附件G:AuCuI()化合物无序化过程的合金基因浓度跟踪研究
G.1 混合焓实验路径的合金基因浓度跟踪法
对于给定成分的合金,由等有序度Gibbs能平衡路径法获得最小Gibbs能()-T路径(见图G.1(a)),在平衡等有序度(-T)网络图中绘制(-T )亚平衡路径(见图G.1(b)),随后相继获得混合Gibbs能(-T )(见图G.1(c)),有序度(σ-T )(见图G.1(d))、合金基因浓度((-T)(见图G.2)和其他性质s,x(qs,x-T)亚平衡全息网络路径图(见图G.3~G.18)[6]:(-T)→(-T)→(σ-T)→(()-T)→(q-T)s,xs,xs,x

图G.1 AuCuI()化合物无序化的EHNP和SHNP路径图Fig.G.1 EHNP- and SHNP-charts on disordering AuCuI():(a)Minimal mixed Gibbs energy-Tpath obtained by iso-order degree Gibbs energy equilibrium path method;(b)Experimental mixed enthalpy-T path method based on network chart of iso-order degree mixed enthalpies equilibrium paths, attaching equilibrium-T path;(c)(OABC)and(Oabc)paths of equilibrium and subequilibrium order→disorder transitions, wheredenoting superheated driving Gibbs energy;(d)σe(OABCD)and σs(OabcD)paths of equilibrium and subequilibrium order→disorder transitions, where Δσhdenoting hysteresis order degree

(To be continued)

图G.2 AuCuI()化合物无序化的合金基因浓度跟踪图Fig.G.2 AG-concentration SHNP charts on disordering AuCuI():(a), (b)Three-dimension-T-i and-T-i SHNP charts;(c), (d)Two-dimension iso-order degree-i and-i SHNP charts;(e), (f)Two-dimension iso-Gibbs energy level-σ and-σ SHNP charts
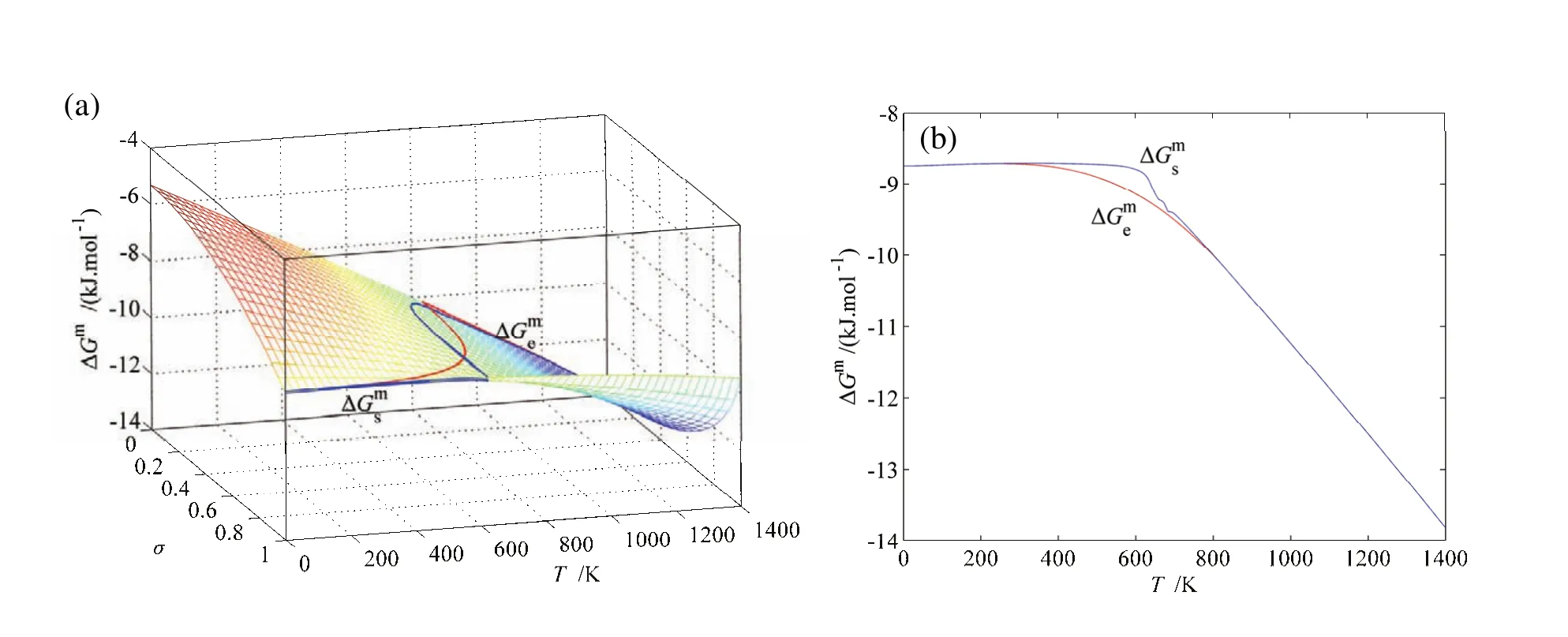
图 G.3 AuCuI()化合物无序化时载有平衡和亚平衡路径的ΔGm-平衡全息网络路径图Fig.G.3 EHNP charts with EHNP and SHNP curves of the first order thermodynamic properties on disordering AuCuI():(a)Three-dimension mixed Gibbs energy ΔGm-T-σ EHNP chart with-T and-T paths;(b)-T and-T paths

