静电场轨道阱质谱的进展
李 明,马家辰,李红梅,熊行创,江 游,黄泽建,方 向
(1.中国计量科学研究院,北京 100013;2.哈尔滨工业大学威海分校,山东 威海 264209)
静电场轨道阱质谱的进展
李 明1,马家辰2,李红梅1,熊行创1,江 游1,黄泽建1,方 向1
(1.中国计量科学研究院,北京 100013;2.哈尔滨工业大学威海分校,山东 威海 264209)
静电场轨道阱是近年来新兴的一种质谱质量分析器,它利用离子在特定静电场中运动频率的不同对阱内离子进行质量分析,由于其具有较高的分辨率和质量准确度,被广泛应用于化学、生物学、医学等领域。本工作对静电场轨道阱质谱的形成过程和基本原理进行了详细介绍;对轨道阱质谱在蛋白质组学、代谢组学等方面的应用做了简要综述;对轨道阱质谱与常压电离技术联用的最新进展进行了评述,并指出电喷雾萃取电离、低温等离子体探针等常压质谱技术与轨道阱质谱的联用将在蛋白质分析、化学合成、化学反应机理研究等诸多领域发挥重要作用,旨在推动我国相关质谱仪器的国产化进程。
轨道阱;质谱;常压离子化;蛋白质组学;代谢组学
质谱技术具有分析速度快、动态范围宽、灵敏度高等优点,被广泛应用于国防、航天、海洋、医药、生物、化学、化工、食品安全、环境保护等诸多领域[1];近年来,诸如蛋白质组学、代谢组学等领域的样品复杂性推动了质谱技术和质谱仪器的快速发展,已有人试图将质谱用于蛋白质芯片的制备和在线表面化学反应等相关研究[2-6]。质谱对分子质量测量的准确度达到10-6时,可以由分子质量推测被测物的可能分子式[7]。通常质谱仪按照质量分析器的类型可分为6大类:四极杆质谱、磁质谱、离子阱质谱、飞行时间质谱、傅里叶变换离子回旋共振质谱(FT-ICR MS)、轨道阱质谱(Orbitrap)等。离子回旋共振质谱的质量准确度可高达10-6级[8];飞行时间质谱的质量准确度可达2×10-6~5×10-6级[9-10];四极离子阱质谱的质量准确度最高能够达到2×10-5[11]级。然而,离子回旋共振需在较高磁场下进行,高磁场由液氦提供的超低温环境(接近绝对零度)中的超导电流获得,仪器操作复杂且维护费用昂贵,每年液氦的费用高达10万元以上;飞行时间质谱对电场的稳定性要求极高,仪器的质量准确度受周围环境(如温度等)影响较大;而轨道阱质谱具有较高的分辨率,且操作简单、易于维护,被广泛应用于蛋白质组学、代谢组学等领域。我国的科学仪器研发工作者已在飞行时间质谱[12]、四极杆[13]和离子阱质谱[14-15]方面取得了诸多丰硕成果,而基于轨道阱的质谱仪器研发工作鲜有报道。本工作拟对轨道阱质谱的工作原理和最新进展进行综述,旨在推动我国质谱仪器国产化进程,打破高端科学仪器长期依赖进口的现状。
1 轨道阱的工作原理
