运动训练和减量训练对心肌哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白和下游信号通路的影响
张 军,曾凡星,王大鹏(.燕山大学 体育学院,河北 秦皇岛 066004;.北京体育大学 运动人体科学学院,北京 00084)
◀运动人体科学
运动训练和减量训练对心肌哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白和下游信号通路的影响
张 军1,曾凡星2,王大鹏1
(1.燕山大学 体育学院,河北 秦皇岛 066004;2.北京体育大学 运动人体科学学院,北京 100084)
研究显示运动训练能激活mTOR信号通路,mTOR信号通路能影响心脏的结构和功能。那么,运动训练和减量训练对心肌哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白(mTOR)和下游信号通路有何影响?值得深入研究。研究方法:72只雄性SD大鼠随机分为8组: 3周大运动量训练组和3周安静对照组、3 d、6 d和2周减量训练组及相应的安静对照组。3周大运动量训练采用上坡跑、坡度10%、速度20 m/min的中等强度运动和26 m/min的大强度运动。然后进行减量训练,运动强度保持不变,运动时间由60 min减少到20 min。持续进行3 d、6 d和2周的减量训练。末次运动后12 h麻醉取血,取左心室肌。Western blotting测mTOR、p70S6激酶(p70S6K)的蛋白表达和磷酸化。心肌组织的形态学利用HE染色光镜观察。研究结果:3周大运动量训练和2周减量训练后,心肌组织的形态没有显著改变,心肌组织没有损伤。3 d减量训练组与安静对照组相比,mTOR(Ser2448)磷酸化有显著差异(P<0.05)。大运动量训练后,心肌p70S6K(Thr389)磷酸化显著增加(P<0.05)。减量训练后,心肌p70S6K显著减少(P<0.05)。S6K磷酸化和激活40S核糖体S6蛋白,有利于蛋白质生物合成。结论:减量训练造成心肌mTOR激活,对心脏有利。3周大运动量训练和2周减量训练后,心肌组织的形态没有显著改变,心肌组织没有损伤。3周大运动量训练后,心肌p70S6K(Thr389)磷酸化显著增加,促进蛋白质翻译,合成蛋白质。然而,减量训练后心肌p70S6K显著减少。S6K脱磷酸减少蛋白质翻译成分的合成,蛋白质合成显著下降。
哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白;p70S6激酶;减量训练
科学训练中的减量训练很重要。关于减量训练对心脏的影响尚不清楚。研究显示运动训练能激活mTOR信号通路,mTOR信号通路能影响心脏的结构和功能。笔者探讨运动训练和减量训练对心肌mTOR的下游信号通路的影响,分析对心脏结构和功能的影响,为科学训练提供实验依据。
1 研究对象与方法
1.1 研究对象
72只雄性SD大鼠,7周龄,北体大实验动物房中饲养,自由饮食、饮水,温度保持在(24±1)℃,相对湿度(50±10)%。
1.2 研究方法
1.2.1 实验分组 大鼠1周适应性训练后,随机分为8组:3周大运动量训练组(E3)和3周安静对照组(C3)、3d(E4)、6d(E5)和2周减量训练组(E6),以及相应的安静对照组(C4、C5和C6)。
1.2.2 实验动物训练方案 运动分为大运动量和减量训练。运动训练采用上坡跑、坡度10%、速度20 m/min的中等强度运动和26 m/min的大强度运动,3周内运动时间逐渐增加。然后进行减量训练,运动强度保持不变,运动时间逐渐减少。持续进行3 d、6 d和2周的减量训练。
1.2.3 主要试剂和方法 用Western blotting方法测定mTOR、p70S6激酶(p70S6K)蛋白和磷酸化。Western blotting过程包括样品准备、制胶、上样、电泳、转膜、封闭、洗膜、一抗孵育、洗膜、二抗孵育、洗膜、化学发光和结果计算等。抗体购自Cell Signaling公司。