图 G.4 AuCuI()化合物无序化时载有平衡和亚平衡路径的-平衡全息网络路径图Fig.G.4 EHNP charts with EHNP and SHNP curves of the first order thermodynamic properties on disordering AuCuI():(a)Three-dimension mixed characteristic Gibbs energy ΔG∗m-T-σ EHNP chart with-T and-T paths;(b)-T and-T paths
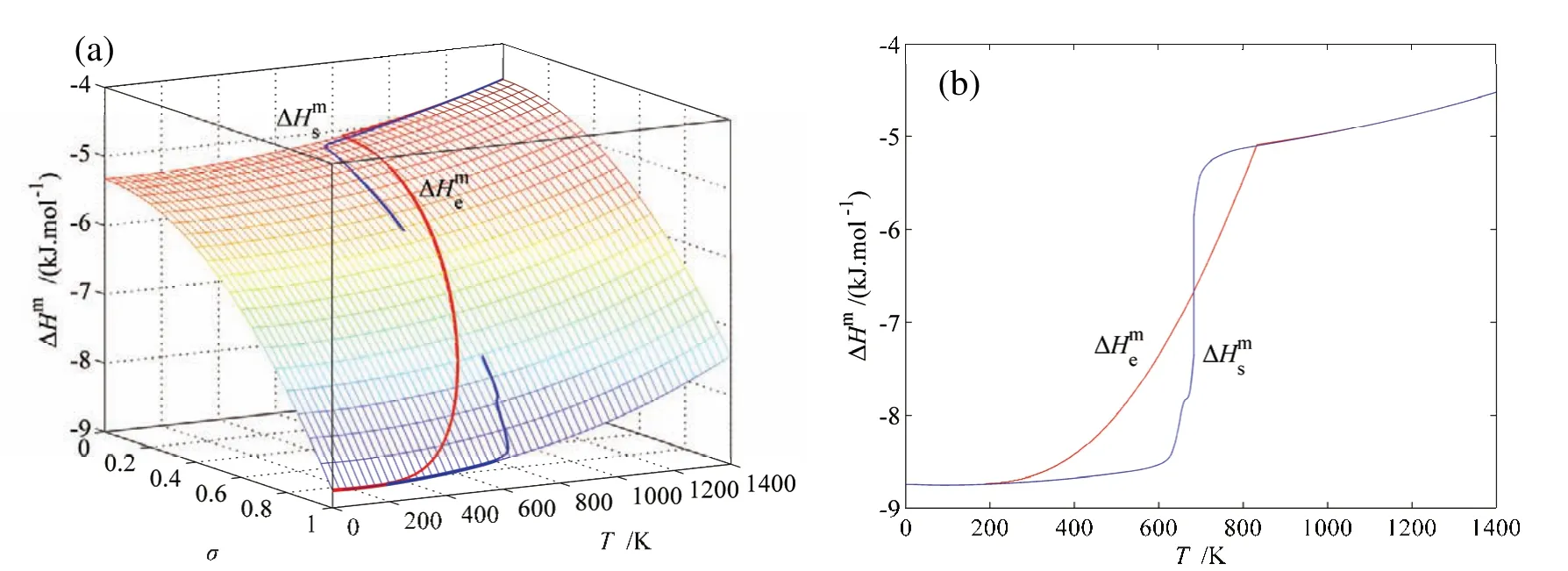
图G.5 AuCuI()化合物无序化时载有平衡和亚平衡路径的ΔHm-平衡全息网络路径图Fig.G.5 EHNP charts with EHNP and SHNP curves of the first order thermodynamic properties on disordering AuCuI():(a)Three-dimension mixed enthalpy ΔHm-T-σ EHNP chart with-T and-T paths;(b)-T and-T paths

图G.6 AuCuI()化合物无序化时载有平衡和亚平衡路径的ΔEm-平衡全息网络路径图Fig.G.6 EHNP charts with EHNP and SHNP curves of the first order thermodynamic properties on disordering AuCuI():(a)Three-dimension mixed potential energy ΔEm-T-σ EHNP chart with-T and-T paths;(b)-T and-T paths
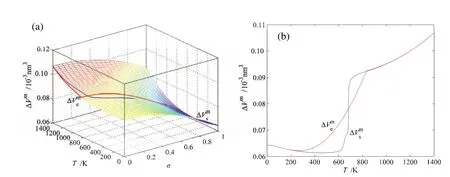
图G.7 AuCuI()化合物无序化时载有平衡和亚平衡路径的ΔVm-平衡全息网络路径图Fig.G.7 EHNP charts with EHNP and SHNP curves of the first order thermodynamic properties on disordering AuCuI():(a)Three-dimension mixed volume ΔVm-T-σ EHNP chart with-T and-T paths;(b)-T and-T paths
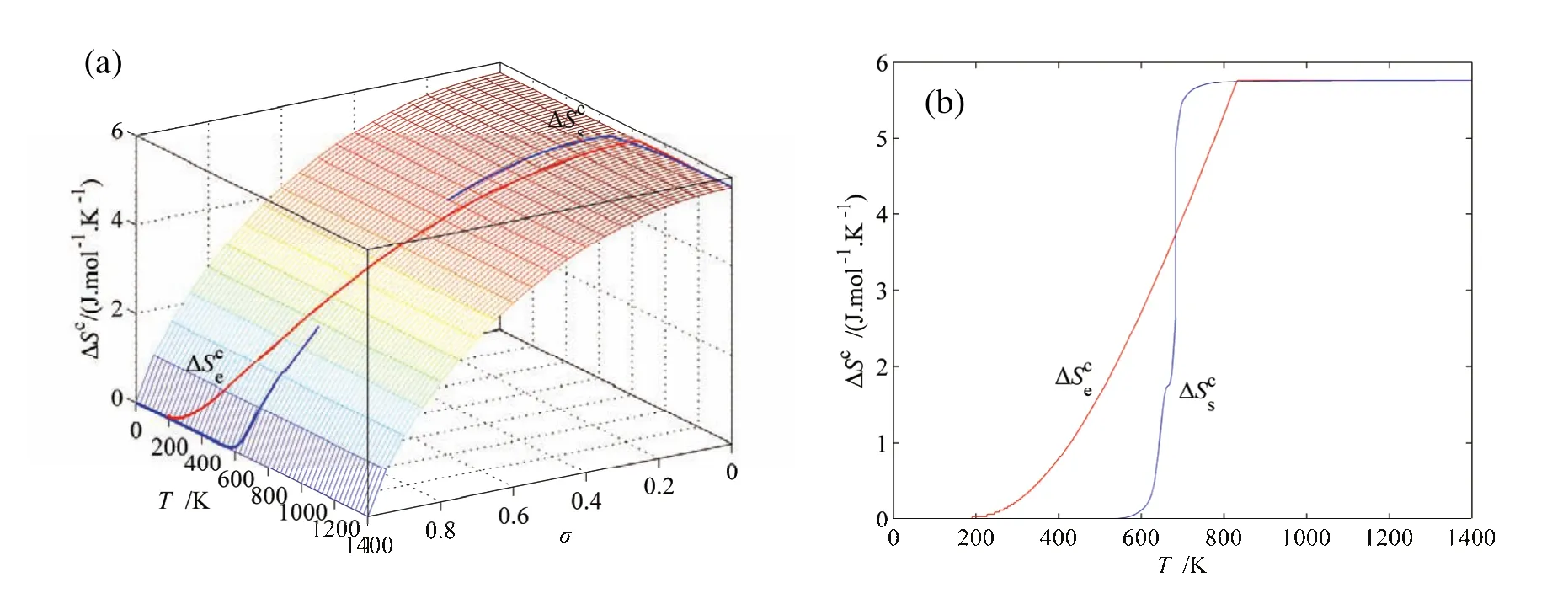
图G.8 AuCuI()化合物无序化时载有平衡和亚平衡路径的Sc-平衡全息网络路径图Fig.G.8 EHNP charts with EHNP and SHNP curves of the first order thermodynamic properties on disordering AuCuI():(a)Three-dimension configurational entropy Sc-T-σ EHNP chart with-T and-T paths;(b)-T and-T paths

