Src激酶抑制剂ZD6474对乳腺癌MCF-7细胞增殖的影响及机制
Src激酶抑制剂ZD6474对乳腺癌MCF-7细胞增殖的影响及机制
赵玉涛,杨迎花,赵剑平
(邯郸市中心医院,河北邯郸 056001)
摘要:目的探讨Src激酶抑制剂ZD6474对乳腺癌MCF-7细胞增殖的影响及机制。方法取对数生长期的MCF-7细胞,分别加入1×10-6 mol/L、1×10-5 mol/L、1×10-4 mol/L、1×10-3 mol/L、1×10-2 mol/L的Src激酶抑制剂ZD6474。采用MTT法测算细胞增殖抑制率。采用Transwell法检测 MCF-7细胞体外侵袭能力。采用Western blotting法检测E-钙黏素(E-cadherin)及β-连环蛋白(β-catenin)蛋白表达。采用报告基因技术检测Snail启动子的转录活性。采用real-time PCR法检测E-cadherin和β-catenin mRNA表达。结果 ZD6474作用浓度为1×10-5 mol/L和1×10-4 mol/L时,细胞增殖抑制率分别为12.2%和27.5%。MCF-7细胞经ZD6474处理后,体外侵袭能力明显下降,1×10-6 mol /L、1×10-5 mol/L、1×10-4 mol/L、1×10-3 mol/L、1×10-2mol /LZD6474作用MCF-7细胞体外侵袭能力分别为8.3%、14.2%、32.6%、51.4%、76.5%。Src激酶抑制剂作用后E-cadherin mRNA和蛋白表达上调,β-catenin mRNA和蛋白表达及Snail启动子转录活性下调。结论 Src蛋白激酶抑制剂ZD6474可抑制乳腺癌细胞增殖,其机制可能通过上调E-caherin表达,下调β-catenin表达,减弱Snail启动子转录活性,从而抑制乳腺癌细胞的侵袭和转移。
关键词:乳腺癌;Src激酶抑制剂;细胞增殖
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2015.45.005
中图分类号:R737.9 文献标志码:A
基金项目:河北省卫生厅科研
作者简介:第一赵玉涛(1977-),女,主管护师,主要从事血液肿瘤研究。 E-mail:1909563788@qq.com
作者简介:通信赵剑平(1976-),女,主管护师,主要从事肿瘤免疫学研究。E-mail:bairui.lv@hotmail.com
收稿日期:(2015-06-24)
Influence of Src kinase inhibitor ZD6474 on breast cancer
MCF-7 cells and its mechanism
ZHAOYu-tao,YANGYing-hua,ZHAOJian-ping
(HandanCentralHospital,Handan056001,China)
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the effects of Src kinase inhibitor ZD6474 on the proliferation of human breast cancer MCF-7 cells and its mechanism. Methods MCF-7 cells in logarithmic phase were treated with different concentrations of Src kinase inhibitor ZD6474 (1×10-6 mol/L, 1×10-5 mol /L, 1×10-4 mol /L, 1×10-3 mol /L and 1×10-2 mol /L). The cell growth inhibition rate was calculated by MTT method. Transwell assay was used to detect the invasion ability of MCF-7 cells in vitro. Western blotting was used to detect the protein expression of Src, E-cadherin and β-catenin. The activity of Snail promoter was detected by reporter gene technology. Real-time PCR was used to detect the mRNA expression of E-cadherin and β-catenin.ResultsWhen the MCF-7 cells were treated with ZD6474 at the concentrations of 1×10-5 mol/L and 1×10-4 mol/L, the inhibition rates were 12.2% and 27.5%. The invasion ability of MCF-7 cells in vitro was significantly decreased after being treated with ZD6474. The invasion abilities of MCF-7 cells treated with 1×10-6 mol/L, 1×10-5 mol/L,1×10-4 mol/L,1×10-3 mol/L and 1×10-2 mol/L ZD6474 were 8.3%, 14.2%, 32.6%, 51.4% and 76.5%, respectively. Src tyrosine kinase inhibitor significantly up-regulated the expression of E-cadherin at protein and mRNA levels, and down-regulated the expression of β-catenin at protein and mRNA levels as well as promoter activity of Snail.ConclusionSrc kinase inhibitor ZD6474 could inhibit the proliferation of breast cancer cells, up-regulate the activity of E-caherin, down-regulate the expression of β-catenin and decrease the activity of Snail promoter, and thus it inhibits the invasion and metastasis of breast cancer cells.
