基于LMI的广域时延多机电力系统的控制与稳定性研究
关琳燕,周 洪,胡文山
(武汉大学动力与机械学院,湖北 武汉 430072)
基于LMI的广域时延多机电力系统的控制与稳定性研究
关琳燕,周 洪,胡文山
(武汉大学动力与机械学院,湖北 武汉 430072)
广域信号通信时延是导致控制器性能下降甚至失效的重要原因之一。针对时滞电力系统的特性,对多机电力系统转子运动方程进行合理的线性化和偏差化,建立时滞线性多机电力系统。通过构造合适的 Lyapunov函数导出了基于自由权矩阵的线性矩阵不等式(LMI)理论的广域时延系统稳定性判据,并设计了相应的全状态反馈控制器。与基于二次线性最优的控制方法相比,保守性更小,控制效果有所提高。通过IEEE3机9节点电力系统模型验证了该控制器的有效性。仿真试验结果表明该控制方法能较好地减小时延带来的不利影响。
广域测量系统;全状态反馈;时延;线性矩阵不等式;稳定性
0 引言
电网规模的扩大及其容量的增加提高了电网运行的经济性,但同时也使得电网运行工况更为复杂。仅依赖局部反馈信息的控制方法对于确保大规模互联电网安全稳定运行的局限性日益突显[1-4]。基于同步相量测量和现代通信广域测量系统(WAMS)的出现为广域控制带来了新的契机[5-7]。WAMS可以反馈系统在同一参考时间下的不同位置的实时信息,提供高精度、高可信度的广域实时信号,有助于从整体层面对机组进行控制[8-9]。
然而广域信号赖以传输的通信系统不可避免地存在时延。以全状态反馈线性最优控制为例,对无时延的理想多机电力系统进行偏差化后,利用Riccati方程得到的全状态反馈的二次型线性最优反馈控制器虽然有良好的控制效果,但对存在时延的实际互联电网控制效果欠佳,甚至导致系统大幅振荡。延迟往往是系统不稳定的根源之一。通信延迟将导致控制器性能变差,甚至失效,从而引起系统运行失稳[10-14]。因此研究时滞对电力系统稳定性的影响十分必要[15-17]。
求解 Riccati方程是早期处理时间域中参数不确定系统的鲁棒性分析和综合问题的主要方法。由于缺乏确定待定参数最优值的方法,人为地确定参数使得这种方法存在一定的保守性。此外,Riccati方程对于复杂的系统(如随机系统、时滞系统等)无通用可行的求解方法[18]。20世纪90年代,线性矩阵不等式(LMI)处理方法再次受到广泛关注,并被应用于控制领域。