介质阻挡放电中亮暗点超六边形斑图的光谱研究
刘 莹,董丽芳,牛雪姣,张 超
河北大学物理科学与技术学院,河北 保定 071002
介质阻挡放电中亮暗点超六边形斑图的光谱研究
刘 莹,董丽芳*,牛雪姣,张 超
河北大学物理科学与技术学院,河北 保定 071002
采用双水电极介质阻挡放电装置,在空气和氩气的混合气体中,首次研究了由中心亮点和暗点组成的亮暗点超六边形斑图。通过观察斑图照片,可以发现暗点位于周围其他三个亮点的质心处,并且亮点和暗点的亮度有所不同,这说明亮点和暗点的等离子体状态可能不同。利用发射光谱法,研究了亮暗点超六边形斑图中亮点和暗点的等离子体参量随氩气含量的变化趋势。首先通过采集氮分子(N2)第二正带系(C3Πu→B3Πg)发射谱线,计算出了亮点和暗点的分子振动温度; 之后利用氮分子离子391.4nm和氮分子394.1nm两条发射谱线的相对强度之比,得到了此斑图中亮点和暗点的电子平均能量; 最后通过氩原子696.57nm(2P2→1S5)谱线的展宽,研究了此斑图中亮点和暗点的电子密度。实验结果发现: 在同一氩气含量下,亮暗点超六边形斑图中暗点的分子振动温度、电子平均能量和电子密度均高于亮点的相应等离子体参量; 保持其他实验参数不变,随着氩气含量从70%变化到95%,亮点和暗点的分子振动温度和电子密度均是逐渐增大的,而电子平均能量则是逐渐减小的。亮点和暗点的等离子状态的不同,说明二者的放电机制可能不同。进一步采用高速录像机对斑图进行短曝光拍摄,发现亮点存在沿面放电,这些沿面放电交汇形成暗点。
介质阻挡放电; 分子振动温度; 电子平均能量; 电子密度
引 言
介质阻挡放电(DBD)是一种非平衡态交流气体放电,广泛应用于众多工业领域中[1-5]。为了提高工业生产应用效率,需要测量介质阻挡放电中的等离子体参量。等离子体参量的测量方法种类很多,其中发射光谱法因其是一种无干扰的测量方法,而成为等离子体诊断中应用最为广泛的一种[6,7]。这种方法主要是通过对谱线线型、谱线宽度和相对强度之比的分析,来确定等离子体的多个参量,例如分子振动温度、电子密度等。介质阻挡放电的放电形式可分为两类: 体放电(VD)和沿面放电(SD)。对于这两种放电的研究已有很多被报道[8,9],但对它们的放电性能的研究较少。由以往的研究可知,体放电和沿面放电的放电机制不同,因此等离子体状态也不同。本工作主要采用发射光谱法,对亮暗点超六边形斑图中亮点和暗点的分子振动温度、电子平均能量和电子密度几个等离子体参量随氩气含量的变化进行了研究,进一步比较了沿面放电和体放电这两种放电机制的不同。其实验结果不仅对于研究亮暗点超六边形斑图的形成机制有重要价值,也对沿面放电和体放电在不同领域的应用有重要意义。
1 实验部分
