以吡嗪四甲酸为配体的配合物的合成及表征
高洪苓 毕艳霞 张琴琴 崔建中
(天津大学理学院化学系,天津300072)
以吡嗪四甲酸为配体的配合物的合成及表征
高洪苓 毕艳霞 张琴琴 崔建中*
(天津大学理学院化学系,天津300072)
合成了两种金属配合物{[Cu2(pztc)(4,4′-bpy)(H2O)4]·6H2O}n(1),{(H2bpe)[Cd(pztc)(H2O)2]·2.5H2O}n(2)(H4pztc=吡嗪-2,3,5,6-四甲酸,bpy=4,4′-联吡啶,bpe=1,2-二(4-吡啶基)乙烯),测定了其晶体结构,并对其进行了红外光谱、荧光光谱和热重分析等表征。两种配合物均为二维层状结构,但其中吡嗪四酸的配位方式不同。配合物2具有蓝色的荧光,最大荧光发射峰在475 nm。测试了配合物1的电子顺磁共振谱,结果显示Cu2+的特征谱带。
吡嗪-2,3,5,6-四甲酸;二维结构;荧光光谱;电子顺磁共振
0Introduction
The self-assembled construction of coordination polymers has not only led to the creation of a huge number of MOFs of diverse topologies and aesthetic beauty,but also produced a series of functional materials with special magnetism,nonlinear optics, and luminescence properties[1-4].The strategy of using metalionsandorganiccarboxylatesasstarting building blocks to get extended networks has been of great interest for the chemists[5-6].In the previous works our group have proved that hetero-cyclic polycarboxylic acids,such as pyrazine-2,3,5,6-tetracarboxylic acid(H4pztc)and 6-methyl-2,3,5-pyridinetricarboxylicacid(H3mptc),acting as multidentate carboxylate ligands containing both N-and O-atoms are good candidates to form multiple coordination modes.Both of them are excellent choices for the constructions of metal organic complexes[7-9].Up to now,some complexes of these ligands have been synthesized[10-14].Herein,we expect that pyrazine-2,3,5,6-tetracarboxylic acid act as bridging ligand to achieve the expected networks and we have successfully prepared two new complexes finally.In 1,Cu(Ⅱ)ions are interconnected to 1D chains structure with pztc4-ligands.Such 1D chains are further bridged by 4,4′-bpy to build a 2D lattice structure.In 2,two Cd(Ⅱ)ions are connected by pztc4-ligand togenerate[Cd2(pztc)2(H2O)4],which can be extended to a 2D framework by coordination bonds.
1Experimental
1.1 General
Pyrazine-2,3,5,6-tetracarboxylic acid was synthesized according to a literature method[15]and the other chemicals purchased were reagent grade and used without further purification,Elemental analysis for C,H and N were performed on a Perkin-Elmer 240 CHN elemental analyzer.Infrared spectra were obtained in KBr pellets on a Bruker TENOR 27 spectrophotometer in the range of 400~4 000 cm-1. Thermal gravimetric analysis(TGA)curves were obtained from a NETZSCH TG 209 instrument with a heating rate of 10℃·min-1.Fluorescence spectra were measured on an F-4500 fluorescence spectrophotometer at room temperature.
1.2 Syntheses of the complexes
Complex 1:A mixture of Cu(NO3)2·3H2O(0.024 2 g,0.10 mmol)dissolved in 5 mL H2O and 4,4′-bpy (0.015 6 g,0.10 mmol)dissolved in 3 mL H2O was stirred for 0.5 h at room temperature.Then an aqueous solution of H4pztc(0.012 8 g,0.05 mmol)(5 mL)was added to the mixture.The resulting mixture was continuously stirred for 2 h and filtered.Blue crystals were obtained from the filtrate after slow evaporation of the solution at the room temperature for 7 days.Yield:32%based on Cu.Elemental analysis (%)Calcd.For C18H28Cu2N4O18:C,30.22;H,3.94;N, 7.83;Found:C,30.21;H,3.96;N,7.82.IR(KBr pellet,cm-1):3 344s,1 633vs,1 404s,1 300m,1 155 m,805m,580m.
