Effects of Reducing Application Amount of Base Fertilizer and Increasing Application Time of Leaf Fertilizer on Corn Yield
Mengmeng LI,Zhao LIU
Yunshan Farm,Hulin 158420,China
Responsible editor:Tingting XU Responsible proofreader:Xiaoyan WU
In recent years,with the development of agricultural modernization and increased demand for corn,the application amount of base fertilizer is trended to be increased.The increased application amount of base fertilizer can increase the corn yield to some extent.However,it can also decrease the utilization efficiency of base fertilizer,aggravating environmental pollution.In addition,the waste amount of base fertilizer is also increased[1-3].Therefore,it has become a research focus to explore updated fertilization pattern in the area of cultiva tion on the basis of ensuring yield[4-5].In order to maintain the sustainable development of agriculture and to reduce environmental pollution,the application amount of fertilizer should be reduced as greatly as possible.The declined yield,caused by reduced application amount of base fertilizer,can be compensated by increasing spaying time of leaf fertilizer.Studies have shown that the increased spaying time of leaf fertilizer can increase corn yield[6-7].However,the increased application amount of leaf fertilizer will also increase cultivation costs.So it is essential to find the most appropriate application frequency and time of leaf fertilizer.
Materials and Methods
Overview on test site
The test was carried out in the dry land test area of Yunshan Farm in Hulin City,Heilongjiang Province.The test soil was albic soil with pH of 5.44,organic matter of 5.6%,alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen of 275.6 mg/kg,available phosphorus of 21.1 mg/kg and available potassium of 165.1 mg/kg.The test site had flat terrain,good drainage and medium fertility.The tilling and ridging were all completed in autumn.The last-season crop was soybean.
Materials
The leaf fertilizer was composed of biotin,potassium dihydrogen phosphate and urea.The corn cultivar was Demeiya No.3.
Test treatments
Atotal of 13 treatments were designed,including 165 kg/hm2of base fertilizer and one time of spraying of leaf fertilizer at 7-leaf stage (T1),165 kg/hm2of base fertilizer and two times of spraying of leaf fertilizer at 10-leaf stage(T2),165 kg/hm2of base fertilizer and three times of spraying of leaf fertilizer at 13-leaf stage (T3),165 kg/hm2of base fertilizer and four times of spraying of leaf fertilizer at 16-leaf stage(T4),210 kg/hm2of base fertilizer and one time of spraying of leaf fertilizer at 7-leaf stage (T5),210 kg/hm2of base fertilizer and two times of spraying of leaf fertilizer at 10-leaf stage(T6),210 kg/hm2of base fertilizer and three times of spraying of leaf fertilizer at 13-leaf stage (T7),210 kg/hm2of base fertilizer and four times of spraying of leaf fertilizer at 16-leaf stage(T8),255 kg/hm2of base fertilizer and one time of spraying of leaf fertilizer at 7-leaf stage (T9),255 kg/hm2of base fertilizer and two times of spraying of leaf fertilizer at 10-leaf stage (T10),255 kg/hm2of base fertilizer and three times of spraying of leaf fertilizer at 13-leaf stage (T11),255 kg/hm2of base fertilizer and four times of spraying of leaf fertilizer at 16-leaf stage (T12) and 300 kg/hm2of base fertilizer and spraying of clean water(CK).
Test design and methods
The test adopted randomized block design.There were three replicates for each of the treatments.The area of each plot was 32.5 m2.There were 5 rows,in length of 10 m,in each of the plot,and the spacing between two adjacent rows was 0.65 m.The ridging was carried out by machine,while the ditching,fertilization and sowing were all completed by hand.In the fertilizer,the N:P:K was 1.6:1:0.6.The planting density was 75 000 plants/hm2.For the application of leaf fertilizer,the use amount of water was 225 kg/hm2.After the sowing and before the emergence of seedlings,the acetochlor·metribuzin·butylate was sprayed once for controlling weeds.During the growth period of corn,the intertillage was carried out three times by machine.
