HDL影响冠心病患者血小板ox-LDL诱导活化的体外分析
李运田,杜大勇,杨升华,柳 杨
(中国人民解放军第三〇五医院心脏中心,北京 100017)
论著·临床研究
HDL影响冠心病患者血小板ox-LDL诱导活化的体外分析
李运田,杜大勇,杨升华,柳 杨
(中国人民解放军第三〇五医院心脏中心,北京 100017)
目的 探讨高密度脂蛋白(HDL)对氧化低密度脂蛋白(ox-LDL)诱导的人血小板活化的影响。方法将洗涤血小板按照等体积分为3组,Ⅰ组加入100 μg/mL HDL;Ⅱ、Ⅲ组均加入PBS,3组均置于37 ℃环境下孵育15 min。Ⅰ、Ⅱ组加入50 μg/mL ox-LDL;Ⅲ组加入PBS,3组均在37 ℃再孵育15 min。应用流式细胞仪检测3组CD62P表达水平,应用透射电镜观察3组血小板的形态结构。结果3组的血小板CD62P表达率差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),且Ⅱ组(29.26±5.91)%>Ⅰ组(15.37±1.49)%>Ⅲ组(2.05±0.85)%;3组的血小板CD62P平均荧光强度(MFI)存在差异(P<0.05),且Ⅱ组(3.97±0.64) >Ⅰ组(2.51±0.53)>Ⅲ组(1.50±0.10)。Ⅱ组血小板脱颗粒比Ⅰ组更明显,Ⅲ组未发生脱颗粒。结论HDL能显著抑制ox-LDL体外诱导的血小板活化。
冠心病;脂蛋白类,HDL;血小板;氧化低密度脂蛋白;动脉粥样硬化
冠心病患者的病理基础是动脉粥样硬化,而研究已证实循环氧化低密度脂蛋白(ox-LDL)水平与动脉粥样硬化程度呈正相关[1]。病理生理学研究证实ox-LDL可以通过多种途径激活血小板,进而导致冠状动脉的急性或亚急性血栓栓塞。最近临床研究也证实,在急性冠脉综合征患者体内ox-LDL与血小板相互作用形成的复合体水平明显增加[2]。由于高密度脂蛋白(HDL)能够作用于血小板上清道夫受体BI(SRBI),从而抑制其活化[3]。但是目前基础研究对于HDL是否具有抑制ox-LDL诱导血小板活化的功能尚缺乏,因此本研究对HDL体外抑制ox-LDL诱导的血小板活化能力进行探讨。
1 材料与方法
1.1 仪器与试剂 高密度脂蛋白(密度1.06~1.21 g/mL)、氧化低密度脂蛋白(北京协生生物科技有限责任公司);无钙磷酸盐缓冲液(PBS);抗人CD61-FITC、抗人CD62P-PE、PE标记鼠IgG1,k同型对照(eBioscience公司,美国);前列腺素E1(PGE1,大连美仑生物科技有限公司);HEPES粉末(Amresco公司,美国);Tyrode′s液(北京迈晨生物科技有限公司);离心机(Heraeus Labofuge400R,德国);自动血细胞计数仪(Beckman Coulter,美国);流式细胞分析仪(Beckman Coulter Epics XL,美国)。超薄切片机( Leicaemuc7,德国);透射电镜(Hitachi,H-7650,日本)。
1.2 标本采集及血小板分离 选取本院就诊的冠心病患者作为本研究血小板的提供者,所有患者均符合WHO的冠心病临床诊断标准,入选标准:(1)无高血压、血液病、糖尿病、肾病等影响血小板功能的疾病;(2)无吸烟嗜好及近1个月未大量饮酒;(3) 近2周内未服用任何影响血小板功能的药物;(4)所有供血者均签署知情同意书。本研究经本院伦理委员会批准。所有患者均在清晨空腹状态下,从肘正中静脉采血28 mL,弃去前2 mL,采血过程中注意不使用压脉带,注射器抽吸应均匀迅速。血液样本立即贴壁轻轻注入盛有ACD抗凝剂的离心管中,抗凝剂ACD与全血体积比为1∶6,颠倒混匀。
