弱 Gorenstein FP-内射模
陈文静, 杨晓燕
(西北师范大学数学与统计学院,甘肃 兰州730070)
1 引言及预备知识
令R是具有单位元的结合环,所有涉及的模均是酉模.对任意的模M,用M+表示模M的示性模HomZ(M,Q/Z).对未作解释的标记、事实和概念,参见文献[1-2].
E.E.Enochs等[3]引入了 Gorenstein 平坦模的概念.E.E.Enochs等[4]在一般环上引入了Gorenstein投射模和Gorenstein内射模的概念.近年来,众多学者对Gorenstein投射模、Gorenstein内射模和Gorenstein平坦模进行了大量的研究,参见文献[5-9].D.Bennis 等[10]引入了强 Gorenstein 投射模、强Gorenstein内射模和强Gorenstein平坦模的概念.他们证明了一个模是Gorenstein投射(内射)的当且仅当它是一个强Gorenstein投射(内射)模的直和项.
Z.H.Gao 等[11]引入了 Gorenstein FP-内射模的概念,利用Gorenstein FP-内射模对FP-自内射凝聚环进行了刻画.Z.H.Gao[12]引入了弱Gorenstein投射模、弱Gorenstein内射模和弱Gorenstein平坦模的概念,通过这些模类对QF环和FC环进行了刻画.同时引入了弱Gorenstein FP-内射模的概念,证明了在左凝聚环上如果M是弱Gorenstein FP-内射左R-模,那么M+是弱Gorenstein平坦右 R-模.Z.H.Gao[13]引入了强 Gorenstein FP-内射模的概念,通过强Gorenstein FP-内射模对FC环进行了刻画.
本文研究了弱Gorenstein FP-内射模,证明了凝聚环上弱Gorenstein FP-内射模是强Gorenstein FP-内射模的直和项,利用弱Gorenstein FP-内射模对FP-自内射环进行了刻画,讨论了凝聚环上FP-内射模类、Gorenstein FP-内射模类和弱Gorenstein FP-内射模类之间的联系.
首先回顾一些概念.称左R-模M是FP-内射(或绝对纯)的[14-15],如果对任意有限表示左R-模P,.左R-模M的FP-内射维数FP-idR(M)定义为使得的最小的 n.环 R的左 FP-内射整体维数 l.FP-dim(R)定义为所有左R-模的FP-内射维数的上确界.称左R-模M是Gorenstein FP-内射模[11],如果存在一个FP-内射左R-模的正合列

使得,并且对任意投射维数有限的有限表示左R-模P,HomR(P,E)是正合的.称左R-模M是强Gorenstein FP-内射模[13],如果存在一个FP-内射左R-模的正合列
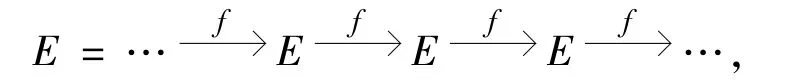
使得M≅Im(f),并且对任意投射维数有限的有限表示左R-模P,HomR(P,E)是正合的.
2 弱Gorenstein FP-内射模




命题2.9设R是左凝聚环,并且每个内射左R-模有有限的平坦维数.如果M是弱Gorenstein FP-内射左R-模,那么M+是Gorenstein平坦右R-模.
证明由文献[11]的命题3.7和本文命题2.8,结论显然.
称R是n-FC环[17],如果R是双边凝聚环且FP-idR(R)≤n,FP-id(R)R≤n.
推论2.10[12]设R是n-FC环.如果M是弱Gorenstein FP-内射左 R-模,那么M+是Gorenstein平坦右R-模.
推论2.11设R是 n-FC环.如果 M是Gorenstein FP-内射左 R-模,那么M+是Gorenstein平坦右R-模.
称左R-模M是强余纯平坦模[18],如果对任意内射右R-模I及i≥1,
命题2.12设R是n-FC环,M是弱Gorenstein FP-内射左R-模,则以下等价:
1)M+是弱Gorenstein平坦右R-模;
2)M+是Gorenstein平坦右R-模;
3)M+是强余纯平坦右R-模;
4) (M+)+是Gorenstein内射左R-模.
证明由推论2.10,M+是Gorenstein平坦右R-模.因为R是n-FC环,所以由文献[12]的命题3.8 知,1)⇔2)⇔3)⇔4).
命题得证.
定理2.13设R是任意环,则以下等价:
1)每个左R-模是弱Gorenstein FP-内射的;
2)每个投射左R-模是FP-内射的;
3)每个自由左R-模是FP-内射的;
4)环R是左FP-自内射的.
证明1)⇒2) 设P是投射左R-模.由1),P是弱Gorenstein FP-内射左R-模.由命题2.3,存在短正合列,其中E是FP-内射左R-模,N是弱Gorenstein FP-内射左R-模.因为P是投射左R-模,所以短正合列0是可裂的.因此E≅N⊕P.又因为E是FP-内射左R-模,所以由文献[16]的引理2.1知,左R-模P是FP-内射的.
2)⇒1) 设M 是左 R-模,为M的一个内射分解,为M的一个投射分解.因为内射左R-模是FP-内射的,又由2),每个投射左R
-模是FP-内射的,所以存在FP-内射左R-模的正合列

