终末期氧化蛋白产物与狼疮性肾炎的相关性
谢 震陈源汉王有为万慧颖刘杨英周 敏
·论著·
终末期氧化蛋白产物与狼疮性肾炎的相关性
谢 震1陈源汉2王有为1万慧颖1刘杨英1周 敏1
目的: 明确终末期氧化蛋白产物(AOPP)与狼疮性肾炎(LN)的相关性。方法: 检测56 例LD患者和36例LD合并LN患者血清中AOPP水平并分析AOPP水平与LN之间的相关性。结果:LD+LN患者中AOPP为(105.6±28.5)μmol/L高于LD患者的(64.6±20.4)μmol/L。LD+LN患者高AOPP者(>84.5 μmol/L)者较低AOPP者ds-DNA和尿蛋白水平更高,eGFR和补体C3水平更低。多变量二分类Logistic回归模型中,AOPP水平升高是发生LN的独立危险因素,AOPP每增加10 μmol/ L,发生LN的危险增加24%(95%可信区间1.166~1.915)。结论: AOPP可能和LN发病有关,有可能作为早期预测LN的指标。
终末期氧化蛋白产物; 狼疮性皮炎; 狼疮性肾炎
系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)致病机制复杂,可造成多器官系统损伤,皮肤和肾脏最容易受累及。常见的狼疮性皮炎包括蝶形红斑、指(趾)腹红斑、盘状红斑、冻疮样损害等[1]。由于治疗方案和预后差别很大,区分单纯性狼疮性皮炎(lupus dermatitis,LD)和狼疮性肾炎(lupus nephritis,LN)具有重要临床意义。
近年来,终末期氧化蛋白产物(advanced oxidationprotein products,AOPP)被广泛用作某些自身免疫性皮肤病和肾脏疾病的标志物[2-5]。部分SLE患者的AOPP水平升高[6,7],AOPP能否作为狼疮性肾炎的标志物?本实验在以狼疮性皮炎为首发表现的人群中进行了病例-对照研究。
1 资料与方法
1.1研究对象 入选以LD为首发表现的系统性红斑狼疮患者,这些对象均随访6个月以上。根据是否同时合并肾炎分为狼疮性皮炎(LD)组和狼疮性皮炎合并肾炎(LD+LN)组,在随访期内发生肾损伤的初诊LD者纳入LD+LN组。排除标准包括:①累及肾外其它器官;②研究前4周有感染的临床表现或检验依据;③糖尿病人群。共纳入92例研究对象,年龄(32±12)岁,其中LD组56例,LD+LN组36例。30例LN患者进行了经皮肾穿刺活检,根据WHO分型方法,IV型21例,III型6例,V型2例,IV+V型1例。
标本使用符合赫尔辛基宣言和医学伦理,并征得了研究对象的知情同意。
1.2临床指标 按照美国风湿病学会标准判断SLE分类标准的临床表现和血液学指标[8]。根据本单位实验室指标,定义补体C3<0.8 g/L为低补体血症。根据EPI公式估算肾小球滤过率(eGFR)反映肾功能[9]。
1.3血清AOPP检测 收集患者血清用于AOPP检测。简要步骤为:将200 μL血样或氯胺-T(Sigma,用于标准曲线)加入96孔板(Corning Costar,New York,NY),血清混合20 μL乙酸,氯胺-T混合30 μL碘化钾:乙酸反应液(1∶2体积比),立刻检测340 nm吸光度值(ThermoMultiskan MK3,Finland)。设3个复孔,加样后3 min内能完成检测[10]。