Complex 2:A mixture of Cd(NO3)2·4H2O(0.007 7 g,0.025 mmol)dissolved in 8 mL H2O and H4pztc (0.006 4 g,0.025 mmol)dissolved in 8 mL H2O was stirred for 0.5 h at room temperature.Then the alcoholic solution of bpe(0.004 6 g,0.025 mmol)(3 mL)was added to the mixture.The pH value was adjusted to 2.1 by HNO3(5%).The resulting mixture was continuously stirred for 2 h and filtered.Colorless crystals were obtained from the filtrate after slow evaporation of the solution at the room temperature for 7 days.Yield:35%based on Cd.Elemental analysis (%)Calcd.For C20H21CdN4O12.5:C,38.14;H,3.36;N, 8.90;Found:C,38.18;H,3.37;N,8.91.IR(KBr pellet,cm-1):3 450s,2 921s,2 850s,1 754m,1 604 vs,1 421m,1 397m,1 141w,831m,765m,536m.
1.3 X-ray crystallography
Single crystal X-ray diffraction measurements of 1 and 2 were recorded on a BRUKER SMART-1000 CCD diffractometer,equipped with graphite-monochromatized Mo Kα radiation(λ=0.071 073 nm),using a ω-φ scan.The structures were solved by direct methodsandrefinedbyfull-matrixleast-squares techniques on F2using the SHELXS and SHELXL-97[16].Anisotropic thermal parameters were assigned to all non-hydrogen atoms.Hydrogen atoms were located andincludedattheircalculatedpositions.The crystallographic data and structural refinement information for 1 and 2 are listed in Table1 .