1.3 洗涤血小板制备 ACD抗凝血100 g于室温下离心15 min,获得富含血小板血浆(platelet-rich plasma,PRP),PRP中加入0.5 μM PGE后500 g离心10 min,弃上清液,以改良台式液(137 mM NaCl,2.7 mM KCl,12 mM NaHCO3,0.4 mM NaH2PO4,5 mM HEPES,0.1%葡萄糖,0.35%BSA,pH7.4)轻轻悬起沉淀血小板,500 g再离心10 min,弃上清液,以Tyrode′s液轻轻悬起,由自动血细胞计数仪计数,并调整其浓度为(3~5)×108/mL。
1.4 洗涤血小板的分组 将洗涤血小板按照等体积分为3组,分别为:Ⅰ组加入100 μg/mL HDL;Ⅱ组与Ⅲ组均加入PBS。3组均置于37 ℃环境下孵育15 min。Ⅰ组与Ⅱ组均加入50 μg/mL ox-LDL;Ⅲ组加入PBS,3组均在37 ℃环境下再孵育15 min。
1.5 流式细胞仪检测 孵育后的样品分别加入抗人CD61-FITC及抗人CD62P-PE暗箱孵育20 min,加入等量Tyrode′s液后上机检测。以CD61-FITC-SSLOG圈门,保证血小板阳性率达98%以上,各组均设同型对照以排除非特异性荧光干扰。以CD62P阳性表达率及平均荧光强度作为结果,用FCS Express 4 De Novo Software(美国,2012)分析软件分析。来自不同供血者的实验重复至少5次。
1.6 透射电镜观察 将3组血小板分别经2%的多聚甲醛加2.5%的戊二醛前固定,新锇酸后固定,洗涤,乙醇逐级脱水,环氧丙烷树脂包埋,切片及醋酸双氧铀与柠檬酸铅染色等程序后,于透射电镜下观察各组的形态改变。
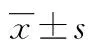
2 结 果
2.1 各组血小板CD62P表达的比较 3组的血小板CD62P表达率存在差异(P<0.05),且Ⅱ组(29.26±5.91)%>Ⅰ组(15.37±1.49)%>Ⅲ组(2.05±0.85)%;3组的血小板CD62P平均荧光强度(MFI)存在差异(P<0.05),且Ⅱ组(3.97±0.64)>Ⅰ组(2.51±0.53) >Ⅲ组(1.50±0.10),见表1,图1、2。
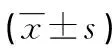
表1 3组间CD62P表达的比较
a:P<0.05,b:P=0.016,c:P=0.002,与Ⅰ组比较。

A:Ⅲ组(PBS孵育);B:Ⅱ组(ox-LDL孵育);C:Ⅰ组(ox-LDL+HDL孵育)。
图1 血小板CD62P阳性表达率
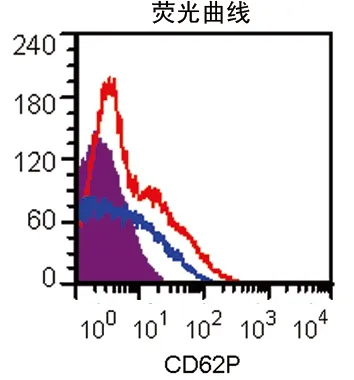
紫色:Ⅰ组;红色:Ⅱ组;蓝色:Ⅲ组。
图2 3组血小板 CD62P表达荧光强度
2.2 各组透射电镜下血小板形态的比较 在透射电镜下,Ⅲ组的血小板呈圆饼状,有完整包膜及环形管状系统,内部颗粒(α颗粒、致密体等)清晰可见;Ⅱ组血小板包膜破裂,α颗粒大量释放,Ⅰ组血小板较Ⅲ组表现为包膜不完整,有释放现象发生,而较Ⅱ组的血小板脱颗粒现象明显受到抑制(图3)。
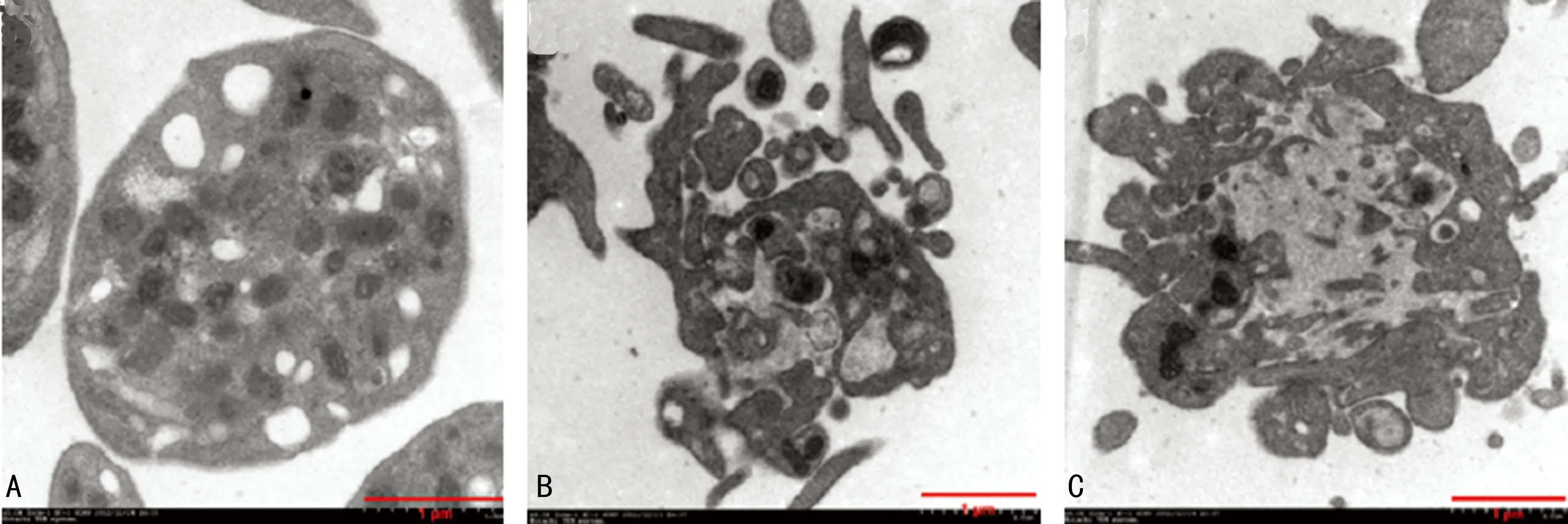
A:Ⅲ组;B:Ⅱ组;C:Ⅰ组。
图3 3组血小板透射电镜下形态(×40 000)
3 讨 论