图 G.9 AuCuI()化合物无序化时载有平衡和亚平衡路径的ΔUm.v-平衡全息网络路径图Fig.G.9 EHNP charts with EHNP and SHNP curves of the first order thermodynamic properties on disordering AuCuI():(a)Three-dimension generalized vibration energy-T-σ EHNP chart with-T and-T paths;(b)-T and-T paths

图G.10 AuCuI()化合物无序化时载有平衡和亚平衡路径的ΔSv-平衡全息网络路径图Fig.G.10 EHNP charts with EHNP and SHNP curves of the first order thermodynamic properties on disordering AuCuI():(a)Three-dimension generalized vibration entropy ΔSv-T-σ EHNP chart with-T and-T paths;(b)-T and-T paths
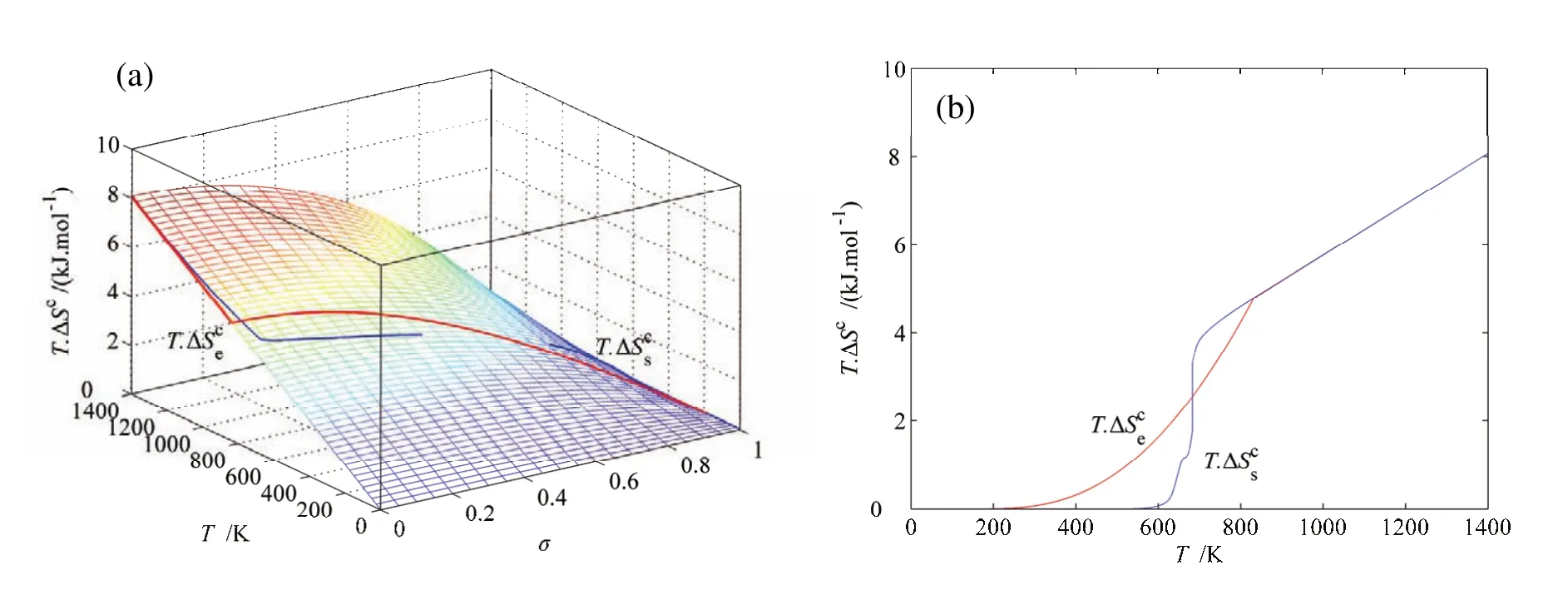
图 G.11 AuCuI()化合物无序化时载有平衡和亚平衡路径的TSc-平衡全息网络路径图Fig.G.11 EHNP charts with EHNP and SHNP curves of the first order thermodynamic properties on disordering AuCuI():(a)Three-dimension configurational entropy energy TSc-T-σ EHNP chart with-T and-T paths;(b)-T and-T paths

图G.12 AuCuI()化合物无序化时载有平衡和亚平衡路径的TΔSv-平衡全息网络路径图Fig.G.12 EHNP charts with EHNP and SHNP curves of the first order thermodynamic properties on disordering AuCuI():(a)Three-dimension generalized vibration entropy energy TΔSv-T-σ EHNP chart with-T and-T paths;(b)-T and-T paths
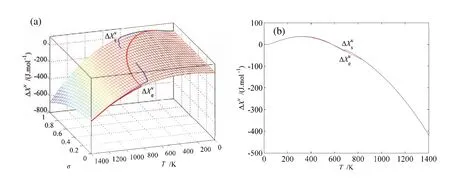
图 G.13 AuCuI()化合物无序化时载有平衡和亚平衡路径的ΔXv-平衡全息网络路径图Fig.G.13 EHNP charts with EHNP and SHNP curves of the first order thermodynamic properties on disordering AuCuI():(a)Three-dimension generalized vibration free energy ΔXv-T-σ EHNP chart with-T and-T paths;(b)-T and-T paths