许多控制问题可以转化为线性矩阵不等式的可行性问题,并通过凸优化问题的内点法得到有效解决[19-22]。通过构造合适的Lyapunov泛函数并适当引入自由权矩阵使得到的判据有更小的保守性[23-25]。本项研究工作基于 Lyapunov稳定性理论,采用线性矩阵不等式这一有效工具,提出线性时滞系统分析和综合的方法与结果,并通过3机9节点系统验证其控制效果及保守性。
1 考虑时延的广域电力系统线性模型
本地反馈信号的局域控制中,时延通常可以不予以考虑。但在电力系统的广域控制中,由于时延可高达数十乃到数百毫秒,对控制效果造成的影响不可忽略[26-27]。WAMS中,信号由底层的PMU传输至数据处理中心的过程中,时滞产生的相关因素主要有传感器延迟、信号处理时间、数据封闭时间以及通信网络的传输时间[28-29]。电力系统的广域反馈信号时延d可用式(1)表示。
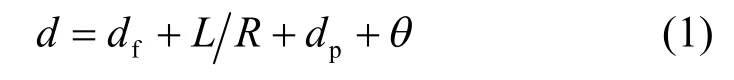
式(1)描述了总通信延迟d的来源。df是数据采集、处理、转换带来的延时,L是传输的数据量,R是网络基本传输速率。在一定的网络结构和测量技术下, df和LR值可以确定,是恒定延时。 dp是信号在网络中传递的延时,其值取决于网络的传输介质及传输距离。是随机时延,和 dp都是变化时延。
n台机组的多机电力系统的转子运动方程线性化、偏差化后有全状态量反馈的转子运动方程式
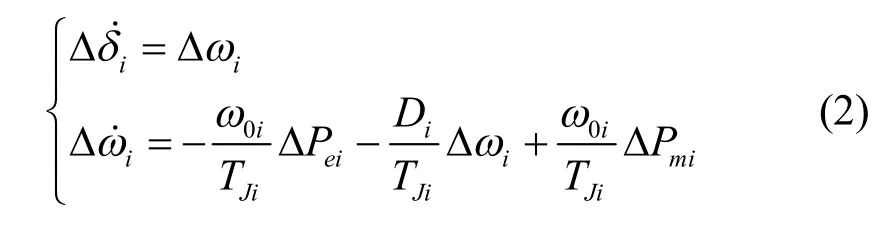
其中,线性化后的第i台机组的发电机输出电磁功率偏差为


其中:

本文的目的是设计增益矩阵K使时延的多机电力系统(4)稳定。
2 基于LMI的状态反馈控制器设计
为了导出系统(4)稳定的条件,以下引用一个引理。
1) S<0;
即可通过条件2)、3)判断矩阵S负定。
定理 存在适当维数的对称矩阵X, Y, Q, Z及标量d,满足以下矩阵不等式
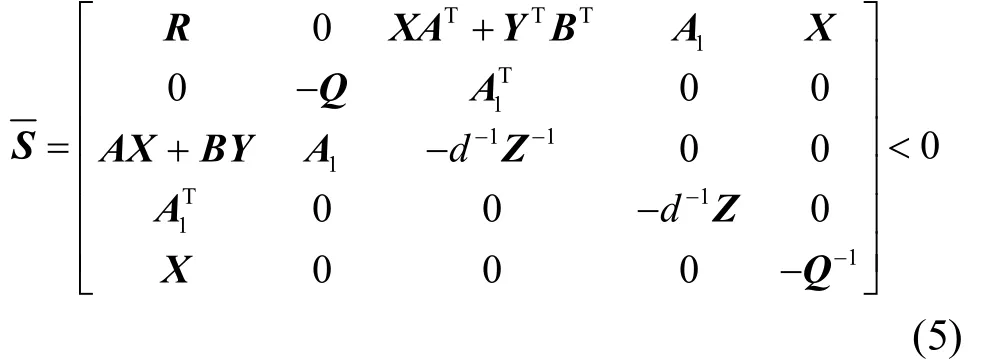
证明:定义如下Lyapunov函数
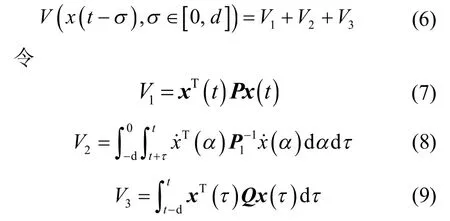
对V求导,有

线性不等式(10)中
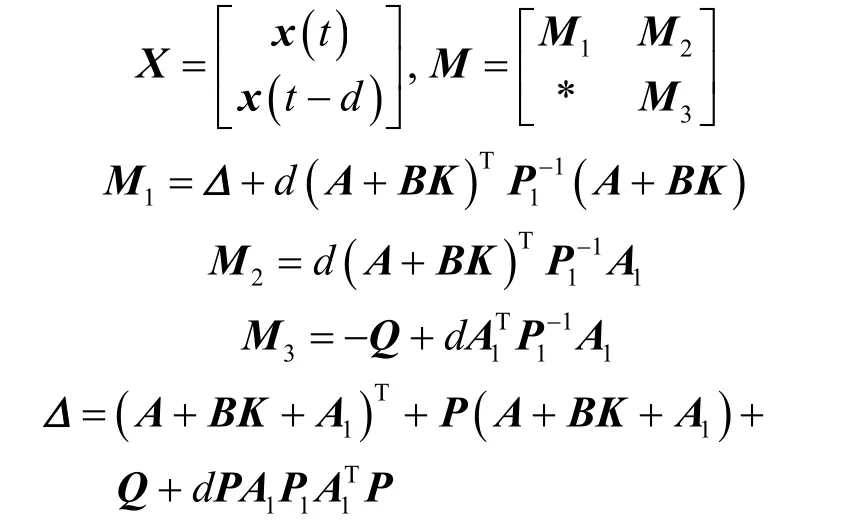