Key words: breast carcinoma; Src kinase inhibitor; cell proliferation
女性乳腺由皮肤、纤维组织、乳腺腺体和脂肪组成,乳腺癌是发生在乳腺腺上皮组织的恶性肿瘤[1]。乳腺癌中女性占99%,男性仅占1%。乳腺癌发病率占全身各种恶性肿瘤的7%~10%,仅次于子宫癌[2]。肿瘤上皮间质转变和肿瘤浸润及转移的关系备受关注,可使无侵袭的肿瘤细胞获得浸润能力,促进肿瘤形成局部浸润和远端转移[3]。Src基因是第一个被发现的有内在酪氨酸激酶活性的人类癌基因。Src蛋白作为非受体酪氨酸激酶,介导黏附因子、趋化因子、生长因子等多条下游信号通路[4,5]。2014年9月~2015年4月,我们探讨了Src激酶抑制剂ZD6474对乳腺癌MCF-7细胞增殖的影响及机制。现报告如下。
1材料与方法
1.1材料人乳腺癌MCF-7细胞购于中国科学院上海细胞生物研究所。Src激酶抑制剂ZD6474购自AstraZeneea公司;单克隆抗体购自Biotech公司;化学发光HRP底物购自Millipore公司;Real-time PCR系统购自ABI公司;Transwell购自Costar公司;双荧光报告基因检测系统购自Promega公司;二甲基亚砜(DMSO)、DMEM 培养基、MTT购自Promega公司。
1.2细胞培养人乳腺癌MCF-7细胞用含10%胎牛血清的DMEM培养基,在5%CO2、37 ℃饱和湿度培养箱中培养。
1.3细胞增殖抑制率的测算采用 MTT法。取对数生长期的MCF-7细胞,制成悬液,进行细胞计数,取5×103个细胞接种至96孔板中,37 ℃、5% CO2饱和湿度培养24 h后,实验组分别加入不同浓度(1×10-6mol /L、1×10-5mol/L、1×10-4mol/L、1×10-3mol/L、1×10-2mol/L)的Src激酶抑制剂ZD6474,分别设置细胞对照(对照组)及空白对照,每组样本设5个复孔,温育48 h后,加入MTT,培养2 h后于490 nm处测定吸光度值(A值)。细胞增殖抑制率=(1-实验组A值/对照组A值)×100%。
1.4MCF-7细胞体外侵袭能力检测采用Transwell法。SRC激酶抑制剂ZD6474处理对数生长期的MCF-7细胞48 h后,将8 μm孔径聚碳酸酯微孔滤膜的Transwell小室4 ℃预冷后,小室上层均匀平铺25 μL Matrigel胶,37 ℃孵育3 h。将含5×105个细胞的0.1% BSA悬液加到上室,下室加入600 μL的0.1% BSA,37 ℃培养24 h。取出膜,膜上层剩余细胞,甲醛固定膜下层细胞,苏木精染色,高倍光学显微镜下计数,取平均值,计算百分比。
