关节镜下治疗创伤复发性Bankart损伤疗效分析
李彦林 王国梁 何川 李建 郑家礼 陈广超 李松 余洋
·论著·
关节镜下治疗创伤复发性Bankart损伤疗效分析
李彦林 王国梁 何川 李建 郑家礼 陈广超 李松 余洋
目的探讨肩关节镜下Bankart损伤重建术治疗复发性肩关节前脱位的临床疗效。方法自2010年6月至2014年4月随访60例应用肩关节镜下Bankart损伤重建术治疗的复发性肩关节前脱位患者,随访10~38个月,平均26.6个月;年龄15~45岁,平均29岁。60例患者均为前方单方向性不稳定,术前平均脱位次数为6.5次(2~17次)。手术中采用缝合锚进行Bankart损伤重建术。随访时采用ASES评分和Constant-Murley评分进行功能评估。结果60例患者手术前及终末随访时ASES平均评分为(83.5±3.2)分与(97.1±2.1)分(t=4.79,P>0.01),肩关节平均前屈上举角度为(163.8±6.0)°与(185.4±3.9)°(t=4.87,P>0.01),外展角度为(90±1.1)°与(135.4±9.9)°(t=6.40,P>0.01),外旋角度为(57.6±4.3)°与(86.5±5.2)°(t=5.43,P>0.01);术前及终末随访时Constant-Murley平均评分为(77.6±3.5)分与(97.2±3.2)分(t=5.06,P>0.01)。终末随访时所有病例均未发生术后再脱位,术后残存恐惧试验阳性4例(6.7%)。所有患者均恢复术前工作,52例(86.7%)恢复到第一次脱位前的运动水平。结论肩关节镜下微创行Bankart损伤重建手术是治疗复发性肩关节前脱位的有效方法之一,术前病例选择、术中关节镜下操作技术及术后功能康复锻炼是手术成功的关键。
肩关节脱位;关节镜;Bankart损伤
复发性肩关节脱位(或创伤性肩关节不稳)始于第一次肩关节脱位,该脱位损伤了稳定肩关节的韧带。当盂唇从关节盂上撕裂时,这些韧带的稳定作用就不复存在,创伤性肩关节不稳定的发展与盂缘和周围韧带损伤的类型和程度密不可分。Bankart损伤是发生肩关节复发性前脱位最常见的原因,修复和重建肩关节前方的稳定结构,是治疗复发性肩关节前脱位的关键。随着关节镜技术的发展和普及,肩关节镜下微创治疗复发性肩关节前脱位已被越来越多的医师采用。2010年6月至2014年4月,我们于关节镜下采用金属缝合锚内固定修复Bankart损伤治疗60例复发性肩关节前脱位患者,取得良好临床疗效,现报道如下:
资料与方法
一、一般资料
我院自2010年6月至2014年4月,在肩关节镜下行Bankart损伤重建术治疗60例复发性肩关节前脱位患者。随访10~38个月,平均26.6个月。年龄15~45岁,平均29岁。60例患者均为前方单方向性不稳定,术前平均脱位次数为6.5次(2~17次)。术后肩关节功能恢复时间为6周,均未发生再脱位。本组患者均除外肩袖全层撕裂、肩峰撞击征等。
二、影像学检查
术前均拍摄肩关节正位、侧位及肩关节冈上肌出口位X线片(图1~3),CT扫描、MRI及肩关节去除肱骨头后CT三维重建(图4),术前X线片均未见肩关节明显的骨折,CT三维重建未见明确的骨性Bankart损伤,所有MRI均表现为前侧盂唇与关节盂缘之间有高信号,其中3例盂唇消失(图4,5)。

