EGFR-TKIs在晚期EGFR受体突变肺鳞癌患者中的临床应用
吴洪波 李明智 史亮 陶虹 唐俊舫 刘喆
·临床研究与应用·
EGFR-TKIs在晚期EGFR受体突变肺鳞癌患者中的临床应用
吴洪波 李明智 史亮 陶虹 唐俊舫 刘喆
目的:探讨表皮生长因子受体酪氨酸激酶抑制剂(epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors,EGFR-TKIs)对具有表皮生长因子受体(epidermal growth factor receptor,EGFR)突变的晚期肺鳞癌患者临床疗效。方法:回顾性分析首都医科大学附属北京胸科医院2010年1月至2016年7月收治的2 317肺鳞癌患者,筛选出有明确随访记录的7例确诊具有EGFR突变的肺鳞癌患者,使用EGFR-TKI如吉非替尼、厄洛替尼治疗,直至疾病进展(progressive disease,PD)。结果:使用EGFR-TKI治疗后,患者客观缓解率(objectire response rate,ORR)42.9%,疾病控制率(disease control rate,DCR)100%(7/7),中位无进展生存期6.1个月。结论:EGFR-TKI对EGFR突变的肺鳞癌患者具有一定临床疗效。但本研究病例数少仅有7例,亟需更多的病例来进行补充研究及验证上述结论。
表皮生长因子受体酪氨酸激酶抑制剂肺鳞状细胞癌基因突变
肺鳞癌在肺癌的发病率中处于第2位,仅次于肺腺癌,约占30%左右[1]。随着医学技术的发展,当前晚期肺腺癌的治疗原则已发生改变,对于有表皮生长因子受体(epidermal growth factor receptor,EGFR)突变的肺腺癌患者,口服靶向药物酪氨酸激酶抑制剂(tyrosine kinase inhibitor,TKI)如吉非替尼、厄洛替尼已替代化疗作为一线治疗方案,患者的客观缓解率(objective response rate,ORR)、无疾病进展生存期(progression free survival,PFS)、治疗期间的生存质量,均显著优于化疗者[2]。然而晚期肺鳞癌的治疗仍局限于以化疗为主,TKI在肺鳞癌患者应用并不广泛,原因在于其对肺鳞癌患者EGFR突变的鳞癌患者临床疗效并不明显。本研究回顾性分析2010年1月至2016年7月收治的有EGFR突变并经TKI临床治疗的肺鳞癌患者并复习相关文献,探索TKI在肺鳞癌患者中的应用价值,为临床使用此类药物提供依据。
1 材料与方法
1.1 病例资料
选取首都医科大学附属北京胸科医院2010年1月至2016年7月收治的肺鳞癌患者2 317例,均有经手术、气管镜或肺穿刺所取得的明确组织病理学诊断。患者经突变检测有EGFR突变,并且接受吉非替尼或厄洛替尼治疗,有详细的随访记录。研究因素包含ORR及PFS。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 服药方法吉非替尼治疗,250 mg/d,厄洛替尼治疗,150 mg/d。直至疾病进展(progressive disease,PD)。
1.2.2 疗效评估依据实体肿瘤疗效评价标准RECIST 1.1版,包括:1)完全缓解(complete response,CR);2)部分缓解(partial response,PR);3)疾病稳定(stable disease,SD);4)PD;5)ORR=(CR+PR)/总例数×100%;6)疾病控制率(disease control rate,DCR)=(CR+PR+SD)/总例数×100%。
