术前口服可乐定对脊柱手术患者全麻苏醒的影响
术前口服可乐定对脊柱手术患者全麻苏醒的影响
邓嘉陵1,李军祥2,杨小霖2
(1.四川省南充市东方医院麻醉科;2.川北医学院附属医院麻醉科,四川南充637000)
【摘要】目的:观察脊柱手术患者术前口服可乐定对全麻苏醒的影响。方法:将64例ASAⅠ-Ⅱ级,18~60岁,择期行椎管减压、脊柱融合手术的患者随机分为术前口服可乐定组(200 μg)和安慰剂组(维生素C 600 mg)。麻醉诱导采用芬太尼2 μg/kg、异丙酚1~2 mg/kg及维库溴铵0.1 mg/kg。气管插管后机械通气,调整吸入异氟烷浓度维持BIS 40~50,间断给予维库溴铵维持肌松。调整呼吸参数维持ETCO235~40 mmHg。记录患者一般资料,芬太尼、异丙酚用量、麻醉时间、拔管时间、低血压或高血压发生率。结果:可乐定组患者芬太尼用量少于安慰剂组(2.11±0.87 vs 3.68±0.93,P<0.05),拔管时间早于安慰剂组(9.88±6.12 vs 13.62±9.74,P<0.05),异丙酚用量、低血压及心动过缓发生率组之间没有统计学意义(P>0.05)。结论:脊柱手术的患者,术前给于可乐定能减轻麻醉所需麻醉药的用量,加快麻醉后复苏,并且不增加低血压和心动过缓的发生率。
【关键词】可乐定,异氟烷,全身麻醉,麻醉复苏
脊柱手术通常伴随明显的失血和血流动力学的波动,并需要大剂量的阿片类药物来抑制应激反应[1-3]。强镇痛药物的快速清除和/或快速耐受,可能会增加术后疼痛的发生[4]。行脊柱手术的患者术前多伴有慢性疼痛,围术期多使用阿片类、NSAIS类或其他治疗慢性疼痛的药物。因此需要提供类阿片药物或者减少痛觉过敏的麻醉技术以阻止医源性的术后痛觉过敏[5]。目前广泛的做法是将强效的阿片类药物与非阿片类药物或者α2受体兴奋剂复合使用[6]。本研究旨在观察术前口服可乐定对阿片类药物的需求和术后麻醉复苏的影响。
1 材料和方法
1.1纳入标准
64例ASAⅠ-Ⅱ级,18~60岁,择期行椎管减压、脊柱融合手术的患者。
1.2排除标准
孕妇,心、肝、肾、呼吸系统的疾病,活动或智力障碍,对α2受体激动剂过敏,在使用β受体阻滞剂、α2受体激动剂、抗惊厥类药物、精神类药物等的患者。
1.3方法
将符合纳入标准的患者随机分别于术前口服盐酸可乐定片(200 μg)或维生素C 1片(600 g),患者不知道具体分组。患者常规监测ECG、无创动脉血压(NIBP)、脉搏氧饱和度(SpO2),局麻下行桡动脉穿刺置管,监测动脉血压(ABP)。麻醉诱导采用芬太尼2 μg/kg、异丙酚1~2 mg/kg及维库溴铵0.1 mg/kg。3 min后行气管插管。麻醉维持使用O2、Air、异氟烷(FiO250%)。维持ETCO235~40 mm-Hg。调整异氟烷浓度维持BIS 40~50。调节呼吸参数维持ETCO235~40 mmHg,间断给予维库溴铵维持肌松。当HR或SBP高于基础值的20%给予异丙酚0.5 mg/kg,若效果不佳再给于芬太尼0.5 μg/kg;当SBP低于基础值的20%,使用麻黄碱10~15mg静注;当HR低于50次/min时,给予阿托品0.25~0.5 mg静注。缝合皮肤时,调低异氟醚给予浓度至维持呼末浓度的50%,皮肤缝合结束时停止吸入异氟烷。给予新斯的明50 μg/kg拮抗残余肌松药作用。当患者清醒,自主呼吸能维持SPO2>95%,并能按指令活动上肢时,拔除气管导管。
1.4评估指标
记录患者一般资料、芬太尼及异丙酚用量、麻醉时间、拔管时间(停止异氟烷到拔管时间)、低血压或高血压发生率。
