CEA、CYFRA21-1和TSGF对晚期非小细胞肺癌化放疗疗效的评估价值
彭秋平,柯传庆,冯青青
解放军第94医院 肿瘤科,江西南昌 330002
CEA、CYFRA21-1和TSGF对晚期非小细胞肺癌化放疗疗效的评估价值
彭秋平,柯传庆,冯青青
解放军第94医院 肿瘤科,江西南昌 330002
目的探讨血清癌胚抗原(carcinoembryonic antigen,CEA)、细胞角蛋白19片段(CYFRA21-1)和肿瘤特异性生长因子(tumor specific growth factor,TSGF)对晚期非小细胞肺癌(non-small cell lung cancer,NSCLC)化放疗疗效的评估价值。方法选取2009年1月- 2012年1月我院收治的54例诊断明确的初治晚期NSCLC患者,先行长春瑞滨+顺铂全身化疗2周期,再予肺癌立体定向放射治疗。在第一周期化疗前和立体定向放疗结束后3个月,采集患者静脉血,检测CEA、CYFRA21-1和TSGF血清浓度。结果54例综合治疗后3个月,PR 21例,SD 18例,PD 15例。肺鳞癌化放疗后,血清CYFRA21-1和TSGF水平均明显降低;肺腺癌化放疗后,血清CEA和TSGF水平均显著下降(均P<0.01)。治疗有效(PR)组血清CEA、CYFRA21-1和TSGF值明显降低(P<0.05);治疗无效(NC+PD)组血清CEA、CYFRA21-1和TSGF浓度无明显变化(P>0.05)。结论晚期NSCLC化放疗前后,血清CEA、CYFRA21-1和TSGF水平变化与组织学类型有关,可通过监测CEA、CYFRA21-1和TSGF血清浓度变化来评估NSCLC化放疗疗效。
肺癌;肿瘤标记物;癌胚抗原;细胞角蛋白19片段;肿瘤特异性生长因子
肺癌是我国最常见的恶性肿瘤,以非小细胞肺癌(non-small cell lung cancer,NSCLC)为主。大多数NSCLC确诊时已失去手术机会,化放疗为主的综合治疗是晚期NSCLC的主要治疗选择[1-2]。近年来,随着血清肿瘤标记物检测技术的提升和新的标记物出现,肿瘤标记物在肺癌中的临床应用价值日益受到关注[3-4]。目前,肿瘤标记物应用于肺癌诊断的报道较多,而在肺癌疗效分析中的应用研究相对较少[4-6]。本研究拟通过检测晚期NSCLC化放疗综合治疗前后血清癌胚抗原(carcinoembryonic antigen,CEA)、细胞角蛋白19片段(CYFRA21-1)和肿瘤特异性生长因子(tumor specific growth factor,TSGF)的浓度变化,评价肿瘤相关标记物对晚期NSCLC近期疗效的指导意义。
表1 NSCLC综合治疗前后血清肿瘤标记物变化Tab. 1 Serum level of tumor markers in advanced NSCLC patients before and after treatment(-±s)
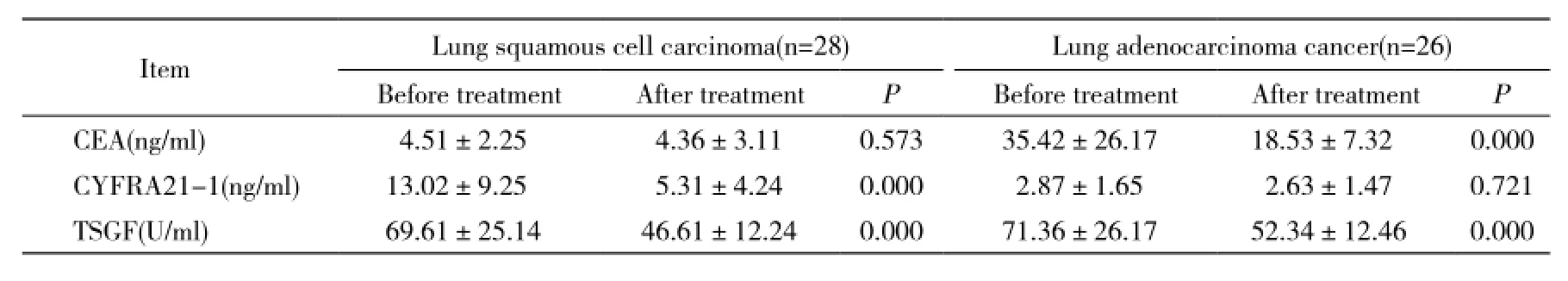
表1 NSCLC综合治疗前后血清肿瘤标记物变化Tab. 1 Serum level of tumor markers in advanced NSCLC patients before and after treatment(-±s)
ItemLung squamous cell carcinoma(n=28)Lung adenocarcinoma cancer(n=26) Before treatmentAfter treatmentPBefore treatmentAfter treatmentP CEA(ng/ml)4.51±2.254.36±3.110.57335.42±26.1718.53±7.320.000 CYFRA21-1(ng/ml)13.02±9.255.31±4.240.0002.87±1.652.63±1.470.721 TSGF(U/ml)69.61±25.1446.61±12.240.00071.36±26.1752.34±12.460.000
