Comparative Study of Photosynthetic and Fluorescence Characters of the Grape under High Temperature and High Light in Turpan
Yang JIA,Kang LIAO*,Wei MA,Zhenbin JIANG,Qiangwei LUO,Feng SUN,Guohong WU
1.Research Centre of Feature Fruits,Xinjiang Agriculture University,Urumqi 830052,China;
2.Development Research Center for Grapes and Muskmelons of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region,Shanshan 838200,China
Responsible editor:Xiaoxue WANG Responsible proofreader:Xiaoyan WU
Light is the most important energy source that plants transform into chemical energy by photosynthesis and stored in the body,but excessive light inhibited photosynthesis even causes photo oxidative damage of photosynthetic apparatus.The phenomenon of light-induced reduction of photosynthesis efficiency higher than the energy that the photosynthesis itself can use is called photo inhibition[1].Usually,high temperature and high light often occur at the same time,and even last for a long time.Turpan in Eurasia hinterland is one of the famous inland basins in the world,and the terrain is low-lying and occlusive having significant continental basin climate characteristics.
High temperature and strong light are the main reasons that caused the active center of the potential activity and the efficiency of light conversion decreased,inhibiting the photosynthetic electron transport.Besides,the leaf photosynthetic mechanism was hurt and finally reduced the photosynthetic rate[2].Chlorophyll fluorescence parameters reflect not only the damage degree of high temperature and strong light,but also the enzymatic defense system that in order to alleviate the damage of high temperature and strong light stress[3].The region of Turpan is extreme drought and summer heat,with the highest temperature 47.6 ℃,and the daily maximum temperature in summer ≥40 ℃.Turpan is a famous grape-producing area in the world that the grape planting area over 9 333 333.33 hm2,whose production reached more than 150 million tons,and total production accounted for 52.84% of the whole grape production in Xinjiang.The new varieties constantly updated with the development of grape industry,and the adaptability of different new varieties to the climate is different.In this paper,the photosynthetic physiology of varieties was applied to the response of photosynthetic and fluorescence parameters of different grape varieties under high temperature and strong light in Turpan region,providing practice guidance and laying theoretical basis for the grape variety breeding and cultivation techniques.
Materials and Methods
Test location and materials
The experiment was conducted in Development Research Center for Grapes and Muskmelons of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region in Shanshan of Xinjiang.tested cultivars:Thompson Seedless,Centennial Seedless,Flame Seedless,Crimson Seedless,Red Globe and Kyoho.The tree age is 10 years old and the cultivation method was the horizontal scaffolding,with plant and row spacing of 1 m×5 m.
Test time
The test was divided into two temperature and light conditions (T1 and T2).Specifically,T1 was late 13:30 -16:00 noon in mid-July,with average daily temperature of vineyard at 34.25 ℃,and maximum temperature of 44-45.5 ℃.Moreover,photo synthetically active radiation continuously met the highest 1 900-2 000μmol/(m2·s),and minimum relative humidity in the range of 11%-15%for 4 h.In contrast,T2 was at 11:00-13:00 in early July,with vineyard average daily temperature of 31.49 ℃,maximum temperature of 36-37 ℃,and the highest photo synthetically active radiation 1 600-1 750 μmol/(m2·s).

Table1 The photosynthetic parameters under different temperature and light of different grape varieties
Test method
Using America Li-6400 portable photosynthesis system,the research adopted open pneumatic measuring photosynthetic physiological parameters,selected 3 growth moderations,without plant diseases or pests.As for growth potential plants,each plant was selected from branches with 5 function leaves.It is notable that the periods concerning T1 and T2 may be repeated every 3 days.
Fluorescence parameters used British Hansatech FMS-2 portable pulse modulation fluorometer determination,with the time the same and the same leaf as the photosynthetic physiological parameters.Furthermore,the research made use of a selfdesigned program,involving the gain of 50,modulated 3 in 35 s,and a light(37) with 11,85,0.7,diameter ΦPSR.It is notable that the leaf that to be measured must be guaranteed in real time in terms of light intensity and sufficient light adaptation,in order to get the parameters,including steady-state fluorescence (Fs),maximum fluorescence (Fm′ ),variable fluorescence(Fv′),initial fluorescence(Fo′),and obtain the actual photochemical efficiency(ΦPSⅡ) and PSⅡelectron transport rate (ETR),and dark adapted leaves 30 min,and determine dark adaptation,such as maximum fluorescence (Fm),variable fluorescence(Fv),and initial fluorescence (Fo).The calculation formula for the maximal photochemical efficiency of photosystem Ⅱwas (Fv/Fm)=(Fm-Fo)/Fm,the actual photochemical efficiency(ΦPS Ⅱ)=(Fm′-Fs)/Fm′,nonphotochemical quenching coefficient(NPQ)=(Fm -Fm′ )/Fm′,and photochemical quenching coefficient (qP) =(Fm′ -Fs)/(Fm′-Fo′).In addition,the T1 and the T2 time periods should be repeated every three days.