CCDC:1039147,1;1039296,2.
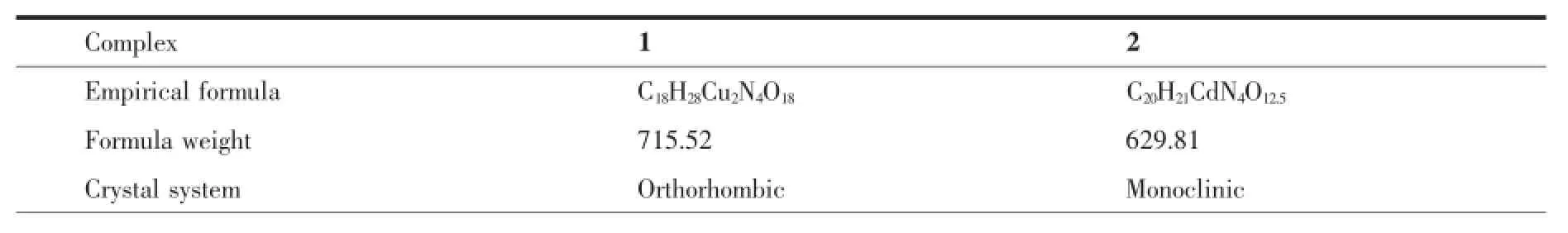
Table1 Crystal data and structure refinement information for 1 and 2
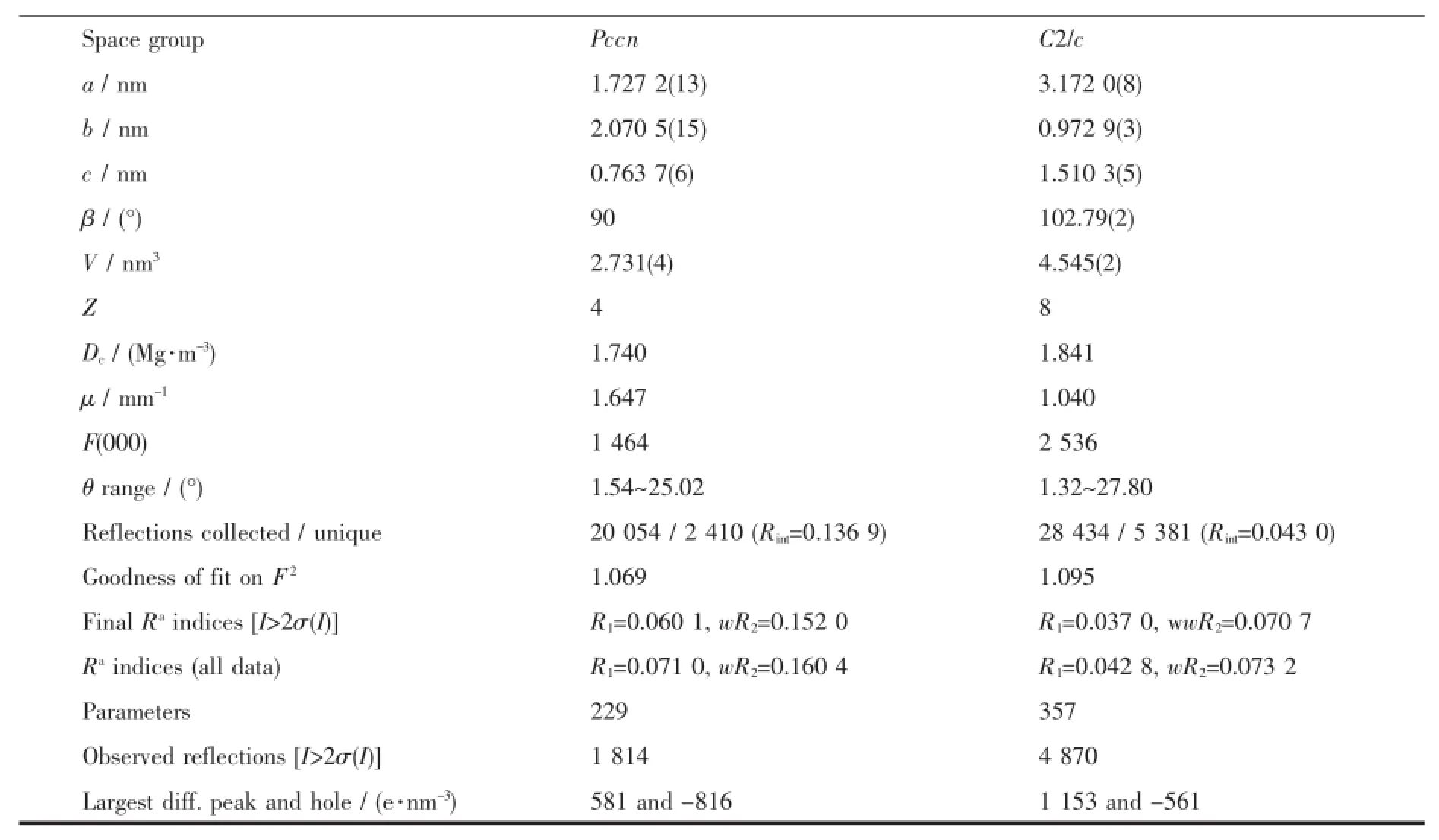
Continued Table1
2Results and discussion
2.1 Structure description
Complex 1 is a copper complex.Complex 1 displays a 2D architecture with the orthorhombic space group.The asymmetric unit contains one Cu(Ⅱ)center,half pztc4-anion,half 4,4′-bpy molecule,two coordinated water molecules,several lattice water molecules.As shown in Fig.1 a,each Cu(Ⅱ)center adopts a distorted octahedral arrangement and is coordinated with two oxygen atoms(O5 and O6)from two water molecules and two nitrogen atoms(N1 and N2)from one pztc4-ligand and one 4,4′-bpy ligand in the equatorial plane,the axial positions are occupied by two oxygen atoms(O1 and O4A)from two pztc4-ligands.The Cu-O bond lengths range from 0.197 4(4) to 0.231 6(4)nm,and the Cu-N bond lengths are in the range of 0.201 3(5)~0.243 9(4)nm.