要使式(10)成立,则

则式(10)可写为
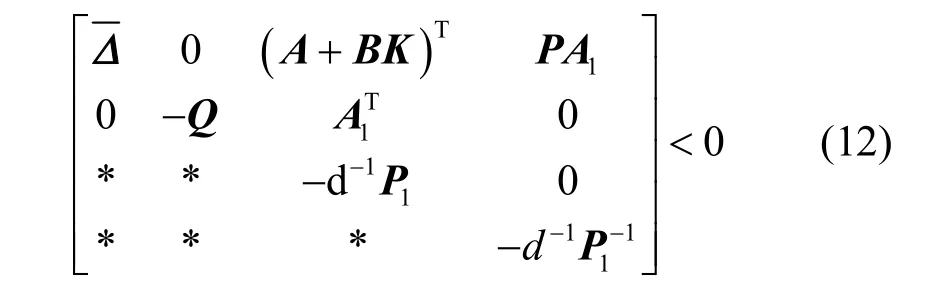

系统(4)稳定的问题转换成在式(13)、式(14)的条件下使) 取得最小值的问题。具体算法如下:
1) 首先找到满足式(13)、式(14)中3个矩阵不等式的所有未知矩阵变量的一个可行解,令迭代次数 k = 0。
3) 验证所求出的最优解是否满足(5),若满足,则得解。若不满足,检查k是否达到规定的迭代次数,如果达到,则系统无解;否则,令转到步骤2)继续执行程序。
引理 2 二次线性最优反馈控制求解控制向量的方法步骤如下。
1) 规定二次型性能指标为
3 算例分析
利用IEEE标准的3机9节点系统(图1)模型来验证本文控制方法的有效性。图2中给出广域时延系统仿真框图。
系统初始稳态运行时,有:

0 s时刻2号机组转速出现0.5%的扰动,有w2= 0.995。
三组发电机均配有一个控制器,根据引理2可求得增益矩阵:
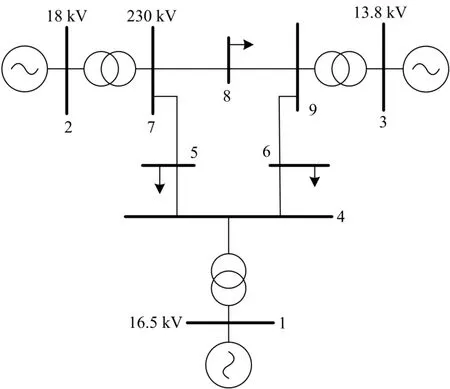
图1 IEEE 3机9节点系统Fig. 1 IEEE 3-machine 9-bus system

图2 广域时延系统仿真框图Fig. 2 Simulation block diagram of the wide-area time-delay system

图3给出8个不同时延下线性最优控制和基于LMI的控制方法功角差和角速度差仿真效果对比。由图3(a)~3(c)可以看出,在1~3.2 s的时延下两种控制方法都可以使系统稳定。但是,基于LMI的控制方法显然更优于线性最优控制的方法,其功角差控制曲线稳定时幅值为后者的一半,角速度差控制曲线也更快稳定。图3(d)表明,在3.4 s时延下,二次线性最优控制得到的曲线已经开始出现大幅振荡。图3(f)中,时延增大至4.1 s,二次线性最优控制得到的曲线振荡加剧,虽然有收敛的趋势,但效果很不理想。图3(g)中,二次线性最优控制的曲线呈等幅振荡。时延增至4.4 s时,如图3(h)所示,二次线性最优控制已经不能使系统稳定了。仿真结果比较如表1。


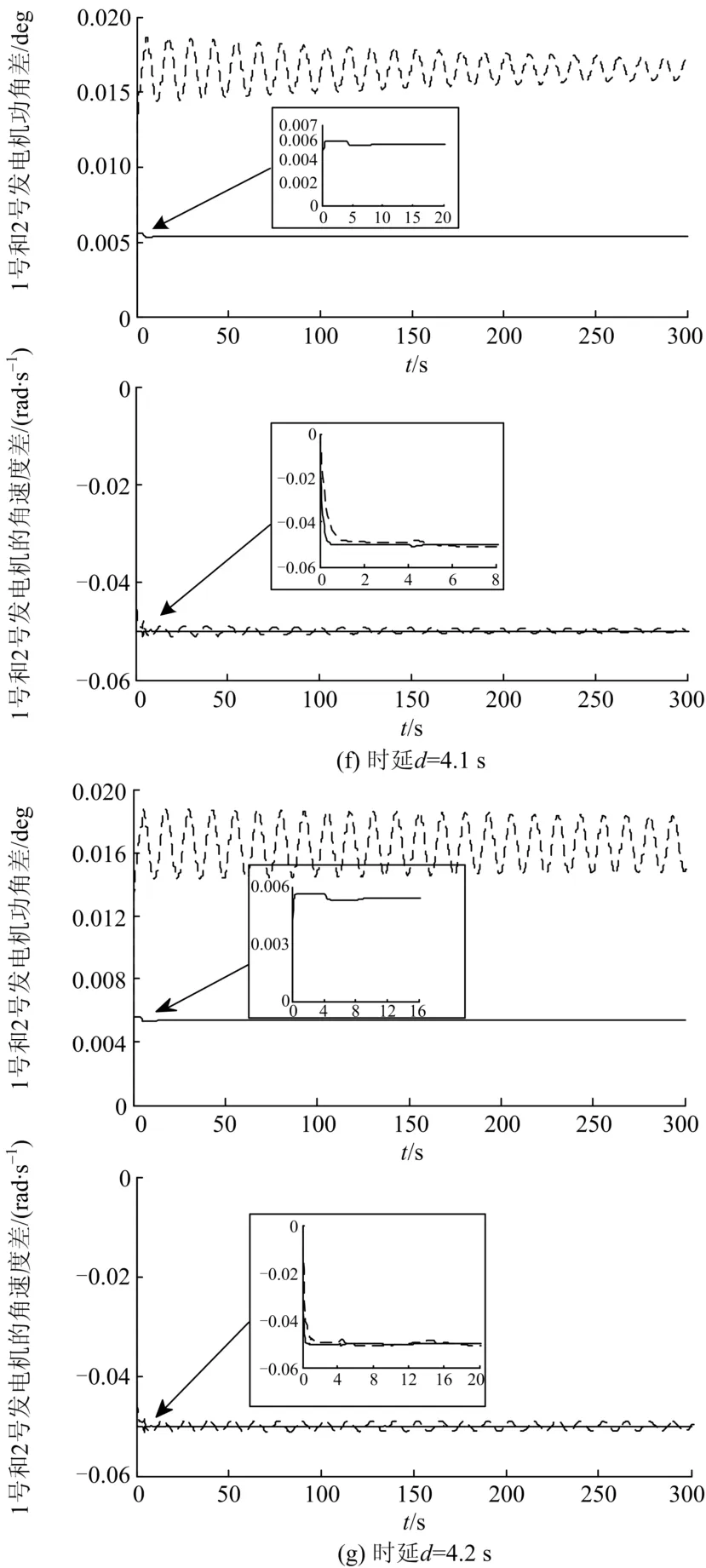