图G.14 AuCuI()化合物无序化时载有平衡和亚平衡路径的c-x-T平衡全息网络路径图pFig.G.14 The second order thermodynamic properties (heat capacity)on disordering AuCuI():(a)-T and-T paths on cp-x-T EHNP diagram;(b)-T and-T paths

图G.15 AuCuI()化合物无序化时载有平衡和亚平衡路径的c-T-σ平衡全息网络路径图pFig.G.15 The second order thermodynamic properties (heat capacity)on disordering AuCuI():(a)-T and-T paths on c-T-σ EHNP diagram;(b)-σ and-σ pathsp

图 G.16 AuCuI()化合物无序化时载有平衡和亚平衡路径的热膨胀α-x-T平衡全息网络路径图Fig.G.16 The second order thermodynamic properties (thermal expansion coefficient)on disordering AuCuI():(a)αe-T and αs-T paths on α-x-T EHNP chart;(b)αe-T and αs-T paths
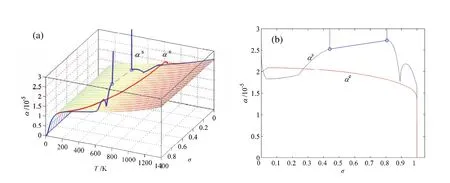
图 G.17 AuCuI()化合物无序化时载有平衡和亚平衡路径的热膨胀α-T-σ平衡全息网络路径图Fig.G.17 The second order thermodynamic properties (thermal expansion coefficient)on disordering AuCuI():(a)αe-T and αs-T paths on α-T-σ EHNP diagram;(b)αe-σ and αs-σ paths
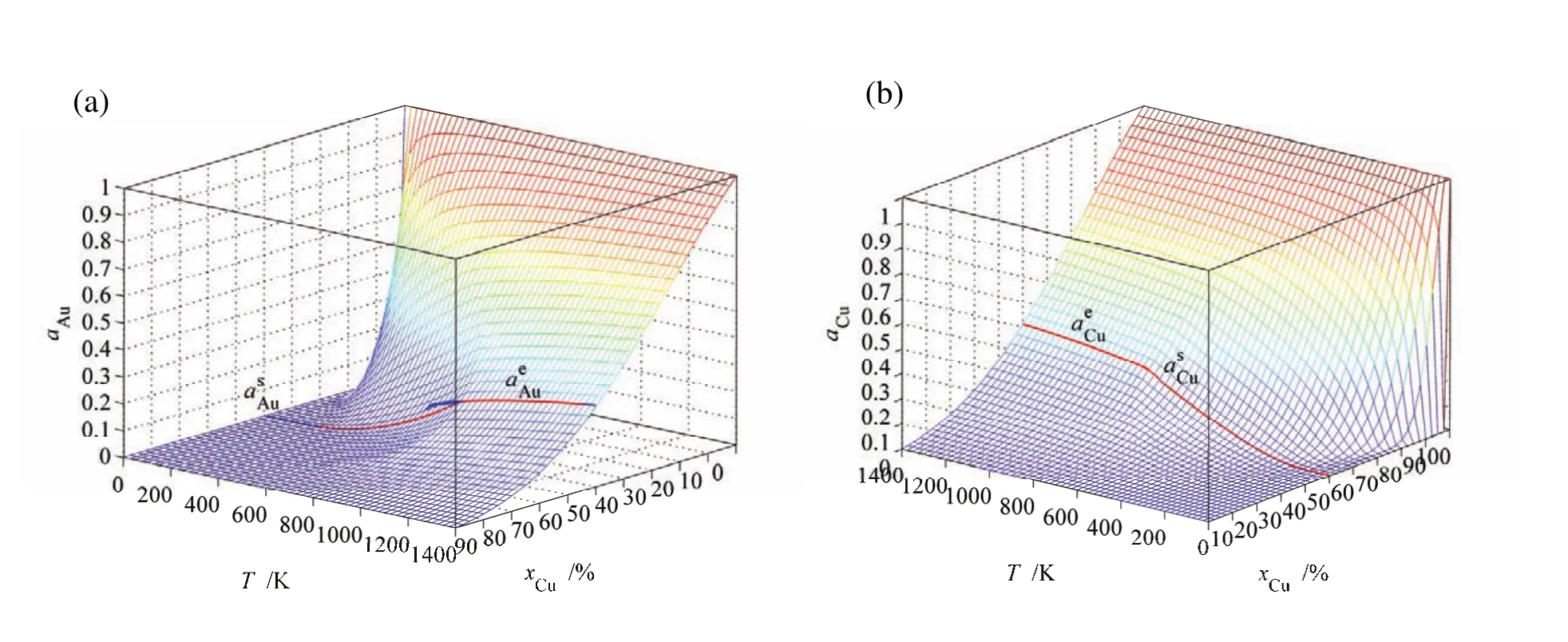
(To be continued)

图G.18 AuCuI()化合物无序化时载有平衡和亚平衡路径的活度a-平衡全息网络路径图Fig.G.18 Activities on disordering AuCuI():(a), (b)-T,-T and-T,-T paths on aAu-x-T and aCu-x-T EHNP diagrams;(c), (d)-T,-T and-T,-T paths;(e), (f)-T,-T and-T ,-T paths on a-T-σ and a-T-σ EHNP charts;(g,h)-σ,-σ and-σ,-σAuCupaths
G.2 AuCuI()无序化路径分析[6]
我们采用实验生成焓路径的合金浓度跟踪法,确定了AuCuI()化合物的统计非均匀亚平衡和递次性有序一无序转变路径:AuCuI()→AuCu(H)→PTP-AuCu →SPAP-AuCu(L)→AuCu(D)。该路径的动力学特征与加热速度的关系受RA-SA机制、过热驱动Gibbs能、跳变有序度,以及高温时原子一空位移动机制等控制:
1)当0≤T<Tonset(593 K)时,它是有序度不变的AuCuI()亚稳期。
