miR-27a对两种结肠癌细胞增殖和侵袭能力的影响
张子雯,傅小一
(江西省宜春学院 医学院,江西 宜春 336000)
miR-27a对两种结肠癌细胞增殖和侵袭能力的影响
张子雯,傅小一
(江西省宜春学院 医学院,江西 宜春 336000)
目的 探讨microRNA-27a(miR-27a)对2种结肠癌细胞增殖和侵袭能力的影响。方法 应用miR-27a反义寡核苷酸(antisense oligonucleotides,ASO)在体外转染结肠癌细胞系SW620和HCT116,设置转染无义序列组作为对照组。RT-PCR检测细胞miR-27a表达;MTT法检测细胞增殖;Transwell小室侵袭实验检测细胞侵袭能力;Western blot检测转染细胞FOXO1蛋白表达。结果 与对照组相比,转染miR-27a ASO后结肠癌细胞系SW620和HCT116的miR-27a表达水平均明显降低(P<0.001),增殖能力和侵袭能力均受到明显抑制(P<0.01),FOXO1蛋白表达均明显增高(P<0.05)。结论 抑制miR-27a表达可显著降低结肠癌细胞系SW620和HCT116的增殖能力和侵袭能力,而调控下游FOXO1蛋白表达可能是miR-27a参与结肠癌细胞增殖和侵袭的主要机制。
miR-27a;结肠癌;增殖;侵袭;FOXO1
结肠癌是常见的消化道恶性肿瘤之一。近年来,随着人们生活方式及饮食习惯的改变,国内外结肠癌发病率及死亡率均呈逐年上升趋势,严重威胁患者的生命健康[1]。但目前对于结肠癌增殖及侵袭的机制尚未完全明确。非蛋白质编码微小RNA(microRNA, miRNA)的出现为恶性肿瘤的研究提供了新思路[2]。越来越多证据显示,miRNA与肿瘤密切相关,miRNA可通过与靶mRNA互补配对,从而调控蛋白翻译过程,在肿瘤细胞增殖、分化、凋亡和基因调控中发挥重要作用[3]。大量研究证实,miR-27a在胃癌、乳腺癌组织中表达明显上升,并可通过调控其下游蛋白表达参与肿瘤细胞增殖和侵袭,但miR-27a在结肠癌中的作用和机制尚未见报道[4-5]。本研究以结肠癌细胞系SW620和HCT116为研究对象,利用反义寡核苷酸(antisense oligonucleotides, ASO)技术抑制细胞中miR-27a表达,观察miR-27a低表达对结肠癌细胞增殖和侵袭能力的影响,旨在为结肠癌临床治疗提供可靠的基础研究依据。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料 结肠癌细胞系SW620和HCT116(ATCC细胞库,美国);胎牛血清、RPMI1640培养基、PBS缓冲液(Hyclon公司);脂质体Lipofectamin 2000(Invitrogen,美国);miR-27a ASO(Applied Biosystems,美国);总蛋白定量测试盒(南京建成,中国)。
1.2 细胞培养 复苏结肠癌细胞系SW620和HCT116,无血清RPMI1640洗涤3次,RPMI1640培养基(1%双抗,10%胎牛血清)重悬浮细胞,置于37 ℃、5% CO2培养箱中培养,每天换液一次。
