正,推导了冲刷条件下的p-y曲线,但该方法仅修正了Pu值。
与Reese方法不同,应变楔(Strain Wedge)方法(以下简称SW法)[8]将桩前楔形体的几何尺寸发展与土体发挥的内摩擦角建立联系,使得桩侧p-y曲线的开展与土体的非线性应力应变关系完全对应。Xu等[9]基于SW法讨论了Duncan-Chang和Mohr-Coulomb土体条件下p-y曲线的区别,而文献[10]对SW方法的楔形体内土体应变均一化假设进行了修正改进。与Reese方法类似,SW方法只适用于地表水平的情况。本文参考了文献[11]的楔形体等效深度修正,考虑了冲刷引起的桩周土体几何形状的改变,将修正SW方法应用于冲刷条件下的水平受荷桩分析。
本文将砂土中的修正应变楔方法推广到考虑冲刷坑几何尺寸的非水平地表条件下,基于坑底以上楔形体的自重荷载得到冲刷条件下的楔形体等效深度,分析冲刷深度对单桩水平承载性能的影响,并与模型试验的结果以及有限元分析进行对比验证。
1 应变楔模型的修正
在水平荷载下,将桩周土体作用等效成弹性地基梁上的非线性弹簧,桩土系统的平衡方程为:

(1)
式中:EI为桩身抗弯刚度;y为桩身水平位移;z为地表以下深度;地基反力模量k=p/y,p为单位桩长提供的土体抗力。
桩顶受水平荷载时,桩前土体处于被动受压状态,应变楔模型[8]假定在桩前形成三维被动土楔,其几何形态由扇形角φm、底角βm和楔形体最大深度H进行描述,如图1所示。随着外荷载的增大,楔形体的尺寸和内部应力应变状态随之发展。根据桩前楔形体土体局部平衡条件和单桩的桩土系统平衡条件进行求解,得到单桩在水平荷载下的响应和相应的p-y曲线。

图1 应变楔模型Fig.1 Basic strain wedge model
应变楔模型假定被动楔对应的桩身水平位移沿深度线性变化(图2),该假设使得楔形体内水平向土体应变大小一样。修正应变楔方法对桩身变形的开展引入了非线性假设(图3),具体实现如下:将桩和应变楔土体沿深度均匀分层,各子层上下界面处的桩身位移分别与该层的桩身偏转角及水平土体应变建立联系,以考虑楔形体内土体应变沿深度的发展变化。假定子层厚度为h,单桩在第i层的上下界面处位移分别为yi-1和yi,则第i层单桩偏移角δi与桩身位移的关系为:

(2)
桩身偏转角与土体水平应变的关系[8]为:
(3)
式中:εvi为土体的竖向应变,εvi=-υεi,υ为土体的泊松比。θmi为βmi的补角,θmi=45°-φmi/2。
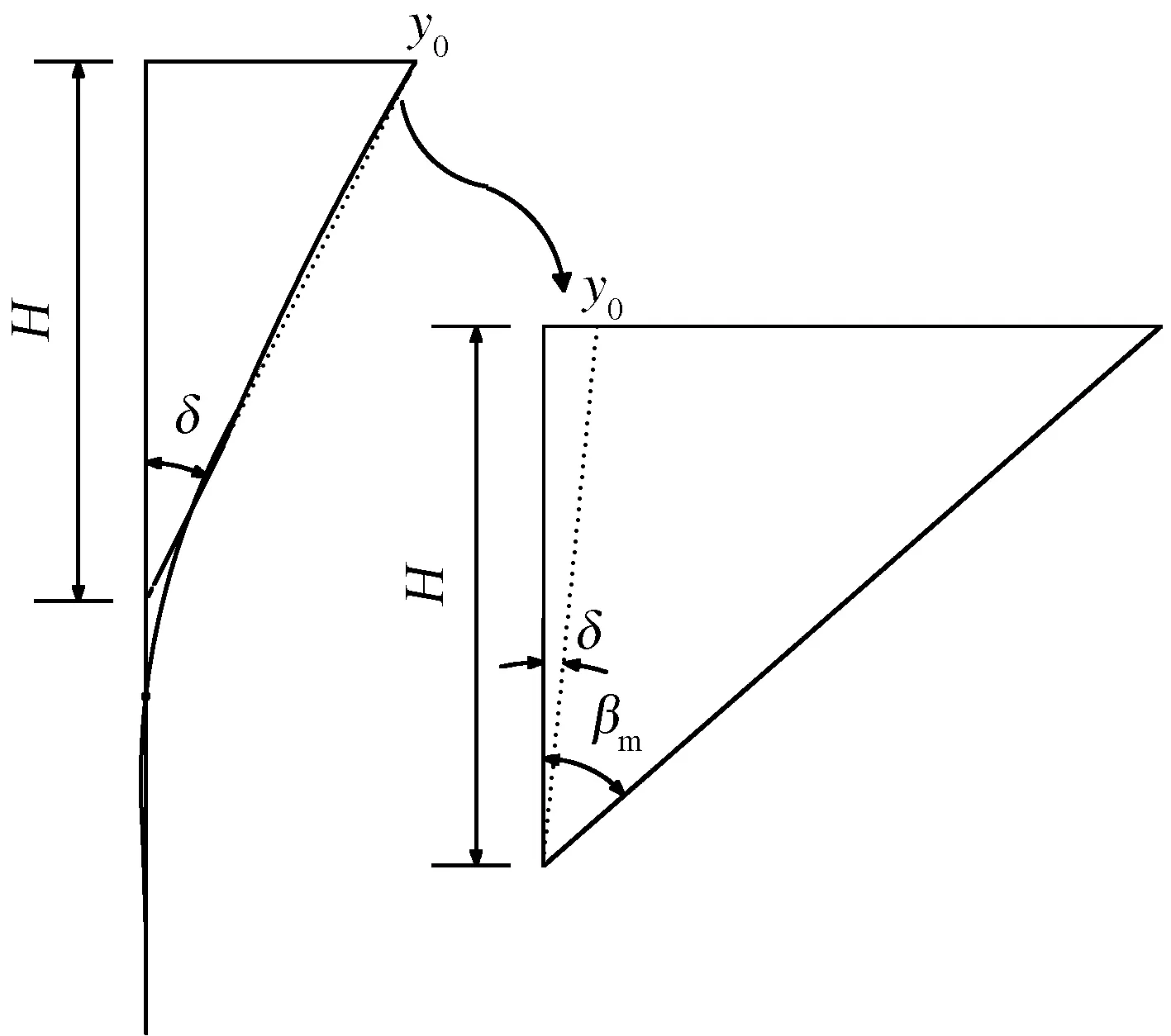
图2 桩身线性位移示意图[8]Fig.2 Linear displacement assumption of a laterally loaded pile in the SW model[8]

图3 修正应变楔模型的桩身非线性位移假定[10]Fig.3 Nonlinear displacement assumption of a laterally loaded pile in the modified SW model[10]
2 冲刷条件下的楔形体等效
冲刷是水流对土体的一种侵蚀行为,会引起桩基础周围土体损失而形成局部冲刷坑。典型冲刷坑剖面如图4所示,由冲刷坑深度Sd、冲刷宽度Sw和冲刷坑坡角θ加以描述。当Sw=∞时为最不利情况,即冲刷深度范围内土层全部被剥蚀。

图4 冲刷坑剖面示意图[6]Fig.4 The profile of a scour hole[6]
应变楔方法[8]仅适用于地表水平的情况,为此需要进行修正。在整个水平加载过程中,针对冲刷坑的几何形态和楔形体的发展状态,将坑底以上土体的自重作用等效为竖向荷载,推导等效深度hs,建立等效应变楔模型(图5)。等效深度hs的求解具体见文献[11]。得到等效深度hs后,结合修正应变楔模型的求解,以实现应变楔模型在冲刷条件下的推广。