1.1轨道阱的形成
轨道阱质量分析器是在早期的Kingdon阱[16]基础上发展起来的。在Kingdon阱中,利用静电场对离子进行存储,结构示于图1。将丝阴极同轴放入两边配有端盖电极的圆柱形阳极。加在丝阴极和圆柱阳极上的直流电压产生径向电势:
Φ=Alnr+B
(1)
其中,r为径向坐标,A和B是在给定电压情况下的两个常数。离子可以在阱内直接产生或在阱外产生后从垂直于丝电极的方向被引入阱内,离子在阱内特定轨道上做围绕丝电极的旋转运动,而加在端盖电极上的推斥电压使离子在轴向保持稳定。Kingdon阱被用于分子束[17]和离子光谱的研究[18-19]。单电荷的分子离子能够在Kingdon阱中存活几秒钟。
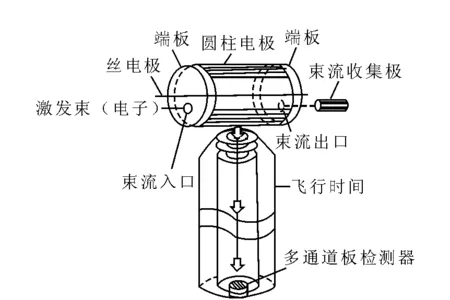
图1 Kingdon阱连接TOF质谱的示意图[20]Fig.1 Schematic of Kingdon trap coupled wih a TOF
1981年Knight[21]改变了Kingdon阱的外电极形状,除了径向的对数项,Knight增加了轴向的四极项。在四极离子阱中的四极电势为:

(2)
Knight阱电势可近似用式(3)来表示:

(3)
这里,r和z代表圆柱坐标系的变量(电势的对称平面处z=0),A和B是与阱形状和电压相关的参数。同Kingdon阱一样,Knight阱中的离子在径向上受到外电极与中间电极间产生的对数电势的限制,在轴向上受四极电势的限制,因此离子在z方向上做谐振荡。Knight阱被用来监测脉冲激光消融获得的离子,离子从外电极z=0的切口处被引入阱中,可通过两种方式对阱中的离子进行监测:1) 离子流在轴向上随时间减小;2) 在丝电极上施加脉冲正电压,并在径向上收集检测离子。也有其他人对Kingdon阱进行改进,例如Mcilraith[22]采用两个丝电极作为内电极;Blümel[23]在DC电压上加一AC电压以提高离子捕获效率。然而,Kingdon阱一直被用于离子的储存,并没有用做质谱的质量分析器。
在Kingdon阱的基础上,Makarov[24]发明了新的质量分析器,即轨道阱,其结构图示于图2。
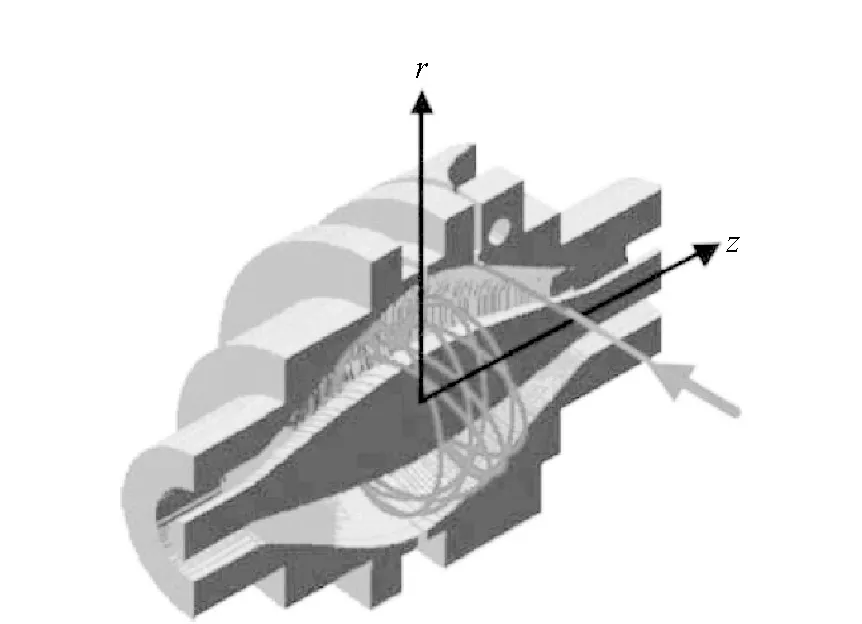
图2 轨道阱质量分析器示意图Fig.2 Schematic of Orbitrap analyzer
轨道阱可视为四极离子阱的变形,不同的是,轨道阱使用静电场,而四极离子阱使用射频电场[14]。轨道阱在轴向上产生的电势可由式(4)表示:

(4)