1.2.4 统计学分析 数据用均数±标准差表示,独立样本T检验,显著性检验水平用P<0.05表示。运动训练组与各自的安静对照组相比,P<0.05表明具有显著性差异。
2 结果与分析
2.1 运动训练和减量训练对大鼠心肌组织形态的影响
HE染色可见各组心肌细胞着色为红色,排列规则,染色均匀,轮廓清晰,纵切面心肌呈长圆柱状。3周大运动量训练和2周减量训练后,心肌组织的形态没有显著改变,心肌组织没有损伤的形态学改变(图1)。
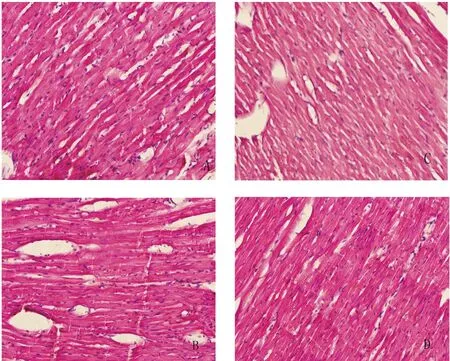
注:A 3周安静对照组;B 3周大运动量训练组;C 2周减量对照组;D 2周减量训练组。图1 大鼠心肌组织HE染色结果(×200)
2.2 运动训练和减量训练对心肌mTOR(Ser2448)磷酸化的影响
3 d减量训练组与安静对照组相比,心肌mTOR(Ser2448)的磷酸化有显著差异(P<0.05)。大运动量训练组与安静对照组相比,心肌mTOR(Ser2448)磷酸化无显著变化(P>0.05)(表1、图2)。
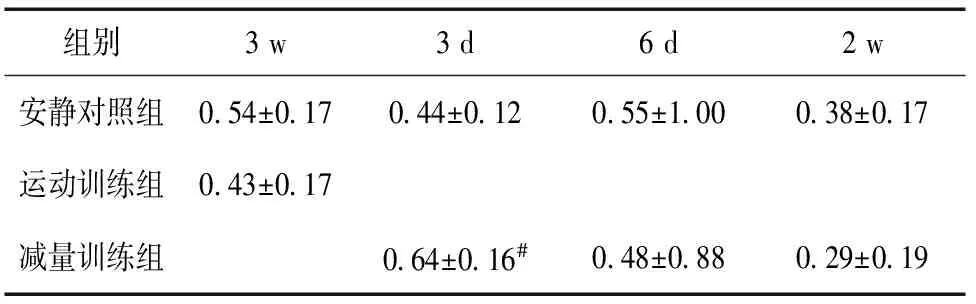
表1 运动训练和减量训练后心肌mTOR(Ser2448)磷酸化的变化
注:#表示与3 d对照组相比,有显著性差异,P<0.05。
2.3 运动训练和减量训练对心肌p70S6K的影响
与各自的对照组相比,3 d、6 d和2周减量训练后,心肌p70S6K均显著减少(P<0.05) (表2、图3)。

表2 运动训练和减量训练后心肌p70S6K的变化
注:#△□分别表示与安静对照组相比,有显著性差异,P<0.05。

图2 运动训练和减量训练后心肌mTOR(Ser2448)磷酸化的变化

图3 运动训练和减量训练后心肌p70S6K的变化
2.4 运动训练和减量训练对心肌p70S6K(Thr389)磷酸化的影响
与3周安静对照组相比,3周大运动量训练后,心肌p70S6K(Thr389)磷酸化显著增加(P<0.05) (表3、图4)。

表3 运动训练和减量训练后心肌p70S6K(Thr389)磷酸化的变化
注:*表示与安静对照组比较,有显著性差异,P<0.05。
3 讨论
3.1 运动训练和减量训练对心肌mTOR的影响
研究发现运动训练激活心肌mTOR信号通路[1]。研究发现间歇性的有氧运动激活大鼠心脏mTOR和下游的信号蛋白[2]。本实验的前期研究发现中等强度的运动后mTOR(Ser2448)磷酸化,运动后6 h达到峰值。大强度的运动后mTOR(Ser2448)磷酸化,运动后6 h达到峰值[3]。本研究发现3周运动训练后减量训练3 d,心肌mTOR(Ser2448)的磷酸化也显著增加,说明运动训练和减量训练造成心肌mTOR的激活,对心脏有利。研究发现,mTOR通过营养素、胰岛素、细胞能量和应激等细胞信号调节[4]。此外,本研究发现3周大运动量训练和2周减量训练后,心肌组织的形态没有显著改变,心肌组织没有损伤。

图4 运动训练和减量训练后心肌p70S6K(Thr389)磷酸化的变化
3.2 运动训练和减量训练对心肌p70S6K的影响
本实验的前期研究发现中等强度与大强度运动后,大鼠心肌p70S6K蛋白含量不变;中等强度运动后12 h磷酸化的p70S6K (Thr389)达到峰值,运动后24 h仍未恢复;而大强度运动后24 h,磷酸化的p70S6K (Thr389)显著降低[5]。研究发现中等强度运动后1 h、6 h和12 h,大鼠骨骼肌S6K(Thr389)磷酸化水平显著提高,24 h后恢复到安静水平。运动后S6K(Thr389)磷酸化与mTOR(Ser2448)磷酸化基本同步[3]。Mascher研究受试者在功率自行车上完成有氧耐力运动,结果骨骼肌mTOR(Ser2448)磷酸化,S6K(Ser424/Thr421)磷酸化[6]。