图5 冲刷条件下等效应变楔模型[11]Fig.5 The equivalent strain wedge model under scour[11]
3 算例验证
高博雷[12]进行了砂土中冲刷条件下单桩水平响应的1g模型试验。试验用土为中密细砂,砂土物理指标见表1。模型桩的尺寸和材料参数见表2。本文选取无冲刷和冲刷深度分别为3.2D和6.4D的三组试验进行分析,冲刷坡角20°,冲刷宽度为零,加载点位于冲刷前地表以上0.16 m处,无冲刷时桩身入土深度0.69 m。为验证计算的可靠性,对试验结果进行三维有限元数值模拟,计算范围:水平方向取30倍桩径,竖直方向桩端向下取10倍桩径。砂土采用MC材料模拟,桩土接触面摩擦系数u=tan(φ/2)[6]。对无冲刷结果进行反演,得到砂土弹模0.3 MPa,泊松比0.3。为保证收敛性,黏聚力取0.5 kPa。考虑到对称性,有限元模型取一半,见图6。

表1 砂土参数

表2 模型桩参数

图6 考虑冲刷的有限元模型Fig.6 Finite element model considering scouring
图7分别给出了三组试验的荷载位移曲线,11.76 N水平荷载时的桩身弯矩分布和桩身变形分布,并给出了本文计算方法和有限元计算结果。由图可见,随着冲刷深度的增大,桩身水平承载性能明显降低,桩身所承受的最大弯矩显著增加,最大弯矩位置也向更深土层移动。
图8给出了11.76 N和27.44 N两种荷载水平下不同冲刷深度时加载点处的桩身水平位移。由图可见:荷载一定时,桩顶位移随着冲刷深度的增大而加速增长;荷载水平较小(11.76 N)时各计算结果吻合较好,而荷载水平较大(27.44 N)时,修正SW法计算的水平位移偏大,尤其是冲刷深度6.4D时。

图7 桩身荷载位移、弯矩分布及变形曲线Fig.7 Curves of load-displacement,bending moment distribution,and deformation of the pile

图8 桩顶位移随冲刷深度的变化Fig.8 Displacements at pile head versus scour depths
图9给出了不同荷载下的桩顶位移比。位移比即某一荷载下所得桩顶位移值与相应无冲刷情况下位移的比值。相同荷载下,冲刷深度6.4D情况比3.2D情况的位移比大,但是随着荷载的增大位移比趋于稳定,冲刷深度3.2D和6.4D时平均位移比分别趋近于1.8和3.0左右。

图9 不同水平荷载下的位移比Fig.9 Ratios of displacements at pile head versus lateral load
图10给出了地表下6.9D处不同冲刷情况下的p-y曲线。由图可见,随着冲刷深度的增大,实测值和修正SW方法p-y曲线的初始斜率和相同位移水平下的土体抗力均有明显降低且成增速下降。有限元计算得到的各冲刷深度下p-y曲线的初始斜率变化不大,仅影响了极限值。

