Green GDP Accounting in Yellow River Delta
Department of Resources and Environment, Binzhou University, Binzhou 256603, China
1 Introduction
The current GDP does not exclude the economic losses arising from environmental pollution, degradation of natural resources, low education, mushrooming population, mismanagement and other factors, so it can not truly reflect the real total national wealth. To truly reflect the level of regional economic development, it is necessary to correct the existing GDP data and make accounting of its green GDP. By estimating the economic losses caused by water pollution, air pollution and noise pollution in Yellow River Delta in 2010, this paper recalculates the green GDP in this typical region, to reflect the true level of economic development in the region, and provide a reference for local authorities to adjust economic development model and achieve coordinated development of environment and economy.
2 Data sources and estimation methods
Table 1 shows the environmental and economic data and methods for estimating the economic losses due to water pollution, air pollution and noise pollution.
3 Results and discussions
3.1WaterpollutionlossestimationAccording to the discharge amount of domestic sewage and industrial wastewater as well as COD and ammonia nitrogen emission in Yellow River Delta in 2009[1-2], we use concentration-value loss factor[3]to estimate the water pollution loss in Yellow River Delta, as shown in Table 2. From Table 2, it can be found that due to COD and ammonia nitrogen pollution, the total waste water value losses in 2009 reached 477.78497 million yuan (domestic sewage, 304.23712 million yuan; industrial wastewater, 173.54785 million yuan), having a certain impact on the regional economic development. According to the product of share of pollution losses in GDP in 2009 and GDP in 2010, the economic losses caused by water pollution in 2010 were estimated at about 541.5814 million yuan.