图1 肩关节正位片,未见异常

图2 肩关节侧位片,无异常

图3 肩关节冈上肌出口位片,为正常肩峰结构
三、手术方法
全身麻醉,侧卧位,冲洗用的生理盐水每3 000 ml加0.1%肾上腺素1 ml,可调式水泵的压力维持在60 mm Hg。术前标记肩关节骨性标记及手术入口。后方入口/关节镜入口:位于肩峰后角向下约2 cm,向内侧约1 cm。前上方入口:在喙突外侧,关节内位于肱二头肌长头腱和肩胛下肌腱上缘之间。前下方入口:在前上方入口下2~3 cm处,关节内尽可能接近肩胛下肌腱上缘。前方两入口安装工作套管,作为器械操作通道。于后方入口进入关节镜,按顺序进行肩关节探查,本组所有病例均可见盂唇-肩关节囊-韧带复合体与盂唇分离、移位(图6),前关节囊和韧带组织松弛。损伤部位多位于肩盂1~5点钟的范围。7例伴有肱骨头软骨损伤,5例伴有盂肱关节软骨退变。采用低温等离子射频消融和刨刀行关节软骨损伤和退变处表面清理。

图4 肩关节去除肱骨头后CT三维重建,盂唇无骨缺损
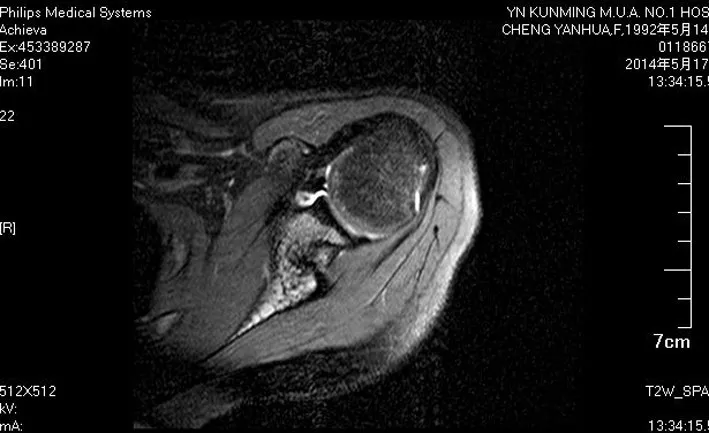
图5 MRI表现为前侧盂唇与关节盂缘之间有高信号
使用肩关节软组织剥离器在肩盂受损处前部,向肩胛颈方向剥离黏连的盂唇-肩关节囊-韧带复合体。用肩盂锉锉去肩唇受损处纤维组织,露出新鲜骨面。通过前下方入口工作套管,将定位器置于肩盂缘2、3、4、5点钟位置。于关节盂成45°角,骨锤叩击定位器,使其在肩盂缘新鲜骨面上形成一个导向孔。移去内芯,金属缝合锚插入定位器中央并拧入至肩盂内,以穿刺缝合器穿刺缝合盂唇-肩关节囊-韧带复合体,进行打结收紧完成固定。固定完成后以探钩再次检查修复效果,用射频消融刀清理创缘(图7)。

图6 关节镜下可见Bankart损伤,盂唇-肩关节囊-韧带复合体与盂唇分离

图7 Bankart损伤重建术后可见分离盂唇已缝合至原位
四、术后处理
术后复查肩关节正侧位片(图8,9),术后采用肩关节外展位支具固定6周,6周内禁止做主动活动。嘱患者活动肘、腕及手,并进行局部理疗、消肿止痛及冰敷治疗。6周后进行保护性康复训练,包括钟摆训练,滑轮器训练。3个月后进行肌力强度康复训练,包括增加关节活动度范围和肌肉的抗阻力训练,耐力训练。6个月后进行运动功能康复训练,加强肩关节周围肌肉锻炼,本体感觉锻炼等,并可进行非对抗性体育活动,包括恢复运动训练功能的专项训练,负重上举、哑铃训练等。术后即刻在康复医师和治疗师的指导下进行术后早期物理治疗和康复训练。物理治疗主要包括早期冷疗减轻疼痛和肿胀,超短波治疗改善局部血液循环,促进肿痛消退和组织愈合,康复训练可改善循环,促进关节囊-盂唇复合体的愈合,加强肌力,增加关节的稳定性,防止关节僵直、肿胀等并发症。
表1 肩关节复发性脱位手术前、后肩关节功能比较(±s)
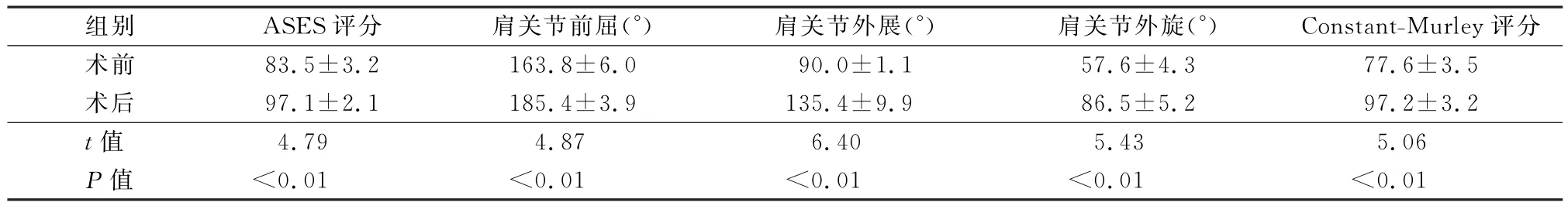
表1 肩关节复发性脱位手术前、后肩关节功能比较(±s)