表2 NSCLC血清肿瘤标记物变化与近期疗效的关系Tab. 2 Relation between serum levels of tumor markers and short-term curative effect in advanced NSCLC patients(-±s)
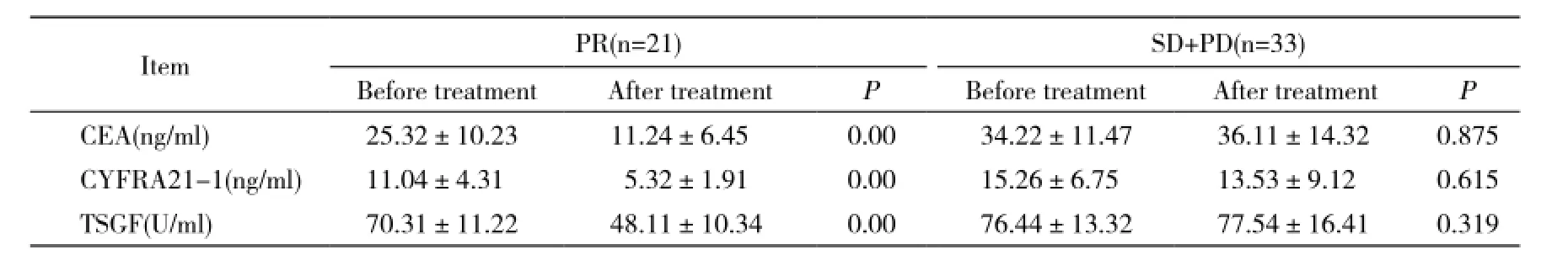
表2 NSCLC血清肿瘤标记物变化与近期疗效的关系Tab. 2 Relation between serum levels of tumor markers and short-term curative effect in advanced NSCLC patients(-±s)
ItemPR(n=21)SD+PD(n=33) Before treatmentAfter treatmentPBefore treatmentAfter treatmentP CEA(ng/ml)25.32±10.2311.24±6.450.0034.22±11.4736.11±14.320.875 CYFRA21-1(ng/ml)11.04±4.315.32±1.910.0015.26±6.7513.53±9.120.615 TSGF(U/ml)70.31±11.2248.11±10.340.0076.44±13.3277.54±16.410.319
PR: partial response; SD: stable disease; PD: progressive disease
资料和方法
1 资料 我院2009年1月- 2012年1月收治的54例晚期初治NSCLC,男37例,女17例;年龄35 ~ 74岁,中位年龄58岁。所有病例均经组织病理学或细胞学证实,其中鳞癌28例,腺癌26例。KPS评分≥70分,心、肝、肾功能无严重损害,除外有中枢系统转移。既往均未接受过手术、放化疗或靶向治疗。
2 治疗方法 化疗与放疗序贯综合治疗。化疗采用长春瑞滨(NVB)40 mg静推,d1、d8,顺铂(DDP)40 mg静滴,d1 ~ d3,28 d重复一周期。第2周期化疗结束后14 d,行肺癌立体定向放射治疗,放射源为60 Co,单次剂量3.0 ~ 4.5 Gy,每日治疗1次,每周治疗5 d,总剂量45 ~ 50 Gy。
3 血清肿瘤标记物检测 于第1周期化疗前和立体定向放疗结束后3个月,采集患者静脉血,检测血清CEA、CYFRA21-1和TSGF水平。CEA和CYFRA21-1检测采用电化学发光技术,按照罗氏Elecsys试剂说明操作。TSGF应用比色法检测,按照TSGF检测试剂(福建新大陆生物技术股份有限公司)说明操作。正常值参考范围分别为:CEA≤3.4 ng/ml, CYFRA21-1<3.3 ng/ml, TSGF<64×103U/L。
4 近期疗效评价 第1周期化疗前和立体定向放疗结束后3个月行胸部CT或MRI检查。按照WHO实体瘤评定标准,近期疗效分为:完全缓解(CR)、部分缓解(PR)、稳定(SD)和进展(PD)。有效包括CR和PR,无效包括SD和PD,以CR+PR计算治疗有效率。
结 果
1 近期疗效 54例NSCLC综合治疗后3个月,根据胸部CT或MRI影像学分析判定,CR 0例,PR 21例,SD 18例,PD 15例。有效(PR)21例,无效(SD+PD)33例,有效率为38.9%(21/54)。
2 不同类型NSCLC血清肿瘤标记物水平 肺腺癌CEA血清浓度高于肺鳞癌,而肺鳞癌CYFRA21-1血清浓度高于肺腺癌,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.01)。肺鳞癌和肺腺癌的血清TSGF浓度差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),见表1。
