Designing an ESP Course with Narrow Reading Approach
Liju Xu

Abstract
The purpose of this paper is to explore whether narrow reading approach can expand students reading competence in an ESP course. The ESP course in discussion focuses on the genre of business report. Participants feedback of a survey has been collected to evaluate their recognition of the teaching and learning approach.
Key words: ESP, narrow reading, vocabulary, oral report, subject matter knowledge,
【分类号】D913
Introduction
Simplified readers are useful for beginning students, but, eventually, learners will want to start accessing authentic texts. Narrow reading can facilitate the transition to these texts, and perhaps permit earlier access to them, by lowering the lexical load required of the learner. (Norbert Schmitt and Ronald Carter) The present study intends to investigate the effects of narrow reading on comprehension of junior students.
Research question: How does the business report reading bring students to the point where they are autonomous acquirers, prepared to improve on their own?
Literature Review
Academic Proficiency consists of two central components: Knowledge of academic language and knowledge of specialized subject matter (Biber, 2006). To help the students to achieve academic proficiency, an ESP course should be designed with the three features. a) Authentic material (Dudley-Evans', 1997). b) Purpose-related orientation. c) Self-direction (Carter, 1983, P.134).
Johns and Dudley-Evans (1991) stated “In ESP practice the single skill is usually reading”(P.305).Richards (1976) and Beasley (1990) maintained that acquiring the ability to read academic texts is of importance for students of English as a foreign language. Celece-Murcia (1991) states that ESP academic reading courses should emphasize both reading to learn and learning by doing. By reading in depth around a particular subject area, students experience marked growth in background knowledge (Dubin & Bycina, 1991).
Business reports in newspapers or magazines in the target language have often been suggested as a good source for reading in an ESP course. However, a potential problem is that the students may not have the prerequisite vocabulary necessary to read them. One way to ease them into authentic texts like these is to use narrow reading, to read texts about a single topic of interest, which helps ensure comprehension and natural repetition of vocabulary and grammar (Krashen, 2004). Narrow reading encourages early specialization. Readers gradually broaden their reading interests (LaBrant, 1958). Key words in topic-related passages tend to recur, easing the lexical burden on readers (Hwang & Nation, 1989). Multiple exposures to recurrent words should facilitate vocabulary learning (Schmitt &Carter, 2000).
Another advantage of narrow reading is that readers become familiar with the topic (Krashen & Brown, 2007) and have much better background knowledge for future passages on that topic (Cho & Krashen, 1994). Focusing on texts on a recurrent topic should give learners the chance to practice reading more quickly and fluently (Schmitt &Carter, 2000).
Design
This article approaches the strategy of narrow reading from the following three perspectives. (1) Data on repeated key words in the business reports to demonstrate how narrow reading lowers the vocabulary load of texts and caters the utilization of background knowledge. (2) Students perceptions of narrow reading for facilitating their reading, vocabulary learning and reporting. (3) Suggestions for teachers to install a narrow reading component into their language classes.
A. Participants
The participants of this study are 263 students from Guangdong University of Foreign Studies (GDUFS) majoring in accounting and auditing, who have had English for general purpose courses for two years and studied basic courses on finance, economics and accounting in Chinese. Two hours per week of Financial English is a compulsory course for 18 weeks. The participants in 6 classes have been divided into experimental and control group, 3 classes of each. The former is to read business reports from newspaper and magazine carefully selected with the narrow reading strategy. The latter is to read a textbook recommended by the authority.
B. Using informal survey to explore the benefits of narrow reading
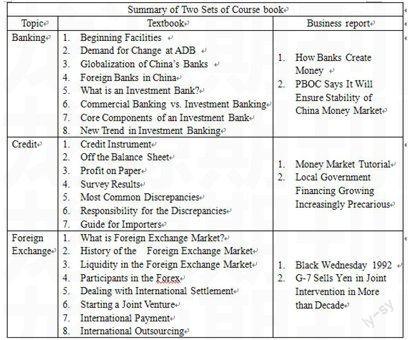
In the textbook for the control group, the textbook covers five topics about banking, credit, foreign exchange, debt management and risk management. Each topic also includes a wide variety of readings. For instance, in the topic of banking there are eight readings, ranging from Beginning Facilities to Globalization of Chinas Banks to New Trend in Investment Banking.
In the business reports for the experiment group, reading are on the same five topics. However, those topics have been divided into two categories. In this study only category one (banking, credit, and foreign exchange) is to be compared and contrasted. There are two readings in each topic. Compared with the textbook, the number of readings is less, but the total amount of words is the same or even more. The choice of the business reports follows two rubrics: a) in content they approach the concept of expansionary monetary policy from different angles in three topics; b) the recurrence of core words for reading comprehension and discussion is calculated.
The rubrics in choosing what business report to read must be decided first. a) Authentic readings. Of the six readings, 2 tutorials come from a British textbook and 4 business reports come from the Bloomberg. b) Content is comprehensible and challenging. Survey has been made on what concepts and terms on the five topics the students have learned in Chinese. 20 concepts are given to the students to do translation from English to Chinese, and then students choose 5 of them to write their explanation in Chinese. From the most frequent concepts chosen and explained by the students, the term of expansionary monetary policy is finally settled to be the focus in choosing the business reports. Two tutorials are given for students to read the basic theories about expansionary monetary policy in English and vocabularies in the field are introduced. Then four business reports from Bloomberg are given, regarding issue related to the theories. All those issues present the effect of expansionary monetary policy at home and abroad. As reading moves from textbook to reality, from China foreign countries, the difficulty level in both academic language and specialized subject matter is growing. However, there are a number of recurrences of the content words, which demonstrates the advantage of narrow reading when it comes to language acquisition. c) After reading an issue, the students are required to summarize the main idea and analyze its reasons, outcomes, or solutions, in the form of either discussion or writing. This is the target of designing the reading activities, to deepen students grasp of language, to incorporate the background knowledge in problem solving and to develop academic proficiency. d) After finishing all the readings in category one, the students are required to reflect on vocabulary again in an informal self-test. They write in three minutes as many words as possible according to whether they have used them in their discussion about issues of monetary market. The purpose of this activity is to let the students see whether they can turn the input into effective output.
