边界条件对旋转薄壁圆柱壳结构自由振动行波特性的影响分析
李文达 杜敬涛 杨铁军 刘志刚


摘要: 建立了弹性约束边界下旋转薄壁圆柱壳结构自由振动行波特性分析模型,通过在边界引入四种约束弹簧,任意边界条件可以通过设置刚度系数而统一得到。基于Sanders薄壳理论对旋转薄壁圆柱壳自由振动的振动能量表达式进行了推导,三个方向的振动位移场通过一种改进傅立叶级数进行展开,带入能量表达式并利用RayleighRitz法进行变换推导,得到旋转薄壁圆柱壳自由振动的系统特征方程。利用MATLAB编程计算,得到行波振动固有频率,通过与现有文献中其他方法比较,验证了本文方法的正确性,随后采用不同几何参数、不同边界条件、不同约束弹簧刚度的算例对振动特性的影响进行分析, 揭示了转速、长径比、厚径比等几何条件以及边界约束弹簧刚度对旋转薄壁圆柱壳自由振动行波特性的影响规律。关键词: 旋转薄壁圆柱壳; 自由振动; 行波特性; 边界约束; 固有频率
中图分类号: O327 文献标志码: A文章编号: 1004-4523(2016)03-0452-13
DOI:10.16385/j.cnki.issn.10044523.2016.03.011
引言
圆柱壳作为一种基本的结构单元,广泛应用于各个工程领域,如航空航天、动力工程及船舶与海洋工程等,圆柱壳的振动特性及动力学响应受到国内外学者的广泛关注,然而,现有的研究主要针对非旋转情况,对于旋转圆柱壳结构的研究尚不充分。
关于旋转圆柱壳振动特性的研究最早可追溯到1890年,Bryan[1]首次对旋转圆柱壳的固有特性进行了研究,并提出行波振动现象。这一发现引起了研究者的极大兴趣,在此基础上,后续学者通过研究了解到圆柱壳体变形速度方向与壳体转动角速度方向会导致科氏力(Coriolis Force)。随后,Taranto和Lessen[2]研究了科氏力对旋转圆柱壳振动特性的影响,得出了旋转圆柱壳体振动分析中必须考虑科氏力影响的结论。 Srinivasan和Lauterbach[3]研究了无限长旋转薄壁圆柱壳的固有特性, 讨论了科氏力和离心力对前后行波波速的影响规律。Zohar和 Aboudi[4],Wang和Chen[5]则针对有限长旋转圆柱壳进行了相应的动力学研究。近几年,刘彦琦等人[67]基于Love壳体理论研究了不同边界和几何参数对旋转薄壁圆柱壳振动特性的影响,然而并未对前、后行波特性进行分析。韩清凯等[8]对旋转薄壁圆柱壳的高节径振动特性以及篦齿结构的影响进行了分析。项松等[9]则基于Love理论给出了旋转功能梯度圆柱壳的固有频率计算方法。项爽[10]对旋转功能梯度材料圆柱壳的振动特性进行了研究。
目前,国内外已有大量关于旋转圆柱壳动力学特性的研究文献,然而对具有除简支简支边界以外其他复杂边界条件的旋转薄壁圆柱壳动力学特性的研究还比较少见。对于不同边界条件下的旋转圆柱壳,可以采用不同的分析方法对其振动特性进行分析。Saito和Endo[11]应用三角函数和Galerkin法求得了两端固支条件下的旋转圆柱壳振动固有频率;Penzes和 Kraus[12]利用复指数函数研究了具有不同边界条件的旋转圆柱壳的固有特性;Lam和 Loy[1314]对比了分别采用Donnell,Flügge,Love,Sanders四种壳体理论的两端简支边界条件下旋转圆柱壳的前、后行波特性,并将广义微分求积法(Generalized Differential Quadrature Method)引入到旋转圆柱壳的振动分析中来,在考虑离心力、科氏力和初始张力的情况下分析了转速、厚径比等因素对两端简支(SS)、两端固支(CC)、一端固支一端简支(CS)、一端固支一端自由(CF)四种边界条件下的圆柱壳固有频率的影响。Li等[15]综合分析了旋转薄壁、厚壁圆柱壳、圆锥壳的振动固有特性。
