Anaerobic biodegradation of RDX and HMX with different co-substrates☆
Zongkuan Liu *,Lei Zhang ,Yonghong Liu ,Yan ling He
1 Department of Environm ental Science and Technology,School of Hum an Settlements and Civil Engineering,Xi'an Jiaotong University,Xi'an 710049,China
2 Department of Chemical Engineering,Xi'an Jiaotong University,Xi'an 710049,China
3 Departm ent of Environm ental and Chemica l Engineering,Xi'an Polytechnic University,Xi'an 710048,China
Keyw ords:Anaerobic biodegradation Co-substrate Octahydro-1,3,5,7-tetranitro-1,3,5,7-tetrazocine Hexahyd ro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine W astewater
ABSTRACT
1.Introduction
Hexahyd ro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine(RDX)and octahyd ro-1,3,5,7-tetran itro-1,3,5,7-tetrazocine(HMX)are two of the main com ponen ts in high explosives[1-6],which are widely usedinternationally in the field of national defense andindustrial engineering.Their manu factu ring and application processes produce a great deal of munition waste[7].For instance,an estimated 3.13×108kg of mun ition waste exists in military stockpiles(USA)[8].Because of the poor degradability of these hazardous wastes,especially RDX and HMX[9-11],num erous acres of soils and vo lum es of groundwater are seriously con tam inated by the production and application of the explosives,p resen ting environmental and health prob lem s[11,12].Therefore,disposing of the wastes,especially in the form of wastewater,becom es a necessity.
In order to disposewaste substances,m anymethodshavebeen suggested and studied forapplications,which can be categorizedinto physical,chemical and biological ones based on treating principles.Physical methods,such as adsorption,ex traction and mem brane separation,p resent lim ited promising for applications,because no pollutant is degradedin the treating process,and sometimes a second pollu tan t is produced du ring the treatm en t[1].Chemical methods are main ly concentrated on the usage of u ltravio let irradiation and catalysts such as water dioxide and ozone[12,13].Although the percentage of degradation is higher,they are un favorab le for applications due to relatively higher cost.Bio logical methodis now the mostly studied one for treating explosive wastes and energy con taining substances[16,17].How ever,the time needed to com pletely oxidize RDX or HMX is generally long.
Recently,physicochemical[1,12,13]and biochemical methods[14,15]are widely usedin disposing of wastes,especially,biochemical methodis the mostly em ployed app roach owing to its environm en t friend ly characteristic.In consideration of applications,novel catalyst with higher degradation efficiency,good scalability,and low er cost are expectedin biochemical methods.In th is study,simulated RDX and HMX wastewaters[13,16,17]are treated anaerobically with or without co-substrates such as amm onium chloride,dextrose,sodium acetic,sodium nitrate and sulfate.Them echanism for biodegradation of RDX and HMX,and the op tim al parameters for large scale application of the method are presented.
2.Experimental
2.1.Materials
Dex trose,amm onium ch loride,sodium acetic,sodium nitrate and su lfate are all analytical grade from Tian jin Kerm el Chemical Reagen ts Developm en t centre(China).RDX and HMX are analytical grade from Xi'an Modern Research Institute(China).Theorganism swere anaerobic granu lar sludge(average diameter of 2 mm)from an upflow anaerobic sludge bedin ou r laborato ry.The sludge with concentration of 1000 mg·L-1and pH of 7.0 at(35 ± 2)°C was characterized according the method describedin reference[18].All other reagents were used as received and deionized water was used for all experiments.Simulated RDX and HMX wastewaters were prepared with deionized water[19].
Before initialization of the anaerobic biodegradation,nourishing solu tion and solu tion of trace elements(Tab le 1),yeast oil and NaHCO3were added to the sim ulated wastewater.The volum e ratio of nourishing solu tion and that of the solution of trace elements to the simulated RDX and HMX wastewater were both 1/500.The final concentrations of the yeastoiland NaHCO3,which play the buffering role in the sam ple,were 0.2 and 0.55 g·L-1,respectively.