Findings and Suggestions
A. Students recognition of narrow reading and criticism on the course design
At the end of the study for 18 weeks when two testing groups have finished the required readings, the students fill out an informal questionnaire, which asks them to consider their ease of reading and vocabulary learning and to use a figure from 1 to 100 to name it. Of 263 participants, 62.86% of the students in the experimental group and 47.22% in the control group respond favorably.
The students in the experimental group consider that the business report reading provides them with opportunities to reinforce the listed vocabulary, both receptively and productively, generally in the context of discussion about financial content. The criticism focuses mainly on the length and difficulty of the reading. The students generally regard that the reading in the textbook should be less than 1,000 words. When they are reading business report, they hope teachers to provide more background information related to economy and certain economic policies, otherwise it is difficulty to understand some sentences in it. Some students even express the need of Chinese translation for some sentences.
B. Adopting one reading comprehension test to collect students reaction
At the end of the study, one reading comprehension exercise is given to the students in both groups in class to finish independently. It is a business report named “Emerging Markets Act to Stem Capital Flight” with 1,206 words. After reading, there are two tasks. The first is to choose the best answer to six questions. Each of the questions has four possible answers. In this part, vocabulary and the understanding of basic content are tested. The second task is to answer three questions. The students are required to elaborate the answers with examples from the reading.
When comparing the answers to the exercises, the difference between two groups obviously lies in the second task. In average, students in the experiment group write longer paragraphs with 47 more words that those in the control group. They provide more detailed analysis to explain their understanding so as to display their mastery of theory. When the instruction requests at least 3 factors influencing the value of a countrys currency, 71% of students in the experimental group choose to provide and explain more than 3 factors, while 58% in the control group. The figures show that narrow reading provides repeated exposures necessary to consolidate both content knowledge and language. An ESP course designed with narrow reading strategy can facilitate students output of content knowledge and language.
C. Incorporating narrow reading into the ESP course design
The case for reading as an aid to vocabulary learning seems to be strong, both in terms of providing the repetition necessary to establish new words in the learners mind and in supplying the different contexts necessary to elaborate and expand the richness of knowledge about those words. The question remains, however, of how best to encourage and organize such reading (Norbert Schmitt and Ronald Carter). Here are several suggestions teachers can do to promote narrow reading in particular.
1. Collect business reports on a given topic in a newspaper or magazine or even on line for students to read. This should not be difficult since the national and international media will cover the major issues in the business world.
2. Business reports are authentic materials difficulty for the students in general with request of both language and content knowledge. Therefore the students background knowledge and language ability must be analyzed before a topic is chosen. As the students will read a number of business reports, it is suggested to choose one domestic first and then to expand to international. This implies to lessen the unfamiliar vocabulary and unknown content knowledge.
3. Students are encouraged to read different business reports on the topics and invited to share in the class.
4. When designing an assignment, the teacher can let the students choose from a list one topic they are interested in. They are required to collect several business reports about that topic to bring to the class to share.
5. A teacher can introduce Krashens narrow reading strategy to the students. Since the time constraint for ESP courses, it is impossible for the students to read all related to their major in one year or in the university. Narrow reading strategy may guide them to following their own interest and to explore with their own effort.
Conclusion
Regarding ESP Litwack (1979) states that certain steps must be followed in developing ESP curricula, such as analyzing learners needs, designing authentic materials, finding relevant and appropriate discourse, deciding on language activities and tasks, re-editing the design, and finally piloting and evaluating the materials. My small survey suggests that selection of business reports facilitated by the narrow reading strategy can permit students access to more content knowledge by lowering the vocabulary load required. The negative feedback suggests the necessity of re-editing the design. It is essential to tailor the authentic business report to help reading with the utilization of background knowledge.
References
Beasley. C. J. (1990).Content-based language instruction :Helping ESL/EFL students with language and study skills at tertiary level. TESOL in Context,1, 10-14.
Biber, D. (2006).University language: A corpus-based study of spoken and written registers. New York: John Benjamins
Cho, K.S., & S. Krashen, S. (1994).Acquisition of vocabulary from the Sweet Valley Kids series. Journal of Reading, 37, 662-667.
Johns,A . M.,& Dudley Evans,T. (1991).English for specific purposes:International in scope,specific in purpose.TESOL Quarterly,25(2),297-314.
Krashen,S. (2004).The Case For Narrow Listening.Language Magazine, 3(5),17-19.
Krashen, S. & Brown, C. L. (2007)What is Academic Language Proficiency? Singapore Tertiary English Teachers Society
Litwack, D. M. (1979).Procedure: The key to developing an ESP curriculum. TESOL Quarterly.13, 383-391.
Richards,J.C. (1976).Teaching English for science and technology (Series 2).Singapore:Singapore University Press
Schmitt, Norbert & Carter, Ronald. (2000)The Lexical Advantages of Narrow Reading for Second Language Learners. TESOL journal, spring.