1.2.3 随访情况随访时间截止时间为2016年7月。PFS按开始接受治疗至PD或尚未进展的末次随访时间计算。
1.3 统计学分析
采用SPSS 19.0软件进行统计学分析。PFS采用Kaplan-Meier法进行生存分析。
2 结果
2.1 临床特征
将2010年1月至2016年7月收治肺鳞癌患者2 317例,明确检测有EGFR突变且使用TKI治疗并有详细随访记录的肺鳞癌患者仅7例。患者在服用厄洛替尼或吉非替尼之前病情均已进展为Ⅳ期,靶向治疗前都曾经过一线或多线化疗。其中男性5例,女性2例,男女比例为2.5:1.0。年龄49~72岁,中位年龄51岁。吸烟患者5例均为男性。5例EGFR突变为19外显子缺失突变,2例为21外显子L858突变(表1)。
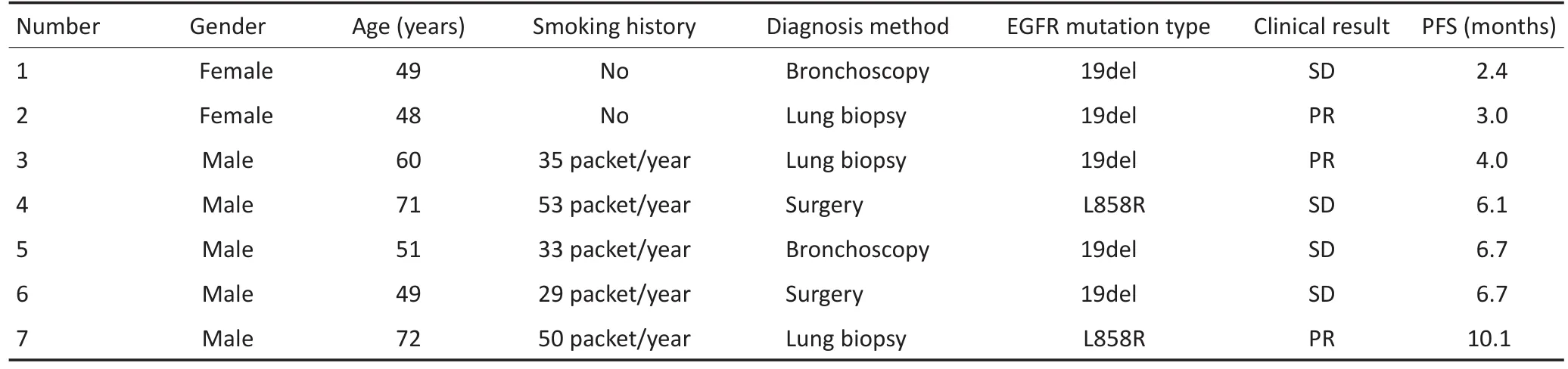
表17 例患者临床特征及疗效Table 1Clinical features and results of 7 cases
2.2 临床疗效
使用靶向药物治疗后,ORR为42.9%,DCR为100%。中位无进展生存期(median progression-free survival,mPFS)为6.1个月(图1)。
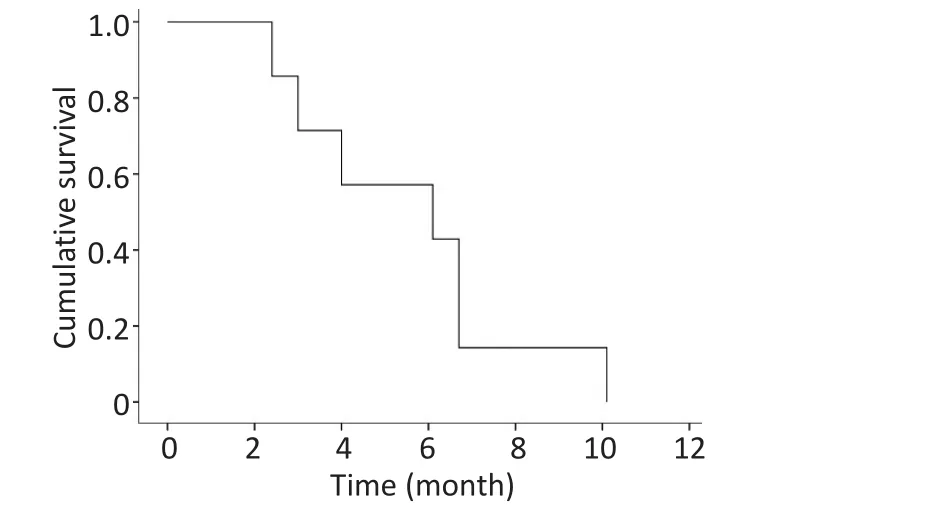
图17 例患者的PFS曲线Figure 1Progression free survival curves of 7 patients
3 讨论
晚期肺鳞癌以化疗为其最重要的治疗手段。但是ORR为30%~40%,中位生存时间约1年[3],化疗同时存在不良反应,疗效并不乐观。
随着医学技术进展,研究发现EGFR基因突变是部分肺癌患者的致瘤驱动基因,而TKI类药物如吉非替尼或厄洛替尼则可以针对这类患者进行靶向治疗,临床疗效显著,尤其以肺腺癌患者明显。但是,临床上TKI类药物并没有在肺鳞癌患者当中得到广泛使用。一方面,因肺鳞癌患者EGFR突变很少,文献报道为3.3%~4.6%[4]。某些研究甚至认为,纯肺鳞癌中无EGFR基因突变[5]。另一方面,一些研究报道TKI治疗有EGFR突变的肺鳞癌患者临床疗效并不明显。如有研究发现存在EGFR基因敏感突变的肺鳞癌患者,应用TKI药物治疗后PFS为1.4~3.9个月,ORR约为25%[6],远较TKI治疗肺腺癌的PFS(9~13个月)与ORR(60%~70%)差[7]。Shukuya等[8]回顾性分析21例具有EGFR突变的鳞癌患者,接受吉非替尼治疗的ORR、DCR及PFS分别为27%、67%~70%和3个月,均远低于有EGFR突变的肺腺癌患者的66%、92%~93%和9.4个月。
突变率少且临床获益不明显使得TKI在肺鳞癌患者中未广泛使用。因此,对于是否常规检测肺鳞癌患者的EGFR突变仍有争论。国际肺癌研究协会以及分子病理协会不推荐在不具有腺癌成分的肺鳞癌手术标本中检测EGFR基因突变[9]。而美国国立综合癌症网站(national comprehensive cancer network,NCCN)建议对肺鳞癌尤其是不吸烟、小活检组织或混合型鳞癌应考虑进行EGFR基因突变检测[10]。