1.5Src、E-cadherin及β-catenin蛋白表达检测采用Western blotting法。将人乳腺癌MCF-7细胞接种于直径10 cm培养皿上,待细胞长满培养皿的90%时,给予不同浓度的Src激酶抑制剂ZD6474(1×10-6mol /L、1×10-5mol/L、1×10-4mol/L、1×10-3mol /L、1×10-2mol /L),37 ℃下温育6 h,用预冷的PBS漂洗2次,立即加入300 mL细胞裂解液,14 000 r/min离心5 min,取上清液,用蛋白分析试剂测量提取蛋白的浓度。取80 μg蛋白质,应用12% SDS-PAGE法进行分离后,转移至PVDF膜,5%的脱脂牛奶室温封闭1 h,加入兔抗人Src酪氨酸磷酸化特异性多克隆抗体1∶500稀释,鼠抗人E-cadherin单克隆抗体1∶500稀释,鼠抗人β-catenin单克隆抗体1∶500稀释,1∶200稀释的鼠抗人β-actin单克隆抗体作为内对照,4 ℃反应过夜,用含0.1%Tween 20的TBS洗膜,加入1∶1 000稀释的辣根过氧化物酶标记的二抗,室温下反应1 h,洗膜后显色,将条带结果进行扫描。
1.6Snail启动子转录活性的检测 取对数生长期的MCF-7细胞,接种于6孔板,用不同浓度ZD6474温育6 h,应用Lipofec-tamineTM2000转染pSnail-luc和CMV启动子海肾荧光酶内标报告基因载体24 h后,用双荧光酶测定试剂盒检测Snail启动子的转录活性,计算萤火虫荧光酶激发光子数目和海肾荧光酶激发光子数目的比值。
1.7E-cadherin及β-catenin mRNA表达检测采用real-time PCR法。取对数生长期的MCF-7细胞,接种于6孔板,用不同浓度的Src激酶抑制剂ZD6474在37 ℃条件下温育6 h,2 000 r/min离心10 min、细胞收集后用TRIzol抽提总RNA,并将GAPDH作为内参照,用以下引物序列扩增:GAPDH上游引物序列5′-CCACCCATGGCAAATTCCACTA-3′,下游引物序列5′-GATGGGAATTCCATTGATGACA-3′;β-catenin上游引物序列5′-GCTCTTCGTCATCTGACCAGCC-3′,下游引物序列5′-GAGCAAGGTCACAGAGGACCC-3′; E-cadherin上游引物序列5′-CACTGACACCAACGATAATCC-3′,下游引物序列5′-TCAGTGTGGTGATTACGACGTT-3′。扩增条件:预变性94 ℃,5 min,共进行35个循环扩增,每一循环包括95 ℃ 5 s、65 ℃ 35 s。
1.8统计学方法采用SPSS11.0统计软件。数据统计采用t检验与方差分析。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2结果
2.1ZD6474对人乳腺癌MCF-7细胞增殖能力的影响 1×10-6mol /L、1×10-5mol/L、1×10-4mol/L、1×10-3mol /L、1×10-2mol /L的ZD6474处理MCF-7细胞后,MCF-7细胞增殖明显受抑,且随着药物浓度的加大,细胞增殖的抑制作用越明显,且呈现剂量依赖性。在ZD6474浓度为1×10-6mol/L、1×10-5mol/L、1×10-4mol/L、1×10-3mol /L、1×10-2mol /L时,MCF-7细胞增殖抑制率分别为5.3%、12.1%、27.8%、48.6%、67.3%。