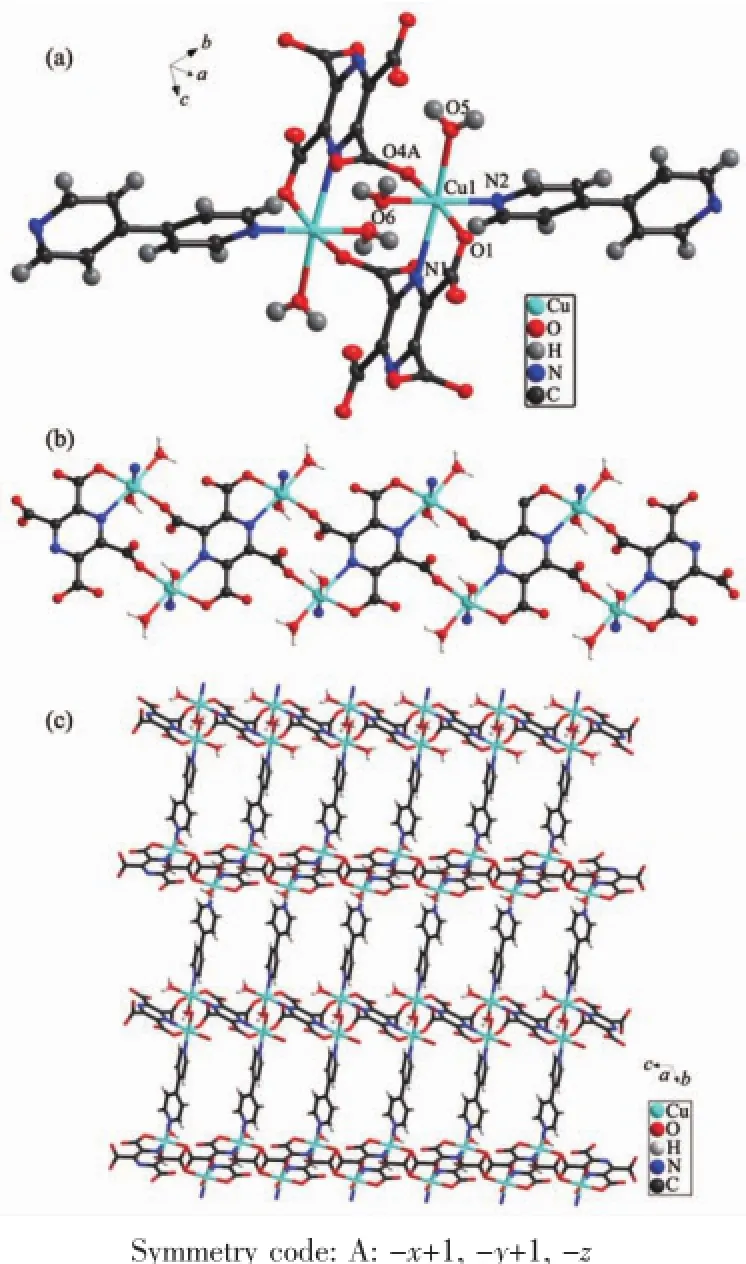
Fig.1 (a)Coordination environment of the Cu ion of 1 shown at the 50%probability level;(b)1D chain structure connected by Cu(Ⅱ)and pztc4-;(c)2D grid structure of 1
In complex 1,H4pztc was completely deprotonated,one pztc4-ligand is connected with four Cu(Ⅱ)ions:two Cu exhibit bidentate chelating coordination modes;twoCuexhibitmonodentatecoordination modes.The pztc4-ligands are joined to form 1D chain by Cu(Ⅱ)ions as shown in Fig.1 b.The 1D chains areconnected by 4,4′-bpy to assemble the 2D lattice structure as shown in Fig.1 c.
Complex 2 is a cadmium complex and crystallizes in a monoclinic system,C2/c space group.The asymmetric unit contains one Cd(Ⅱ)cation,one pztc4-ligand,one free H2bpe2+molecule,two coordinated water and two and a half lattice water molecules. Each Cd(Ⅱ)center is coordinated with four oxygen atoms(O1,O8,O1A,O10)from two pztc4-anions and one water molecule and one nitrogen atoms(N1)in the equatorial plane.The axial positions are occupied by two oxygen atoms(O4B and O9)from the third pztc4-anion and one water molecule respectively presented in Fig.2 a.The Cd(Ⅱ)center adopts a distorted pentagonal bipyramidal geometry.