1.4统计学方法 SPSS 13.0进行统计分析。两组间比较采用两独立样本t检验,两变量的相关性采用Pearson相关性分析。用多变量Logistic回归模型分析合并肾炎的危险因素,用优势比(OR值)及其95%可信区间评价危险因素和危险性之间的相关性强度。定义双侧P<0.05为差别具有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1两组间的一般情况 两组间年龄、性别、临床症状与体征(包括关节炎、口腔溃疡及浆膜腔积液)没有统计学差别。与LD组相比,LD+LN患者dsDNA和血清AOPP水平更高,补体C3水平无显著性差异(表1)。
2.2LD+LN患者高AOPP亚组和低AOPP亚组各项指标比较 根据AOPP中位数84.5 μmol/L将LD+ LN患者分为高AOPP亚组和低AOPP亚组。两亚组间比较,高AOPP亚组dsDNA和蛋白尿水平更高,eGFR和补体C3水平更低(表2)。血清AOPP和蛋白尿水平具有相关性(r=0.336,P=0.008)(图1),与eGFR负相关(r=-0.412,P<0.001)(图2)。
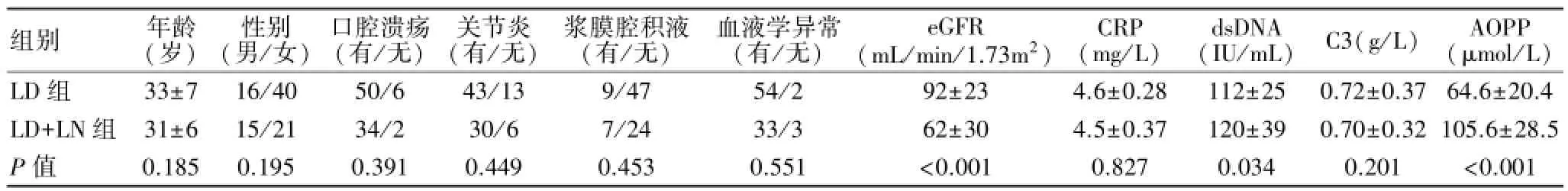
表1 LD组与LD+LN组一般情况及血清检测指标比较
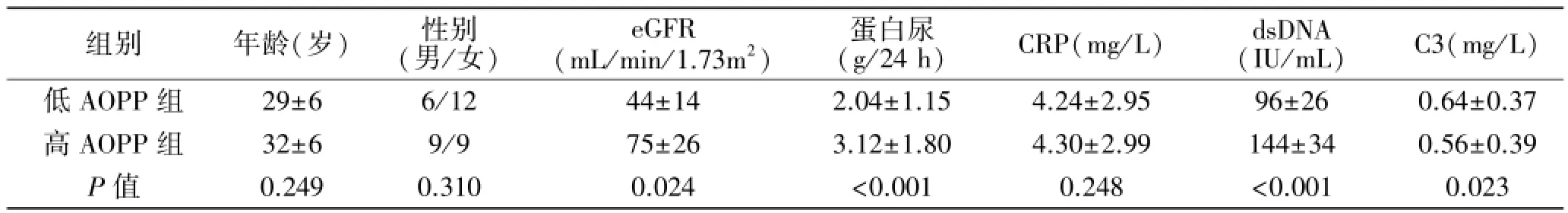
表2 LD+LN患者不同AOPP亚组间一般情况及血清检测比较
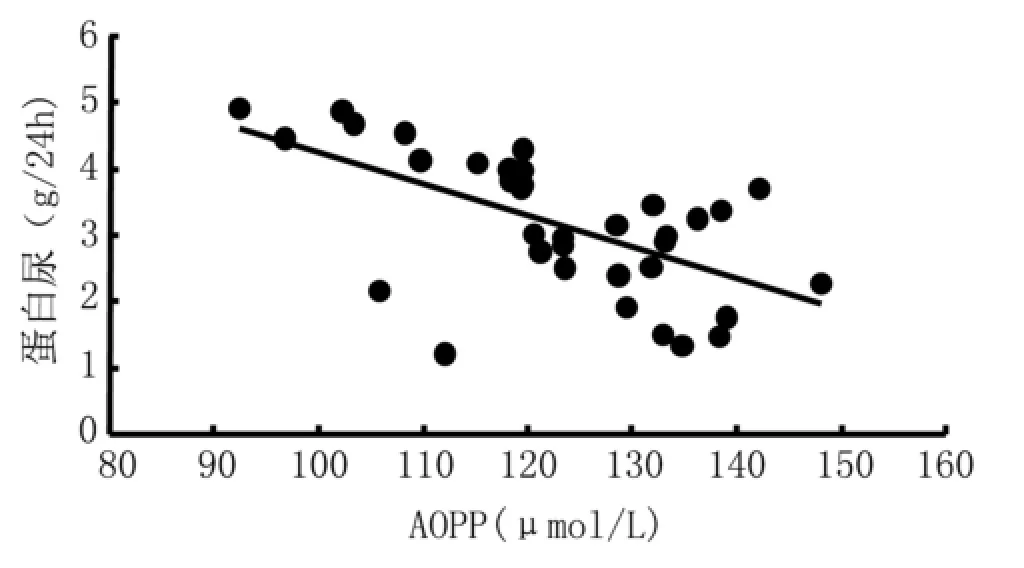
图1 LD+LN组患者血清AOPP和蛋白尿水平的相关性

图2 LD+LN组患者血清AOPP和dsDNA水平的相关性
2.3AOPP和狼疮性肾炎发生的相关性 将抗dsDNA水平(10 IU/mL为增加单位)、补体C3(100 mg/L为下降单位)和AOPP(10 μmol/L为增加单位)纳入多变量二分类Logistic回归模型进行分析,结果显示对于以LD为首发表现的系统性红斑狼疮患者,AOPP每增加10 μmol/L,发生LN的危险增加24%(95%可信区间1.166~1.915,P=0.001);抗dsDNA水平升高以及补体C3下降都不是LN发生的独立危险因素。
3 讨论
中性粒细胞介导的氧化应激是狼疮性肾炎发生的重要机制[11]。AOPP是中性粒细胞内髓过氧化物酶产生的氧化应激产物[12],是慢性肾脏病发生和进展的重要损伤分子[13-15]。AOPP的主要成分为具有双酪氨酸结构的氧化白蛋白。利用双酪氨酸结构在340 nm具有特殊吸光度的特点,Witko等于1996年开发了用分光光度法检测血浆AOPP的方法[16]。由于其简便经济,近年得到了广泛使用,被作为一种反映炎症相关氧化应激的生物学标志物[16]。近年发现,血浆中纤维蛋白原成分不具有AOPP的生物学特性,用血清作为检测样本能更好地应用于临床[10]。
利用以LD为首发表现的SLE患者血清,本文实验观察到LD+LN患者AOPP水平较LD组更高;AOPP和反映LN病情的蛋白尿、eGFR、补体C3及抗dsDNA抗体具有相关性;在92例对象中,AOPP水平升高是合并LN的独立危险因素。这些初步结果说明AOPP可能和LN发生有关,可能具有早期预测LN的作用。