第3期李文达,等: 边界条件对旋转薄壁圆柱壳结构自由振动行波特性的影响分析振 动 工 程 学 报第29卷除上述经典的解析方法外,传递矩阵法和有限元法在壳体动力学分析中也大量应用。洪杰等[1617]通过传递矩阵法离散求解了转动薄壁壳体的行波振动频率,并采用瞬态激振方法对壳体进行了振动测试,验证了理论分析结果。曹航和朱梓根[18]通过扩展商用有限元软件的分析功能,实现了对转动壳体行波振动的分析。Chen和Zhao[19]等人采用有限元法对高速旋转圆柱壳的固有特性进行了研究。Padovan[20]利用有限元法研究了旋转圆柱壳的行波振动特性。Guo,Zheng和Chu[21]利用有限元法分析了旋转圆柱壳的振动特性, 比较了大挠度变形、边界条件和旋转速度对旋转圆柱壳的固有频率和模态的影响。
本文首次采用一种改进傅立叶级数方法和RayleighRitz法对旋转薄壁圆柱壳行波振动特性及边界约束影响进行分析研究,计算得到不同几何参数、不同边界条件、不同约束弹簧刚度情况下行波振动固有频率,并就上述因素对振动特性的影响进行了分析。
3结论
本文采用一种改进傅立叶级数和RayleighRitz法相结合,对旋转薄壁圆柱壳行波特性进行了分析,研究了边界约束弹簧对转动薄壁圆柱壳行波频率的影响,得到如下结论:
(1)本文采用一种改进傅立叶级数对旋转薄壁圆柱壳结构三个方向上的位移函数进行展开,基于Sanders薄壳理论的能量原理,结合RayleighRitz方法,建立了旋转薄壁圆柱壳结构自由振动行波特性分析模型,数值结果表明本文模型有效可行,能够快速收敛,并具有良好的精确性。
(2)旋转薄壁圆柱壳的行波无量纲频率参数ωf′和ωb′随着环向波数n的增大呈现先下降后上升的趋势;随着转速Ω′的增大而升高;随着厚径比H/R的增大而升高;随着长径比L/R的增大先下降,当长径比足够大后,行波无量纲频率趋于稳定值。
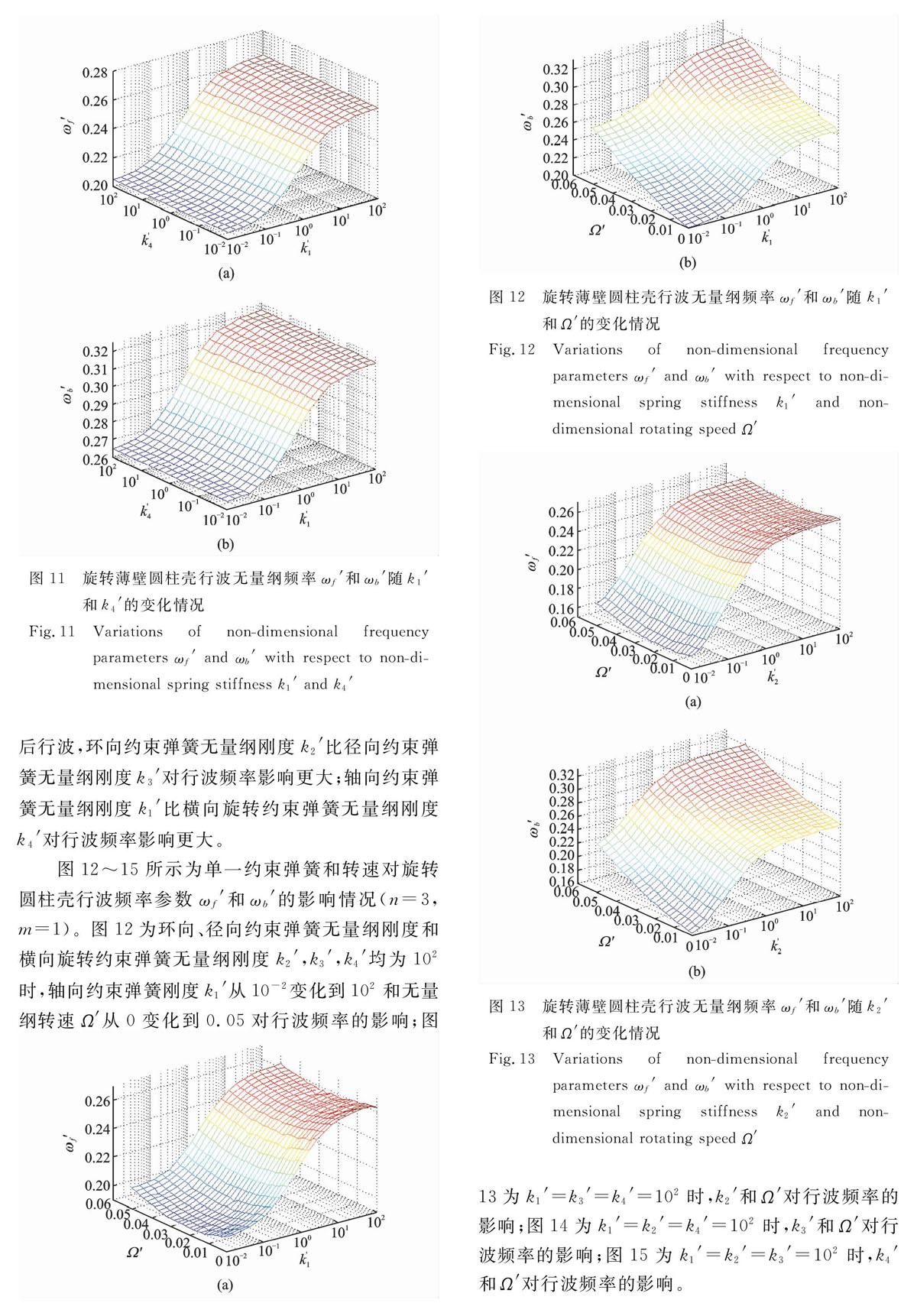
(3)当旋转薄壁圆柱壳一端固定,另一端只存在一种弹簧约束时,随着轴向约束弹簧k1′、环向约束弹簧k2′、径向约束弹簧k3′无量纲刚度的增大,前、后行波频率ωf和ωb均在刚度为10-2~102范围内大幅度上升,后趋于稳定,但横向旋转弹簧k4′对行波频率影响不大。
(4)对于旋转薄壁圆柱壳的前、后行波频率参数ωf′和ωb′,环向约束弹簧刚度k2′比径向约束弹簧刚度k3′对其影响更大,轴向约束弹簧刚度k1′比横向旋转约束弹簧刚度k4′对其影响更大,即轴向和环向约束弹簧比径向约束弹簧和横向旋转弹簧对转动薄壁圆柱壳动力学特性的影响更大。
(5) 在每一种边界约束变量设置下,当旋转薄壁圆柱壳的无量纲转速为某一固定值时,前、后行波无量纲频率参数ωf′和ωb′变化趋势相同且随转速的增大变化不大,这说明转速的改变对转动薄壁圆柱壳行波频率随边界约束弹簧刚度的变化作用不大。
参考文献:
[1]Bryan G H. On the beats in the vibration of a revolving cylinder on bell [J]. Proceeding of the Cambridge Philosophical Society, 1890, 7:101—111.
[2]Di Taranto R A, Lessen M. Coriolis acceleration effect on the vibration of a rotating thinwalled circular cylinder [J]. ASME Journal of Applied Mechanics, 1964, 31:700—701.
[3]Srinivasan A V, Lauterbach G F. Traveling waves in rotating cylindrical shells [J]. Journal of Engineering for Industry, 1971, 93:1229—1232.
[4]Zohar A, Aboudi J. The free vibrations of a thin circular finite rotating cylinder [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 1973, 15:269—278.
[5]Wang S S, Chen Y. Effects of rotation on vibrations of circular cylindrical shells [J]. Journal of the Acoustical Aociety of America, 1974, 55: 1340—1342.
[6]刘彦琦,褚福磊. 几何参数对旋转薄壁圆柱壳振动特性的影响[J]. 振动与冲击, 2012, 13:22—25.
Liu Yanqi, Chu Fulei. The effects of geometric parameters on the vibration characteristics of thin rotating cylindrical shells [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2012, 13:22—25.
[7]刘彦琦,秦朝烨,褚福磊. 不同边界条件下旋转薄壁圆柱壳的振动特性[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 01:5—9.
Liu Yanqi, Qin Zhaoye, Chu Fulei. The vibration characteristics of thin rotating cylindrical shells under various boundary conditions [J]. Journal of Tsinghua University (Natural Science), 2012, 01:5—9.
[8]韩清凯,王宇,李学军. 旋转薄壁圆柱壳的高节径振动特性以及篦齿结构的影响[J]. 中国科学:物理学 力学 天文学, 2013, 04:436-458.
