A Note on the Maximal Functions on Weighted Harmonic AN Groups
Yurong WU Shiliang ZHAO
1 Introduction
Let(H,d)be a metric space andϱis a Borel measure onH.Denote byB(x,r)the open ball with centerx∈Hand of radiusr>0.
For a locally integrable functionf,the centered Hardy-Littlewood maximal function offis defined as
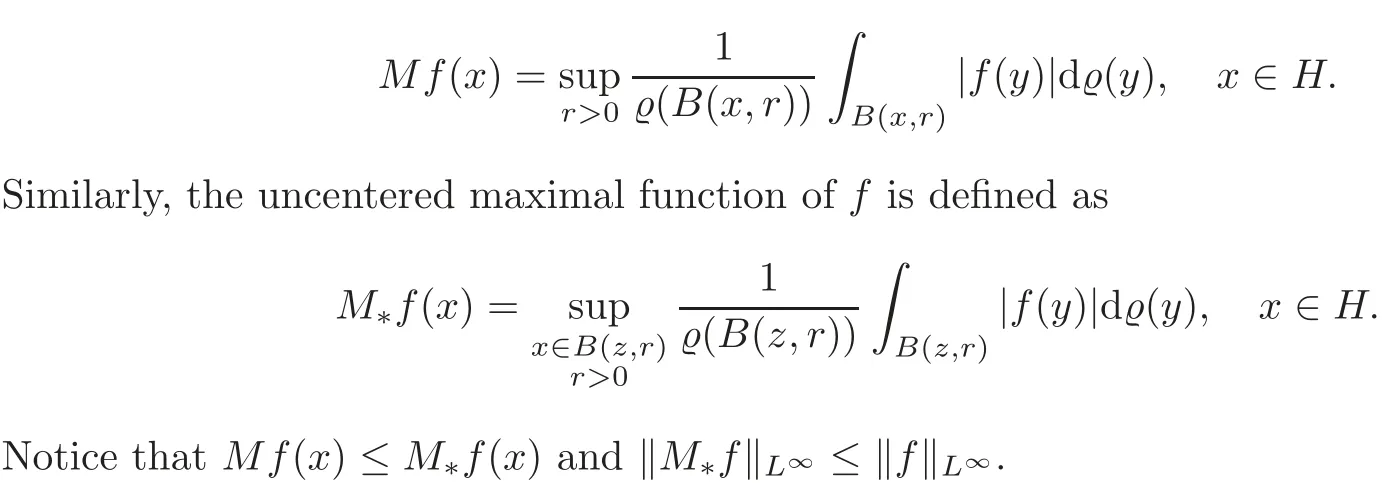
If the measureϱsatisfies the doubling condition,thenM∗is of the weak type(1,1)(see[4]).
It becomes complicated if the measureρdoes not satisfy the doubling condition,for example,whenHis a space of exponential growth.In this case,MandM∗generally have different properties.
A typical example is the non-compact symmetric space.In 1974,Clerc and Stein[3]obtained theLp(p>1)boundedness for the centered maximal functionM.Subsequently,Strömberg[14]proved thatMis of the weak type(1,1).For non-compact symmetric spaces of real rank 1,Ionescu proved in[12]that the uncentered maximal functionM∗is bounded fromL2,utoL2,vif and only ifu=1,v=∞.On the other hand,he obtained in[11]thatM∗is bounded onLpin the sharp rangep∈(2,∞]on symmetric spaces of arbitrary real rank.
Manuscript received 30 August,2014.Revised January 4,2015.
1Department of Mathematics,Fudan University,Shanghai 200433,China.
E-mail:wuyurong2003@163.com zhaoshiliang2013@gmail.com
Another example is the cuspidal manifold Cusp(X)=R+×X(see[5]).In[6–7],Li studied the centered maximal functionMand the uncentered maximal functionM∗on Cusp(X)and its weighted cases.Precisely,givenN≥0,denote bydXthe distance of X and dμXthe induced measure respectively,then the geodesic distance of Cusp(X)(see[5])is given by