组别 ASES评分 肩关节前屈(°) 肩关节外展(°) 肩关节外旋(°) Constant-Murley.5术后 97.1±2.1 185.4±3.9 135.4±9.9 86.5±5.2 97.2±3.2t值评分术前 83.5±3.2 163.8±6.0 90.0±1.1 57.6±4.3 77.6±3 4.79 4.87 6.40 5.43 5.06P值 <0.01 <0.01 <0.01 <0.01 <0.01
图8 术后肩关节正位片,锚钉位置良好

图9 术后肩关节侧位片,锚钉位置良好
结 果
术后3周、6周、3个月、6个月及1年门诊随访,此后每年随访一次,60例患者手术前及终末随访时进行ASES平均评分,肩关节前屈上举、外展、外旋角度及终末随访时平均Constant-Murley评分采用配对t检验处理,P<0.05差异有统计学意义,见表1。终末随访时所有病例均未发生术后再脱位,术后残存恐惧试验阳性4例(6.7%)。
讨 论
肩关节由关节盂和肱骨头以及周围的肩关节囊和韧带组成,正常情况下肱骨头在关节盂内,当外伤造成肱骨头脱出关节盂即为肩关节脱位,根据肱骨头脱位的方向分为肩关节前脱位和后脱位。常见的是肩关节前脱位,致伤原因有跌倒压在外展并强力被迫过顶的手臂上、肩部的直接击打、手臂强力被迫外旋;肩关节向后脱位不常见,常常与癫痫发作或电击有关,此时肩部的肌肉强力收缩造成脱位。Bankart损伤是肩关节盂唇前下方在前下盂肱韧带复合体附着处的撕脱性损伤,因肩关节前脱位引起,是造成习惯性前方不稳定和脱位的基本损伤。Bankart损伤经常伴随发生关节囊的异常,超过30%的患者会有前下盂肱韧带复合体的延长及松弛。经典的Bankart损伤为纤维性Bankart损伤:即关节囊破裂,盂肱韧带连同附着的关节盂唇从关节盂上撕脱,肩关节前脱位时最常见的是下盂肱韧带-盂唇复合体损伤,占创伤性肩关节前脱位的85%。治疗因患者首次脱位时的年龄而异,当患者首次脱位时年龄<30岁,再次脱位的可能性>80%,建议手术治疗,修补撕裂的韧带及盂唇;但如果患者首次脱位时年龄>30岁,再次脱位的可能性就大为减少,可以先行保守治疗[1-2]。本组患者均有明确的外伤史,伤后首诊均为手足牵引复位关节,复位后未得到充分的制动固定,盂唇-肩关节囊-韧带复合体未能愈合,这样易致复发性脱位。
关节镜辅助下治疗复发性肩关节脱位已经成为治疗肩关节疾病的一种不可或缺的治疗手段,Bankart损伤采用关节镜手术的理想患者是从事非接触性运动伴有Bankart病变,而且其盂唇本身没有变性,肩关节盂肱下韧带及盂肱中韧带质量良好者[3]。许多研究[4-7]报道,关节镜下治疗Bankart损伤修复肩关节前方不稳的效果优于切开手术。
本组采用的金属带线锚钉在松质骨中具有多点固定和高稳定性,其钉尾带有缝针的不可吸收缝线,适合腱骨结合处韧带肌腱的固定,操作简便,效果可靠,安全有效,对韧带肌腱的修复与重建提供了极大的方便[8]。金属骨锚具有以下优势:(1)操作简便,只需暴露骨面,能简便地完成肌腱与骨的接触固定,手术时间短,固定牢固;(2)手术创伤小,手术剥离范围小,软组织损伤轻;(3)避免了对骨骼进行过多操作所带来的骨骼畸形而影响生长发育的并发症;(4)Press-fit固定方式使其在皮质骨下固定牢靠,预置的Ethibond缝线在软组织愈合期间能保持长时间拉力,使肌腱修复后强度良好,且与骨质连结紧密,适宜于术后早期开展功能锻炼,防止关节僵硬;(5)由于骨锚固定牢靠,手术后关节内固定时间由6周减少到3~4周,适宜于早期进行功能锻炼,减少关节僵硬的机会;(6)骨锚为永久置入物,若无骨锚松动退出,影响关节活动、压迫皮肤或出现无法控制的伤口感染,一般无需取出,避免二次手术的痛苦[9-10]。