Haddad等观察急性运动后,与对侧肌肉相比,p70S6K磷酸化增加2.5倍,然后迅速下降,说明一次运动后p70S6K激活的持续时间有限,而有规律地多次运动引起p70S6K持续激活。在第二次运动后,p70S6K磷酸化增加得到加强,第二次运动后40 h仍有显著增加[7]。本实验研究发现3周大运动量训练后,心肌p70S6K(Thr389)磷酸化显著增加,促进蛋白质翻译,合成蛋白质。然而,减量训练后,心肌p70S6K显著减少。而在减量训练过程中,心肌p70S6K逐渐升高,而p70S6K(Thr389)磷酸化和p70S6K(Thr389)磷酸化/p70S6K逐渐降低。
S6K是mTOR下游的重要效应物。PI3K/Akt途径介导增殖的上游信号后,mTOR磷酸化并激活S6K。随后,S6K磷酸化和激活40S核糖体S6蛋白,促进40S核糖体亚基募集到有翻译活性的多核糖体,有5’TOP序列的mRNAs翻译增加。这些有5’TOP序列的mRNAs编码核糖体蛋白、延伸因子,如eEF1α和eEF2、poly A结合蛋白和胰岛素样生长因子II,是蛋白质生物合成的基础。S6K脱磷酸减少蛋白质翻译成分的合成,蛋白质合成显著下降[8-10]。S6K通过提高mRNA翻译控制细胞生长,5’TOP mRNA翻译需要S6K[11]。rpS6是S6K的下游因子,一般认为rpS6磷酸化是S6K激活的结果。S6K能增加与eIF4B和eEF2激酶的接触。eEF2激酶通过磷酸化翻译延长因子eEF2使其受到抑制。S6K能使eEF2激酶磷酸化,抑制其活性,从而提高eEF2的活性[12]。S6K使eIF4B磷酸化,促进其募集到起始复合物。mTOR通过调节S6K产生有效的翻译起始或延长过程[13]。
4 结论
运动训练和减量训练能引起心肌mTOR激活,是对心脏有利的因素。3周大运动量训练和2周减量训练后,心肌组织的形态没有显著改变,心肌组织没有损伤。3周大运动量训练后,心肌p70S6K(Thr389)磷酸化显著增加,促进蛋白质翻译,合成蛋白质。然而,减量训练后,心肌p70S6K显著减少。S6K脱磷酸减少蛋白质翻译成分的合成,蛋白质合成显著下降。
[1] 张军,曾凡星,崔凤海.减量训练对心肌mTOR上游信号蛋白PI3K和Akt的影响[J].北京体育大学学报,2014,37(1):64-70.
[2]Ole Johan Kemi,Marcello Ceci,Ulrik Wisloff.Activation or inactivation of cardiac Akt/mTOR signaling diverges physiological from pathological hypertrophy[J].J.Cell.Physiol,2008,214:316-321.
[3]张军.大运动量和减量训练对心肌mTOR和CaN/NFAT信号的影响[D].北京:北京体育大学,2014.
[4]O’Reilly KE,Rojo F,She QB,et al.mTOR inhibition induces upstream receptor tyrosine kinase signaling and activates Akt[J].Cancer Res,2006,66(3):1-8.
[5]廖静雯.长期不同强度运动对心肌mTOR下游信号的作用研究[D].北京:北京体育大学,2013.
[6]Mascher H,Andersson H,Nilsson PA,et al.Changes in signalling pathways regulating protein synthesis in human muscle in the recovery period after endurance exercise[J].Acta Physiol (Oxf),2007,191(1):67-75.