这里,r和z代表圆柱坐标系的变量,k为场曲率,Rm为特性半径。稳定离子的运动轨迹包括围绕丝电极的轨道运动和z方向的振荡。从式(4)可看出,独特的电极形状产生的静电场不存在r和z的交叉项。因此,在z方向上存在独特的四极场。离子在z方向上的运动与运动半径r和相位φ完全无关。离子的质荷比(m/z)只与离子在z方向上的运动频率相关,即:

(5)
与傅里叶变换离子回旋共振质谱[25]类似,轨道阱采用影像电流法[26]对阱内离子进行检测,通过傅里叶变换将得到的时域信号转换为频域信号,而离子的运动频率与离子的质荷比相关,从而可得到样品的质谱图。尽管离子的径向运动频率和角频率也与质量相关,而轴向频率与离子能量和离子的空间位置完全无关,因此检测时使用轴向频率。离子的运动频率与离子能量无关,所以轨道阱具有高分辨率和高质量准确度等优点。由于阱电势与质荷比无关,并且具有比FT-ICR和Paul离子阱更大的阱体积,轨道阱在高质量端具有很高的空间电荷储存能力,因此轨道阱具有较高的质量范围。
目前,轨道阱质量分析器已被赛默飞世尔公司成功商品化[27],推出多款基于轨道阱技术的质谱仪器。例如,Q Exactive 质谱仪实现了四极杆的目标离子选择性能与高分辨、高准确度的轨道阱检测技术相结合;LTQ Orbitrap XL和LTQ Orbitrap Velos将线性离子阱与轨道阱联用,多级碎裂技术能够对分析物提供最佳结构表征。此外,商品化的轨道阱质谱在进行串联质谱分析时,除了碰撞诱导解离技术(CID),还可选择使用更高能量碰撞诱导解离(HCD)以及电子转移解离(ETD),可应用于复杂体系目标物的定性研究。
1.2离子在静电场轨道阱中的运动
1.2.1离子的捕获 与其他线性离子阱类似,离子进入轨道阱之前先进入用于离子存储的四极阱,在四极阱内与中性气体发生多次碰撞以降低离子能量,然后缓慢(20~50 ms)升高四极电势,当控制离子引出的离子门被打开后,离子获得进行离子注入和进入轨道运动的必要能量。
离子被引入轨道阱后,阱电场强度逐渐增加,离子随场强增加的运动情况示于图3[7]。在离子到达对面电极之前,增加阱电场是为了避免离子与丝电极发生碰撞,并通过挤压离子轨迹,使更多的新离子(高质荷比)被注入阱内。当所有离子都进入阱内后,调节丝电极的电压为一固定值,随即进行影像电流检测。场强增加的时间取决于分析物的质量范围,通常为20~100 ms。
1.2.2离子在轨道阱中的运动 离子围绕丝电极的旋转运动尽管与质量分析没有关系,但也同样重要,因为必须在径向上对离子进行限制,才能使离子在轨道阱中稳定存在。离子绕丝电极的旋转运动与离子的动能有关,可将其比作360 °静电场分析器,其运动轨迹可用式(6)描述:
r=2eV/eE
(6)
这里,r为离子轨迹半径,eV是离子动能,eE是离子所受电场力。从式(6)可看出,离子轨迹半径与离子质量无关,只与离子动能有关。因此,在离子被注入轨道阱之前,仔细调节离子的能量是质量分析顺利进行的关键。