实验装置如图1所示,主要由水电极、高压电源、光谱仪、数字示波器组成。水电极由两个端面对称且装满水的圆柱形玻璃管组成,两侧用石英玻璃封住,各自在一侧用金属铜环连接至高压电源的电极。将水电极平行放置在充满氩气和空气混合物的真空密闭室里,中间放一块边长L为3 cm, 厚度d为2.4 mm的六边形边界。用数码相机(Canon Powershot G16)记录放电照片。利用高压探头(Tektronix P6015A)测量外加电压,并通过数字示波器(Tektronix DPO4104B)采集和存储。通过透镜放大成像,利用光纤探头将亮点和暗点的光分别导入到光谱仪(ACTON SP-2758, CCD: 1 340×400 Pixels, 光栅300, 800, 2 400 G·mm-1, 分辨率0.005 nm),控制计算机采集和存储光谱。用高速录像机(pco. dimax 9000000207)拍摄短曝光时间斑图照片。
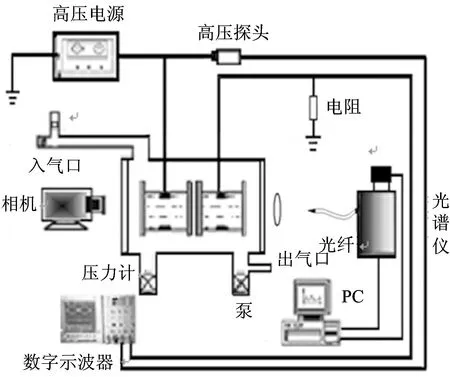
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of the experimental setup
2 结果与讨论
图2给出了亮暗点超六边形斑图的照片。由图2(a)可看出,亮暗点超六边形斑图是在电压值较高的情况下获得的,由暗点和亮点组成,斑图中暗点的位置位于周围其他三个亮点的质心处。从图2(b)中可以更清晰地看见亮暗点结构,分别由L和D指出,且亮点和暗点的亮度相差很大,说明这两种点的等离子体状态可能不同。为了进一步研究亮点和暗点的不同,采用发射光谱法,测量了亮点和暗点的等离子参量。

Fig.2 Discharge images of hexagonal super-lattice pattern with light spot and dim spot
实验中,中心波长设为390 nm, 选择300 G·mm-1的光栅,采集了氮分子第二正带系(C3Πu→B3Πg)波长范围在360~420nm之间的发射谱线,如图3所示。采用第二正带系的两组振动序带: (0-2,1-3,2-4)和(0-3,1-4,2-5)[10],对其进行处理,计算出了亮暗点超六边形斑图中亮点和暗点的分子振动温度。
图4给出了亮暗点超六边形斑图中亮点和暗点的分子振动温度随氩气含量的变化关系。由图中可以看出,在相同氩气含量条件下,暗点的分子振动温度要高于亮点的。保持其他参数不变,随着氩气含量由70%增大至95%,亮点和暗点的分子振动温度都随着氩气含量的增加而增大。亮点的分子振动温度在2 300~2 600K范围内,暗点的分子振动温度在2 400~2 900K范围内。
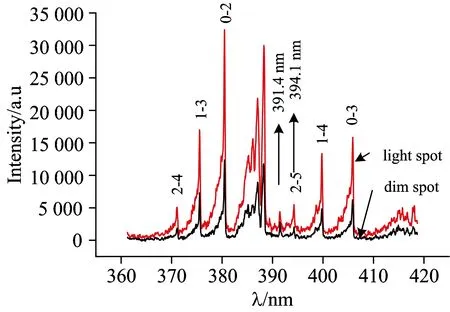
Fig.3 Emission spectra in the range of 360~420 nm
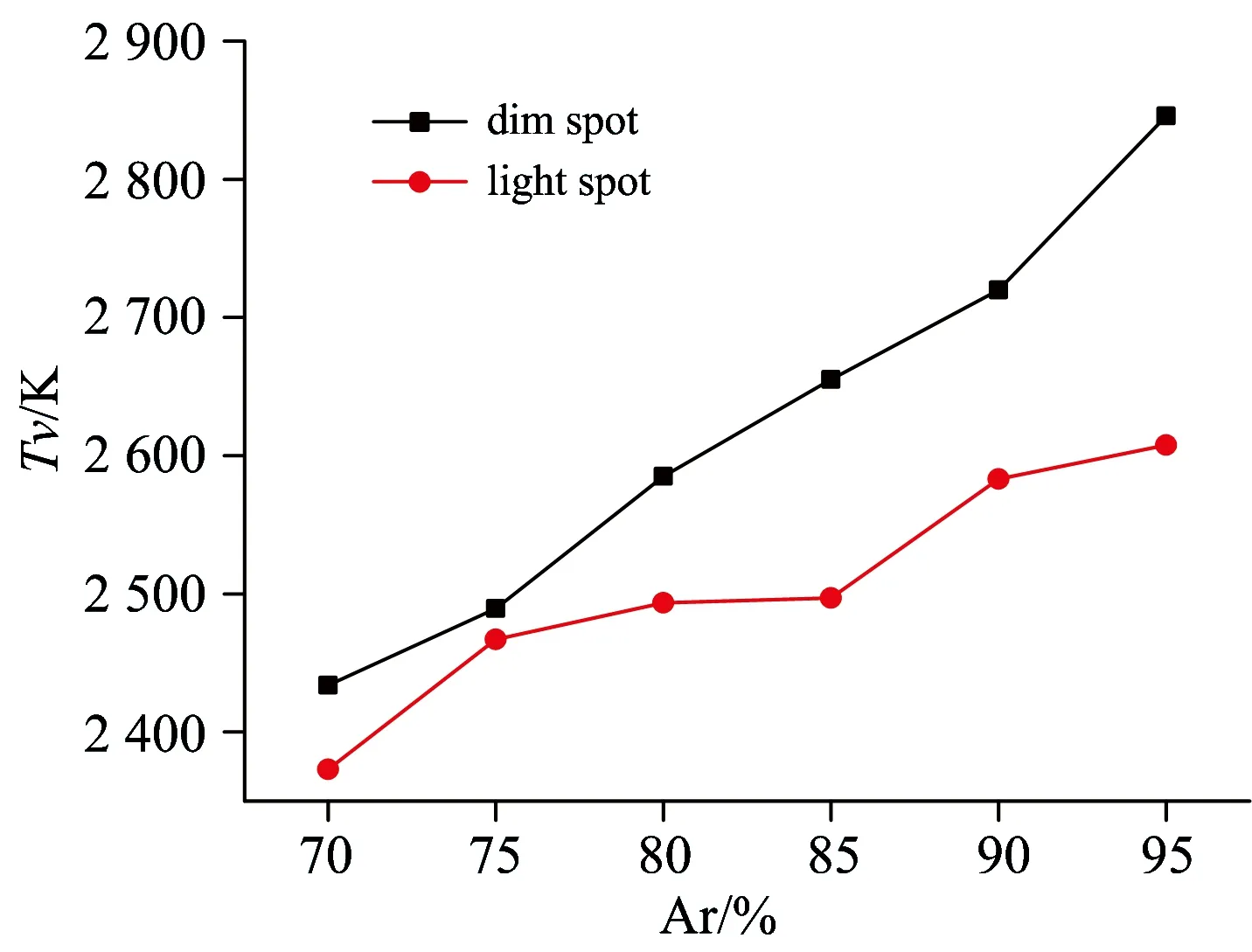
Fig.4 Variation of molecular vibration temperature of two kinds of spots as a function of argon concentration