越来越多的研究表明循环中的ox-LDL水平与心血管疾病具有密切关系,ox-LDL不仅是冠心病的独立危险因素,也是动脉粥样硬化发生、发展的重要危险因素。已有基础研究发现ox-LDL不仅参与泡沫细胞的形成,损伤内皮功能,而且也是血小板的独立活化剂[4]。ox-LDL主要通过与血小板表面多种受体相作用,如:SR-A[5]、CD36[6]、Lox-1[4],PAF-receptor[7]和SR-PSOX/CXCL16[8],进而启动信号转导机制,上调血小板CD62P表达[5],促进血小板聚集[9],因此ox-LDL诱导血小板活化在动脉粥样硬化的发生、发展及急性冠脉综合征(ACS)的发生中起重要作用。临床研究也显示,在ACS患者体内及支架急性再狭窄时,循环中的ox-LDL的水平均会明显增加[10]。此外有研究表明,循环血液中突然升高的ox-LDL是心血管事件发生的预测因子[11],并且ox-LDL与血小板的相互作用致血小板活化在ACS中起重要作用[2]。HDL不仅可逆向转运胆固醇、改善内皮功能、抗炎、抗氧化,而且还可抑制血小板活化[3]。有研究证实,SR-BI也表达于鼠血小板表面,并且发现SR-BI缺乏的鼠体内未醚化的胆固醇升高。利用SR-BI基因敲除小鼠研究表明,SRBI受体缺乏,会导致脂质代谢障碍,重要的是还会导致血小板高反应性及脂质超载[12]。进一步研究发现,血小板的高反应性与人的SR-BI基因的不同密切相关[13]。最新研究证实,HDL是通过与血小板上SR-BI受体结合从而发挥抑制血小板活化的[14]。然而冠心病患者血小板受ox-LDL诱导活化后能否被HDL所抑制目前尚缺乏充足临床研究证实,因此本研究选取血小板CD62P为靶点,在体外分析ox-LDL刺激血小板后HDL的抑制效应。
研究结果显示,HDL(100 μg/mL)能够抑制ox-LDL诱导的冠心病患者血小板的活化过程,且此效应与CD62P受体水平有相关性,表现为Ⅰ组的CD62P表达低于Ⅱ组,但是高于Ⅲ组;同时Ⅱ组血小板脱颗粒比Ⅰ组更明显,Ⅲ组未发生脱颗粒,这表明HDL虽能够明显抑制ox-LDL诱导的血小板活化,但血小板活化水平仍较PBS对照组高。本研究结果也提示HDL抑制ox-LDL诱导的血小板活化可能是心血管事件保护作用的重要原因之一。然而由于本研究是体外研究,因此在体内是否也存在HDL可抑制ox-LDL诱导的活化尚需进一步研究。
[1]Toshima S,Hasegawa A,Kurabayashi M,et al.Circulating oxidized low density lipoprotein levels:a biochemical risk marker for coronary heart disease [J].Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol,2000,20(10):2243-2247.
[2]Stellos K,Sauter R,Fahrleitner M,et al.Binding of oxidized low-density lipoprotein on circulating platelets is increased in patients with acute coronary syndromes and induces platelet adhesion to vascular wall in vivo-brief report [J].Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol,2012,32(8):2017-2020.