Han Qingkai, Wang Yu, Li Xuejun. High nodal diameter vibration characteristics of rotating thin cylindrical shell and the influence of labyrinth structure [J]. Chinese Science: Physics, Mechanics and Astronomy, 2013, 04:436—458.
[9]项松,李广超,张魏,等. 旋转功能梯度圆柱壳的固有频率计算[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2012, 03:332—341.
Xiang Song, Li Guangchao, Zhang Wei, et al. Calculation of natural frequency of rotating functionally graded cylindrical shell [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2012, 03: 332—341.
[10]项爽. 旋转功能梯度材料圆柱壳的振动特性研究[D]. 郑州:河南科技大学, 2013.
Xiang Shuang. Study on vibration characteristics of rotating cylindrical shell with functionally graded materials [D]. Zhengzhou: University of Science and Technology of He′nan, 2013.
[11]Saito T, Endo M. Vibration of finite length, rotating cylindrical shells [J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 1986, 107:17—28.
[12]Penzes L E, Kraus H. Free vibrations of prestressed cylindrical shells having arbitrary homogeneous boundary conditions [J]. AIAA, 1972, 10: 1309—1313.
[13] Lam K Y, Loy C T. Analysis of rotating laminated cylindrical shells by different thin shell theories [J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 1995, 186(1): 23—35.
[14] Lam K Y, Loy C T. Influence of boundary conditions for a thin laminated rotating cylindrical shell [J]. Comp. Struct., 1998, 41: 215—228.
[15]Li H, Lam K Y, Ng T Y. Rotating Shell Dynamics [M]. Oxford: Elsevier, 2005.
[16]洪杰, 郭宝亭, 朱梓根. 高速转动壳体行波振动实验研究[J]. 航空动力学报, 1998, 13(4):390—458.
Hong Jie, Guo Baoting, Zhu Zigen. Experimental study on traveling wave vibration of high speed rotating shell [J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 1998, 13(4):390—458.
[17]洪杰, 郭宝亭, 朱梓根. 高速旋转薄壁壳体的行波振动理论与实验研究[J]. 航空发动机, 1999, (1): 40—44.
Hong Jie, Guo Baoting, Zhu Zigen. Traveling wave vibration theory and experimental research of high speed rotating thin shell [J]. Aeroengine, 1999, (1):40—44.
[18]曹航,朱梓根. 转动壳体行波振动的有限元分析方法[J]. 航空动力学报, 2002, 17(2): 222—225.
Cao Hang, Zhu Zigen.The finite element analysis method of traveling wave vibration of rotating shells [J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2002, 17(2): 222—225.
[19]Chen Y, Zhao H B, Shen Z P, et al. Vibrations of high speed rotating shells with calculations for cylindrical shells [J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 1993, 160:137—160.
[20]Padovan J. Traveling waves vibrations and buckling of rotating anisotropic shells of revolution by finite elements [J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 1975, 11: 1367—1380.
[21]Guo D, Zheng Z C, Chu F L. Vibration analysis of spinning cylindrical shells by finite element method [J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2002, 39:725—739.
[22]Soedel W. Vibrations of shells and plates [J]. Marcell Dekker, 1992:1—361.
[23]曹志远. 板壳振动理论[M]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社,1989:263—462.
Cao Zhiyuan. The Shell Vibration Theory [M]. Beijing: Chinese Railway Press, 1989:263—462.
[24]Liew K M, Ng T Y, Zhao X, et al. Harmonic reproducing kernel particle method for free vibration analysis of rotating cylindrical shells [J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2002, 191:4141—4157.
[25]孙述鹏. 转动薄壁圆柱壳的动力学特性研究[D]. 哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学,2013.
Sun Shupeng. Study on the dynamic characteristics of rotating thin cylindrical shell [D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2013.
[26]Li W L. Free vibrations of beams with general boundary conditions [J]. Sound Vib., 2000,237(4), 709—725.
[27]Li W L. Dynamic analysis of beams with arbitrary elastic supports at both ends [J]. Sound Vib., 2001, 246(4), 751—756.
[28] Li W L. Vibration analysis of rectangular plates with general elastic boundary supports [J]. Sound Vib., 2004, 273, 619—635.
[29]Loveday P W, Rogers C A. Free vibration of elastically supported thin cylinders including gyroscopic effects[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 1998, 217(3): 547—562.
[30]Li W L. Vibrations of circular cylindrical shells with general elastic boundary restraints[J]. Journal of Vibration and Acoustics, 2013, (135)2,024501.