Then on the weighted manifoldwhereβsatisfies(1.4)withα>−1,the following result has been established in[8]for the centered maximal functionMμβand uncentered maximal functionM∗,μβassociated with dμβ:
Theorem DMμβis bounded from and therefore is bounded onis bounded on Lpfor p>1.
For more results about maximal functions in the setting of exponential growth(see for example[1–2,9–10,13]and references therein).In this article,we study the maximal functions on weighted harmonic AN groups.
This paper is organized as follows.In Section 2 we will present some facts about harmonic AN groups and in Section 3 we will state our main results and give an explanation.
Throughout this paper,Cwill denote various constants which depend only on the dimension.A≾BmeansA≤CBwith such aC,andA∼Bstands forA≤CBandB≤CA.
2 Main Results and the Interpretation
In this section,we consider the maximal functions on the harmonic AN groupsS=R+×H(2n,m).We will point out that the methods used in[6–8]can be applied to this case.
In what follows,we consider the measure dμ=aσ−Q−1dadxdρand dμβ=β(a)dadxdρonS,whereβsatisfies(1.4)withα>−1.
Denote byMandM∗the centered and uncentered maximal functions associated with the measure dμ,respectively,and byMμβandM∗,μβthe centered and uncentered maximal function associated with the measure dμβrespectively.
Set

Then we can obtain the following theorems,of which we omitt the detailed proofs.

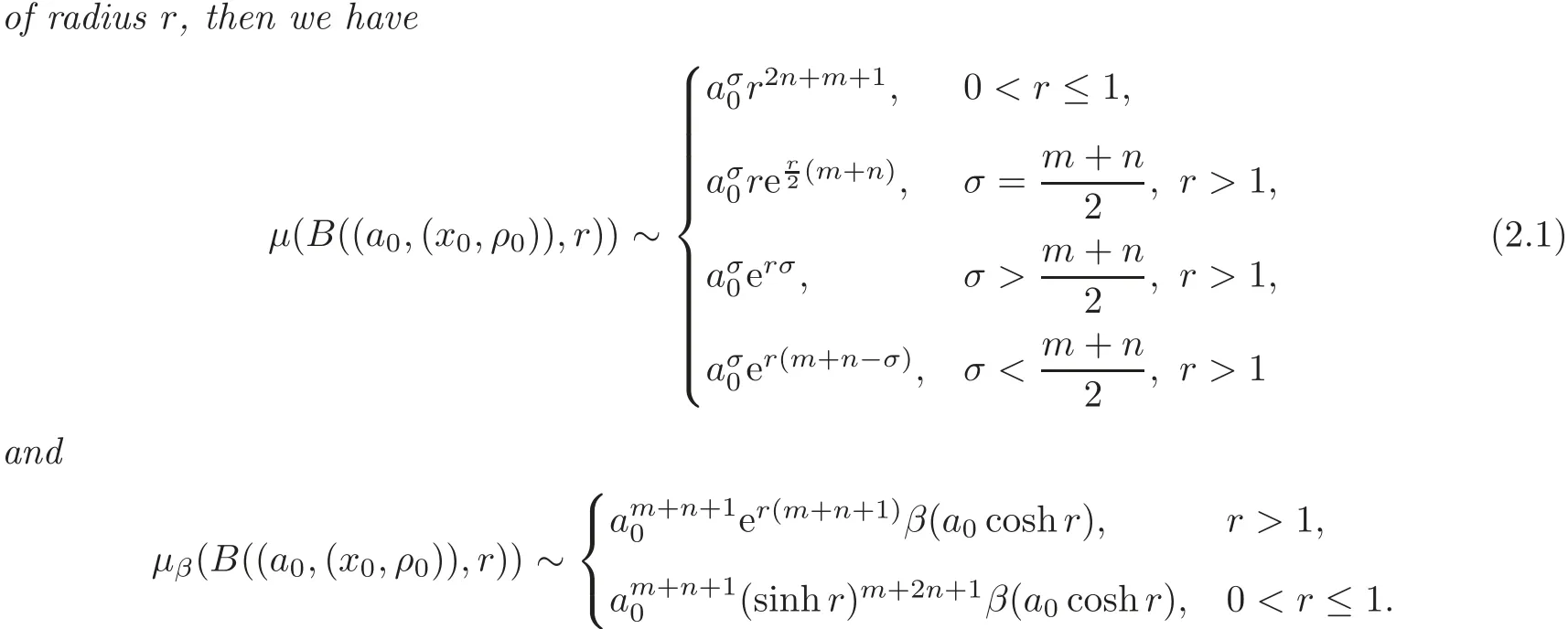
We point out that the above volume estimates ofr>1 can be obtained by Proposition 4.1 of[7]and Corollary 4.2 of[8]sincedandd∗(see the following Remark 2.2)are equivalent for larged.
Remark 2.1 Whenσ=0 in Theorem 2.1,the weak type(1,1)boundedness ofMhas been obtained in[1].
Remark 2.2 The above theorems can be interpreted by the models in[6–8].