本组病例术后均获随访,平均随访时间为26.6个月,均未发现再脱位现象。通过分析本组病例手术前、后肩关节的功能,术后肩关节平均前屈上举角度明显提高,平均外展90°外旋明显增加,Gonstant-Murley评分明显增多。本组病例有4例术后残存恐惧试验阳性,考虑患者盂唇-肩关节囊-韧带复合体与盂唇分离较大,术中难以完全复位及患者不适当的运动有关。因此,关节镜下行Bankart重建手术能恢复复发性前脱位肩关节的稳定性,术后肩关节的功能得到明显改善,取得较好的疗效,镜下实施Bankart重建手术,可改善预后,促进肩关节功能恢复,加速康复进程,值得临床推广。鉴于本研究病例样本量相对较少,随访时间较短,远期效果还有待临床进一步观察。
[1] 龚熹,崔国庆,王健全,等.复发性肩关节前脱位的临床病理表现[J].中华骨科杂志,2006,26(6):399-403.
[2] Owens BD,Nelson BJ,Duffey ML,et al.Pathoanatomy of first-time,traumatic,anterior glenohumeral subluxation events[J].J Bone Joint Surg Am,2010,92(7):1605-1611.
[3] Miniaci A,Codsi MJ.Thermal capsulorrhaphy for the treatment of 273 shoulder instability[J].Am J Sports Med,2006,34(8):1356-1363.
[4] Rook RT,Savoie FH 3rd,field LD.Arthroscopic treatment of instability attributable to capsular injury or laxity[J].Clin Orthop Relat Res,2001(390):52-58.
[5] Kartus J,Kartus C,Povacz P,et al.Unbiased evaluation of the arthroscopic extra-articular technique for Bankart repair:a clinical and radiographic study with a 2-to 5-year follow-up[J].Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc,2001,9(2):109-115.
[6] Arce G,Arcuri F,Ferro D,et al.Is selective arthroscopic revision beneficial for treating recurrent anterior shoulder instability?[J].Clin Orthop Relat Res,2012,470(4):965-971.