3.2AirpollutionlossestimationAccording to the population data and PM10concentration in Yellow River Delta in 2010, we use Poisson regression and proportional hazards model[4-6], to estimate the health risk economic losses and excess mortality economic losses caused by PM10pollution. The results are shown in Table 3, 4. In 2010, the health risk economic losses caused by respirable particulate matter (PM10, reference concentration of 40 μg/m3) in Yellow River Delta reached 163.1369 million yuan, and the excess mortality economic losses reached 33.4742 million yuan, a total of 196.6111 million yuan.
3.3NoisepollutionlossestimationBy WTP method[7], we study the residents’ willingness to pay for improving noise environment pollution in Binzhou City, and estimate the losses caused by noise pollution. We calculate the residents’ willingness to pay in other regions by adjusting the income level. The ratio of per capita willingness to pay for the two regions is equal to the ratio of per capita annual income. Through questionnaires and statistical analysis, it is found that 71.3% of residents are willing to pay for improving environmental noise, an average of 3.64 yuan/(person·month). The population data about Yellow River Delta in 2010 are obtained from the relevant statistical yearbook, and the residents’ willingness to pay in other regions is adjusted by the per capita GDP. The ratio of per capita willingness to pay for the two regions is equal to the ratio of per capita GDP. The pollution loss estimation results are shown in Table 5. The economic losses caused by noise pollution in Yellow River Delta reached 594.2768 million yuan in 2010.
Table1Thedataandmethodsforestimatingtheenvironmentalpollutionlosses
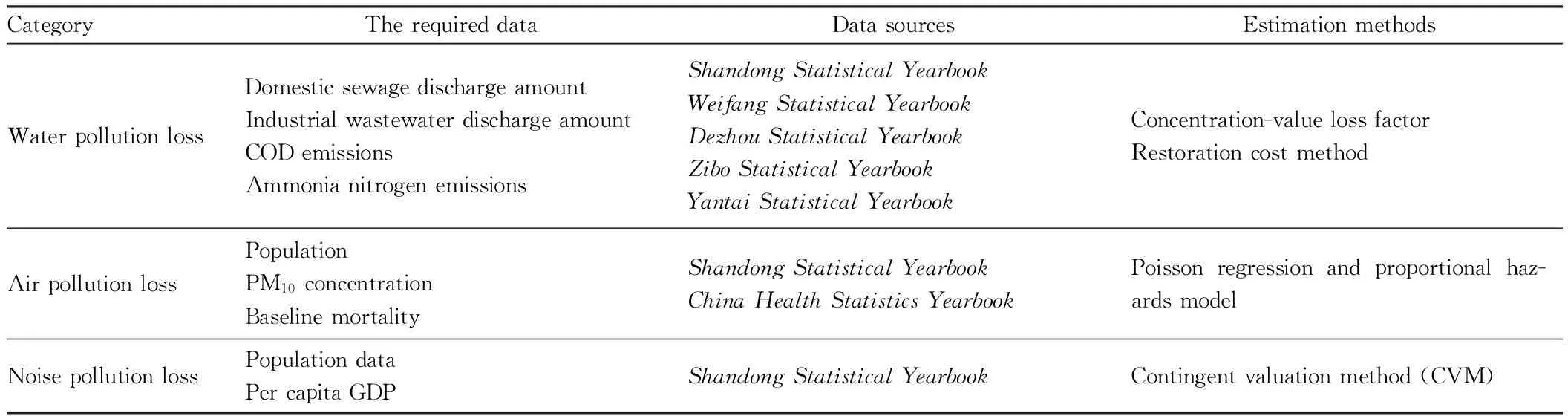