[7]Haddad F,Adams G R.Selected contribution,acute cellular and molecular responses to resistance exercise[J].J Appl Physiol,2002,93(1):394-403.
[8]Fumarola C,La Monica S,Alfieri RR,et al.Cell size reduction induced by inhibition of the mTOR/S6K-signaling pathway protects Jurkat cells from apoptosis[J].Cell Death Differ,2005,12(10):1344-1357.
[9]Lang CH,Frost RA.Endotoxin disrupts the leucine-signaling pathway involving phosphorylation of mTOR,4E-BP1,and S6K1 in skeletal muscle[J].J Cell Physiol,2005,203(1):144-55.
[10]张军,曾凡星,高原,等.大运动量和减量训练对心肌mTOR和下游信号蛋白4E-BP1的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志,2015,34(3):235-241.
[11]Radimerski T,Montagne J,Rintelen F,et al.dS6K-regulated cell growth is dPKB/dPI(3)K-independent,but requires dPDK1[J].Nat Cell Biol,2002,4(3):251-255.
[12]Browne GJ,Finn SG,Proud CG.Stimulation of the AMP-activated protein kinase leads to activation of eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase and to its phosphorylation at a novel site,serine 398[J].J Biol Chem,2004,279(13):12220-12231.
[13]Raught B,Peiretti F,Gingras AC,et al.Phosphorylation of eucaryotic translation initiation factor 4B Ser422 is modulated by S6 kinases[J].Embo J,2004,23(8):1761-1769.
责任编辑:郭长寿
Effects of Training and Tapering on Myocardium mTOR and Backward Position of mTOR Signal Pathway
ZHANG Jun1,ZENG Fanxing2,WANG Dapeng1
(1.Physical Education College,Yanshan University,Qinhuangdao 066004,Hebei,China;2.Sport Science College,Beijing Sport University,Beijing 100084,China)
Researches reveal that training activates mTOR signal pathway.mTOR signal pathway affects the formation and function of the heart.How do the training and tapering influence mTOR and backward position of signal pathway? It deserves further research.Methods:the 72 SD rats are divided into 8 groups randomly;3 weeks rest control group,3 weeks intensive training group,3 days rest control group,3 days tapering training group,6 days rest control group,6 days tapering training group,2 weeks rest control group,and 2 weeks tapering training group.We adopted moderate intensity(20 m/min,grade of 10%)and high intensity(26 m/min,grade of 10%) by turn in 3 weeks intensive training.Training time prolonged gradually from 60 min to 120min.After 3 weeks of intensive training,the process of tapering training followed.This process also adopted moderate intensity(20 m/min,grade of 10%)and high intensity(26 m/min,grade of 10%) by turn.But the training time decreased gradually.Tapering training included 3 kinds:3 days,6 days and 2 weeks tapering training.The left ventricle cardiac muscle has been got,and been tested for mTOR and p70S6K protein expression and protein phosphorylation by Western blotting.The conformation of cardiac muscle organization was observed by HE coloration in the light mirror.Results:The conformation of cardiac muscle organizations weren’t changed significantly after 3 weeks of great volume of training and 2 weeks of tapering.There were not any injuries in the cardiac muscles.MTORSer2448 phosphorylation increased significantly after tapering 3 days.P70S6K (Thr389) phosphorylation increased significantly after 3 weeks intensive training (P<0.05).P70S6K decreased significantly in cardiac muscle after tapering (P<0.05).S6K1 dephosphorylation decreases the synthesis of components of the protein translation system and results in a profound decrease in protein synthesis.Conclusions:Tapering can induce the activation of myocardium mTOR and is good for the heart.The conformation of cardiac muscle organizations wasn’t changed significantly after 3 weeks of great volume of training and 2 weeks of tapering.P70S6K (Thr389) phosphorylation increased significantly after 3 weeks intensive training which resulted in some protein translation increase,and in favor of protein synthesis.P70S6K decreased significantly in cardiac muscle after tapering which resulted in some protein translation decreased,and some protein synthesis decreased.
mTOR;p70S6K;tapering
2016-02-27;
2016-03-21
燕山大学博士基金项目(B920);燕山大学青年教师自主研究计划课题(15SKB009)。
张 军(1981—),男,讲师,博士,主要研究方向为运动与心血管结构和功能。
G804.7
A
1004-0560(2016)02-0082-04