也有部分研究报道TKI在具有突变的鳞癌患者中有临床应用价值。如一项研究报道EGFR突变肺鳞癌患者经厄罗替尼治疗后较无突变患者PFS、OS均明显延长[11]。另一项研究报道有EGFR突变肺鳞癌患者PFS为8个月,而无EGFR突变患者的PFS为1.53个月,临床获益明显[12]。一项Meta分析也认为虽然鳞癌患者突变稀少,但是应用TKI能延长突变鳞癌患者的PFS及OS[13]。Xu等[14]回顾性分析29个突变阳性及151个突变阴性接受TKI治疗的肺鳞癌患者,发现总生存期(overall survival,OS)18.04个月vs. 14.03个月,PFS为3.93个月vs.1.94个月,均有改善。本组病例研究发现,经过厄洛替尼或吉非替尼治疗后,患者ORR为42.9%,DCR为100%,mPFS达到6.1个月。这项研究中患者的PFS及ORR均较既往部分研究结果更好,是否与病例数少有关系,还亟需收集更多的病例来进行验证。本研究中EGFR突变患者男性居多,且均有吸烟史,mPFS较女性明显延长,与Clark等[15]报道男性吸烟肺鳞癌患者从厄洛替尼治疗中获益结果明显一致。而肺腺癌患者EGFR突变优势人群多见于女性及不吸烟者。可见肺鳞癌患者突变的特点与肺腺癌不同。
有2例肺鳞癌患者确诊来源于手术标本,也检测到EGFR突变,患者的PFS均达到6个月。因此,虽然国际肺癌研究协会不推荐在不具有腺癌成分的鳞癌组织标本(即手术标本)行EGFR检测,可见手术标本中也具有EGFR突变。因此,手术标本不应该作为是否行EGFR检测的判定标准。另外,NCCN指南建议对肺鳞癌尤其是不吸烟患者应考虑行EGFR检测,但是本研究显示5例突变男性患者均有长期吸烟史,吸烟数均>20包/年。因此,吸烟不应作为EGFR突变的优势人群判定原则之一。
本研究中有2例患者PFS在3个月以内,突变类型也属于TKI敏感类型,但PFS较另5例患者明显减少。2例患者均为女性,性别因素是否起作用?或是否EGFR突变丰度的差别造成上述研究结果?相关原因仍需要进一步研究。
综上所述,虽然鳞癌患者EGFR突变很少,但是TKI药物对于具有EGFR突变的肺鳞癌患者具有一定的临床效果。虽然获益不如肺腺癌患者明显,但是对于一些老年无法耐受化疗的患者以及众多已经对化疗药物产生多药耐药的患者,TKI药物是一项重要的补充治疗手段。本研究病例数较少,仅为7例,尚需更多的病例进行研究以验证上述结论。
[1]Heist RS,Sequist LV,Engelman JA.Genetic changes in squamous cell lung cancer:a review[J].J Thorac Oncol,2012,7(5):924-933.
[2]Khozin S,Blumenthal GM,Jiang X,et al.U.S.Food and Drug Administration approval summary:Erlotinib for the first-line treatment of metastatic non-small cell lung cancer with epidermal growth factor receptor exon 19 deletions or exon 21(L858R)substitution mutations[J].Oncologist,2014,19(7):774-779.
[3]Mitsudomi T.Advances in target therapy for lung cancer[J].Jpn J Clin Oncol,2010,40(2):101-106.