2.2ZD6474 对人乳腺癌MCF-7细胞体外侵袭能力的影响 MCF-7细胞经ZD6474处理后,体外侵袭能力明显下降,1×10-6mol /L、1×10-5mol/L、1×10-4mol/L、1×10-3mol/L、1×10-2mol /L ZD6474作用后,MCF-7细胞体外侵袭能力分别为8.3%、14.2%、32.6%、51.4%、76.5%。
2.3ZD6474对MCF-7细胞Src、E-cadherin及β-catenin蛋白表达的影响MCF-7细胞经ZD6474(1×10-6mol /L、1×10-5mol/L、1×10-4mol/L、1×10-3mol /L)处理后,Src、E-cadherin及β-catenin蛋白表达呈明显剂量依赖性(P均<0.05),结果见表1、图1、图2。
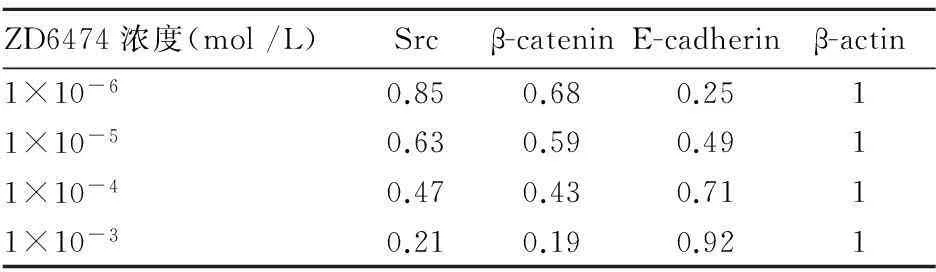
表1 不同浓度的ZD6474对MCF-7细胞中Src、
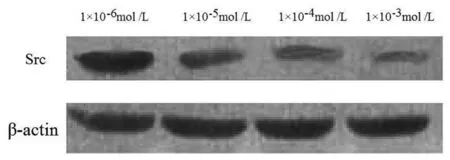
图1 ZD6474对MCF-7细胞中Src蛋白表达的影响
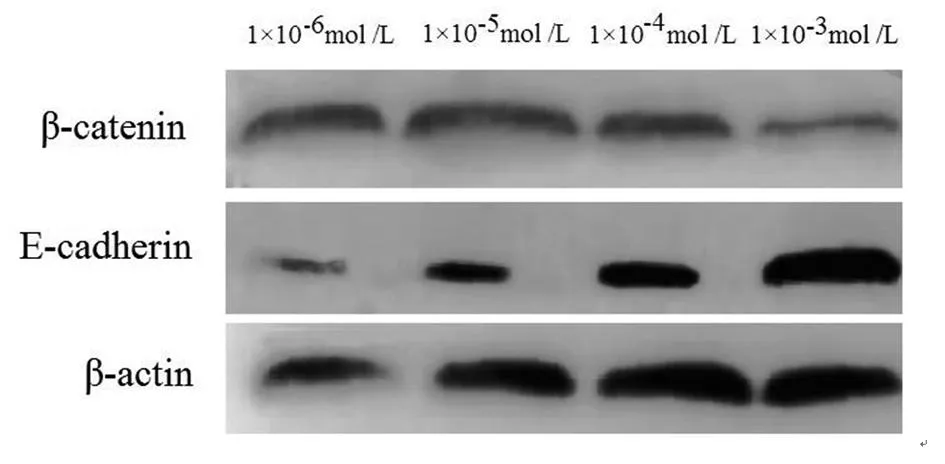
图2 ZD6474对MCF-7细胞中E-cadherin和
2.4ZD6474对MCF-7细胞Snail启动子转录活性的影响ZD6474作用人乳腺癌MCF-7细胞后,Snail启动子转录活性随ZD6474浓度的增加而减弱。对照、1×10-6mol /L、1×10-5mol/L、1×10-4mol/L、1×10-3mol /L、1×10-2mol /L的ZD6474作用后,MCF-7细胞Snail启动子转录活性分别为100%、57.3%、49.6%、35.2%、19.4%、11.2%。
2.5ZD6474对MCF-7细胞E-cadherin、β-catenin mRNA表达的影响经ZD6474处理后,E-cadherin mRNA表达呈明显上升趋势,并随着ZD6474浓度增加,E-cadherin mRNA表达增加,β-catenin mRNA表达呈下降趋势,并呈剂量依赖性(P<0.05,表2)。
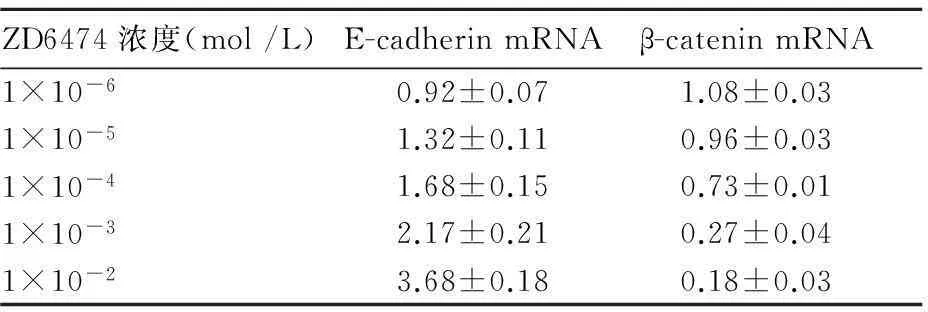
表2 不同浓度的ZD6474对MCF-7细胞中E-cadherin、
3讨论
目前乳腺癌已成为威胁女性身心健康的常见肿瘤。临床应用的内分泌治疗是采用药物或去除内分泌腺体的方法来调节机体内分泌功能[6,7],减少内分泌激素的分泌量,从而达到治疗乳腺癌的目的,乳腺并不是维持人体生命活动的重要器官,原位乳腺癌并不致命,但由于乳腺癌细胞丧失了正常细胞的特性,细胞之间连接松散,容易脱落。癌细胞一旦脱落,游离的癌细胞可随血液或淋巴播散全身,形成转移,危及生命[8~10]。尽管近些年来对乳腺癌的研究已取得了很大进展,但对于其发病机制和转移机制尚不清楚。