图10 地表下6.9D深度处的p-y曲线Fig.10 p-y curves at a depth of 6.9D
4 结论
(1)冲刷条件下建立的分析水平受荷桩的修正应变楔方法是常规应变楔方法的进一步推广,通过模型试验和有限单元法验证了其有效性。
(2)冲刷深度的增加对桩水平承载力性能的下降作用明显。本文计算得到冲刷深度3.2D和6.4D情况下的桩顶位移比呈逐渐下降趋势,分别趋近于平均值1.8和3.0。
(3)相比有限元计算的p-y曲线结果,本文修正SW方法与实测结果更为接近。
References)
[1]Liang F Y,Bennett C R,Parsons R L,et al.A Literature Review on Behavior of Scoured Piles under Bridges[C]//International Foundation Congress & Equipment Expo 2009-In Site Testing,Analysis,and Reliability of Foundations,2009:482-489.
[2]Ni S H,Huang Y H,Lo K F.Numerical Investigation of the Scouring Effect on the Lateral Response of Piles in Sand[J].Journal of Performance of Constructed Facilities,2011,26(3):320-325.
[3]Prendergast L J,Gavin K.A Review of Bridge Scour Monitoring Techniques[J].Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering,2014,6(2):138-149.
[4]Achmus M,Kuo Y S,Abdel-Rahman K.Numerical Investigation of Scour Effect on Lateral Resistance of Windfarm Monopoles[C]//The Twentieth International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference.International Society of Offshore and Polar Engineers,2010.
[5]Li F,Han J,Lin C.Effect of Scour on the Behavior of Laterally Loaded Single Piles in Marine Clay[J].Marine Georesources & Geotechnology,2013,31(3):271-289.
[6]Lin C,Han J,Bennett C R,et al.Analysis of Laterally Loaded Piles in Sand Considering Scour Hole Dimensions[J].Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering,2014,140(6):213-226.
[7]Reese L C,Cox W R.Analysis of Laterally Loaded Piles in Sand[C]//Offshore Technology in Civil Engineering@ sHall of Fame Papers from the Early Years.ASCE,1974,95-105.
[8]Ashour M,Norris G,Pilling P.Lateral Loading of a Pile in Layered Soil Using the Strain Wedge Model[J].Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering,1998,124(4):303-315.
[9]Xu L Y,Cai F,Wang G X,et al.Nonlinear Analysis of Laterally Loaded Single Piles in Sand Using Modified Strain Wedge Model[J].Computers and Geotechnics,2013,51:60-71.
[10]杨晓峰,张陈蓉,黄茂松,等.砂土中桩土侧向相互作用的应变楔模型修正[J].岩土力学(录用).
YANG Xiao-feng,ZHANG Chen-rong,HUANG Mao-song,et al.The Modification of Strain Wedge Method for the Lateral Soil-pile Interaction in Sand[J].Rock and Soil Mechanics (Accepted).(in Chinese)
[11]杨晓峰,张陈蓉,袁聚云.砂土中考虑冲刷的水平受荷桩等效应变楔方法[J].岩土力学,2015,36(10):2946-2950.
YANG Xiao-feng,ZHANG Chen-rong,YUAN Ju-yun.Equivalent-strain Wedge Method for Laterally Loaded Pile in Sand Considering Scouring Effect[J].Rock and Soil Mechanics,2015,36(10):2946-2950.(in Chinese)
[12]高博雷.砂土中受冲刷影响的水平受荷桩基础模型试验与数值与分析[D].上海:同济大学,2015.GAO Bo-lei.Model Test and Numerical Simulation of the Influence of Scouring on the Lateral Response of Pile Foundations in Sand[D].Shanghai:Tongji University,2015.(in Chinese)
Modified Strain Wedge Calculation of Single Pile in Sand under Scour
YANG Xiao-feng1,2,ZHANG Chen-rong1,2,HUANG Mao-song1,2,YUAN Ju-yun1,2,GAO Bo-lei1,2
(1.Department of Geotechnical Engineering,College of Civil Engineering,Tongji University,Shanghai 200092,China;2.Key Laboratory of Geotechnical and Underground Engineering of Ministry of Education,Tongji University,Shanghai 200092,China)
Scour can induce soil loss around the pile foundations of engineering structures in deep water and the degeneration of the lateral bearing capacity of pile foundations caused by scour is being paid more and more attention.The strain wedge (SW)method is an effective p-y curve technique for predicting the response of piles under lateral loading.It assumes that a three-dimensional passive soil wedge forms to resist the movement of a laterally loaded pile and that the dimensions and mobilized friction angle of the soil wedge develop as the lateral load increases.However,in order to improve and extend the ability of the SW method,a modified SW method is developed which introduces the assumption of nonlinear lateral deflection of the pile resulting in non-uniform soil strain,rather than uniform strain in the soil wedge.In addition,by equating the soil weight above the bottom of the scour hole to a vertical load,the problem of the SW method being only suitable for horizontal ground surfaces is solved.The validity of the method is confirmed by the measured results of a model test and the finite element method.Results show that the lateral bearing capacity of the pile sharply declines as scour depth increases.The average ratio of lateral displacements at the pile head tended to 1.8 and 3.0 when scour depths were 3.2D and 6.4D (D=outer diameter of pile),respectively.Compared with the results of p-y curves from the finite element method,the results from the modified SW method are much more satisfactory than those measured.
scour; laterally loaded piles; modified strain wedge method; sand soil; p-y curve
2016-04-26
国家973计划课题(2013CB036304),国家自然科学基金项目(51378392)
杨晓峰(1986-),男,博士研究生,从事桩基工程研究。E-mail:xiaofengsile@163.com。通信作者:张陈蓉(1982-),女,副研究员,主要从事桩基工程科研与教学工作。E-mail:zcrong33@tongji.edu.cn。
TU473
A
1000-0844(2016)04-0549-05
10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2016.04.0549