3 综合治疗前后血清肿瘤标记物变化 28例鳞癌化放疗后,血清CYFRA21-1和TSGF水平均明显降低,差异均有统计性意义(P<0.01);血清CEA水平虽有所下降,但差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。26例腺癌化放疗后,血清CEA和TSGF水平均下降明显,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.01);血清CYFRA21-1水平虽有所下降,但差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),见表1。
4 肿瘤标记物变化与近期疗效的关系 21例PR患者CEA、CYFRA21-1和TSGF值,与治疗前相比均明显降低(P<0.05);而33例NC+PD患者CEA、CYFRA21-1和TSGF均无明显变化(P>0.05),见表2。
讨 论
CEA是最早应用于肺癌诊断的肿瘤标记物,肺癌CEA阳性率可达40% ~ 80%,尤其是肺腺癌更为显著[7-8]。本组资料也显示,肺腺癌血清CEA浓度明显高于肺鳞癌。有研究发现,NSCLC的血清CEA浓度变化与含顺铂化疗疗效有较好的相关性[6,9]。本研究显示,化放疗综合治疗后,肺腺癌血清CEA水平明显下降,治疗有效(PR)组的CEA浓度显著降低,而治疗无效(SD+PD)组CEA水平无下降。
CYFRA21-1为细胞角蛋白19片段,是检测NSCLC的新一代的肿瘤标记物。CYFRA21-1对肺鳞癌特异性较好,对肺鳞癌诊断有辅助作用[10-12]。本组资料显示,肺鳞癌血清CYFRA 21-1值明显高于肺腺癌。本研究还发现,化放疗综合治疗后,肺鳞癌治疗有效(PR)组血清CYFRA21-1水平明显下降,而治疗无效(SD+PD)组血清CYFRA21-1浓度无降低。
TSGF是一类分子质量相对不大的可溶性肽类物质,对肿瘤生长、扩散和转移有促进作用。正常情况下,TSGF由T细胞或单核细胞分泌产生,血清含量较低。恶性肿瘤细胞可分泌、释放TSGF。在肿瘤早期,TSGF即可升高,阳性率可达70%以上。TSGF是一种广谱性、敏感性较高,特异性较差的肿瘤标记物[13-15]。本组资料显示,肺鳞癌与肺腺癌的血清TSGF浓度无明显差异;化放疗后,治疗有效(PR)组治疗前后TSGF水平显著下降,治疗无效(SD+PD)组TSGF水平无变化。
总之,CEA、CYFRA21-1和TSGF血清浓度变化与NSCLC化放疗疗效相关。但CEA、CYFRA21-1对NSCLC有相对组织特异性,而TSGF对肺鳞癌和肺腺癌无特异性。在临床实践中,可根据NSCLC类型有针对性地选择肿瘤标记物组合进行疗效监测,并与肿瘤影像学变化相结合,综合分析评价疗效,指导治疗方案的调整。
1 Jensen AD, Münter MW, Bischoff HG, et al. Combined treatment of nonsmall cell lung Cancer NSCLC stage III with intensity-modulated RT radiotherapy and cetuximab: the NEAR trial[J]. Cancer,2011, 117(13): 2986-2994.
2 张冠中,焦顺昌,杨纪华.培美曲塞单药或联合铂类治疗非小细胞肺癌86例分析[J].解放军医学院学报,2013,34(4):319-321.
3 郭菲,高静,高艳红.糖尿病患者肿瘤标志物分析[J].军医进修学院学报,2012,33(9):933-935.
4 张岚.肺癌相关肿瘤标志物研究现状[J].临床肺科杂志,2012,17(10):1870-1872.