使得.因此 M 是弱 Gorenstein FP-内射的.
同理可证1)⇔3).
3)⇔4) 设 F 是自由左R-模,则 F≅R(A).由文献[16]的引理2.1,左R-模F是FP-内射的当且仅当左R-模R是FP-内射的.定理得证.
推论2.14设R是左凝聚环,则以下等价:
1)每个左R-模是弱Gorenstein FP-内射的;
2)每个左R-模是Gorenstein FP-内射的;
3)每个投射左R-模是FP-内射的;
4)每个自由左R-模是FP-内射的;
5)环R是左FP-自内射的.
证明由命题2.8和定理2.13,结论显然.
注2.15已知,有限表示平坦模类与有限表示投射模类是同一个类.由定理2.13知,投射的FP-模类与自由的FP-模类是同一个类.因此有限表示自由的FP-模类、有限表示投射的FP-模类和有限表示平坦的FP-模类是同一个类.
称左R-模M是Gorenstein内射模[3],如果存在一个内射左R-模的正合列

使得,并且对任意内射左R-模Q,HomR(Q,E)是正合的.Gorenstein投射左R-模的定义是对偶的.
命题2.16设R是双边凝聚环,则以下等价:
1)环R是左FP-自内射的;
2)每个弱Gorenstein FP-内射左R-模是Gorenstein平坦的;
3)每个Gorenstein内射左R-模是Gorenstein平坦的;
4)每个内射左R-模是Gorenstein平坦的;
5)每个Gorenstein投射左R-模是弱Gorenstein FP-内射的;
6)每个投射左R-模是弱Gorenstein FP-内射的;
7)每个Gorenstein平坦左R-模是弱Gorenstein FP-内射的;
8)每个平坦左R-模是弱Gorenstein FP-内射的;
9)环R是FC环.
以上1)~8)等价于右的情形.
证明因为R是双边凝聚环,所以由命题2.8知,弱Gorenstein FP-内射左R-模是Gorenstein FP-内射的.因此由文献[11]的定理3.6知,1)⇔2)⇔3)⇔4)⇔5)⇔6)⇔7)⇔8).因为 R 是双边凝聚环,所以R是左和右FP-自内射的的当且仅当R是FC 环,所以1)⇔9).
命题得证.
命题2.17FP-内射左R-模是弱Gorenstein FP-内射左R-模.反之,当R是左凝聚环且l.FP-dim(R)<∞时,弱Gorenstein FP-内射左R-模是FP-内射左R-模.
证明由注2.2,只需证当R是左凝聚环且l.FP-dim(R)<∞时,每个弱Gorenstein FP-内射左R-模是FP-内射左R-模.不失一般性,设l.FP-dim(R)=m<∞,下对m进行数学归纳.
1)若m=0,则任意左R-模是FP-内射的,结论显然.
2)假设m≥1.设M是弱Gorenstein FP-内射左R-模.由命题2.3,存在一个左R-模的正合列,其中每个Ei是FP-内射左R-模.设,则有是正合的.因为FP-idR(L)≤m,R是左凝聚环,所以由文献[14]的引理3.1知,M是FP-内射左R-模.命题得证.

命题2.18设R是左凝聚环.如果l.FP-dim(R)<∞,那么FP-内射模类,Gorenstein FP-内射模类,弱Gorenstein FP-内射模类是同一个类.
证明由命题2.8和命题2.17,结论显然.
[1] Anderson F W,Fuller K R.Rings and Categories of Modules[M].New York:Springer-Verlag,1992.
[2] Rotman J J.An Introduction to Homological Algebra[M].London:Academic Press,1979.
[3]Enochs E E,Jenda O M G,Torrecillas B.Gorenstein平坦模[J].南京大学学报数学半年刊,1993,10(1):1-9.
[4] Enochs E E,Jenda O M G.Gorenstein injective and projective modules[J].Math Zeit,1995,220(1):611-633.
[5] Mao L X,Ding N Q.Gorenstein FP-injective and Gorenstein flat modules[J].J Algebra Appl,2008,7:491-506.
[6] Bennis D.Rings over which the class of Gorenstein flat modules is closed under extensions[J].Commun Algebra,2009,37:855-868.
[7] Yang X Y,Liu Z K.Gorenstein projective,injective and flat modules[J].J Aust Math Soc,2009,87:395-407.
[8] Bennis D,Mahdou N.Global Gorenstein dimension[J].Proc Am Math Soc,2010,138:461-465.
[9] Yang X Y,Liu Z K.Strongly Gorenstein projective,injective and flat modules[J].J Algebra,2008,320(7):2659-2674.
[10] Bennis D,Mahdou N.Strongly Gorenstein projective,injective and flat modules[J].J Pure Appl Algebra,2007,7:491-506.
[11] Gao Z H,Wang F G.Coherent rings and Gorenstein FP-injective modules[J].Commun Algebra,2012,40:1669-1679.
[12] Gao Z H.Weak Gorenstein projective,injective and flat modules[J].J Algebra Appl,2013,12(2):3841-3858.
[13] Gao Z H.On strongly Gorenstein FP-injective modules[J].Commun Algebra,2013,41:3035-3044.
[14] Stenströ m B.Coherent rings and FP-injective modules[J].J London Math Soc,1970,2:323-329.
[15] Maddox B H.Absolutely pure modules[J].Proc Am Math Soc,1967,18:155-158.
[16] Jain S.Flat and FP-injectivity[J].Proc Am Math Soc,1973,41:437-442.
[17] Ding N Q,Chen J L.Coherent rings with finite self-FP-injective dimenson[J].Commun Algebra,1996,24:2963-2980.
[18] Enochs E E,Jenda O M G.Copure injective resolutions,flat resolvents and dimension[J].Comment Math Univ Carolin,1993,34:203-211.