sothen the models in[6–8]remain valid and similar results can be obtained for the maximal functions associated withd∗.
Thanks to the inequalitywe can prove that the distancesdandd∗are in some sense equivalent for larged∗,that is,there exists a constantC>0 such that for

Therefore,we can use the methods in[6–8]whendis large.On the other hand,the local maximal functions are always of the weak type(1,1)according to[4]since the measures dμand dμβsatisfy the local doubling property by Lemma 2.1.Thus we obtain Theorems 2.1–2.4 for the centered and uncentered maximal functions associated withd.
Remark 2.3 Li pointed out in[8]that harmonic AN groups are a typical example of the spaces of quasi-hyperbolic type,that is,there exists a constantC>1 such that

AcknowledgementWe are grateful to Prof.Li H.Q.for his useful suggestions and help.
[1]Anker,J.P.,Damek,E.and Yacoub,C.,Spherical analysis on harmonic AN groups,Ann.Scuola Norm.Super.Pisa.Cl.Sci.,23,1996,643–679.
[2]Chen,J.C.and Wang,S.L.,On boundedness of Hardy-Littlewood maximal function operator on Riemannian manifolds,Chin.Ann.Math.,Ser.B,14,1993,69–76.
[3]Clerc,J.L.and Stein,E.M.,Lp-multipliers for noncompact symmetric spaces,Proc.Nat.Acad.Sci.USA,71,1974,3911–3912.
[4]Coifman,R.and Weiss,G.,Analyse harmonique non commutative sur certains espaces homog`enes,Lecture Notes in Mathematics,vol.242,Springer-Verlag,Berlin,1971.
[5]Li,H.Q.,Analyse sur les vari´et´es cuspidales,Math.Ann.,326,2003,625–647.
[6]Li,H.Q.,La fonction maximale de Hardy-Littlewood sur une classe d’espaces m´etriques mesurables,C.R.Math.Acad.Sci.Paris,338(1),2004,31–34.
[7]Li,H.Q.,La fonction maximale non centre sur les vari´et´es de type cuspidale,J.Funct.Anal.,229,2005,155–183.
[8]Li,H.Q.,Les fonctions maximales de Hardy-Littlewood pour des mesures sur les vari´et´es cuspidales,J.Math.Pures Appl.,88,2007,261–275.
[9]Lohou´e,N.,Fonction maximale sur les vari´et´es de Cartan-Hadamard,C.R.Math.Acad.Sci.Paris,300,1985,213–216.
[10]Lohou´e,N.,Estimations de la fonction maximale de Hardy-Littlewood,Bull.Soc.Math.France,135(1),2007,135–169.
[11]Ionescu,A.D.,A maximal operator and a covering lemma on non-compact symmetric spaces,Math.Res.Lett.,7,2000,83–93.
[12]Ionescu,A.D.,An endpoint estimate for the Kunze-Stein phenomenon and related maximal operators,Ann.of Math.,152,2000,259–275.
[13]Lohou´e,N.,Minoration du volume des grosses boules sur les groupes de Lie semi-simples,J.Anal.Math.,95,2005,133–145.
[14]Strömberg,J.O.,Weak typeL1estimates for maximal functions on non-compact symmetric spaces,Ann.of Math.,114,1981,115–126.
 Chinese Annals of Mathematics,Series B2016年2期
Chinese Annals of Mathematics,Series B2016年2期
- Chinese Annals of Mathematics,Series B的其它文章
- On Unitary Invariant Weakly Complex Berwald Metrics with Vanishing Holomorphic Curvature and Closed Geodesics∗
- Witten’s D4Integrable Hierarchies Conjecture∗
- Gröbner-Shirshov Basis for Degenerate Ringel-Hall Algebras of Type
- Fixed Point Theorems for(p,q)-Quasi-Contraction Mappings in Cone Metric Spaces
- Approximate Representation of Bergman Submodules∗
- A Parameterization of the Canonical Bases of Affine Modified Quantized Enveloping Algebras∗