Results and Analysis
The difference of photosynthetic parameters of different grape varieties
As shown in Table1,three photosynthetic parameters were significantly lower than that of the T2 time period.Although Thompson Seedless between the 2 time periods had reduced greatly,the value of Photo with remaining 5 species had significant difference,which indicated that there was no significant difference in each of the remaining 5 varieties under high temperature and high light,but red globe showed the minimum value.The value of Cond and Trmmol kept the same as Photo,but the value of Ci was opposite,and higher than that of the T2.Additionally,Thompson Seedless and Red Globe showed significant differences,and no significant differences were among the other 4 cultivars.
The difference of photosynthetic parameters of different Grape varieties
As shown in Fig.1,the values of Fs,Fm′,Fv′,and Fo′ under the light adaptation and Fm,Fv,Fo under dark adaptation in 6 grape varieties have big differences.Specifically,under light adaptation,the 4 values of fluorescence parameters of Red Globe and Kyoho were obviously higher compared with other 4 varieties,followed by Thompson Seedless,Crimson Seedless,Flame Seedless,and the lowest is Centennial Seedless.In contrast,the values of three fluorescence parameters under the dark adaptation were significantly higher.The six varieties of fluorescence parameters order showed different with that of light adaptation.Red Globe reached the maximum value of Fm and Fv,followed by Thompson Seedless,Kyoho,Crimson Seedless,Flame Seedless,and the lowest was Centennial Seedless.
By comparing the fluorescence parameters at different temperatures,it showed that except of NPQ,the values of Fv/Fm,ΦPSⅡand qP all decreased,which was the same as the previous findings of the effects of high temperature stress on other plants[4-5].There was none significant differences of Fv/Fm among six varieties in T2 time period,which was in consistent with the T1 time period.During T2 time period,the ΦPS Ⅱof Kyoho and red globe were significantly lower than other varieties,but the ΦPSⅡof Centennial Seedless and Flame Seedless was significantly lower than that of Thompson Seedless and Kyoho in T1 time period.There was none significant difference of NPQ among six varieties in the T2 time period,and Kyoho was significantly higher than Thompson Seedless,Crimson Seedless and Centennial Seedless.But in T1 time period,Kyoho was significantly lower than Centennial Seedless,and in T2 time period the qP values of Kyoho and Red Globe were significantly lower compared with other varieties,and in T1 time period Centennial Seedless had significant differences with Thompson Seedless,which was significantly lower compared with other varieties.In the T2 time the ETR of Flame Seedless was significantly higher than Kyoho and Red Globe,but in T1 time period Thompson Seedless and Kyoho were significantly higher than other varieties,and Centennial Seedless was significantly lower than other varieties.
Discussion
Photosynthesis is one of the mostsensitive physiological processes of plants under high temperature stress that the inhibition of photosynthesis may occur before other stress characteristics appear[6-7].In general,there is a balance in absorption and utilization of light energy of plants that will be broken by environmental stress.Shortterm imbalance leads to the decrease of photochemical efficiency,and longterm imbalance may lead to the irreversible damage of plant photosynthetic organs (such as optical system II).High temperature weakens the utilization effectiveness of light energy of plant leaves,and there will produce a mass of reactive oxygen when the light energy that plants absorbed was more than photosynthetic utilization and light protection ability[8-10],finally leading to the damage of plants.The research result showed that the photosynthetic mechanism of 6 grape varieties was hurt in varying degrees at the T1.By comparing of the photosynthetic parameters of six varieties,in addition to Thompson Seedless,it can be concluded that the net photosynthetic rate of other 5 varieties was 0.0 μmol/(m2·s),significantly lower than that at T2.Wu thought that the lighter high-temperature stress leads to the decrease of net photosynthetic rate by stomatal factors,and severe high temperature stress leads to the decrease of net photosynthetic rate by non-stomata factors[11].In this paper,Thompson Seedless belonged to the stomatal factor causing decrease of the photosynthetic rate,while the remaining 5 varieties was the non-stomatal factor,causing decrease of the photosynthetic rate.This result indicated that the 5 varieties were more sensitive to the stress than Thompson Seedless.Xu suggested that inhibition of photosynthesis is produced by the increase of impedance of mesophyll cells to gas diffusion,the decrease of CO2solubility,the decrease of Rubisco affinity for CO2,and by the decrease in the thermostability of key components of photosynthetic mechanism[12].This research showed that the intercellular CO2of varieties that got higher net photosynthetic rate and stomatal conductance was lower than that in the varieties that got lower net photosynthetic rate and stomatal conductance.The high temperature and light lead to increase of the leaf temperature rapidly,increased the vapor pressure gradient in the inside and outside of leaf,expedited the transpiration rate,evaporated the water to atmosphere directly by epidermal cells and guard cells,forced to decline the leaf water potential,and increased stomata resistance[13].With increasing of temperature of 44-45 ℃,the transpiration rate of 6 grape changed from increasing to decreasing,and the transpiration rate was different in the different varieties.