5 王慧敏,钟华,金波,等.血清肿瘤标志物预测晚期非小细胞肺癌靶向治疗疗效的临床价值[J].肿瘤,2012,32(12):1021-1024.
6 穆新林,高占成,叶阮健.血清CEA、CYFRA21-1的变化与化疗客观疗效的相关性[J].中国肺癌杂志,2009,12(9):1051-1054.
7 Grunnet M, Sorensen JB. Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) as tumor marker in lung cancer[J]. Lung Cancer, 2012, 76(2):138-143.
8 Hanagiri T, Sugaya M, Takenaka M, et al. Preoperative CYFRA 21-1 and CEA as prognostic factors in patients with stage I non-small cell lung Cancer[J]. Lung Cancer, 2011, 74(1): 112-117.
9 Li L, Song LH, Ding SC, et al. Clinical value of CEA and CYFRA21-1 as an assessment indicator of therapeutic efficacy in advanced non-small cell lung Cancer patients[J]. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi, 2010, 32(11): 850-854.
10 Wang J, Zhang N, Li B, et al. Decline of serum CYFRA21-1 during chemoradiotherapy of NSCLC: a probable predictive factor for tumor response[J]. Tumour Biol, 2011, 32(4): 689-695.
11 Lin XF, Wang XD, Sun DQ, et al. High Serum CEA and CYFRA21-1 Levels after a Two-Cycle Adjuvant Chemotherapy for NSCLC: Possible Poor Prognostic Factors[J]. Cancer Biol Med,2012, 9(4):270-273.
12 Li X, Asmitananda T, Gao L, et al. Biomarkers in the lung Cancer diagnosis: a clinical perspective[J]. Neoplasma, 2012, 59(5):500-507.
13 陈芳华,骆曦,饶万楷.恶性肿瘤特异性生长因子对恶性肿瘤的诊断价值[J].国际检验医学杂志,2011,32(11):1183-1184.
14 Deng B, Tan QY, Fan XQ, et al. Clinical value of assaying tumor supplied group of factor/tumor specific growth factor in patients with solitary pulmonary nodule[J]. Clin Lung Cancer, 2011, 12(3):192-196.
15 甄拴平.肺癌患者3项标志物检测的临床价值[J].检验医学与临床,2012,9(10):1217-1218.
Value of CEA, CYFRA21-1 and TSGF in assessing the curative effect of combined chemotherapy and radiotherapy on advanced non-small cell lung cancer
PENG Qiu-ping, KE Chuan-qing, FENG Qing-qing
Department of Oncology, Chinese PLA 94 Hospital, Nanchang 330002, Jiangxi Province, China
FENG Qing-qing. Email: ncfqqing@126.com
ObjectiveTo study the value of CEA, CYFRA21-1 and TSGF in assessing the curative effect of combined chemotherapy and radiotherapy on advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).MethodsFifty-four advanced NSCLC patients admitted to our hospital from January 2009 to January 2012 underwent two cycles of whole body chemotherapy with NVB and DDP followed by stereotactic radiotherapy. Blood samples were taken from the patients before the frst cycle of chemotherapy and 3 month after stereotactic radiotherapy for the measurement of their serum CEA, CYFRA21-1 and TSGF levels.ResultsOf the 54 patients who received 3 months of combined chemotherapy and radiotherapy, 21 had PR, 18 had SD, and 15 had PD. The serum CYFRA21-1 and TSGF levels and the serum CEA and TSGF levels were signifcantly lower in patients with lung squamous cell carcinoma and in those with lung adenocarcinoma cancer, respectively, after combined chemotherapy and radiotherapy (P<0.01). The serum CEA, CYFRA21-1 and TSGF levels were signifcantly lower in responders than in non- responders (P<0.05) while no signifcant change was observed in non-responders after combined chemotherapy and radiotherapy (P>0.05).ConclusionThe serum CEA, CYFRA21-1 and TSGF levels are related with the histopathological type of advanced NSCLC before and after combined chemotherapy and radiotherapy. The curative effect of combined chemotherapy and radiotherapy on advanced NSCLC can thus be assessed by monitoring the serum CEA, CYFRA21-1 and TSGF levels.
lung cancer; tumor marker; carcinoembryonic antigen; cytokeratin-19 fragment; tumor specifc growth factor
R 734.2
A
2095-5227(2014)01-0034-03
10.3969/j.issn.2095-5227.2014.01.011
2013-06-06
彭秋平,男,博士,副主任医师。研究方向:恶性肿瘤内科治疗。Email: qiupingpeng@126.com
冯青青,男,学士,主任医师。Email: ncfqqing@126.com