AOPP可能受多种因素干扰。糖尿病和潜在的感染可能导致AOPP水平的升高[17],因此我们入选病例时排除了这部分对象。本文入选的对象为以LD为首发的SLE患者,区分是否合并LN的依据是6个月的随访数据,不排除LD组含有部分迟发LN患者。另外,本研究的样本数较小,无法进一步对皮损类型和LN类型进行亚组分析。因此,本研究的结果还有待更大样本和更长时间的研究来进行验证。
[1]Okon LG,Werth VP.Cutaneous lupus erythematosus:diagnosis and treatment[J].Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol,2013,27(3):391-404.
[2]Descamps-Latscha B,Witko-Sarsat V,Nguyen-Khoa T,et al.Early prediction of IgA nephropathy progression:proteinuria and AOPP are strong prognostic markers[J].Kidney Int,2004,66(4):1606-1612.
[3]Yazici C,Kose K,Calis M,et al.Increased advanced oxidation protein products in Behcet's disease:a new activity marker[J].Br J Dermatol,2004,151(1):105-111.
[4]Li HY,Hou FF,Zhang X,et al.Advanced oxidation protein products accelerate renal fibrosis in a remnant kidney model [J].J Am Soc Nephrol,2007,18(2):528-538.
[5]Servettaz A,Guilpain P,Goulvestre C,et al.Radical oxygen species production induced by advanced oxidation protein products predicts clinical evolution and response to treatment in systemic sclerosis[J].Ann Rheum Dis,2007,66(9):1202-1209.
[6]Lozovoy MA,Simao AN,Panis C,et al.Oxidative stress is associated with liver damage,inflammatory status,and corticosteroid therapy in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus[J].Lupus,2011,20(12):1250-1259.