氮分子离子谱线和氮分子谱线的相对强度比可反映电子平均能量。因此,本实验通过计算氮分子离子391.4 nm谱线与氮分子394.1 nm的相对强度之比,研究了电子平均能量随氩气含量的变化,如图5所示。由图可知,亮暗点超六边形斑图中暗点比亮点的电子平均能量要高; 随着氩气含量增加,亮点和暗点的电子平均能量均逐渐减小。

Fig.5 Variation of the ratio of intensity of the nitrogen molecule ion line and nitrogen molecule line as a function of argon concentration
中心波长选为696 nm, 选用2400 G·nm-1的光栅,采集了发射谱线。利用处理后得到的氩原子696.5 nm(2P2→1S5)的谱线展宽[6],研究了亮暗点超六边形斑图中亮点和暗点的电子密度,如图6所示。由图可知,暗点的谱线线宽要高于亮点的。改变氩气含量,研究了亮暗点超六边形斑图中亮点和暗点的谱线线宽随氩气含量的变化,其结果图7所示。粗略来讲,谱线的线宽可反映电子密度大小[10]。实验结果表明,亮点和暗点的电子密度随着氩气含量的增加而增大。

Fig.6 Profiles of the spectral line 696.5 nm of two kinds of spots
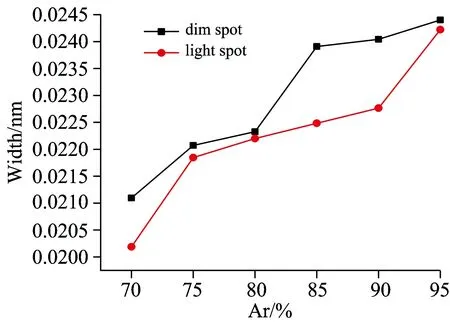
Fig.7 Variation of broadenings of spectral line 696.5 nm of two kinds of spots as a function of argon concentration
以上光谱结果表明,亮暗点超六边形斑图中亮点和暗点的等离子状态是不同的。为了进一步研究它们放电机制的不同,采用高速录像机对此斑图进行短曝光拍摄,其结果如图8所示。实验发现,亮点对应于体放电,暗点对应沿面放电,亮点周围的沿面放电交汇形成暗点。
3 结 论
采用双水电极介质阻挡放电装置,在空气和氩气的混合气体中,首次研究了由中心亮点和暗点组成的亮暗点超六边形斑图。采用发射光谱法,研究了亮暗点超六边形斑图中亮点和暗点的等离子体参量随氩气含量的变化。结果发现: 在相同氩气含量下,亮暗点超六边形斑图中暗点的分子振动温度、电子平均能量和电子密度均高于亮点的相应等离子体参量; 随着氩气含量从70%变化到95%,亮暗点超六边形斑图中亮点和暗点的分子振动温度和电子密度均是逐渐增大的,而亮点和暗点的电子平均能量则是逐渐减小的。采用高速录像机对斑图进行短曝光拍摄,发现亮点存在沿面放电,亮点的沿面放电交汇形成暗点。实验结果对进一步研究此斑图的形成有重要意义。
[1] Sinclair J, Walhout M. Physical Review Letters, 2012, 108: 035005.