1.3 转染 待结肠癌细胞系SW620和HCT116生长至对数生长期,收集细胞,调整细胞浓度至1×105个/mL,将细胞悬液加至6孔细胞培养板,采用脂质体Lipofectamin 2000分别将无义序列(Control)和miR-27a ASO转染至SW620和HCT116细胞中,转染终浓度为80 nmol/L,转染6 h换液,48 h后收集细胞,备用。
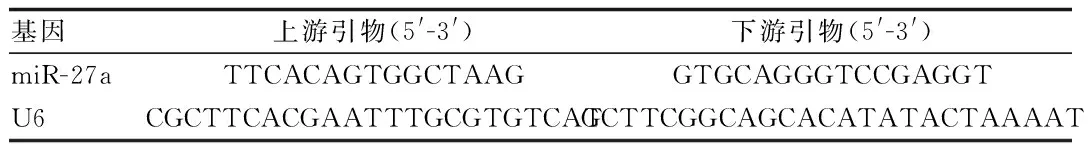
表1 引物序列Tab.1 The primer sequence
1.5 MTT法检测细胞增殖 收集对数生长期的结肠癌细胞系SW620和HCT116,调整细胞浓度至5×106个/mL,加入96孔培养板,每孔200 μL,培养板置于37 ℃ CO2培养箱中孵育24 h;分别转染无义序列(Control)和miR-27a ASO,转染终浓度为80 nmol/L,转染6 h换液,培养结束后每孔加入50 μL MTT工作液(2 mg/mL),37 ℃孵育4 h,离心弃上清,每孔加入150 μL DMSO(4% 1.0 M HCl),OD450nm读值,每组设3个平行对照。
1.6 Transwell小室侵袭实验检测细胞侵袭能力 RPMI1640培养基(1%双抗,10%胎牛血清)加至24孔板,600 μL/孔;于小室基膜上预铺设基质胶,将Transwell小室置于24孔板,静置5 min,收集转染后细胞并分别接种于小室,各小室接种细胞数量为5×104个/mL。细胞置于37 ℃、5%CO2培养箱中分别培养24 h,取出小室,擦去小室基膜表面细胞,95%酒精室温固定15 min,结晶紫室温染色10 min,随机选取3个视野于高倍镜下计数,实验重复3次。
1.7 Western blot检测FOXO1蛋白表达 分别收集无义序列(Control)和miR-27a ASO转染后的SW620和HCT116细胞,PMSF裂解液提取细胞总蛋白,总蛋白定量测试盒测定总蛋白浓度,按4:1比例分别加入5×loading buffer和蛋白样品,煮沸3 min,配制聚丙烯酰胺凝胶,上样,跑胶1.5 h,0 ℃ 100 V转膜1 h,5%脱脂乳室温封闭1.5 h,FOXO1抗体稀释1000倍后4 ℃孵育过夜,洗膜3次,二抗孵育2 h,ECL试剂显色,进行蛋白表达定量分析。
2 结果
2.1 转染miR-27a ASO对结肠癌细胞系SW620和HCT116 miR-27a表达的影响 RT-PCR结果显示,与转染无义序列(Control)相比较,转染 miR-27a ASO后结肠癌细胞系SW620和HCT116的miR-27a表达水平明显降低,组间比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.001),见图1。
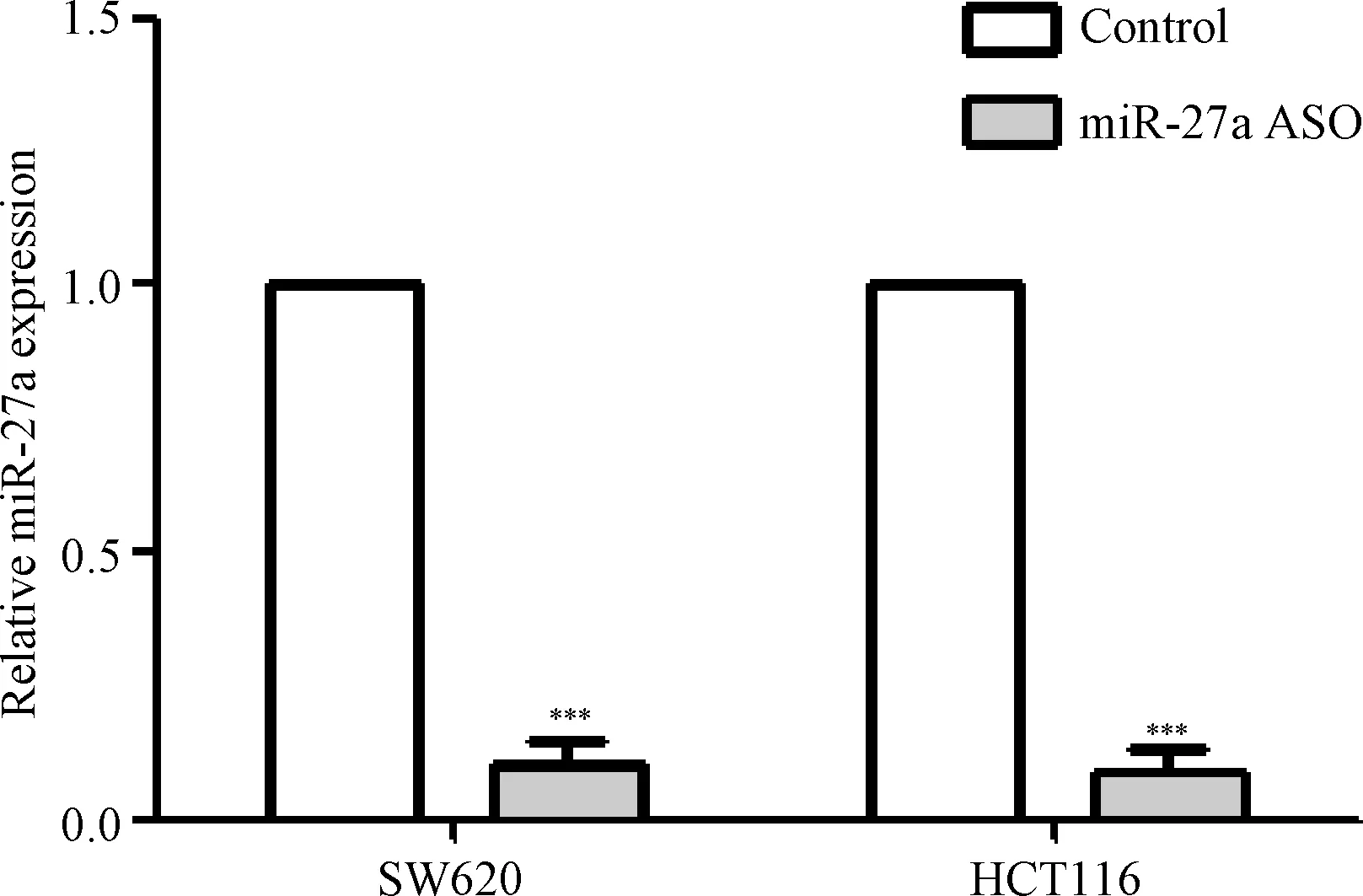
图1 转染miR-27a ASO后结肠癌细胞系SW620和HCT116 miR-27a表达情况***P<0.001,与对照组比较Fig.1 Expression of miR-27a in colorectal cancer cells of SW620 and HCT116 transfected with miR-27a ASO***P<0.001, compared with control group