[7] Zaffagnini S,Marcheggiani Muccioli GM,Giordano G,et al.Long-term outcomes after repair of recurrent post-traumatic anterior shoulder instability:comparison of arthroscopic transglenoid suture and open Bankart Reconstruction[J].Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc,2012,20(5):816-821.
[8] 涂明中,陈立,曹博,等.关节镜下GⅡ锚钉固定治疗肩关节Bankart损伤[J].临床骨科杂志,2011,14(1):47-48.
[9] Tokish JM,Mcbratney CM,Solomon DJ,et al.Arthroscopic repair of circumferential lesions of the glenoid labrum:surgical technique[J].J Bone Joint Surg Am,2010,92(Suppl 1 Pt 2):130-144.
[10] Ozorak M,Kokavec M,Svec A.Arthroscopic management of anterior instability of the shoulder[J].Ortop Traumatol Rehabil,2014,16(2):111-118.
Clinical curative effect of the arthroscopic reconstruction for recurrent anterior dislocation of the shoulder
Li Yanlin,Wang Guoliang,He Chuan,Li Jian,Zheng Jiali,Chen Guangchao,Li Song,Yu Yang.Department of Sports Medicine,the First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University,Kunming 650032,China
BackgroundRecurrent dislocation of shoulder joint(or traumatic shoulder instability)initiates from the first shoulder dislocation,compromising the ligaments for stability of the shoulder.When the labrum is torn from the glenoid,the stable function of these ligaments is lost.The progression of traumatic shoulder instability and the type and degree of injuries in glenoid labrum and surrounding ligaments are inextricably linked.Bankart injury is the most common cause of recurrent anterior shoulder dislocation,and the rehabilitation and reconstruction of stable structure in anterior shoulder is critical for the treatment of recurrent anterior dislocation of the shoulder joint.With the development and popularization of the arthroscopic technique,shoulder arthroscopic surgery in the treatment of recurrent anterior dislocation of the shoulder joint has been adopted by increasing surgeons.From June 2010 to April 2014,60 patients of recurrent anterior shoulder dislocation were treated arthroscopically with metallic suture anchor Bankart repair to explore its clinical efficacy.MethodsClinical data:From June of 2010 to April of 2014,sixty patients in our hospital were treated with arthroscopic reconstruction for Bankart injury of recurrent anterior dislocation of the shoulder.The patients were followed up for 10~38 months and the mean time was 26.6 months.Their agesranged from 15 to 45 years with an average of 29 years.Each of 60 cases had a unidirectional instability of anterior shoulder,and the average number of dislocation before surgery was 6.5 times(2-17 times).Suture anchor was applied for reconstruction of Bankart injury.ASES score and Constant-Murley score were adopted for the functional assessment during follow-ups.The postoperative recovery time of shoulder function was 6 weeks without redislocation in each case.Complete rotator cuff tear,subacromial impingement syndrome,etc.were excluded from this group of patients.Imaging examination:X-ray films of anteroposterior view,lateral view and supraspinatus outlet view,CT scanning,MRI and CT three-dimensional reconstruction with humeral head removed were done preoperatively.No obvious bone defect was shown on preoperative X-ray films,no definite bony Bankart injury was revealed on CT three-dimensional reconstruction,and all MRI showed hyperintense between anterior labrum and glenoid rim with 3 cases of glenoid labrum disappeared.Operative methods:After successful general anesthesia,the patient was placed in lateral position.Every 3000 ml saline for flushing purpose was added with 1 ml of 0.1%epinephrine,and the pressure of adjustable water pump was maintained at 60 mm Hg.The bony markers and surgical portals were marked before operation.Posterior portal/arthroscopic portal:2 cm below the posterior corner of acromion.Anterosuperior portal:in the lateral side of coracoid process and between the long head of the biceps tendon and upper margin of the subscapularis tendon inside the joint.Antroinferior portal:2~3 cm below the anterosuperior portal and close to the upper margin of the subscapularis tendon inside the joint as much as possible.Two arthroscopic working cannulas were positioned as working channels.The