图3 各时延下两种控制方法对系统的控制效果比较Fig. 3 Comparison of performance of the two kinds of control methods with several time delays
时延是引起广域系统不稳定,控制器性能下降的重要原因之一。仿真结果说明,二次线性最优控制的方法不适合存在时延的广域系统。二次线性最优控制方法对于时滞独立系统有良好的控制效果,对非常小的时延有一定的控制作用,但是控制效果有限。二次线性最优控制方法在时滞依赖系统中,得到的控制曲线调节长,稳态误差大,控制效果并不理想。时延增大后,二次线性最优控制曲线振荡次数陡增,调节时间过长,根本无法起到控制作用。基于 LMI的控制方式能有效消除广域系统中时延带来的危害,及时稳定系统。基于LMI的控制方式相比于最优线性控制方式的控制曲线不仅超调量小,而且调节时间短,对于较大的时延有良好的调节效果。系统时滞独立的条件严苛,不考虑时滞的情况是相当保守的。引入自由权矩阵的 Lyapunov泛函方法保守性低,充分考虑了时延带来的不利影响。
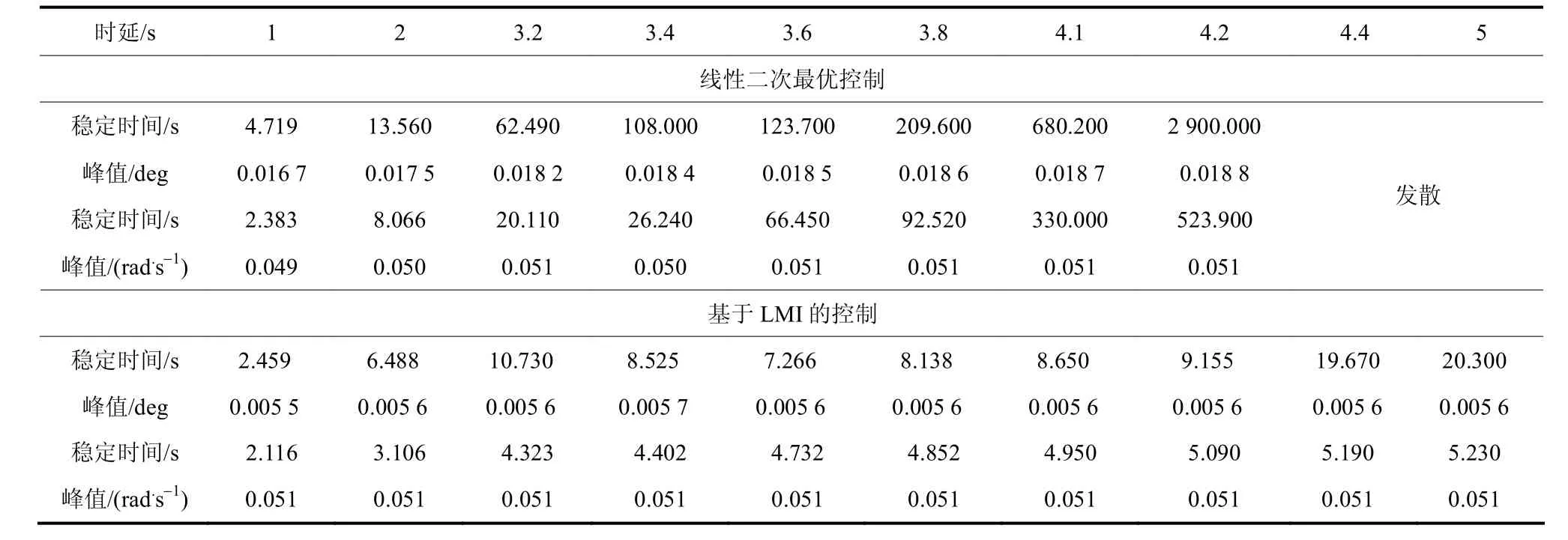
表1 两种控制方法对功角差及角速度差的控制仿真结果比较Table 1 Comparison of the simulation results of the two kinds of control methods for the differences of power angle and angle velocity
4 结束语
大规模互联电网的信息传送延迟是电网不稳定的一个重要诱因。与Riccati方程处理方法相比,LMI处理方法保守性更低,普适性更强。采用LMI方法设计的时滞电力系统状态反馈控制器能够有效地消减时滞给电网带来的负面影响。3机9节点系统的仿真验证了所设计的控制器的有效性。
[1] 程云峰, 张欣然, 陆超, 等. 广域测量技术在电力系统中的应用研究进展[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2014, 42(4): 145-153. CHENG Yunfeng, ZHANG Xinran, LU Chao. Research progress of the application of wide area measurement technology in power system[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2014, 42(4): 145-153.
[2] KAHROBAEIAN A, IBRAHIM MOHAMED Y A R. Networked-based hybrid distributed power sharing and control for islanded microgrid systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2015, 30(2): 603-617.
[3] 姚致清, 于飞, 赵倩, 等. 基于模块化多电平换流器的大型光伏并网系统仿真研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2013, 33(36): 27-33. YAO Zhiqing, YU Fei, ZHAO Qian, et al. Simulation research on large-scale PV grid-connected systems based on MMC[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2013, 33(36): 27-33.
[4] 姚致清, 赵倩, 刘喜梅, 等. 基于准同步原理的逆变器并网技术研究[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2011, 39(24): 123-126, 131. YAO Zhiqing, ZHAO Qian, LIU Ximei, et al. Research on grid-connected technology of inverter based on quasi synchronous principle[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2011, 39(24): 123-126, 131.