2.2 抑制miR-27a表达对结肠癌细胞系SW620和HCT116增殖水平的影响 MTT增殖实验结果表明,与转染无义序列(Control)相比较,转染miR-27a ASO可明显抑制结肠癌细胞系SW620和HCT116增殖水平,组间比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.01),见图2、图3。
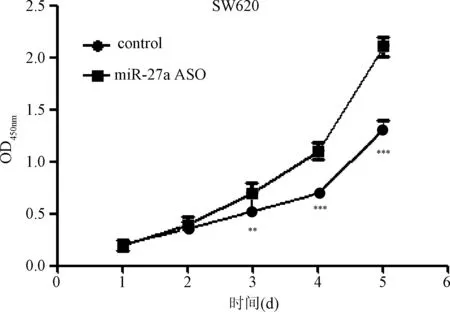
图2 抑制miR-27a表达对结肠癌细胞系SW620增殖水平的影响**P<0.01,***P<0.001,与对照组比较Fig.2 The effect of miR-27a expression inhibited on proliferation of colorectal cancer cells of SW620**P<0.01,***P<0.001,compared with control group
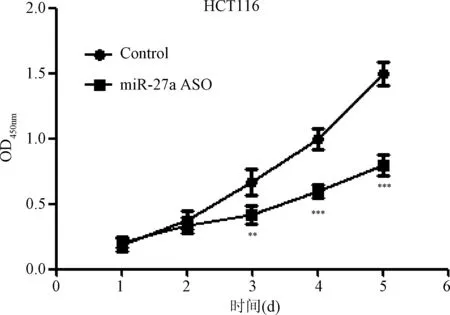
图3 抑制miR-27a表达对结肠癌细胞系HCT116增殖水平的影响**P<0.01,***P<0.001,与对照组比较Fig.3 The effect of miR-27a expression inhibited on proliferation of colorectal cancer cells of HCT116**P<0.01, ***P<0.001,compared with control group
2.3 抑制miR-27a表达对结肠癌细胞系SW620和HCT116侵袭能力的影响 Transwell小室侵袭实验结果表明,与转染无义序列(Control)相比较,转染miR-27a ASO可明显抑制结肠癌细胞系SW620和HCT116侵袭能力,组间比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.001),见图4。
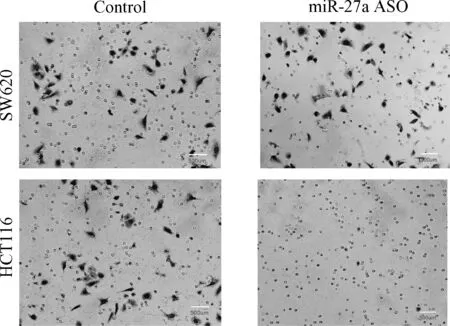
图4 Transwell小室侵袭实验结果Fig.4 The experimental results of transwell chambers
2.4 抑制miR-27a表达对结肠癌细胞系SW620和HCT116 FOXO1蛋白表达的影响 Western blot结果显示,与转染无义序列(Control)相比较,转染miR-27a ASO可明显上调结肠癌细胞系SW620和HCT116 FOXO1蛋白表达,组间比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),见图5、图6。
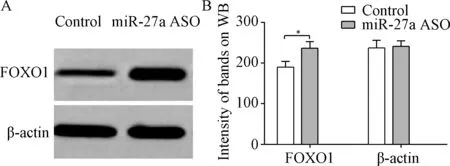
图5 结肠癌细胞系SW620 FOXO1蛋白表达情况Fig.5 The expression of FOXO1 protein in colorectal cancer cells of SW620