1.5统计学分析
据采用均数±标准差或百分数表示,使用SPSS15.0分析。计数资料采用卡方检验,计量资料采用t检验。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1一般资料比较
两组患者一般资料比较没有统计学意义(P>0.05),见表1。
2.2两组患者术中情况比较
可乐定组患者芬太尼用量少于安慰剂组(2.11±0.87 vs 3.68±0.93,P<0.05),拔管时间早于安慰剂组(9.88±6.12 vs 13.62±9.74,P<0.05),异丙酚用量和低血压(51.6% vs 60.6%)及心动过缓(12.9% vs 12.1%)发生率两组之间没有统计学意义(P>0.05),见表2。
表1 两组患者一般资料比较(±s)
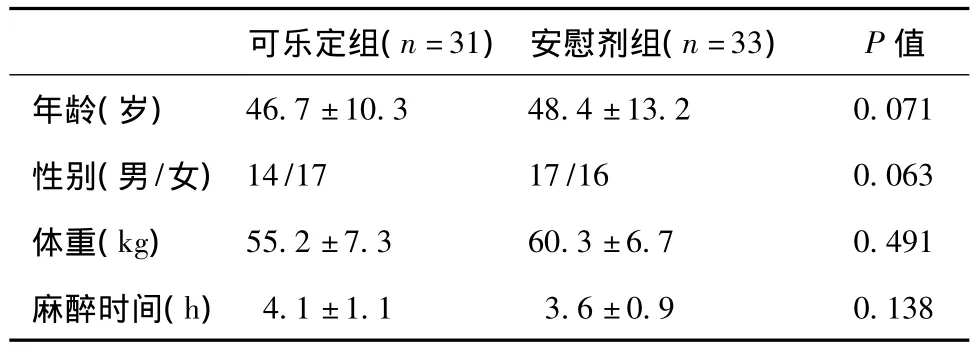
表1 两组患者一般资料比较(±s)
可乐定组(n =31)安慰剂组(n =33) P值年龄(岁)46.7±10.3 48.4±13.2 0.071性别(男/女)14/17 17/16 0.063体重(kg) 55.2±7.3 60.3±6.7 0.491麻醉时间(h)4.1±1.1 3.6±0.9 0.138
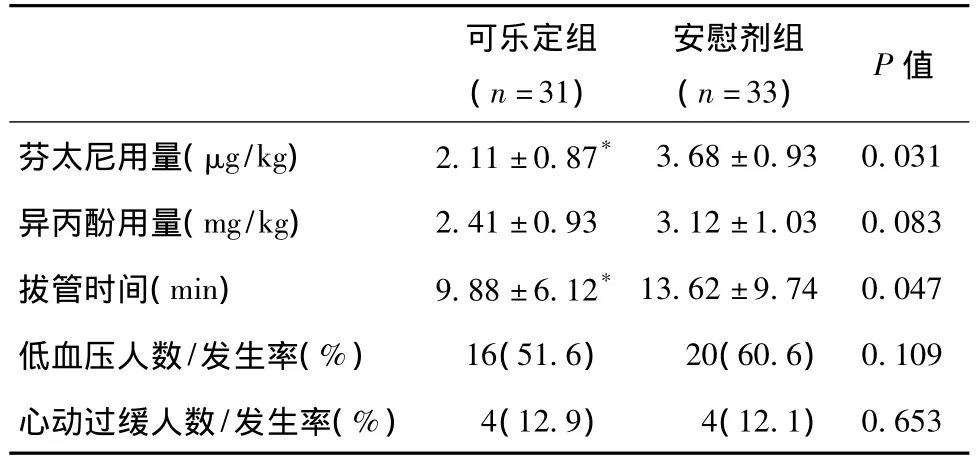
表2 两组患者术中情况和麻醉恢复情况比较
3 讨论
α2受体兴奋剂具有协同阿片类药物的镇痛作用,而不增加痛觉过敏和副作用的发生,甚至能减少阿片类药物的痛觉过敏[7-10]。α2受体兴奋剂和阿片类药物通过不同的受体调节镇痛作用,α2受体兴奋剂增加阿片类的镇痛作用而不增加其副作用,并同时具有镇静、抗交感作用。本实验通过术前给予可乐定后对麻醉药物的需求、麻醉后复苏、血流动力学变化的观察发现,可乐定组在维持相同的麻醉深度情况下,能明显减少患者对芬太尼的需求量,这很大程度上与α2受体兴奋剂具有镇静、镇痛作用,并且具有抗交感的作用有关。Woodcock等[11],Marchal等[12]研究发现,在ENT手术患者单次给予可乐定会减少麻醉所需异氟烷浓度。
术前使用可乐定(2.5~5 μg/kg)会延长异氟烷麻醉后苏醒时间,本研究使用200 μg(3.3 μg/kg)可乐定术前给药麻醉苏醒时间为(9.88±6.12)min,麻醉苏醒时间短于Goyagi等[13]的研究结果。两个研究的苏醒时间的差距可能是因为Goyagi等[10]的研究没有采用BIS监测麻醉深度容易导致麻醉过深,并且其停用异氟烷的时机也较晚,从而导致麻醉苏醒时间较长。
低血压和心动过缓是α2受体兴奋剂常见的并发症。本研究发现术前给予可乐定200 μg组的患者和对照组患者两者的发生没有差异。可见术前给予可乐定200 μg没有增加术中低血压和心动过缓的发生率。
总之,脊柱手术的患者,术前给予可乐定能减轻所需麻醉药用量,加快麻醉后恢复。
参考文献
[1]Poon KS,Wu KC,Chen CC,et al.Hemodynamic changes during spinal surgery in the prone position[J].Acta Anesthesiol Taiwan,2008,46(2 ):57-60.
[2]Edgcombe H,Carter K,Yarrow S.Anesthesia in the prone position [J].Br J Anesth,2008,100(2):165-183.