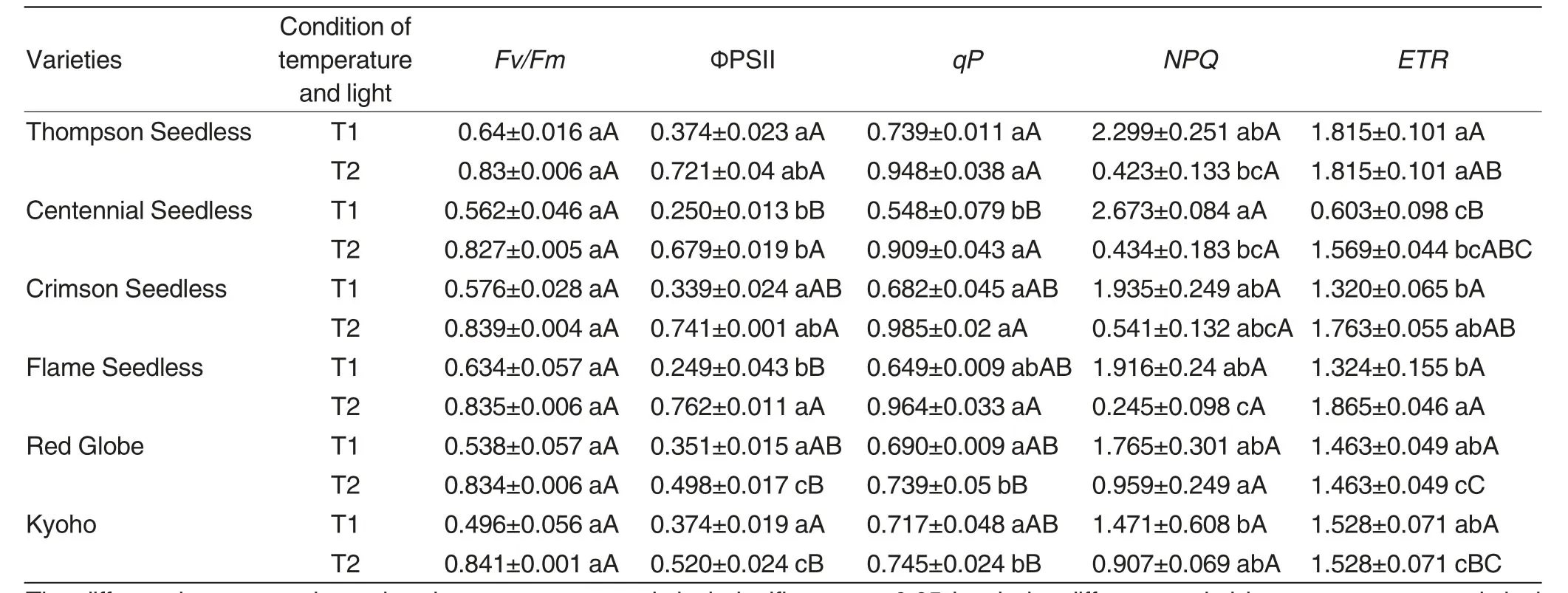
Table2 The fluorescence parameters under different temperature and light of different Grape varieties
Chlorophyll fluorescence was closely related to the process of various reactions in photosynthesis,and the impact of any stress on photosynthesis could be reflected by the dynamic variation that was induced by the internal chlorophyll fluorescence.The internal representation of plant ecological environment fitness mechanism is chlorophyll fluorescence.Fv/Fm had proved to be a quick and sensitive index of photo inhibition[14-16].By comparing of the fluorescence parameters of 6 varieties under the two kinds of natural conditions found that the photosynthesis of 6 varieties had been inhibited by strong light,but the inhibition degree of different varieties was different.Furthermore,the order of light inhibition degree of 6 varieties photosynthesis from high to low was Thompson Seedless,Flame Seedless,Crimson Seedless,Centennial Seedless,Red Globe,and Kyoho.ΦPS Ⅱreflected the actual capture rate for primary energy of the reaction center of photo system Ⅱ under partial shutdown conditions,and the changes of Fv/Fm reflected the injury degree of photo system Ⅱ under high temperature stress[17].Therefore,the reaction center of photo system Ⅱof 6 varieties had been destroyed or irreversibly inactivated,in which the damages of Kyoho and Red Globe were relatively serious.qP usually used to reflect the redox state of photo system Ⅱoriginal electron acceptor QA and the number of photo system Ⅱopen center.The high qP value indicated that the activity of electron transport of photo system Ⅱwas higher and the velocity of photosystem Ⅱwas more higher.In this study,the high temperature and strong light reduced the value of qP,which was in consistent with the predecessors’research[18]; NPQ reflected whether the light energy that was absorbed by photo system Ⅱantenna pigment is used for photosynthetic electron transport and dissipated in the form of heat.When the reaction center antenna pigment of photosystem Ⅱabsorbed excess light energy,if it is didn’t timely dissipated,it will cause the inactivation or damage of photosynthetic mechanism.So,NPQ is a self-protection mechanism,and has certain protective effects on photosynthetic mechanism[19].The value of NPQ of 6 species at T2 was lower than that in T1,and the NPQ of 6 specie at the same time period also was different.This result indicated that the selfdefend ability of photosynthetic organization of different varieties was different.This research showed that the NPQ values of Kyoho and Red globe at T2 was relatively high,but the selfdefend ability under the high temperature and strong light was significantly lower compared with other varieties.