恶性肿瘤发生发展、浸润和转移是一个极其复杂的过程。Src基因是第一个被发现的有内在酪氨酸激酶活性的人类癌基因。Src蛋白作为非受体酪氨酸激酶,介导生长因子、黏附因子、趋化因子等多条下游信号通路[10]。乳腺癌组织中Src表达显著升高,且常存在异常活化,介导下游多条信号通路的改变。Src的过度表达和活化在调节肿瘤血管生成、细胞增殖、生存、迁移及侵袭等方面起重要作用[11~13]。ZD6474作为Src 激酶抑制剂,迄今鲜见其对肿瘤细胞生物学特性的影响及机制研究[14]。Src是一种膜相关的无需受体的信号传导蛋白激酶,在各类细胞与细胞间的黏附分子接头中大量存在于肝癌细胞中。E-cadherin的胞质区域通过细胞质蛋白与细胞骨架的肌动蛋白丝相连,亦是细胞转移的抑制因子,能降低癌细胞的转移能力[15~17]。因此,本研究通过ZD6474处理人乳腺癌MCF-7细胞,然后检测其增殖和转移能力的变化,从而阐明ZD6474对乳腺癌细胞增殖和转移的作用。Src 激酶在多数恶性肿瘤组织中过表达,在外界信号通过细胞表面受体传导入细胞内的过程中,Src 活化并磷酸化细胞内大量的酶作用底物,通过复杂的信号传导到E-caherin,最终影响细胞间黏附能力。
本研究我们发现,人乳腺癌MCF-7细胞经ZD6474处理后,Src、β-catenin蛋白表达水平明显降低,E-cadherin 表达水平显著增高。通过肿瘤细胞黏附实验和体外侵袭实验发现,乳腺癌MCF-7细胞经ZD6474处理后,黏附及侵袭能力显著下降,且呈浓度依赖性。MTT试验检测人乳腺癌MCF-7细胞的增殖情况,结果显示ZD6474能明显抑制细胞的增殖。
Snail是一种锌指转录因子,有促进细胞迁移的作用,与肿瘤浸润和转移密切相关。沉默肿瘤细胞中Snail表达能显著抑制肿瘤的生长与侵袭。乳腺癌细胞MCF-7被Src特异性阻断剂作用后,Snail启动子转录活性随阻断剂浓度的增加而减弱,提示Snail高表达与乳腺癌侵袭和转移明显相关,这些现象表明如果抑制Src激酶表达,有可能使 E-caherin表达上调,降低恶性肿瘤的转移。
综上所述,Src激酶抑制剂ZD6474对乳腺癌细胞增殖有良好的抑制作用,其机制可能是通过上调E-caherin表达,下调β-catenin表达,减弱Snail启动子转录活性,从而抑制乳腺癌细胞的增殖和侵袭能力。
参考文献:
[1] Elsberger B. Translational evidence on the role of Src kinase and activated Src kinase in invasive breast cancer[J]. Crit Rev Oncol Hemat, 2015,89(3):343-351.