[5] BOBBA R B, DAGLE J, HEINE E, et al. Enhancing grid measurements: wide area measurement systems, naspinet, and security[J]. IEEE Power and Energy Magazine, 2012, 10(1): 67-73.
[6] 邵雅宁, 唐飞, 刘涤尘, 等. 一种适用于 WAMS量测数据的系统暂态功角稳定评估方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2015, 43(6): 33-39. SHAO Yaning, TANG Fei, LIU Dichen, et al. An approach of transient angle stability assessment in power system for WAMS measured data[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2015, 43(6): 33-39.
[7] 黄弘扬, 徐政, 华文, 等. 基于广域测量系统的发电机强励控制方案[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2013, 41(6): 49-56. HUANG Hongyang, XU Zheng, HUA Wen, et al. Forced excitation control scheme based on wide-area measurement system[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2013, 41(6): 49-56.
[8] JIANG L, YAO W, WEN J Y, et al. Delay-dependent stability for load frequency control with constant and time-varying delays[C] // Power & Energy Society General Meeting, 2009. PES '09. IEEE, 2009, 27(2): 1-6.
[9] 李鹏, 刘成斌, 姜涛, 等. 智能电网下的电网安全性与稳定性[J]. 电网与清洁能源, 2013, 29(2): 33-37, 42. LI Peng, LIU Chengbin, JIANG Tao, et al. Power system security and stability in smart grid[J]. Advances of Power System & Hydroelectric Engineering, 2013, 29(2): 33-37, 42.
[10] 蔡超豪. 存在时滞影响的发电机励磁的H∞控制[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2009, 37(8): 5-9. CAI Chaohao. H∞ control of generator excitation with time-delay[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2009, 37(8): 5-9.
[11] 罗珂, 吕红丽, 霍春岭, 等. 基于LMI的时滞电力系统双层广域阻尼控制[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2013, 41(24): 16-22. LUO Ke, LÜ Hongli, HUO Chunling, et al. Two layer inter-area damping control of power systems considering time-delay based on LMI[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2013, 41(24): 16-22.
[12] 张放, 程林, 黎雄, 等. 广域闭环控制系统时延的分层预测补偿[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2014, 34(19): 3194-3201. ZHANG Fang, CHENG Lin, LI Xiong, et al. Prediction based on hierarchical compensation for delays of wide-area closed-loop control systems[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2014, 34(19): 3194-3201.
[13] 厉文秀. 随机时滞电力系统稳定性分析[J]. 电网与清洁能源, 2015, 31(3): 29-34. LI Wenxiu. Analysis of stability of stochastic time delay power systems[J]. Advances of Power System & Hydroelectric Engineering, 2015, 31(3): 29-34.
[14] 吴俊明, 杨洪明, 杨鑫, 等. 考虑通信时滞和噪声的LED灯参与微电网调频的研究[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2015, 43(8): 49-57.WU Junming, YANG Hongming, YANG Xin, et al. A survey on LED lamps participating in frequency regulation of microgrid considering communication delay and noise[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2015, 43(8): 49-57.
[15] 杨培宏, 刘文颖, 魏毅立, 等. 电力系统广域自适应阻尼控制器设计[J]. 电力系统及其自动化学报, 2013, 25(5): 105-110. YANG Peihong, LIU Wenying, WEI Yili, et al. Design of wide-area adaptive damping controller of power system [J]. Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA, 2013, 25(5): 105-110.
[16] 孙琳, 李天然, 吴华仁, 等. 基于模糊自适应PID的广域阻尼控制[J]. 电力系统及其自动化学报, 2015, 27(5): 28-33. SUN Lin, LI Tianran, WU Huaren, et al. Fuzzy adaptive PID control based wide area damping control[J]. Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA, 2015, 27(5): 28-33.
[17] 谢永涛, 贾嵘, 董开松, 等. 交流微网整体建模及仿真研究[J]. 高压电器, 2015, 51(6): 101-107. XIE Yongtao, JIA Rong, DONG Kaisong, et al. Modeling and simulation of an AC microgrid[J]. High Voltage Apparatus, 2015, 51(6): 101-107.