2)当Tonset<T≤620 K,1.000>σs≥0.990时,它是高有序度合金AuCu(H)的生长期(见图9(a)和(b))。它具有晶胞尺度的不均匀性:含有较多的3(RA-SA)晶胞的早期一(RA-SA)晶胞区,含有较少的3(RA-SA)晶胞的中期一(RA-SA)晶胞区,没有3(RA-SA)晶胞的晚期一AuCuI()晶胞区(见图G.19(c))。
3)当620 K<T≤650 K,0.990>σs≥0.925时,它是统计周期反向(SPAP)AuCuII区的生长期(见图9(c)和(d))。它具有区域尺度的不均匀性:含有较多的3(RA-SA)晶胞的原早期一(RA-SA)晶胞区成长为早期一(SPAP)-AuCuII区,含有较少的3(RA-SA)晶胞的原中期一(RA-SA)晶胞区成长为含有较多的3(RA-SA)晶胞的中期一(RA-SA)晶胞区,原晚期一AuCuI()晶胞区成长为含有较少的3(RA-SA)晶胞的晚期一(RA-SA)晶胞区(见图G.19(d))。此时,亚平衡合金具有区域尺度的不均匀性:AuCu(H)区和SPAP-AuCuII区共存,它可称之为“伪二相(PTP)”AuCu合金。
4)当650 K<T<683 K,0.925>σs>0.807时,它是SPAP-AuCuII合金的成熟期(见图9(e)和(f))。在此阶段,SPAP-AuCuII合金含有早期一,中期一和晚期一(SPAP)-AuCuII区。
5)当0.807≥σs≥0.786时,它是SPAP-AuCuII合金的跳变期(见图9(g)和(h))。在此阶段,跳变合金基因浓度呈现最大“涌现”现象。跳变温度Tj由跳变有序度和过热驱动Gibbs能决定,后者与加热速度有关。
6)当0.4545≥σs>0时,它是低有序度AuCu(L)合金的存在期(见图9(g)和(h))。当σs=0时,即T≥Tc(683 K),合金AuCu(D)处于无序状态。

图 G.19 AuCuI()化合物无序化时3(RA-SA)机制和晶胞尺度与区域尺度不均匀性简图Fig.G.19 The 3(RA-SA)mechanism and schemes of cell-scale and region-scale heterogeneities on disordering AuCuI():(a)AG arranging structure after A-manner alternating in 3(RA-SA)mechanism of threepairs in a single cell;(b)AG arranging structure after B-manner alternating in 3(RA-SA)mechanism of threepairs in a single cell;(c)AuCu(H)alloy containing three regions with cell-scale heterogeneity;(d)PTP-[AuCuI(H)+PAP-AuCuII] alloy containing three regions with region-scale heterogeneity;(e)AG arranging structure of a early SPAP-AuCuII cell
REFERENCES
[1] CAHN R W, HAASEN P.Physical metallurgy[M].Elsevier Science Amsterdam, 1996:1-46.