Conclusion
The adaptive capacity to high temperature and strong light of different grape varieties in Turpan area was different.The orders of photosynthetic capacity from high to low under the condition of temperature at 36-37 ℃,PAR of 1 600-1 750 μmol/(m2·s) was Thompson Seedless>Crimson Seedless >Kyoho>Flame Seedless>Centennial Seedless>Red Globe,and under the condition of temperature at 44-45.5 ℃,and PAR of 1 900-2 000 μmol/(m2·s),in addition to Thompson Seedless was relatively better,the other species maintained lower.The photosynthetic mechanism of Kyoho and Red Globe was damaged the most serious,leads to the decrease of electron transport activity of photosystem II,and ETR became slow.The order of self-defend ability of 6 varieties was Centennial Seedless >Thompson Seedless>Crimson Seedless>Flame Seedless >Red Globe >Kyoho.Additionally,Thompson Seedless and Crimson Seedless were more suitable to the high temperature and strong light environment,while the Kyoho and Red Globe performed weak adaptability.
[1]XU DQ (许大全),ZHANG YZ (张玉忠),ZHANG RX(张荣铣).Photo inhibition of photosynthesis in plants (植物光合作用的光抑制)[J].Plant Physiology Communications(植物生理学通讯),1992,28(4):237-243
[2]WANG ZL(王振磊),CHEN HJ(陈海江),LIN MJ(林敏娟).Effects of high temperature and strong light stress on photosynthetic,physiological characteristics and fluorescence parameters of squash seedlings (高温强光胁迫对西葫芦幼苗光合生理特性及荧光参数的影响)[J],Journal of Yangzhou University(Agricultural and Life Science Edition) 扬州大学学报( 农业与生命科学版),2009,36(9):1261-1268.
[3]LUO HB(罗海波),MA L(马苓),DUAN W(段伟),et al.Influence of heat stress on photosynthesis in Vitis vinifera L.cv.Cabernet Sauvignon(高温胁迫对‘赤霞珠’ 葡萄光合作用的影响)[J].Scientia Agricultura Sinica(中国农业科学),2010,43(13):2744-2750.
[4]WANG ZL(王振磊),CHEN HJ(陈海江),LIN MJ (林敏娟),et al.Photo inhibition and recovery of photosynthesis in pear leaves(黄金梨和鸭梨叶片光合作用的光抑制及其恢复的比较研究)[J].Acta Horticulturae Sinica (园艺学报),2009,36(9):1261-1268.
[5]WANG BL (汪炳良),XU M (徐敏),SHI QH (史庆华)et al.Effects of high temperature stress on antioxidant systems,ChloroPhyll and ChloroPhyll fluorescence parameters in early cauliflower leaves(高温胁迫对早熟花椰菜叶片抗氧化系统和叶绿素及其荧光参数的影响)[J].Scientia Agricultura Sinica(中国农业科学),2004,37(8):1245-1250.