Tab le 1 Com position of nou rishing solution and solution of trace elements
2.2.Determination of RDX and HMX concentrations
A chrom atographic system consisting a Hitachi-7110 pum p,a 25 μl in jector(Micro liter™#702),a Hitachi-7420 u ltravio let detector and a temperature con tro lling module for HPLC-UV analysis[20,21]was used for determination of concentrations of RDX and HMX during the anaerobic biodegradation process.Specifically,25 μl of the RDX wastewater was directly in jectedinto a Microsorb-MV 100 C18 colum n(25 cm×4.6mm,5μm).Them obile phaseof the colum n wasa mixture of methanol and water with a vo lum e ratio of7/3 and the flow-rate was 1 ml·m in-1.The colum n temperature wasm ain tained at35 °C,and the running timewas 30m in.An u ltraviolet detector setat 230 and 254 nm was used to detect RDX and HMX,respectively.The analyzing softw are was T2000Ch rom atographicW ork from ShanghaiTianm eiScien tific Instrum en t Ltd.(China).
2.3.Anaerobic biodegradation experim ent
Anaerobic biodegradation ofRDX and HMXwastewaterswascarried out in anaerobic bottle,where various kinds and am oun ts of cosubstratessuch asdextrose,amm onium ch loride,sodium acetic,sodium nitrate,or sodium su lfate were present.As a control,the anaerobic biodegradation of RDX and HMX was carried out withoutany co-substrate.
3.Results and Discussion
3.1.Anaerobic biodegradation without substrate
without any substrates added,the wastewater was anaerobically biodegraded with a constant concentration of the sludge(1000 mg·L-1,Fig.1).The RDX concentration decreased d rastically in the first 3 days,and then decreased gradually.In the end,the concentrations of RDX and HMX decreased from the initial 32.9 mg·L-1to 1.96 and 3.2 mg·L-1,respectively,with co rresponding degradation percentage of 95.1%and 92%.Although most of RDX and HMX in the wastewater is degraded by the sludge,their final concentrations do no t meet the requ irement for industrial wastewater discharge standard(RDX concentration ≤ 1.50 mg·L-1)(National Standard of Ch ina,GB 4275-8 and GB/T 13900-92)[22,23]and various substrates shou ld be added to enhance their degradation percentages.
3.2.Anaerobic biodegradation with amm onium chloride as co-substrate
Amm onium ch loride is one of the comm only used nitrogen con taining sources forbiodegradation ofwastewaters.How ever,with amm onium ch loride added to the RDX or HMX wastewater,no significan teffect on the degradation efficiency can be observed(Fig.1).As w e all know,the nitrogen released during degradation of wastes can be consum ed by microorganism s andis therefore beneficial for their grow th.How ever,the mo lar ratio of nitrogen to carbon(N/C)in both RDX and HMX mo lecu les is 2/1(Fig.2),which is higher than the mo lar ratio of N/C needed forbiodegradation of these substances.Therefore,with nitrogen con tain ing amm onium ch loride added,no significan t effect can be detected.

Fig.1.Anaerobic biodegradation of RDX(A)and HMX(B)with amm onium chloride at different concentrations.
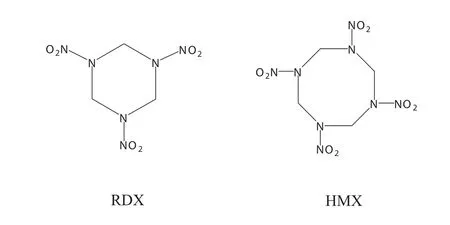
Fig.2.M olecular structure of RDX and HMX.
3.3.Anaerobic biodegradation with dextrose as co-substrate
Dextrose is one of the comm only em ployed co-substrate because of the easiness of its decom position by microorganism s,as w ell as its low cost[24,25].All degradation percentages of RDX and HMX are higher than that of con tro l sam ple without co-substrate,andincreases with the concentration of dextrose(Fig.3).
For the positive effect of dex trose on degradation of RDX and HMX,it is assum ed that(a)dextrose reduces the toxicity and supp ression of RDX and HMX to microo rganism s[26,27];(b)dex trose provides adequate carbon source and energy for microo rgan ism s,resulting in large numbers of b red microo rganism s,which also exhibit higher activity[28-30];(c)with catalyzing of microorgan ism s,som e substances are produced by substrates,which play a key role in helping microorganism s producing specific enzym es to degrade RDX and HMX[31,32];(d)reductive hyd rogen en tity(NADPH++H+)is produced with dex trose,accelerating the splitting of N ring in RDX and HMX mo lecu les[29,33,34];and(e)the degradation of RDX and HMX with dextrose alters the characters of the sludge andim proves its absorbing capacity for RDX and HMX[35].
3.4.Anaerobic biodegradation with sodium acetic as co-substrate
For sodium acetic as co-substrate,Fig.4 show s similar results to that of dextrose,but the performance is not as good as that of dextrose.It is then concluded that specific substrates shou ld be em ployed for the anaerobic biodegradation of RDX and HMX due to their selectivity.The rich carbon con tainedin the mo lecu les of sodium acetic will effectively balance the excessive nitrogen released du ring biodegradation of RDX and HMX,favoring then the grow th of microorganism s and the form ation of an in tegrated microorganism food cycle,which will accelerate the biodegradation process in turn.
3.5.Anaerobic biodegradation with sodium nitrate as the co-substrate
Various nitrates are comm on con tam inants in real wastewaters,so sodium nitrate with different concentrations was added to the simulated RDX and HMX wastewater and the influence of nitrate for anaerobic biodegradation of RDX and HMX wasstudied.Fig.5 show s that the degradation percentage of RDXand HMX with sodium nitrate is low er than that without it,and the higher the concentration of sodium nitrate,the low er the degradation percentage,indicating that the presence of sodium nitrate inhibits,to som e ex ten t,the degradation of RDX and HMX,and the overladen sodium nitrate may have negative effect on the anaerobic degradation.
In the process of anaerobic degradation,RDX and HMX mo lecu les function more as the electron accep tor than as the nitrogen provider[24].Therefore,on one hand,nitrate molecules com pete with RDX and HMX for electrons in the reaction,inhibiting the anaerobic degradation ofRDX and HMX;on theotherhand,du ring the denitrification ofnitrate molecu les,either enzym esare needed for anaerobic degradation ofRDX and HMX,or som e other substances that enhance the split of nitrogen con taining ringsand rem ovalofnitrile form,which function asdextrose,p rom oting the anaerobic degradation of RDX and HMX.Low er concentrations of sodium nitrate have positive effect;while higher concentrations have negative effect.