The most interesting thing is that the parallel two Cd(Ⅱ)ions assemble into a binuclear building block [Cd2(pztc)2(H2O)4].This structural unit can continue to be extended to a two-dimensional grid structure(Fig. 2b).
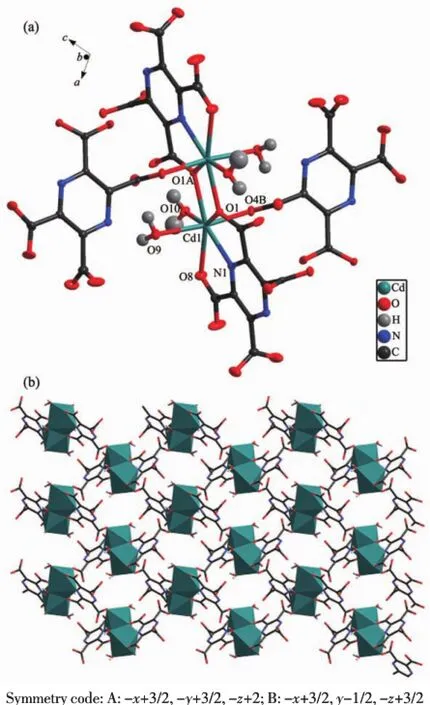
Fig.2 (a)Coordination environment of the Cd iron of 2 is shown at the 50%probability level;(b)2D grid structure of complex 2 by removing H2bpe2+
The H4pztc was also completely deprotonated in 2.Butthecoordinationmodeisdifferentfrom complex 1.One pztc4-ligand is connected with three Cd(Ⅱ)ions:two Cd(Ⅱ)ions exhibit monodentate chelating coordination mode;one Cd(Ⅱ)ion exhibits tridentatecoordinationmode.Thisisanew phenomenon,which is reported for the first time.
In addition,it should be noted that we have added the bpe as the second ligand in the synthesis of the complex 2,but it is not involved in the twodimensional grid structure.This phenomenon can be explained that the bpe ligand is so large that it is difficult to coordinate in the crowded space,but the small pztc4-can coordinate much easier.
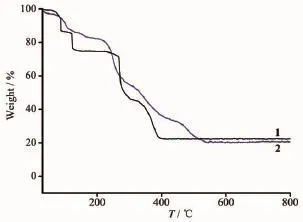
Fig.3 TG curves of 1 and 2
2.2 Thermal analysis(TGA)
Tostudythethermalstabilitiesofthese complexes,thermal gravimetric analyses were carried out for the samples of 1 and 2 by heating the samples from 30 to 800℃in air atmosphere as shown in Fig. 3.For complex 1,the first weight loss of 14.86%from 30 to 110℃is attributed to the loss of free water molecules(Calcd.15.10%).The second weight loss of 10.27%occurred after 118℃,which corresponds to thelossofcoordinatedwatermolecules(Calcd. 10.07%).The third weight loss corresponds to the loss of pztc4-and 4,4′-bpy ligands.Finally,the residue of 22.24%(Calcd.22.23%)might be CuO component. The mass has no change until after 400℃.The TG curve of 2 indicates the first weight loss is about12.27%,corresponding to the loss of water molecules, which is in agreement with the calculated value (12.87%).After the loss of the water molecules,a continuous weight loss occurs,which is due to the degradation of the pztc4-and H2bpe2+ligands.Finally, the residue of 20.27%(Calcd.20.39%)shows CdO component.The mass has no change until after 575℃.The fact is also in agreement with the results of the single-crystal X-ray analysis.
2.3 Fluorescence
As we know,coordination polymers with d10metal centers have excellent luminescent properties and potential applications as luminescent sensing materials[17-18].Considering this,we investigated the luminescent properties of complex 2(Fig.4 )and the free ligands in the solid state at room temperature. The emission band of metal complexes may be assigned to the metal chelation[19].Complex 2 shows a emission band at 475 nm under an excitation of 340 nm,which is similar to that of H4pztc ligand[20](480 nm,λex=300 nm).Compared with the bpe ligand[21](390 nm,λex=280 nm),complex 2 has red-shift of 85 nm.The ligands emissions can be attributed to the π*→n or π*→π transitions[22-24].The emission band forcomplex2isneithermetal-to-ligandcharge transfer(MLCT)nor ligand-to-metal charge transfer (LMCT)in the report[25].It can be attributed to fluorescent emissions from an intraligand excited state[26]. Complex 2 may be the excellent fluorescent materials for blue-light emitting diode devices.