CategoryTherequireddataDatasourcesEstimationmethodsWaterpollutionlossDomesticsewagedischargeamountIndustrialwastewaterdischargeamountCODemissionsAmmonianitrogenemissionsShandongStatisticalYearbookWeifangStatisticalYearbookDezhouStatisticalYearbookZiboStatisticalYearbookYantaiStatisticalYearbookConcentration-valuelossfactorRestorationcostmethodAirpollutionlossPopulationPM10concentrationBaselinemortalityShandongStatisticalYearbookChinaHealthStatisticsYearbookPoissonregressionandproportionalhaz-ardsmodelNoisepollutionlossPopulationdataPercapitaGDPShandongStatisticalYearbookContingentvaluationmethod(CVM)
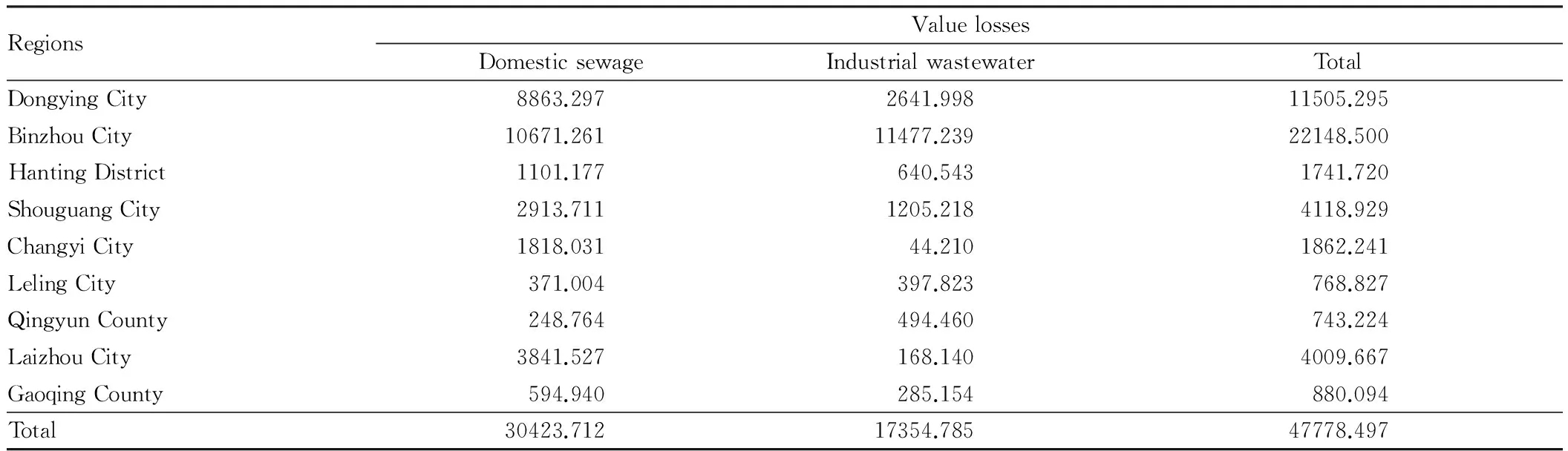
Table 2 The value losses caused by water pollution in Yellow River Delta Unit: 104 yuan
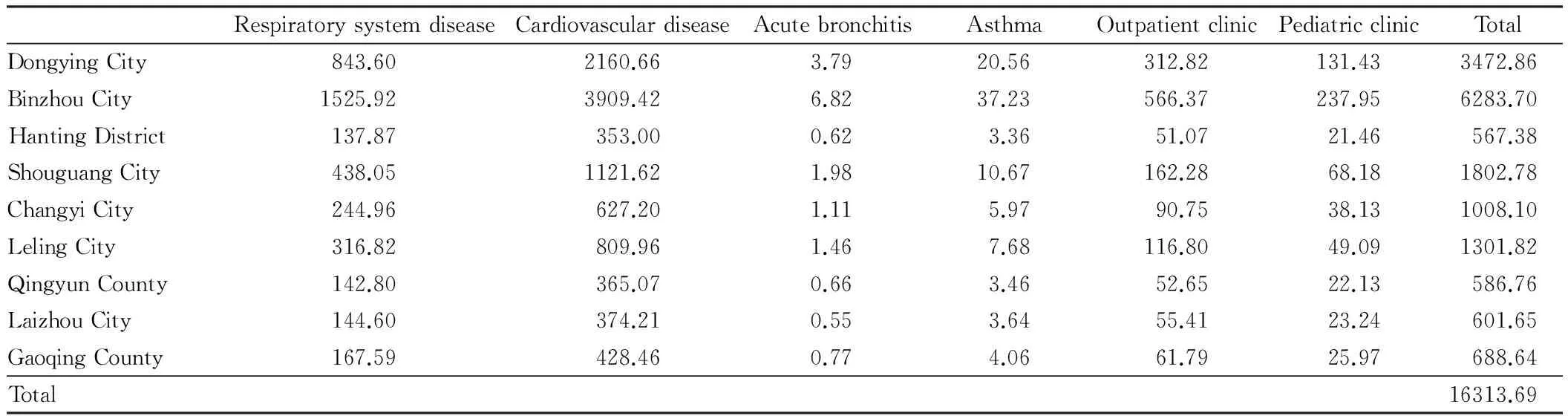
Table 3 The health risk economic losses caused by PM10 in Yellow River Delta in 2010 Unit: 104 yuan
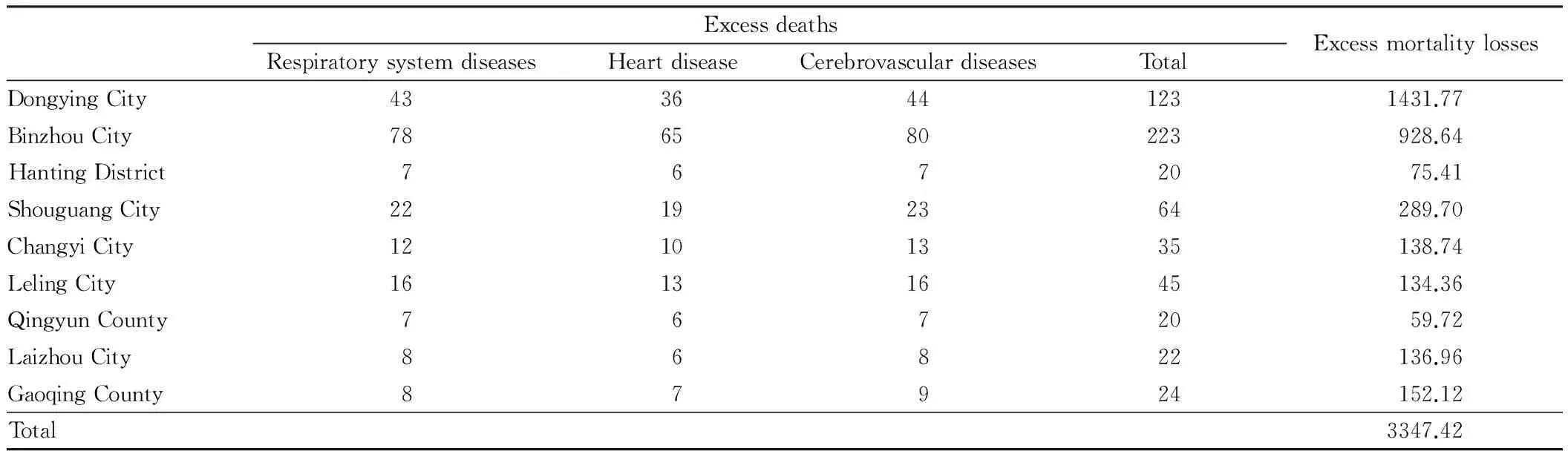

Table 4 The excess mortality economic losses caused by PM10 in Yellow River Delta in 2010 Unit: 104 yuan
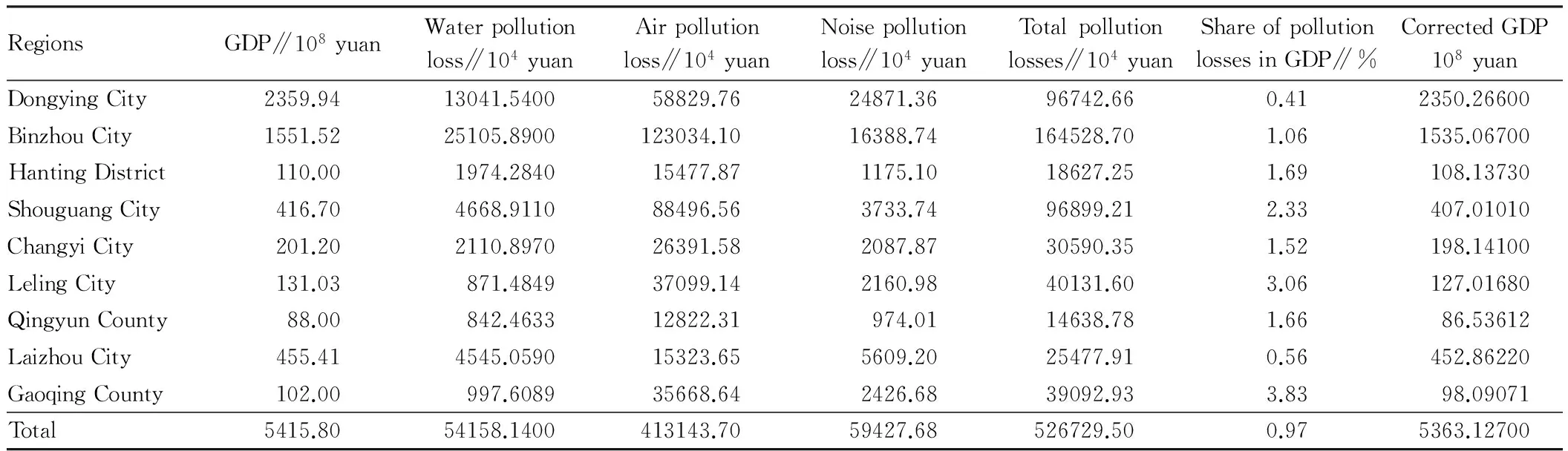
3.4GreenGDPaccountinginYellowRiverDeltaFor the economic losses caused by environmental pollution in Yellow River Delta, this paper mainly estimates the losses caused by water pollution, air pollution and noise pollution in 2010 (water pollution loss of about 541.5814 million yuan; air pollution loss of about 1569.3401 million yuan; noise pollution loss of 594.2768 million yuan; total losses of 2705.198 million yuan). Due to the limited information, this paper does not consider the losses caused by solid waste pollution and radioactive pollution, and the estimated value is small, but it still provides a certain reference for understanding the impact of regional environmental pollution on economic development. In addition, the GDP correction in this paper is not overall correction, and it only estimates the value accounting part. By deducting environmental pollution losses from total GDP, we get a GDP value by the environmental correction, with certain reference value, and the specific accounting results are shown in Table 6, indicating that the environmental pollution losses have a great impact on the local GDP.