Results and Analysis
Yield
The growth and development processes were basically the same among the treatment groups.As shown in Table1,the plant height was trended to be increased with the increased application amount of base fertilizer and application time of leaf fertilizer,but the increase was not large.The plant heights of corn in the treatment groups were all lower than that of CK.The spike length was also trended to be increased with the increased application amount of base fertilizer and application time of leaf fertilizer.When the application amount of base fertilizer reached 210 kg/hm2and the spraying of leaf fertilizer reached two times,the spike length of corn was higher than that of CK by 0.1-0.7 cm.The barren tip was trended to be decreased with the increased application amount of base fertilizer and application time of leaf fertilizer,but the increase was not large.No significant differences were found in barren tip between treatment groups and CK.Both the grain number per spike and the 100-grain weight were increased with the increase of application amount of base fertilizer and application time of leaf fertilizer.The corn yield was also increased with the increased application amount of base fertilizer and spraying time of leaf fertilizer.In the four treatment groups with application amount of base fertilizer of 165 kg/hm2,the corn yields were all lower than that of CK,but the decrements were shortened gradually with the increased spraying time of leaf fertilizer.When the leaf fertilizer was sprayed once,the corn yield was 10.7%lower than that of CK;but when the leaf fertilizer was sprayed four times,the corn yield was 2% lower than that of CK.When the spaying of leaf fertilizer was increased by one time,the decrement of corn yield was shortened by 2.6% -3.2%.In the four treatment groups with application amount of base fertilizer of 210 kg/hm2,when the leaf fertilizer was sprayed once,the corn yield was decreased by 4.8% compared with that of CK; when the leaf fertilizer was sprayed two times,the corn yield was decreased by 0.7% compared with that of CK; when the leaf fertilizer was sprayed three times,the corn yield was increased by 3.4%compared with that of CK; when the leaf fertilizer was sprayed four times,the corn yield was increased by 6.1%compared with that of CK.Among the four-time increases in spraying time of leaf fertilizer,the increments of corn yield ranged from 2.7% to 4.1%.In the four treatment groups with application amount of base fertilizer of 255 kg/hm2,when the leaf fertilizer was sprayed once,the corn yield was decreased by 2%compared with that of CK,but in the other three treatment groups,the corn yields were all increased compared with that of CK with increments ranging from 2.7% to 12.9%.Among the four-time increases in spraying time of leaf fertilizer,the increments of corn yield ranged from 4.6%to 5.6%.
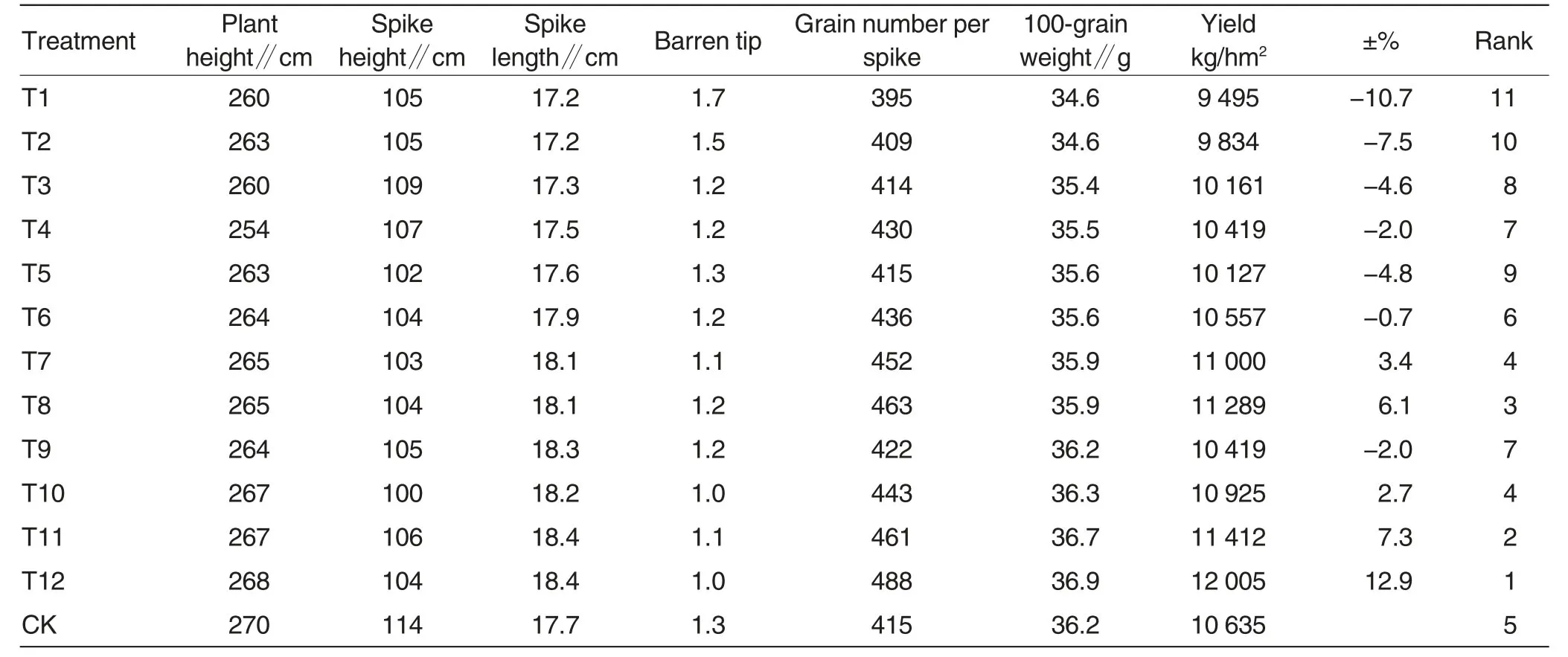
Table1 Appearance of yield traits of corn in each of the treatment groups

Table2 Analysis of economic benefits
Based on the comparison of corn yield among the three application levels of base fertilizer,it could be concluded that the increased corn yield was related to the increase in application amount of base fertilizer.The higher the application amount of base fertilizer is,the higher the increment of corn yield is(Fig.1).