[2] Bernecker B, Callegari T, Blanco S, et al. The European Physical Journal Applied Physics, 2009, 47.
[3] Hou Shiying, Zeng Peng, Liu Kun, et al. High Voltage Engineering, 2012, 38(7):.
[4] Fan Weili, Dong Lifang, Zhao Hai-tao, et al. IEEE Transaction on Plasma Science, 2009, 37(6): 1016.
[5] NIU Zheng, SHAO Tao, ZHANG Cheng, et al(年). High Voltage Engineering, 2011, 37(6): 1536.
[6] Chen Junying, Dong Lifang, Li Yuanyuan, et al. Acta Physica Sinica(物理学报), 2012, 61(7): 075211.
[7] Pu Yudong, Yang Jiamin, Jin Fengtao, et al. Acta Physica Sinica, 2011, 60(4): 045210.
[8] Gao Yenan, Pan Yuyang, Dong Lifang, et al. Phys. Plasmas, 2014, 21: 103515.
[9] Kogelschatz U. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2010, 256: 012015.
[10] DONG Li-fang, ZHU Ping, YANG Jing, et al(董丽芳, 朱 平, 杨 京,等). Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis(光谱学与光谱分析), 2014, 34(4): 915.
*Corresponding author
Study on Hexagonal Super-Lattice Pattern with Light Spot and Dim Spot in Dielectric Barrier Discharge by Optical Emission Spectra
LIU Ying, DONG Li-fang*, NIU Xue-jiao,ZHANG Chao
College of Physics Science and Technology, Hebei University, Baoding 071002, China
The hexagonal super-lattice pattern composed of the light spot and the dim spot is firstly observed and investigated in the discharge of gas mixture of air and argon by using the dielectric barrier discharge device with double water electrodes. It is found that the dim spot is located at the center of its surrounding three light spots by observing the discharge image. Obviously, the brightness of the light spot and the dim spot are different, which indicates that the plasma states of the light spot and the dim spot may be different. The optical emission spectrum method is used to further study the several plasma parameters of the light spot and the dim spot in different argon content. The emission spectra of the N2second positive band(C3Πu→B3Πg)aremeasured,fromwhichthemoleculevibrationtemperaturesofthelightspotandthedimspotarecalculated.Basedontherelativeintensityratioofthelineat391.4nmandtheN2lineat394.1nm,theaverageelectronenergiesofthelightspotandthedimspotareinvestigated.Thebroadeningofspectralline696.57nm(2P2→1S5) is used to study the electron densities of the light spot and the dim spot. The experiment shows that the molecule vibration temperature, average electron energy and the electron density of the dim spot are higher than those of the light spot in the same argon content. The molecule vibration temperature and electron density of the light spot and dim spot increase with the argon content increasing from 70% to 95%, while average electron energies of the light spot and dim spot decrease gradually. The short-exposure image recorded by a high speed video camera shows that the dim spot results from the surface discharges(SDs). The surface discharge induced by the volume discharge (VD) has the decisive effect on the formation of the dim spot. The experiment above plays an important role in studying the formation mechanism of the hexagonal super-lattice pattern with light spot and dim spot. In addition, the studies exert influences on the application of surface discharge and volume discharge in different fields.
Dielectric barrier discharge; Molecule vibration temperature; Average electron energy; Electron density
Nov. 29, 2014; accepted Apr. 19, 2015)
2014-11-29,
2015-04-19
国家自然科学基金项目(11375051), 河北省科技厅重点项目(11967135D)和河北省教育厅重点项目(ZD2010140)资助
刘 莹, 女, 1992年生, 河北大学物理科学与技术学院硕士研究生 e-mail: lying0606@163.com *通讯联系人 e-mail: donglfhbu@163.com
O461.2; O433.4
A
10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2016)02-0364-04