图6 结肠癌细胞系HCT116 FOXO1蛋白表达情况Fig.6 The expression of FOXO1 protein in colorectal cancer cells of HCT116
3 讨论
由于发病隐匿,大多数结肠癌患者确诊时已为晚期,以放化疗为主的综合治疗手段效果欠佳,寻找新的治疗手段是提高结肠癌患者总生存期的关键[6-7]。增殖和侵袭是恶性肿瘤最为明显的生物学特性,也是恶性肿瘤难以治愈的根本原因。如何抑制恶性肿瘤增殖和侵袭能力对控制恶性肿瘤进展和提高存活率具有重要意义[8-10]。肿瘤的增殖和侵袭是一个多因素参与的复杂过程,miRNA对肿瘤增殖和侵袭相关基因表达的调控作用是目前研究的热点[11]。
miRNA是一类具有基因调控功能的内源性非编码小分子RNA,其在肿瘤的发生和发展过程中起着双向调节作用,一方面miRNA可作为抑癌基因抑制促癌相关蛋白表达,另一方面miRNA又可作为促癌基因抑制抑癌相关蛋白表达[12]。研究证实,miR-27a在乳腺癌组织中表达显著上调,并可通过抑制下游基因Myt-1和ZBTB10表达诱导细胞增殖[13]。抑制子宫内膜癌细胞miR-27a表达,可明显增加FOXO1表达水平,从而诱导细胞在G1期停滞并导致细胞凋亡[14]。在胰腺癌中,miR-27a可通过靶向调控胰腺癌细胞Sprouty2蛋白表达,参与细胞增殖过程[15]。上述证据提示miR-27a可能在恶性肿瘤进展中发挥癌基因功能。本研究结果显示,miR-27a在结肠癌细胞系SW620和HCT116中表达水平明显增加,提示miR-27a在结肠癌中起致癌作用。进一步研究证实,采用miR-27a ASO可有效抑制结肠癌细胞系SW620和HCT116中miR-27a表达,同时细胞的增殖和侵袭能力均被明显抑制,这也为证实miR-27a在结肠癌中发挥致癌作用提供了有力佐证。
FOXO1作为FOXO家族成员,在肾癌、乳腺癌、前列腺及子宫内膜癌等多种恶性肿瘤中均呈低表达。在哺乳动物细胞中,FOXO1高表达可抑制细胞增殖,导致细胞周期停滞;而FOXO1低表达则可促进细胞增殖和迁移,抑制细胞凋亡[16-18]。研究显示,T细胞因子(T cell factor,TCF)和β-catenin在结肠癌的发展中其关键作用,FOXO1则可通过与β-catenin相结合阻止其与TCF相互作用,使细胞周期停滞,从而抑制结肠癌发展,故有学者提出,重新激活FOXO1活性可能是治疗结肠癌的一种新策略[19]。本研究结果显示,抑制结肠癌细胞miR-27a表达后,结肠癌细胞FOXO1蛋白表达水平显著提高,同时结肠癌细胞增殖能力和侵袭能力显著降低,故推测miR-27a可能是通过调控下游基因FOXO1表达实现对结肠癌细胞增殖能力和侵袭能力的调节作用,但其具体的作用机制还有待于进一步深入研究。
综上所述,抑制miR-27a表达可显著降低结肠癌细胞系SW620和HCT116的增殖能力和侵袭能力,而调控下游FOXO1蛋白表达可能是miR-27a参与结肠癌细胞增殖和侵袭的主要机制,抑制miR-27a表达可作为临床治疗结肠癌的新思路。
[1] 覃勇,傅仲学,卢伟东,等.姜黄素逆转人结肠癌细胞株HCT-8/VCR多药耐药的研究[J].中国生化药物杂志,2011,32(3):173-175.