[3]Brodde MF,Korporaal SJ,Herminghaus G,et al.Native high-density lipoproteins inhibit platelet activation via scavenger receptor BI [J].Atherosclerosis,2011,215(2):374-382.
[4]Korporaal SJA,Gorter G,van Rijn HJM,et al.Effect of oxidation on the platelet-activating properties of low density lipoprotein [J].Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol,2005,25(1):1-7.
[5]Collot-Teixeira S,Delorenzo F,McGregor JL.Scavenger receptor A and CD36 are implicated in mediating platelet activation induced by oxidized low-density lipoproteins [J].Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol,2007,27(12):2491-2492.
[6]Chen K,Febbraio M,Li W.A specific CD36-dependent signaling pathway is required for platelet activation by oxidized low-density lipoprotein [J].Circ Res,2008,102(12):1512-1519.
[7]Chen R,Chen X,Salomon RG,et al.Platelet activation by low concentrations of intact oxidized LDL particles involves the PAF receptor[J].Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol,2009,29(2):363-371.
[8]Seizer P,Stellos K,Selhorst G,et al.CXCL16 is a novel scavenger receptor on platelets and is associated with acute coronary syndrome[J].Thromb Haemost,2011,105(6):1112-1114.
[9]Holvoet P,Mertens A,Verhamme P,et al.Circulating oxidized LDL is a useful marker for identifying patients with coronary artery disease[J].Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol,2001,21(5):844-848.
[10]Naruko T,Ueda M,Ehara S,et al.Persistent high levels of plasma oxidized low-density lipoprotein after acute myocardial infarction predict stent restenosis [J].Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol,2006,26(5):877-883.
[11]Tsimikas S,Bergmark C,Beyer RW,et al.Temporal increases in plasma markers of oxidized low-density lipoprotein strongly reflect the presence of acute coronary syndromes [J].J Am Coll Cardiol,2003,41(3):360-370.
[12]Korporaal SJ,Meurs I,Hauer AD,et al.Deletion of the high-density lipoprotein receptor scavenger receptor BI in mice modulates thrombosis susceptibility and indirectly affects platelet function by elevation of plasma free cholesterol [J].Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol,2011,31(1):34-42.
[13]Vergeer M,Korporaal SJ,Franssen R,et al.Genetic variant of the scavenger receptor BI in humans [J].N Engl J Med,2011,364(1):136-145.
[14]Hulthe J,Fagerberg B.Circulating oxidized LDL is associated with subclinical atherosclerosis development and inflammatory cytokines (AIR Study) [J].Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol,2002,22(7):1162-1631.
Analysis in vitro of high-density lipoprotein affecting platelet activation induced by oxidized low-density lipoprotein in patients with coronary heart disease*
LiYuntian,DuDayong,YangShenghua,LiuYang
(HeartCenter,305HospitalofPLA,Beijing100017,China)
Objective To investigate the effect of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) on platelet activation induced by oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL) in vitro.Methods Washed platelets separated from the patients with coronary heart disease were divided into three groups,the group Ⅰ (adding HDL 100 μg/mL),the group Ⅱ and group Ⅲ (adding PBS).The platelets of three groups were incubated at 37 ℃ for 15 min.Then,the group Ⅰ and Ⅱ were added with ox-LDL 50 μg/mL and the group Ⅲ was added with PBS.The three groups were incubated at 37 ℃ for 15 min again.The expression levels of CD62P were assessed by flow cytometry and compared among three groups.The structures of platelets were observed by transmission electron microscope (TEM) and compared among three groups.Results The CD62P expression rates were statistically different among three groups (P<0.05) and the sequence was the group Ⅱ (29.26±5.91)%> the group Ⅰ (15.37±1.49)%> the group Ⅲ (2.05±0.85)% (P<0.05).The mean fluorescence intensities (MFI) of CD62P were also statistically different among three groups (P<0.05) and the sequence was the group Ⅱ (3.97±0.64)> the group Ⅰ (2.51±0.53)> the group Ⅲ (1.50±0.10) (P<0.05).The degranulation degree in the group Ⅱ was significantly more than that in the group Ⅰ(P<0.05),whereas the group Ⅲ had no degranulation.Conclusion HDL inhibits can significantly the platelet activation induced by ox-LDL in vitro.
coronary disease;lipoprotein,HDL;platelet;oxidized low-density lipoprotein;atherosclerosis
:10.3969/j.issn.1671-8348.2015.13.010
全军保健科研基金项目(12BJZ29)。
李运田(1965-),博士,主治医师,主要从事冠心病的基础与临床研究。
R541.4
A
1671-8348(2015)13-1756-03
2014-10-08
2015-02-23)