[2] OSTP.Materials genome initiative for global competitiveness[R].Washington D C:Office of Science and Technology Policy, 2011.
[3] 谢佑卿.金属材料系统科学[M].长沙 :中南工业大学出版社, 1998.XIE You-qing.Systematic science of metallic materials[M].Changsha:Central South University of Technology Press, 1998.
[4] XIE You-qing.Systematic Science of Alloys[M].Changsha:Central South University Press, 2012.
[5] XIE You-qing, LI Xiao-bo, LIU Xin-bi, NIE Yao-zhuang, PENG Hong-jian.Alloy gene Gibbs energy partition function and equilibrium holographic network phase diagrams of AuCu-type sublattice system[J].International Journal of Communications, Network and System Sciences, 2013, 12(6):415-442.
[6] XIE You-qing, PENG Hong-jian, LIU Xin-bi, LI Xiao-bo, NIE Yao-zhuang.New atom movement mechanism for tracking path on disordering AuCuI()compound[J].Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24(10):3221-3256.
[7] XIE You-qing, LI Xiao-bo, LIU Xin-bi, NIE Yao-zhuang, PENG Hong-jian.Alloy gene Gibbs energy partition function and equilibrium holographic network phase diagrams of AuCu3-type sublattice system[J].Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24(11):3585-3610.
[8] XIE You-qing, NIE Yao-zhuang, LI Xiao-bo, PENG Hong-jian, LIU Xin-bi.Alloy gene Gibbs energy partition function and equilibrium holographic network phase diagrams of Au3Cu-type sublattice system[J].Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(1):211-240.
[9] XIE You-qing, LIU Xin-bi, LI Xiao-bo, PENG Hong-jian, NIE Yao-zhuang.Holographic alloy positioning design system and holographic network phase diagrams of Au-Cu system[J].Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(3):885-906.
[10] SLATER J C.Electronic structure of alloys[J].Journal of Applied Physics, 1937, 8(6):385-396.
[11] ELLIS D E, AVERRILL F W.Electronic structure of FeCl4anions in the Hartree-Fock-Slater model[J].J Chem Phys, 1974, 60(8):2856-2864.
[12] BAERENDS E J, ELLIS D E, ROS P.Self-consistent molecular Hartree-Fock- Slater calculations.I.The computational procedure[J].Chem Phys, 1973, 2(1):41-51.
[13] KIKUCHI R.A theory of cooperative phenomemena[J].Phys Rev, 1951, 81(6):988-1003.
[14] KIKUCHI R, de FONTAINE D, MURAKAMI M, NAKAMURA T.Ternary phase diagram calculations—II examples of clustering and ordering systems[J].Acta Metallurgica, 1997, 25(2):207-219.
[15] ASTA M, de FONTAINE D.First-principles study of phase stability of Ti-Al intermetallic compounds[J].J Mater Res, 1993, 8(10):2554-2568.
[16] OATES W A, ZHANG F, CHEN S L, CHANG Y A.Improved cluster-site approximation for the entropy of mixing in multicomponent solid solutions[J].Physical Review B, 1999, 59(17):11221-11225.
[17] OZOLINŠ V, WOLVERTON C, ZUNGER A.Cu-Au, Ag-Au, Cu-Ag and Ni-Au Intermetallics:First-principles study of temperature-composition phase diagrams and structures[J].Physical Review B, 1998, 57(12):6427-6443.
[18] BRAGG W L, F R S, WILLIAMS E J.The effect of thermal agitation on atomic arrangement in alloys[J].Proceedings of the Royal of Society A, 1934, 145(2):699-730.
[19] BRAGG W L, F R S, WILLIAMS E J.The effect of thermal agitation on atomic arrangement in alloys II[J].Proceedings of the Royal of Society A, 1935, 51(2):540-566.
[20] ORIANI R A.Thermodynamics of order alloy.II.The gold-copper system[J].Acta Metall, 1954, 2(3):608-615.
[21] RHINES F N, BOND W E, RUMMEL R A.Constitution of order alloys of the system Copper-Gold[J].Trans Amer Soc Met, 1955, 47(2):578-597.