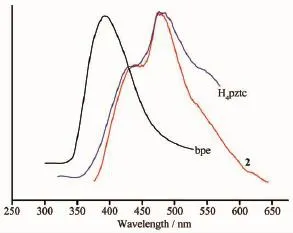
Fig.4 Emission spectra of H4pztc,bpe and complex 2
2.4 EPR
Electron Paramagnetic Resonance(EPR)spectra of 1 was recorded with a Bruker EMX-6/1 X-band, which was set with 100 kHz modulation frequency and 1.997 mW microwavepower.Thestudyis particularlyinstructiveinrevealingcoordination environment of paramagnetic metal ions.The X-band EPR spectra for complex 1 is shown in Fig.5 .Complex 1 has a sharp EPR signal which clear showed the characteristic of Cu(Ⅱ)with I(nuclear spin)=3/2 at room temperature.It has been reported that g∥values can reflect the covalent nature of the metal-ligand bond.If g∥〈2.3,the metal-ligand bond has covalent character[27].The EPR spectrum of the complex showed two peaks from which g∥and g⊥values have been calculated(g∥=2.243,g⊥=2.082).From these values,the EPR parameters match well with that the Cu(Ⅱ)ion is in a distorted octahedral coordination geometry.g∥falls in the 2.20~2.40 and g⊥is in the 2.04~2.09 range.It is evident that the metal-ligand bonds have considerable covalent character[28].Furthermore,the trend g∥〉g⊥〉ge(2.002;free spin value) indicated that the unpaired electron is most likely in theorbital.
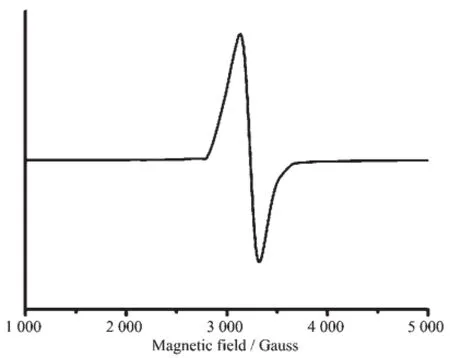
Fig.5 EPR spectra of complex 1
2.5 PXRD patterns analysis
Powder X-ray diffraction(PXRD)experiments have been carried out on the synthesized samples of 1 and 2 in order to confirm their crystalline phase purity.Fig.6 showed that all major peaks of bulk samples of 1 and 2 matched well with the simulated PXRD patterns and suggest the presence of mainly one crystalline phase in the corresponding samples.

Fig.6 PXRD patterns of complexes 1 and 2
3 Conclusions
In summary,two new H4pztc-containing complexes have been successfully synthesized by modifying the reaction conditions.H4pztc shows different coordination modes which reveal various coordination modes of the ligand.It′s worth mentioning that 1 and 2 show 2D structures.Complex 2 shows strong luminescence emission in the visible region and would be potential luminescent sensing materials.Subsequent effort will be focused on the preparation and adsorption property of novel polymers by using the H4pztc,bpe and more metal ions under different conditions.