Fig.3.Anaerobic biodegradation of RDX(A)and HMX(B)with dextrose at different concentrations.

Fig.4.Anaerobic biodegradation of RDX(A)and HMX(B)with acetic sodium at different concentrations.
3.6.Anaerobic biodegradation with sodium su lfate as the substrate
W hen sodium sulfate(with concentration of SO42-)was used as the substrate,no significan t effect can be observed for degradation of RDX and HMX(Fig.6).In spite of their diversity,the sulfate based reducing bacteria are considered as the sam e class as the photosyn thetic nourishing bacteria and can be generally dividedin to two categories from the physiologicalview point.One is like desu lfom onas,which can be reduced to su lfureted hyd rogen with alcohol,lactic acid and som e other aliphatic acids;the other is like desu lfobacter and desu lfococcus,which can be reduced to su lfur with aliphatic acid,especially with acetic acid.The su lfate reducing bacteria are all specific anaerobic substrates,and even at very low concentrations,they dem onstrate metabolizing activity[36].RDX and HMX are finally anaerobically biodegradedin to su lfureted hyd rogen,methane and carbon dioxide in this case.
This experiment focuses on biodegradation of RDX and HMX wastewaters,using direct inocu lation method to treat anaerobic granular sludge.The analysis data show that the effect of su lfate on the degradation of RDX and HMX degradation is very sm all.The following two reasons cou ld accoun t for th is phenom enon:on one hand,it can be found that,under themicroscope,them ainMicrobesaremethanogenic bacteria and acetic acid bacteria,and the am oun t of su lfate reducing bacteria(SRB)is sm all;on the other hand,experim ental periodis indeed short and SRB is lacking extrem ely.

Fig.5.Anaerobic biodegradation of RDX(A)and HMX(B)with sodium nitrate at different concentrations.

Fig.6.Anaerobic biodegradation of RDX(A)and HMX(B)with sodium su lfate at different concentrations.
4.Conclusions
RDX and HMX were anaerobically biodegradedin the presence of various substrates.Nitrogen containing co-substrates such as amm onium ch loridehad no significan teffecton the degradation efficiency,indicating that high N/C mo lar ratio of the substances is su fficien t for the grow th of microorganism s.with dex trose or sodium acetic as cosubstrate,the degradation efficiency of the substances was enhanced with dextrose being better than sodium acetic,and under similar conditions,the degradation percentage of RDX was higher than that of HMX.The substrates acted as carbon and energy sources du ring the biodegradation of RDX and HMX,and balanced the excessive nitrogen released,which are favorab le for the grow th of microorganism s and the form ation of an in tegrated microorganism food cycle.How ever,the presence of nitrate inhibited the biodegradation of RDX and HMX,and the su lfate had no significant effect.
 Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering2015年4期
Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering2015年4期
- Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering的其它文章
- Accurate level set method for simulations of liquid atom ization☆
- Heat transfer augmentation in a circular tube with winglet vortex generators☆
- Influence of im peller diameter on local gas dispersion properties in a sparged mu lti-im peller stirred tank☆
- Pow er dem and and mixing performance of coaxial mixers in a stirred tank with CMC solution
- CFD simulation of high-temperature effect on EHD characteristics in a wire-plate electrostatic precipitator☆
- Em u lsion liquid mem brane for selective extraction of Bi(III)