[3]Elgafy H,Bransford RJ,McGuire RA,et al.Blood loss in major spine surgery: are there effective measures to decrease massive hemorrhage in major spine fusion surgery[J].Spine (Phila Pa 1976),2010,35(9 suppl): S47-56.
[4]Guignard B,Bossard AE,Coste C,et al.Acute opioid tolerance: intraoperative remifentanil increases postoperative pain and morphine requirement[J].Anesthesiology,2000,93(2):409-417.
[5]Vorobeychik Y,Chen L,Bush MC,et al.Improved opioid analgesic effect following opioid dose reduction[J].Pain Med,2008,9 (8):724-727.
[6]Rajpal S,Gordon DB,Pellino TA,et al.Comparison of perioperative oral multimodal analgesia versus IV PCA for spine surgery [J].J Spinal Disord Tech,2010,23(2):139-145.
[7]Meert TF,De Kock M.Potentiation of the analgesic properties of fentanyl-like opioids with α2-adrenoceptor agonists in rats[J].Anesthesiology,1994,81(3):678-688.
[8]Schlimp CJ,Pipam W,Wolrab C,et al.Clonidine for remifentanilinduced hyperalgesia: a double-blind randomized,placebo-controlled study of clonidine under intra-operative use of remifentanil in elective surgery of the shoulder[J].Schmerz,2011,25(3): 290-295.
[9]Belgrade M,Hall S.Dexmedetomidine infusion for the management of opioid-induced hyperalgesia[J].Pain Med,2010,11 (12): 1819-1826.
[10]Zheng Y,Cui S,Liu Y,et al.Dexmedetomidine prevents remifentanil-induced postoperative hyperalgesia and decreases spinal tyrosine phosphorylation of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor 2B subunit [J].Brain Res Bull,2012,87(4):427-431.
[11]Woodcock TE,Millard RK,Dixon J,et al.Clonidine premedication for isoflurane-induced hypotension.Sympathoadrenal responses and a computer-controlled assessment of the vapour requirement[J].Br J Anesth,1988,60(4):388-394.
[12]Marchal JM,Gómez-Luque A,Martos-Crespo F,et al.Clonidine decreases intraoperative bleeding in middle ear microsurgery[J].Acta Anesthesiol Scand,2001,45(5):627-633.
[13]Goyagi T,Tanaka M,Nishikawa T,et al.Oral clonidine premeditation reduces the awakening concentration of isoflurane[J].Anesth Analg,1998,86(2):410-413.
网络出版时间: 2015-3-5 12∶47网络出版地址: http://www.cnki.net/kcms/detail/51.1254.R.20150305.1247.021.html
The effects of oral clonidine for premedication of anesthetic recovery on the spinal operation patients
DENG Jia-ling1,LI Jun-xiang2,YANG Xiao-lin2
(1.Department of Anesthesiology,Nanchong Oriental Hospital;2.Department of Anesthesiology,Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College,Nanchong 637000,Sichuan,China)
【Abstract】Objective: To observe the effects of oral clonidine premedication on the general anesthesia and recovery in patients undergoing spinal surgery.Methods: Sixty-four ASA levelⅠ-Ⅱpatients (18-60 years old)undergoing major spine surgery were randomly allocated to two groups.One group received oral clonidine (200 μg)and the other received placebo (Vitamin C 600 mg)for premedication.Standard anesthesia protocols were followed for induction Fentanyl 2 μg/kg,Propofol 1~2 mg/kg and Vecuronium Bromide 0.1 mg/kg.The mechanical ventilation was performed after the tracheal intubation.And the concentration of isoflurance was adjusted and maintained at the level of BIS 40~50.The Vecuronium Bromide was given inconsistently in order to keep the muscular relaxation.The reference data of breathing is adjusted at the level of ETCO235~40 mmHg.Heart rate,blood pressure,and end-tidal concentrations of isoflurane were monitored.Hypotensive episodes were treated with bolus doses of ephedrine or phenylephrine.Results: The demographic data,duration of anesthesia,propofol requirement were not significant between the two groups.The total dose of fentanyl (2.11±0.87 vs.3.68±0.93)and the recovery time (9.88±6.12vs.13.62±9.74)were decreased in clonidine group.There was no statistical difference in the change of hemodynamic parameters,the incidence of hypotension or bradycardia between the two groups.Conclusion: Clonidine for premedication can reduce the requirement of opoids,facilitate the recovery from inhaled isoflurane anesthesia,and does not increase the incidence of hypotension or bradycardia.
【Key words】Clonidine; Isoflurane; General Anesthesia; Anesthesia recovery
通讯作者:杨小霖,E-mail: yang_xl_yang@126.com
作者简介:邓嘉陵(1971-),男,重庆合川人,主治医师,主要从事临床麻醉和疼痛诊疗工作。
基金项目:南充市科技局支撑项目(110A0076)
收稿日期:2014-09-26
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1005-3697.2015.01.21
【文章编号】1005-3697(2015)01-0090-03
【中图分类号】R614.2
【文献标志码】A