[1]Yaghi O M,O′Keeffe M,Ockwig N W,et al.Nature,2003, 423:705-714
[2]Chen B L,Ockwig N W,Millward A R,et al.Angew.Chem. Int.Ed.,2005,44:4745-4749
[3]Albrecht M,Lutz M,Spek A.L,et al.Nature,2000,406:970 -974
[4]Yang J,Yue Q,Li G D,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2006,45:2857-2865
[5]Li H,Eddaoudi M,O′Keeffe M,et al.Nature,1999,402:276-279
[6]Lu J Y.Coord.Chem.Rev.,2003,246:327-347
[7]Yang A H,Zou J Y,Wang W M,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2014, 53:7092-7100
[8]Quan Y P,Zhao L H,Yang A H,et al.CrystEngComm,2009, 11:1679-1685
[9]Yang A H,Quan Y P,Gao H L,et al.CrystEngComm,2009, 11:2719-2727
[10]Zhao L H,Quan Y P,Yang A H,et al.CrystEngComm,2009, 11:1427-1432
[11]Yang A H,Gao H L,Cui J Z,et al.CrystEngComm,2001, 13:1870-1876
[12]Yan S T,Shi L X,Sun F F,et al.CrystEngComm,2010,12: 3437-3440
[13]Yang A H,Zhang H,Gao H L,et al.Cryst.Growth Des., 2008,8:3354-3359
[14]Yang A H,Zhang H,Yin P,et al.Inorg.Chem.Commun., 2010,13:1304-1308
[15]Wolff L,Dtsch B.Chem.Ges.,1887,20:425-433
[16]Sheldrick G M.SHELXL-97,Program for the Solution of Crystal Structures,University of Göttingen,Göttingen, Germany,1997.
[17]Wang M S,Guo S P,Li Y,et al.J.Am.Chem.Soc.,2009, 131:13572-13573
[18]Kreno L E,Leong K,Farha O K,et al.Chem.Rev.,2012, 112:1105-1125
[19](a)Gan W,Jones S B,Reibenspies J H,et al.Inorg.Chim. Acta,2005,358:3958-3966
(b)Machura B,witlicka A,Nawrot I,et al.Polyhedron,2011, 30:2815-2823
[20]Gao H L,Zhang Q Q,Cheung C W,et al.Inorg.Chem. Commun.,2014,46:194-197
[21]Li F F,Zhang Q Q,Zhao Y Y,et al.RSC Adv.,2014,4: 10424-10433
[22]Yang J,Yue Q,Li G D,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2006,45:2857-2865
[23]Wang X L,Qin C,Wang E B,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2004,43: 1850-1856
[24]Liu H Y,Wu H,Ma J F,et al.Cryst.Growth Des.,2010,10: 4795-4805
[25]Zou J Y,Gao H L,Shi W,et al.CrystEngComm,2013,15: 2682-2687
[26]Wang J J,Gou L,Hu H M,et al.Cryst.Growth Des.,2007, 7:1514-1521
[27]Kamalakannan P,Venkappayya D.Russ.J.Coord.Chem., 2002,28:423-433
[28]Kivelson D,Neiman R.J.Chem.Phys.,1961,35:149-155
Syntheses and Characterizations of Two Complexes with Pyrazine-2,3,5,6-tetracarboxylic Acid
GAO Hong-LingBI Yan-XiaZHANG Qin-QinCUI Jian-Zhong*
(Department of Chemistry,School of Science,Tianjin University,Tianjin 300072,China)
Two complexes with pyrazine polycarboxylic acid,namely{[Cu2(pztc)(4,4′-bpy)(H2O)4]·6H2O}n(1), {(H2bpe)[Cd(pztc)(H2O)2]·2.5H2O}n(2),(H4pztc=pyrazine-2,3,5,6-tetracarboxylic acid,bpe=1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane, 4,4′-bpy=4,4′-bipyridine),have been prepared by modifying the reaction conditions at room temperature and characterized by IR,elemental analysis,thermal gravimetric analysis,fluorescence measurement and single crystal X-ray diffraction analysis.The structures of two complexes are two-dimensional(2D)networks,but H4pztc has different connection modes in 1 and 2.Complex 2 shows good luminescence properties in solid state at room temperature.Electron Paramagnetic Resonance(EPR)spectra of complex 1 is studied.CCDC:1039147,1; 1039296,2.
pyrazine polycarboxylic ligand;two-dimensional network;fluorescent property;electron paramagnetic resonance spectra
O614.121;O614.24+2
A
1001-4861(2015)08-1603-06
10.11862/CJIC.2015.215
2015-03-19。收修改稿日期:2015-05-19。
国家自然科学基金(No.21271137,21473121),教育部先进能源材料化学重点实验室开放基金(南开大学)资助项目。*