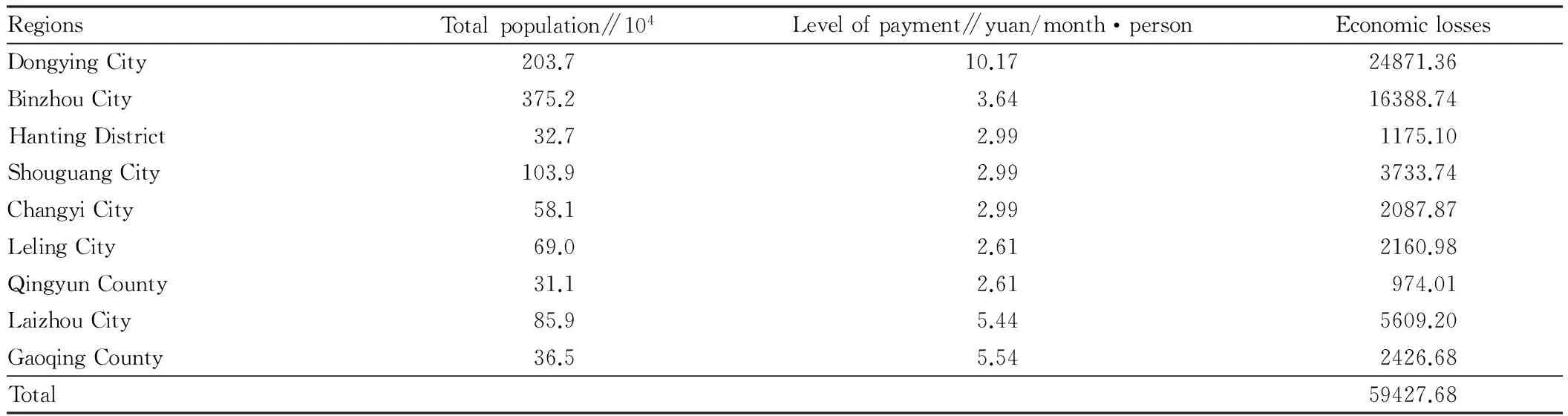
Table 5 The economic losses caused by noise pollution in Yellow River Delta Unit: 104 yuan
Table6GreenGDPaccountingresultsinYellowRiverDeltain2010
RegionsGDP∥108yuanWaterpollutionloss∥104yuanAirpollutionloss∥104yuanNoisepollutionloss∥104yuanTotalpollutionlosses∥104yuanShareofpollutionlossesinGDP∥%CorrectedGDP108yuanDongyingCity2359.9413041.540058829.7624871.3696742.660.412350.26600BinzhouCity1551.5225105.8900123034.1016388.74164528.701.061535.06700HantingDistrict110.001974.284015477.871175.1018627.251.69108.13730ShouguangCity416.704668.911088496.563733.7496899.212.33407.01010ChangyiCity201.202110.897026391.582087.8730590.351.52198.14100LelingCity131.03871.484937099.142160.9840131.603.06127.01680QingyunCounty88.00842.463312822.31974.0114638.781.6686.53612LaizhouCity455.414545.059015323.655609.2025477.910.56452.86220GaoqingCounty102.00997.608935668.642426.6839092.933.8398.09071Total5415.8054158.1400413143.7059427.68526729.500.975363.12700
4 Conclusions
In this paper, through the estimation and analysis, it can be found that due to COD and ammonia nitrogen pollution, the water pollution caused economic losses of about 541.5814 million yuan in the Yellow River Delta in 2010; particulate matter caused health risk economic losses of 163.1369 million yuan, and excess mortality economic losses of 33.4742 million yuan; noise pollution caused economic losses of 594.2768 million yuan. The total losses reach approximately 2705.198 million yuan, accounting for 0.97% of the total GDP. After subtracting the total losses from the total regional GDP (541.58 billion yuan), the revised green GDP is about 536.3127 billion yuan. Obviously, environmental pollution has a certain impact on the economic growth. It is necessary to consider the carrying capacity of the environment, and achieve the coordinated development of environment and economy by adjusting the industrial structure, developing circular economy and so on.