[2] Nishida N,Yokobori T,Mimori K,et al.MicroRNA miR-125b is a prognostic marker in human colorectal cancer[J].International journal of oncology,2011,38(5):1437-1443.
[3] Cekaite L,Rantala JK,Bruun J,et al.MiR-9,-31,and-182 deregulation promote proliferation and tumor cell survival in colon cancer[J].Neoplasia,2012,14(9):868-869.
[4] Tang W,Zhu J,Su S,et al.MiR-27 as a prognostic marker for breast cancer progression and patient survival[J].PloS one,2012,7(12):e51702.
[5] Zhang Z,Liu S,Shi R,et al.miR-27 promotes human gastric cancer cell metastasis by inducing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition[J].Cancer genetics,2011,204(9):486-491.
[6] Cheng H,Zhang L,Cogdell DE,et al.Circulating plasma MiR-141 is a novel biomarker for metastatic colon cancer and predicts poor prognosis[J].PloS one,2011,6(3):e17745.
[7] Smith AR,Marquez R,Tsao B,et al.Tumor suppressor miR-137 inhibits colorectal cancer progression by negatively regulating cancer stem cell marker,Musashi-1[J].Cancer Research,2014,74(19 Supplement):1460-1461.
[8] Tsuchida A,Ohno S,Wu W,et al.miR‐92 is a key oncogenic component of the miR‐17-92 cluster in colon cancer[J].Cancer science,2011,102(12):2264-2271.
[9] Migliore C,Martin V,Leoni VP,et al.MiR-1 downregulation cooperates with MACC1 in promoting MET overexpression in human colon cancer[J].Clinical Cancer Research,2012,18(3):737-747.