[22] KAUFMAN L, BERNTEIN H.Computer calculation of phase diagrams[M].New York:Academic Press, 1970:225.
[23] SUNDMAN B, FRIES S G, OATES W A.A Thermodynamic assessment of the Au-Cu system[J].CALPHAD, 1998, 22(3):335-354.
[24] SUNDMAN B, FRIES S G, OATES W A.A calphad assessment of the Au-Cu system using the cluster variatiation method[J].Z Metallkd, 1999, 90(5):267-273.
[25] HILLERT M.The compound energy formalism[J].Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2001, 320(1):161-176.
[26] OATES W A.Configurational entropies of mixing in solid alloys[J].J Equilibria Diffusion, 2007, 28(1):79-89.
[27] 谢佑卿, 聂耀庄, 李小波, 刘心笔, 彭红建, 李艳芬.FP-SSA框架中Au3Cu型有序合金相的特征原子势能配分函数[J].中国有色金属学报, 2011,21(10):2489-2501.XIE You-qing, NIE Yao-zhuang, LI Xiao-bo, LIU Xin-bi, PENG Hong-jian, LI Yan-fen.Characteristic atom potential energy partition functionof Au3Cu type ordered alloys in FP-SSA Framework[J].The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 21(10):2489-2501.
[28] 刘梓葵.关于材料基因组的基本观点及展望[J].科学通报, 2013, 58(35):3618-3622.LIU Z K.Perspective on materials genome[J].Chin Sci Bull (Chin Ver), 2013, 58(35):3618-3622.
[29] KAUFMAN L, ǺGREN J.First and second generation-birth of the materials genome[J].Scripta Materialia, 2014, 70(1):3-6.
[30] 赵继成.材料基因组计划简介[J].自然杂志, 2014, 36(2):89-104.ZHAO Ji-cheng.A perspective on materials genome initiative[J].Chinese Journal of Nature, 2014, 36(2):89-104.
[31] 谢佑卿, 马柳莺.广义Vegard定律和广义余氏定理[J].中南矿冶学院学报, 1985, 16(3):1-10.XIE You-qing, MA Liu-ying.Generalized Vegard’s law and generalized Yu’s law[J].Journal Central-South Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, 1985, 16(3):1-10.
[32] XIE You-qing, PENG Kun, LIU Xin-bi.Influences of xTi/xAlatomic states, lattice constants and potential-energy planes of ordered FCC TiAl type alloys[J].Physica B, 2004, 344(1/4):5-20.
[33] XIE You-qing, LIU Xin-bi, PENG Kun.Atomic state, potential energies, volumes, stability and brittleness of ordered FCC TiAl3type alloys[J].Physica B, 2004, 353(1/2):15-33.
[34] XIE You-qing, PENG Hong-jian, LIU Xin-bi, PENG Kun.Atomic state, potential energies, volumes, stability and brittleness of ordered FCC Ti3Al type alloys[J].Physica B, 2005, 362(1/4):1-17.
[35] XIE You-qing, TAO Hui-jin, PENG Hong-jian, LIU Xin-bi, PENG Kun.Atomic state, potential energies, volumes, stability and brittleness of ordered FCC TiAl2type alloys[J].Physica B, 2005, 366(1/4):17-37.
[36] XIE You-qing, LIU Xin-bi, LI Xiao-bo, PENG Hong-jian, NIE Yao-zhuang.Potential energies of characteristic atoms on basis of experimental heats of formation of AuCu and AuCu3compounds[J].Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2009, 19(5):1243-1256.
[37] XIE You-qing, LIU Xin-bi, LI Xiao-bo, PENG Hong-jian, NIE Yao-zhuang.Volume sequences of characteristic atoms separated from experimental volumes of AuCu and AuCu3compounds[J].Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2009, 19(6):1599-1617.
[38] XIE You-qing, NIE Yao-zhuang, LIU Xin-bi, LI Xiao-bo, PENG Hong-jian, LI Yan-fen.Potential energies of characteristic atoms separated from first-principles calculated heats of formation of AuCu and AuCu3compounds[C]//XIE You-qing ed.Systematic Science of Alloys.Changsha:Central South University Press, 2012:405-427.
[39] XIE You-qing, NIE Yao-zhuang, LIU Xin-bi, LI Xiao-bo, PENG Hong-jian, LI Yan-fen.Volumes of characteristic atoms separated from first-principles calculated volumes of L10-AuCu and L12-AuCu3compounds[C]//XIE You-qing.Systematic Science of Alloys.Changsha:Central South University Press, 2012:428-460.
[40] 谢佑卿, 马柳莺.晶体价电子结构的理论晶格参量[J].中南矿冶学院学报, 1985, 16(1):1-10.XIE You-qing, MA Liu-ying.The theoretical lattice parameter of the valence electron of crystal[J].Journal Central-South Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, 1985, 16(1):1-10.
[41] XIE You-qing.A new potential function with many-atom interactions in solid[J].Science in China (series E), 1993, 36(1):90-99.
[42] XIE You-qing, ZHANG Xiao-dong, ZHAO Li-ying, MA Xiu-ling.Electronic structure and properties of Cu metal[J].Science in China (series E), 1993, 36(4):487-496.