[18] 马静, 李俊臣, 李益楠, 等. 基于改进自由权矩阵与广义特征值的时滞稳定上限计算方法研究[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2014, 42(18): 1-8. MA Jing, LI Junchen, LI Yinan, et al. Research on time-delay upper-bound of power system wide-area damping controllers based on improved free-weighting matrices and generalized eigenvalue problem[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2014, 42(18): 1-8.
[19] WANG Y, YAN X, ZUO Z, et al. New delay-dependent stability and stabilization of linear system with state and input delays[C] // Control and Decision Conference, 2008. CCDC 2008. Chinese, 2008: 4732-4737.
[20] 张平, 方洋旺, 惠晓滨, 等. 基于统计线性化的随机非线性微分对策逼近最优策略[J].自动化学报, 2013, 39(4): 390-399. ZHANG Ping, FANG Yangwang, HUI Xiaobin, et al. Near optimal strategy for nonlinear stochastic differential games based on the technique of statistical linearization[J]. Acta Automatic Sinica, 2013, 39(4): 390-399.
[21] 蒋栋年, 李炜, 王君, 等. 一类离散非线性时延系统的滑模变结构控制研究[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2013, 30(7): 1971-1974. JIANG Dongnian, LI Wei, WANG Jun, et al. Variablestructure control with sliding mode for discrete nonlinear time delay system[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2013, 30(7): 1971-1974.
[22] JIANG Yilang, JIA Hongjie, JIANG Tao, et al. A model simplification method for solving stability margin of power system with single time-delay[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2014, 38(2): 46-52.
[23] TSAI P W, CHEN C W. A novel criterion for nonlinear time-delay systems using LMI fuzzy Lyapunov method[J]. Applied Soft Computing Journal, 2014, 25: 461-472.
[24] LI Tao, QIAN Wei, WANG Ting, et al. Further results on delay-dependent absolute and robust stability for timedelay Lure's system[J]. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2014, 24(18): 3300-3316.
[25] 惠俊军, 张合新, 孔祥玉, 等. 变时滞不确定中立型系统鲁棒稳定新判据[J]. 控制工程, 2014, 21(4): 501-505. HUI Junjun, ZHANG Hexin, KONG Xiangyu, et al. A new robust stability criteria for uncertain neutral systems with time-varying delays[J]. Control Engineering of China, 2014, 21(4): 501-505.
[26] YANG B, SUN Y. Damping factor based delay margin for wide area signals in power system damping control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2013, 28(3): 3501-3502.
[27] ZHANG C, JIANG L, WU Q H, et al. Delay-dependent robust load frequency control for time delay power systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2013, 28(3): 2192-2201.
[28] MAZENC F, MALISOFF M, NICULESCU S. Reduction model approach for linear time-varying systems with delays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2014, 59(8): 2068-2082.
[29] MAZENC F, NORMAND-CYROT D. Reduction model approach for linear systems with sampled delayed inputs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2013, 58(5): 1263-1268.
(编辑 姜新丽)
Study on control and stabilization for multi-machine power system with wide-area time-delay by LMI
GUAN Linyan, ZHOU Hong, HU Wenshan
(School of Power and Mechanical Engineering, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430072, China)
Time-delay brought by wide-area communication is one of the most important causes leading to the performance degradation and even the failure of the controllers. The motion equation of the generator rotors of the multi-machine power system is linearized and deviated in the paper, in consideration of the characteristics of the time-delay power system. Then, defining a proper Lyapunov function, stabilization criteria based on the linear matrix inequality theory are presented by introducing some weight-free matrices. And the controller with full state feedback is designed. Compared to the linear quadratic optimal control, the controller is less conservative and more effective. The validity of the controller is verified by the IEEE 3-machine 9-bus test system. The simulation results show that the controller can reduce the negative impact caused by the time-delays.
wide-area measurement system; full status feedback; time-delay; linear matrix inequality; stability
10.7667/PSPC151647
:2015-12-25
关琳燕(1990-),女,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为电力系统分析与控制;E-mail: guanlinyan@foxmail.com
周 洪(1962-),男,博士,教授,主要研究方向为多变量过程控制系统、发电厂电网控制系统、网络控制理论与系统、智能建筑控制系统等;
胡文山(1980-),男,博士,副教授,主要研究方向为网络控制系统,智能电网等。