[10] Yu Y,Sarkar FH,Majumdar APN.Down-regulation of miR-21 induces differentiation of chemoresistant colon cancer cells and enhances susceptibility to therapeutic regimens[J].Translational oncology,2013,6(2):180-186.
[11] Siemens H,Neumann J,Jackstadt R,et al.Detection of miR-34a promoter methylation in combination with elevated expression of c-Met and β-catenin predicts distant metastasis of colon cancer[J].Clinical Cancer Research,2013,19(3):710-720.
[12] Bu P,Chen KY,Chen JH,et al.A microRNA miR-34a-regulated bimodal switch targets notch in colon cancer stem cells[J].Cell stem cell,2013,12(5):602-615.
[13] Mertens-Talcott SU,Chintharlapalli S,Li X,et al.The oncogenic microRNA-27a targets genes that regulate specificity protein transcription factors and the G2-M checkpoint in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells[J].Cancer research,2007,67(22):11001-11011.
[14] Guttilla IK,White BA.Coordinate regulation of FOXO1 by miR-27a,miR-96,and miR-182 in breast cancer cells[J].Journal of Biological Chemistry,2009,284(35):23204-23216.
[15] Ma Y,Yu S,Zhao W,et al.miR-27a regulates the growth,colony formation and migration of pancreatic cancer cells by targeting Sprouty2[J].Cancer letters,2010,298(2):150-158.
[16] Zhang H,Pan Y,Zheng L,et al.FOXO1 inhibits Runx2 transcriptional activity and prostate cancer cell migration and invasion[J].Cancer research,2011,71(9):3257-3267.
[17] Zeng Z,Lin H,Zhao X,et al.Overexpression of GOLPH3 promotes proliferation and tumorigenicity in breast cancer via suppression of the FOXO1 transcription factor[J].Clinical Cancer Research,2012,18(15):4059-4069.
[18] Brosens JJ,Lam EWF.Progesterone and FOXO1 signaling:Harnessing cellular senescence for the treatment of ovarian cancer[J].Cell Cycle,2013,12(11):1660-1661.
[19] 甘立霞.FoxO 转录因子在代谢调节及肿瘤抑制中的作用[J].第三军医大学学报,2006,28(12):1347-1350.
(编校:王俨俨,吴茜)
Effect of miR-27a on the proliferation and invasion of two colorectal cancer cells
ZHANG Zi-wen,FU Xiao-yi
(College of Medicine, Yichun University, Yichun 336000, China)
ObjectiveTo evaluate effect of miR-27a on proliferation and invasion of colorectal cancer cells. MethodsThe colorectal cancer cells of SW620 and HCT116 were transfected with miR-27a antisense oligonucleotides (ASO) in vitro, and the above cells transfected with nonsense sequence were as control group. RT-PCR was used to examine the expression levels of miR-27a. MTT method was used to examine the cell proliferation. Transwell matrigel invasion test was used to examine the cell invasion. Western blot was used to examine the protein expression levels of FOXO1. ResultsCompared with control group, after the colorectal cancer cells of SW620 and HCT116 were transfected with miR-27a ASO, the expression levels of miR-27a significant decreased(P<0.001), the ability of proliferation and invasion significant inhibited(P<0.01), the protein expression levels of FOXO1 significant increased(P<0.05). ConclusionInhibiting miR-27a expression could significantly reduce the proliferation ability and invasion ability of SW620 and HCT116. The regulation of downstream FOXO1 protein expression may be the main mechanisms of miR-27a involved in cdorectal cancer cell proliferation and invasion.
miR-27a; FOXO1; colorectal cancer; proliferation; invasion
张子雯,女,本科,高级实验师,研究方向:病理实验教学与病理技术研究,E-mail:2230214069@qq.com;傅小一,通讯作者,男,本科,副主任医师、副教授,研究方向:病理教学与科研,E-mail:ycfxylhl119@163.com。
R735.3
A
1005-1678(2015)02-0024-04