[43] XIE You-qing.Electronic structure and properties of pure iron[J].Acta Metal Mater, 1994, 42(11):3705-3715.
[44] XIE You-qing.Relationship between partial and average atomic volumes of components in Au-Ni alloys[J].Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21(8):1801-1807.
[45] XIE You-qing, ZHANG Xiao-dong, CHEN Jia-yan.Electronic structure and properties of pure Cobalt[J].Science in China (Series E), 1996, 39(4):394-403.
[46] XIE You-qing, LÜ Man-shan, ZHANG Xiao-dong, ZHAO Li-ying.Electronic structure and properties of Ni metal[J].Science in China (Series A), 1993, 36(4):495-503.
[47] XIE You-qing, LIU Xin-bi, PENG Hong-jian, NIE Yao-zhuang, LI Xiao-bo, LI Yan-fen.Characteristic atom arranging crystallogphy of alloy phases for Au-Cu system[J].Science China:Technological sciences, 2011, 54(6):1560-1567.
[48] XIE You-qing, LI Yan-fen, LIU Xin-bi, LI Xiao-bo, PENG Hong-jian, NIE Yao-zhuang.Characteristic atom occupation patterns of Au3Cu, AuCu3, AuCuI and AuCuII based on experimental data of disordered alloys[J].Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21(5):1092-1104.
[49] XIE You-qing, MA Liu-ying, ZHANG Xiao-dong, ZOU Ping, ZHAO Li-ying.Microstructure and properties of Cu-Ni alloys[J].Science in China (Series A), 1993, 36(5):612-623.
[50] LUPIS CHP.Chemical thermodynamics of materials[M].Amsterdam:North-Holland, 1983:438-469.
[51] LUPIS CHP, ELLIOTT J F.Prediction of enthalpy and entropy interaction coefficients by the “central atoms” theory[J].Acta Met, 1967, 15(2):265-276.
[52] 陆学善,梁敬魁.铜金二元系中超结构的形成与点阵间隔的变迁[J].物理学报, 1966, 22(6):669-696.LU Hsueh-shan, LIANG Ching-kwei.The superlattice formation and lattice spacing changes in copper-gold alloys[J].Acta Physica Sinica, 1966, 22(6):659-696.
[53] LU Hsueh-shan, LIANG Ching-kwei.The existence of the superlattice CuAu3in the Cu-Au system[J].Kexue Tongbao, 1966, 17(9):395-396.
[54] LU Hsueh-shan, LIANG Ching-kwei.Experimental evidence of order-disorder transitions as of the second degree [J].Kexue Tongbao, 1966, 17(10):441-443.
[55] SUTCLIFFE C H, JAUMOT F E Jr.Order-disorder in Au-Cu alloy.I.Short-range order in an alloy containing atomic percent Au[J].Acta Metallurgica, 1953, 1(2):725-730.
[56] JAUMOT F E Jr, SUTCLIFFE C H.Order-disorder in Au-Cu alloy.II.The nature of the order-disorder transformation and long-range order[J].Acta Metallurgica, 1954, 2(2):63-74.
[57] SCOTT R E.New Complex phase in the copper-gold system[J].Journal of Applied Physics, 1960, 31(12):2112-2117.
[58] LANG H, UZAWA H, MOHI T, PFEILER W.L12-long-range order in Cu3Au:kinetics and equilibrium as studied by residual resistivity[J].Intermetallics, 2001, 9(1):9-24.
[59] KEATING D T, WARREN B E.Long-range order in beta-brass and Cu3Au[J].Journal of Applied Physics, 1954, 22(3):286-290.
[60] BUTLER B D, COHEN J B.The structure of Cu3Au above the critical temperature[J].J Applied Physics, 1989, 65(6):2214-2219.
[61] 刘大椿.科学活动论[M].北京:人民出版社, 1985:198-204.LIU Da-chun.Theory of scientific activities[M].Beijing:People Press, 1985:198-204.
[62] DUNHAM I, SHIMIZU N, ROE B A, CHISSOE S, HUNT A R, COLLINS J E, BRUSKIEWICH R, BEARE D M, CLAMP M, SMINK L J, AINSCOUGH R, ALMEIDA J P, BABBAGE A, BAGGULEY C, BAILEY J, BARLOW K, BATES K N, BEASLEY O, BIRD C P, BLAKEY S, BRIDGEMAN A M, BUCK D, BURGESS J, BURRILL W D, O'BRIEN K P.The DNA sequence of human chromosome 22[J].Nature, 1999, 402(6761):489-495.
[63] Francis S.Collins, Ari Patrinos, Elke Jordan, Aravinda Chakravarti, Raymond Gesteland, Le Roy Walters.New Goals for the U.S.Human genome Project:1988~2003[J].Science, 1998, 10(282):682-689.
[64] Genome Sequence Database:http://www.ncbi.nim.gov/genome/seq/.
[65] CAO W, CHANG Y A, ZHU J, CHEN S, OATES W A.Thermodynamic modeling of the Cu-Ag-Au system using the cluster/site approximation[J].Intermetallics, 2007, 15(8):1438-1446.
[66] WEI S–H, MBAYE A A, FERRIRA L G, ALEX Zunger.First-principles calculations of the phase diagrams of noble metals:Cu-Au, Cu-Ag and Ag-Au[J].Phys Rev B, 1987, 36(20):4163-4185.
(编辑何学锋)