[2] Fan P, Agboke FA, McDaniel RE. et al.Inhibition of c-Src blocks oestrogen-induced apoptosis and restores oestrogen-stimulated growth in long-term oestrogen-deprived breast cancer cells[J]. Eur J Cancer, 2015,50(2):457-468.
[3] Kirkegaard T, Hansen SK, Larsen SL, et al. T47D breast cancer cells switch from ER/HER to HER/c-Src signaling upon acquiring resistance to the antiestrogen fulvestrant[J]. Cancer Lett, 2014,344(1):90-100.
[4] Yun SJ, Hee JC, Sook JK, et al.Src family kinase inhibitor PP2 enhances differentiation of acute promyelocytic leukemia cell line induced by combination of all-trans-retinoic acid and arsenic trioxide[J].Leukemia Res, 2014,38(8):977-982.
[5] Moschetta M, Telegrafo M, Rella L, et al. Let′s go out of the breast: prevalence of extra-mammary findings and their characterization on breast MRI[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2014,83(6):930-934.
[6] Atthias W, Stefanie S, Young E, et al. Src-kinase inhibitors sensitize human cells of myeloid origin to Toll-like-receptor-induced interleukin 12 synthesis [J] . Blood, 2013,122(7):1203-1213.
[7] Austreid E, Lonning PE, Eikesdal HP, et al. The emergence of targeted drugs in breast cancer to prevent resistance to endocrine treatment and chemotherapy[J]. Expert Opin Pharmacol, 2014,15(5):681-700.
[8] Jie G, Hai G, Xiao W, et al. SRC kinase family inhibitor PP2 promotes DMSO-induced cardiac differentiation of P19 cells and inhibits proliferation[J]. Inter J Cardiol, 2015,167(4):1400-1405.
[9] Fang XQ, Liu XF, Yao L, et al. Somatic mutational analysis of FAK in breast cancer: A novel gain-of-function mutation due to deletion of exon 33[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2014,443(2):363-369.
[10] Kiarashi N, Lo JY, Lin Y, et al. Development and Application of a Suite of 4-D Virtual Breast Phantoms for Optimization and Evaluation of Breast Imaging Systems[J]. IEEE Trans Med Imag, 2014,33(7):1401-1409.
[11] Jiang WW, Li AH, Zheng YP, et al. A semi-automated 3-d annotation method for breast ultrasound imaging: System development and feasibility study on phantoms[J]. Ultra Med Biol, 2014,40(2):434-446.
[12] Moran MS, Schnitt SJ, Giuliano AE, et al. Society of surgical oncology-American society for radiation oncology consensus guideline on margins for breast-conserving surgery with whole-breast irradiation in stages i and II invasive breast cancer[J]. Int J Rad Oncol, 2014,88(3):553-564.
[13] Li HY, Cui XY, Wu W, et al. Pyk2 and Src mediate signaling to CCL18-induced breast cancer metastasis[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2014,115(3):596-603.
[14] Dos S, Tinisha M, Yin WH, et al. The Src and c-Kit kinase inhibitor dasatinib enhances p53-mediated targeting of human acute myeloid leukemia stem cells by chemotherapeutic agents [J]. Blood, 2015,122(11):1900-1913.
[15] Molina JR, Foster NR, Reungwetwattana T, et al. A phase II trial of the Src-kinase inhibitor saracatinib after four cycles of chemotherapy for patients with extensive stage small cell lung cancer: NCCTG trial N-0621[J]. Lung Cancer, 2014,85(2):245-250.
[16] Zhang F, Zhang H, Wang Z, et al. P-glycoprotein associates with Anxa2 and promotes invasion in multidrug resistant breast cancer cells[J]. Biochem Pharmcol, 2014,87(2):292-302.
[17] DeLuca A, DAlessio A, Gallo M. et al. Src and CXCR4 are involved in the invasiveness of breast cancer cells with acquired resistance to lapatinib[J]. Cell Cycle, 2014,13(1):148-156.