Economic benefits
Table2 showed that among the 12 treatment groups,there were five treatments of which the economic benefits were higher than that of CK.In the T12 treatment group,the increment of economic benefits was highest(1 404.9 Yuan/hm2),followed by those of T11 (725.4 Yuan/hm2) and T8(530.1 Yuan/hm2) treatment groups.The yields per plot of T12 and T11 treatments were significantly higher than those of the other treatments(P<0.01),but yield per plot of T1 treatment was significantly higher than those of the other treatments except those of T2 and T3 treatments(P<0.01).
Conclusions
When the application amount of base fertilizer was 165 kg/hm2,the corn yield and economic benefits were all lower than those of CK although the spaying of leaf fertilizer was increased to four times.When the application amount of base fertilizer was 210 kg/hm2,the economic benefits were increased by 305.1 Yuan/hm2compared with that of CK when the leaf fertilizer was sprayed three times,and increased by 530.1 Yuan/hm2when the leaf fertilizer was sprayed four times.When the application amount of base fertilizer was increased to 255 kg/hm2,the economic benefits were increased by 203.4 Yuan/hm2when the leaf fertilizer was sprayed twotimes,increased by 725.4 Yuan/hm2when the leaf fertilizer was sprayed three times,and increased by 1 404.9 Yuan/hm2when the leaf fertilizer was sprayed four times.The differences mentioned above all reached the significant level.

Table3 New multiple range test
In order to reduce environmental pollution,the application amount of fertilizer should be reduced as greatly as possible.The reduced application amount of base fertilizer can be compensated by increased spaying time of leaf fertilizer.In this study,the application amount of base fertilizer ranges from 165 to 225 kg/hm2,and in order to obtain high economic benefits,the leaf fertilizer should be sprayed more than three times.
[1]MEI Y (梅艳),RUAN PJ (阮培均),MA J(马俊).Effect of organic biology compound fertilizer with different base-fertilizer application-rate on maize yield and economic benefit (有机生物复合肥不同底肥施用量对玉米产量及经济效益的影响)[J].Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica(华北农学报),2005,20:27-29.
[2]FU YY (付玉勇),DONG YX (董元香),CHEN ZG (陈志国).Effects of different times of top fertilization on corn yield(不同追肥次数对玉米产量的影响试验研究)[J].Bulletin of Agricultural Science and Technology (农业科技通讯),2013,4:69-71.
[3]ZHANG LY (张丽妍),MENG FS (孟繁盛),LI YG (李艳国),et al.Effects of different fertilizer,fertilization level and fertilization pattern on yield and economic benefit of corn(不同肥料、施肥水平及施用方法对玉米产量及经济效益的影响)[J].Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences(江苏农业科学),2014,42 (11):119-122.
[4]ZHANG YH (张玉华),WU ZJ (武志杰),LIU ZJ(刘子江),et al.Effect of applying different amounts of maize long-lasting special fertilizer on yield and economic benefit(玉米长效专用复合肥不同施肥量对玉米产量和经济效益的影响)[J].Journal of Maize Sciences (玉米科学),2000,8(2):80-83.
[5]WANG YL(王宜伦),LI CH(李潮海),TAN JF(谭金芳),et al.Effect of postponing N application on yield,nitrogen absorption and utilization in super-high-yield summer maize(氮肥后移对超高产夏玉米产量及氮素吸收和利用的影响)[J].Acta Agronomica Sinica(作物学报),2011,37(2):339-347.
[6]ZHOU JG(周建国),GONG LY(龚利云),WEN Q(温泉).Effects of top fertilization at different periods and spraying of Yuhuangjin an leaf fertilizer on maize yield (玉米分期追肥与喷施玉黄金加叶面肥对产量的影响)[J].Jilin Nongye (吉林农业),2011,3:126,147.
[7]LI J(李杰),WANG ZY(王志远),LIU T(刘涛),et al.Influence of leaf-fertilizer on corn growing and yield(喷施叶面肥对玉米生长速度及产量的影响)[J].Inner Mongolia Agricultural Science and Technology (内蒙古农业科技),2005,1:13,42.
——以2020年为例
 Agricultural Science & Technology2015年5期
Agricultural Science & Technology2015年5期
- Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- Effects of Exogenous Glycine Betaine on Oxidation Metabolism in Cucumbers during Low-temperature Storage
- A Preliminary Study on Genetic Variation of gE Gene of an Epidemic Pseudorabies Virus Strain and Its Pathogenicity to Piglets
- Development and Application of a Quantitative Competitive PCR Assay for Detecting Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae
- A New Rapid and Batch-oriented Crushing Method for DNA Extraction from Maize Leaves
- Screening,Identification and Fermentation Property of a Yeast Strain R6 Accumulating Alpha-ketoglutaric Acid
- Effects of Green Manure Rotation on Rice Growth Dynamics and Nitrogen Uptake and Utilization