[6]GENTY B,BRIANTAIS J M,BAKER N R.The relationship between the quantum yield of photosynthesis electron transport and quenching of chlorophyll fluorescence [J].Biochemica et Biophysica Acta,1989,990:87-92.
[7]QUINN P J,WILLIAMS W P.Environmentally induced changes in chloroplast membranes and their effects on photosynthetic function.In:Barber J,Baker N R (eds).Photosynthetic Mechanisms and the Environment [J].Amsterdam:Elsevier Science Publishers,Biomedical Division,1985:1-47.
[8]MIILLER P,LI XP,NIYOGI KK.Non-Photochemical Quenching.A response to excess light energy[J].Plant Physiology,2001,125:.1558-1566.
[9]CHEN LS,LI PM,CHENG LS.Effects of high temperature coupled with high light on the balance between photooxidation and photoprotection in the sun-exposed peel of apple [J].Planta,2008,228:745-756.
[10]LI PM,CHENG L.The shaded side of apple fruit becomes more sensitive to photo inhibition with fruit development[J].Physiologic Plantarum,2008,134:282-292.
[11]WU HY (吴韩英),SHOU SY (寿森炎),ZHU ZJ (朱祝军).Effect of high temperature stress on photosynthesis and chlorophyll fluorescence in sweet pepper(Capsicum fructescens L).(高温胁迫对甜椒的光合作用和叶绿素荧光的影响)[J].Acta Horiculturae Sinica(园艺学报),2001,28(6):517-521.(in Chinese)
[12]YU SW(余叔文),TANG ZC(汤章城).et al.plant physiology and molecular biology(植物生理与分子生物学)[M].Beijing:science press(北京:科学出版社),1998:262-276
[13]HE J(何军),XU X(许兴),LI SH(李树华)et al.Study on diurnal changes of photosynthesis and transpiration of Cynanchum komarovii and Glycyrrhiza uralensis in different stage(不同时期牛心朴子和甘草光合蒸腾日变化的研究)[J].Acta Bot.Boreal.-Occident.Sin (西北植物学报),2003(10):1676-1681.
[14]JIA HS (贾虎森),CAI SY (蔡世音),LI DQ (李得全),et al.Effects on photosynthesis of mango seedlings treated with calcium under soil drying stress(土壤干旱胁迫下钙处理对芒果幼苗光合作用的影响)[J].Journal of Fruit Seience(果树科学),2000,17(1):52-56.
[15]GUO LW (郭连旺),XU DQ (许大全),SHEN YG(沈允钢).The cause of midday decline of photosynthetic efficiency in cotton leaves under field conditions (田间棉花光合次序中午降低的原因)[J].Acta Phytophysiologica sinica(植物生理学报),1994,20(4):360-366.
[16]KAUSE G H.Photo inhibition of photosynthesis evolution of damaging and protective mechanism [J].Physical Plant,1988,74:566-570.
[17]ZHANG SR (张守仁).A discussion on chlorophyll fluorescence kinetics parameters and their significance(叶绿素荧光动力学参数的意义及讨论)[J].Chinese Bulletin of Botany (植物学通报),1999,16(4):444—448.
[18]SUN Y(孙艳),XUN WJ(徐伟君),FAN AL(范爱丽).Effects of salicylic acid on chlorophyll fluorescence and xanthophyll cycle in cucumber leaves under high temperature and strong light(高温强光下水杨酸对黄瓜叶片叶绿素荧光和叶黄素循环的影响)[J].Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (应用生态学报),2006,17(3):399-402.
[19]SONG LL(宋丽莉),ZHAO HQ(赵华强),ZHU XQ (朱小倩),et al.Effect of high temperature stress on photosynthesis and chlorophyll fluorescence of rice(高温胁迫对水稻光合作用和叶绿素荧光特性的影响)[J].Journal of Anhui Agri.Sci.(安徽农业科学),2011,39(22):13348-13353.
 Agricultural Science & Technology2015年5期
Agricultural Science & Technology2015年5期
- Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- Effects of Exogenous Glycine Betaine on Oxidation Metabolism in Cucumbers during Low-temperature Storage
- A Preliminary Study on Genetic Variation of gE Gene of an Epidemic Pseudorabies Virus Strain and Its Pathogenicity to Piglets
- Development and Application of a Quantitative Competitive PCR Assay for Detecting Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae
- A New Rapid and Batch-oriented Crushing Method for DNA Extraction from Maize Leaves
- Effects of Reducing Application Amount of Base Fertilizer and Increasing Application Time of Leaf Fertilizer on Corn Yield
- Screening,Identification and Fermentation Property of a Yeast Strain R6 Accumulating Alpha-ketoglutaric Acid