arthroscopy was put in through the posterior portal to explore the shoulder joint in order.The labrum-shoulder joint capsule-ligament complex was found detached and shifted from the glenoid labrum and the anterior joint capsule and ligaments were aneuros in all cases of this group.The injury sites were often located in the range of 1~5 o′clock.7 patients were with articular cartilage lesion of humeral head and 5 patients were with glenohumeral cartilage degeneration.Radiofrequency ablation and cartilage-plasty were adopted for surface cleaning of articular cartilage injury and degeneration.The shoulder joint soft tissue detacher was used in the front of the damaged glenoid to dissect the adhesive labrum-shoulder joint capsule-ligament complex to the direction of scapular neck.The fibrous tissue was rasped off at the damage of labrum with glenoid file,exposing the fresh bone.The locator was put at the glenoid rim of 2,3,4,5 o′clock position through the antroinferior working cannula.Employed the bone mallet to percuss the locator with in an angle of 45°with glenoid to make a pilot hole on the fresh bony surface of glenoid.The inner core was removed and the metal suture anchor was put in the center of locator and screwed in the glenoid.The labrum-shoulder joint capsule-ligament complex was sutured with suture penetrator device with the knot tied to complete the fixation.After finishing the fixation,the repair effect was rechecked with probe and the wound margin was cleaned by radiofrequency ablation.Postoperative management:Postoperative examination of shoulder joint includes radiographs,and the shoulder joint is fixed with abduction orthosis for 6 weeks with active movement prohibited.The patient is advised to exercise elbow,wrist and hand,and be given local physical therapy,pain relief and icing.Protective rehabilitation,including pendulum training and pulley device training,is allowed 6 weeks later.Rehabilitation for muscle strength begins 3 months later,consisting of increased joint range of motion,resistance training of muscle and endurance training.After 6 months motor function recovery is initiated to strengthen the exercises of muscles around the shoulder joint,proprioception,etc.,and non-contact sports activities can be engaged,including special training of restoration movement function,weight lifting,dumbbell training,etc.Immediate postoperative physical therapy and rehabilitation is performed under the guidance of rehabilitation physicians and therapists.Physical therapy mainly contains early cold compress to relieve pain and disperse swelling,ultrashort wave therapy to improve local blood circulation and promotion of soreness subsiding and tissue healing.Rehabilitation can improve circulation,promote joint capsule-labrum complex healing,strengthen muscle,increase joint stability,and prevent joint stiffness,swelling and other complications.ResultsOutpatient follow-upswere carried out 3 week,6 week,3 month,6 month and 1 year after operation and henceforth once each year.The mean ASES score before operation and at the final follow-ups,the angle of anteflexion,abduction and external rotation,and the mean Constant-Murley score at the final followups of 60 patients were processed by paired t-test and a value ofP<0.05 was considered statistically significant.No postoperative redislocation occurred in all patients during the final follow-up.Postoperative residual Crank test was positive in 4 patients(6.7%).All patients restored preoperative work with 52 patients(86.7%)restored to the sports level before the first dislocation.DiscussionArthroscopic Bankart repair is one of the effective methods for treatment of recurrent anterior dislocation of the shoulder,the proper case selection,and arthroscopic technique during operation and strict postoperative functional rehabilitation are the keys to successful operation.
Shoulder dislocation;Arthroscopy;Bankart Injury
Wang Guoliang,Email:200301144@163.com
2014-08-07)
(本文编辑:李静)
10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-5790.2014.04.003
云南省医学学科带头人项目(D-201207);云南省创新团队项目(2014HC018)
650032 昆明医科大学第一附属医院运动医学科
王国梁,Email:200301144@163.com
李彦林,王国梁,何川,等.关节镜下治疗创伤复发性Bankart损伤疗效分析[J/CD].中华肩肘外科电子杂志,2014,2(4):219-224.