[7]Hanasand M,Omdal R,Norheim KB,et al.Improved detection of advanced oxidation protein products in plasma[J]. Clin Chim Acta,2012,413(9-10):901-906.
[8]Hochberg MC.Updating the american college of rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus[J].Arthritis Rheum,1997,40(9):1725.
[9]Levey AS,Stevens LA,Schmid CH,et al.A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate[J].Ann Intern Med,2009,150(9):604-612.
[10]Chen YH,Shi W,Liang XL,et al.Effect of blood sample type on the measurement of advanced oxidation protein products as a biomarker of inflammation and oxidative stress in hemodialysis patients[J].Biomarkers,2011,16(2):129-135.
[11]Knight JS,Kaplan MJ.Lupus neutrophils:'NET'gain in understanding lupus pathogenesis[J].Curr Opin Rheumatol,2012,24(5):441-450.
[12]Capeillere-Blandin C,Gausson V,Nguyen AT,et al.Respective role of uraemic toxins and myeloperoxidase in the uraemic state[J].Nephrol Dial Transplant,2006,21(6):1555-1563.
[13]Shi XY,Hou FF,Niu HX,et al.Advanced oxidation protein products promote inflammation in diabetic kidney through activation of renal nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase[J].Endocrinology,2008,149(4):1829-1839.
[14]Zhou LL,Hou FF,Wang GB,et al.Accumulation of advanced oxidation protein products induces podocyte apoptosis and deletion through NADPH-dependent mechanisms [J].Kidney Int,2009,76(11):1148-1160.
[15]Cao W,Xu J,Zhou ZM,et al.Advanced oxidation protein products activate intrarenal renin-angiotensin system via a CD36-mediated,redox-dependent pathway[J].Antioxid Redox Signal,2013,18(1):19-35.
[16]Witko-Sarsat V,Friedlander M,Capeillere-Blandin C,et al.Advanced oxidation protein products as a novel marker of oxidative stress in uremia[J].Kidney Int,1996,49(5):1304-1313.
[17]Kalousova M,Skrha J,Zima T.Advanced glycation endproducts and advanced oxidation protein products in patients with diabetes mellitus[J].Physiol Res,2002,51(6):597-604.
(收稿:2015-12-22 修回:2016-03-12)
Relationship between advanced oxidation protein products and lupus nephritis
XIE Zhen1,CHEN Yuanhan2,WANG Youwei1,WAN Huiying1,LIU Yangying1,ZHOU Min1.
1.Department of Dermatology,Sichuan Academy of Medical Sciences&Sichuan Provincial People's Hospital,Chengdu 610000,China;2.Department of Nephrology,Guangdong General Hospital,Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences,Guangzhou 510080,China
Corresponding author:CHEN Yuanhan,E-mail:johnchen76@126.com
Objective:To determine the relationship between advanced oxidation protein products (AOPP)and lupus nephritis(LN).Methods:The level of AOPP in 36 patients with lupus dermatitis(LD)complicated with LN and 56 LD patients without LN were detected and the relationship between AOPP and LN was analyzed.Results:The level of AOPP in LD accompanied with LN patients was(105.6±28.5)μmol/L,which was higher than that in the patients with LD but without LN(64.6±20.4 μmol/L).The level of ds-DNA and urine protein in the patients with high level AOPP(>84.5 μmol/L)was higher than those in the patients with low level of AOPP,and the level of eGFR and complement C3 was lower than those in the patients with low level of AOPP.In multivariable logistic regression model,AOPP level was an independent risk factor for lupus nephritis and the renal risk would increase by 24%,as every 10 μmol/L of AOPP was increased(95%CI 1.166-1.915).Conclusion:AOPP is associated with the onset of LN and may be a potential biomarker for LN.
advanced oxidation protein products;lupus nephritis;lupus dermatitis
陈源汉,E-mail:johnchen76@126.com
1四川省医学科学院四川省人民医院皮肤病性病研究所,四川成都,610000
2广东省医学科学院广东省人民医院肾内科,广东广州,510080