[1] Shandong Provincial Statistics Bureau. Shandong Statistical Yearbook
(2009)[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press,2010. (in Chinese).
[2] Weifang, Dezhou, Zibo, Yantai Statistics Bureau. Weifang, Dezhou, Zibo, Yantai Statistical Yearbook(2009)[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press,2010. (in Chinese).
[3] JAMES LD. Water resources planning economics [M]. CHANG XH,etal. (Translator). Beijing: China Water & Power Press,1984. (in Chinese).
[4] HONG XJ, KAN HD, CHEN BH. Methods of health risk assessment of urban air pollution [J].Journal of Environment and Health,2005,22(1):62-64. (in Chinese).
[5] XIE P, LIU XY, LIU ZR,etal. Exposure-response functions for health effects of ambient particulate matter pollution applicable for China [J]. China Environmental Science,2009,29(10):1034-1040. (in Chinese).
[6] JING LB, QIN Y, XU ZY. Relationship between air pollution and acute and chronic respiratory diseases in Benxi [J]. Journal of Environment and Health,2000,17(5):268-270. (in Chinese).
[7] XU YH, SHAN HG. The estimation of economic losses of environmental pollution in Dalian City [J]. Liaoning Urban and Rural Environmental Science & Technology,2001,21(5):38-41. (in Chinese).
 Asian Agricultural Research2016年9期
Asian Agricultural Research2016年9期
- Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Empirical Study on the Relationship between Organizational Flexibility and Performance of Agricultural Enterprise
- Correlation between Employment Quality and Skill Training of Land-expropriated Farmers
- A Study on Spatial Distribution of Commercial Housing Prices in Xiangtan City
- Design and Experiment of Fluid Dynamic Ultrasonic Water Aerator
- The Relation between Age Structure of Population and Resident Consumption Based on Endogenous Growth Theory
- Effect of Different Pretreatments on Explosion Puffing Drying of Hami Melon at Modified Temperature and Pressure in Xinjiang