[4]Dearden S,Stevens J,Wu YL,et al.Mutation incidence and coincidence in non small-cell lung cancer:meta-analyses by ethnicity and histology(mutMap)[J].Ann Oncol,2013,24(9):2371-2376.
[5]Pan Y,Wang R,Ye T,et al.Comprehensive analysis of oncogenic mutations in lung squamous cell carcinoma with minor glandular component[J].Chest,2014,145(3):473-479.
[6]Brooks AN,Kilgour E,Smith PD.Molecular pathways:fibroblast growth factor signaling:a new therapeutic opportunity in cancer[J]. Clin Cancer Res,2012,18(7):1855-1862.
[7]Sequist LV,Heist RS,Shaw AT,et al.Implementing multiplexed genotyping of non-small-cell lung cancers into routine clinical practice [J].Ann Oncol,2011,22(12):2616-2624.
[8]Shukuya T,Takahashi T,Kaira R,et al.Efficacy of gefitinib for nonadenocarcinoma non-small-cell lung cancer patients harboring epidermal growth factor receptor mutations:a pooled analysis of published reports[J].Cancer Sci,2011,102(5):1032-1037.
[9]Leigh NB,Rekhtman N,Biermann WA,et al.Molecular testing for selection of patients with lung cancer for epidermal growth factor receptor and anaplastic lymphoma kinase tyrosine kinase inhibitors:American society of clinical oncology endorsement of the college of American pathologists/international association for the study of lung cancer/association for molecular pathology guideline [J].J Clin Oncol,2014,32(32):3673-3679.
[10]National Comprehensive Cancer Network.NCCN clinical practice guideline in oncology[J].2015.[Epub ahead print].
[11]Hata A,Katakami N,Yoshioka H,et al.How sensitive are epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors for squamous cell carcinoma of the lung harboring EGFR gene-sensitive mutations[J]? J Thorac Oncol,2013,8(1):89-95.
[12]Cappuzzo F,Ciuleanu T,Stelmakh L,et al.Erlotinib as maintenance treatment in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer:a multicentre, randomised,placebo-controlled phase 3 study[J].Lancet Oncol, 2010,11(6):521-529.
[13]Ameratunga M,Pavlakis N,Gebski V,et al.Epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors in advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the lung:a meta-analysis[J].Asia Pac J Clin Oncol,2014, 10(3):273-278.
[14]Xu J,Chu T,Jin B.Epidermal Growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in advanced squamous cell lung cancer[J].Clin Lung Cancer,2016,17(4):309-314.
[15]Clark GM,Zborowski DM,Santabarbara P,et al.Smoking history and epidermal growth factor receptor expression as predictors of survival benefit from erlotinib for patients with non-small-cell lung cancer in the national cancer institute of canada clinical trials group study BR21[J].Clin Lung Cancer,2006,7(6):389-394.
(2016-09-08收稿)
(2016-11-07修回)
(编辑:杨红欣 校对:郑莉)
Clinical efficacy of EGFR-TKIs for advanced squamous-cell lung cancer patients with EGFR mutations
Hongbo WU,Mingzhi LI,Liang SHI,Hong TAO,Junfang TANG,Zhe LIU
Hongbo WU;E-mail:doctorwu75@163.com
Department of Medical Oncology,Beijing Chest Hospital,Capital Medical University,Beijing 101149,China.
epidermal growth factor receptor,tyrosine kinase inhibitors,squamous-cell lung cancer,mutation

10.3969/j.issn.1000-8179.2016.24.063
首都医科大学附属北京胸科医院肿瘤科(北京市101149)
吴洪波doctorwu75@163.com
AbstracObjective:To investigate the clinical efficacy of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors(EGFR-TKIs)in the treatment of squamous-cell lung cancer patients with EGFR mutations.Methods:We screened out seven patients who were diagnosed with EGFR mutations and received EGFR-TKIs,such as gifitinib or erlotinib,from 2,317 squamous-cell lung cancer patients treated at the Beijing Chest Hospital from January 2010 to July 2016.Results:After using EGFR-TKIs,the objective response rate was 42.9%, the disease control rate was 100%,and the median progression-free survival was 6.1 months.Conclusion:EGFR-TKIs exert a certain clinical curative effect on patients with EGFR mutations in squamous-cell lung cancer.However,given that only seven cases are presented in this research group,more cases are needed for further research to verify the above conclusion.
吴洪波专业方向为肺癌的内科治疗。
E-mail:doctorwu75@163.com