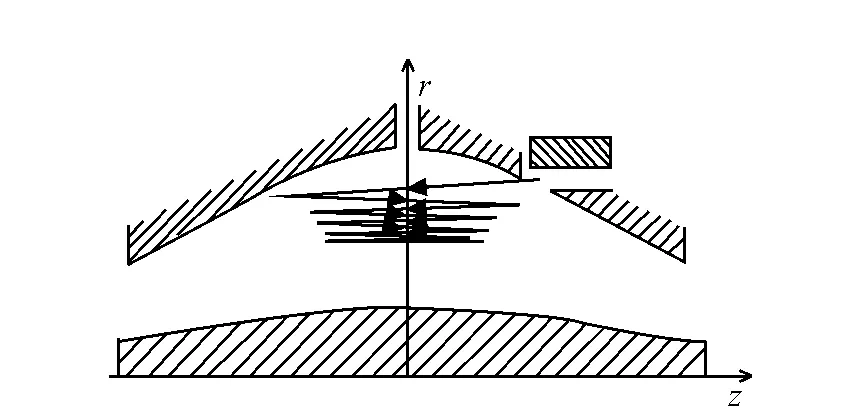
图3 轨道阱中离子随场强增加被压缩的运动情况Fig.3 The motion of ions in Orbitrap as the field strength is increased
1.2.3轴向运动和离子检测 轨道阱采用影像电流检测器[26]对阱内离子进行检测。对于给定质荷比的离子,其轴向频率与离子的初始参数完全无关,而径向频率和旋转频率与初始半径和离子能量有关。因此,相同质荷比的离子能够沿z轴方向以同一频率连续振荡几十次甚至几百次;与之相反,离子的径向运动和旋转运动的频率因离子初始参数不同而有所变化。在振荡50~100次后,离子径向运动和旋转运动产生的影像电流分别被各自相反方向的影像电流所抵消,因此,径向运动频率和旋转运动频率不会在谱图中出现。另一方面,轴向振荡会保持不变,产生的影像电流信号差分放大后被检测。由于轨道阱形状的瑕疵、离子与少量中性分子的碰撞、空间电荷效应等因素,轴向影像电流最终也会逐渐消失。
理论上,轨道阱也可采用电子倍增器作为检测器。Makarov[24]提出在丝电极的静电场上加一RF电压,以改变阱内离子在轴向和径向所受电场力强度。此时,离子径向运动方程变得非常复杂,而轴向符合Mathieu方程[14],可在质量选择不稳定模式下将离子从轴向引出并获得信号。
1.3影响轨道阱性能的因素
1.3.1质谱分辨率 通常四极质谱的分辨率为0.6~0.8 u,离子回旋共振质谱的分辨率为百万,轨道阱质谱的分辨率虽略低于离子回旋共振质谱,也可高达几十万。电场缺陷引起的交叉项和非谐振效应是影响轨道阱质谱分辨率的重要因素。电场缺陷主要由以下因素产生[28]:电场形状的缺陷,如离子注入的狭缝等;机械加工的精度;高压电源的稳定性。轨道阱的分辨能力随质量的增大而减弱,因为大质量的离子与背景气体的碰撞截面增大,因此,对蛋白等高质量化合物进行高分辨测量时,超高真空非常重要。另外,增加检测时间,也可提高轨道阱质谱的分辨率。
1.3.2质量准确度 质量准确度依赖于仪器对相邻质谱峰的分辨能力,因此影响分辨率的因素同样会影响质量准确度。一些其他因素也会影响质量准确度,如空间电荷效应、离子注入时初始位置的微小差别、微弱的电场交叉项等。优化仪器参数后,轨道阱的质量准确度很容易达到2×10-6~5×10-6。选择合适的信噪比、使用内标的情况下,质量准确度可达到1×10-6[29]。在使用外标情况下,由于丝电极的散粒噪声、热敏感性、以及高压电源输出的微小变化都会影响测量的质量准确度,这些因素产生的质量误差比空间电荷效应产生的误差要大很多[30]。为获取最佳分辨能力和质量准确度,商品化仪器配置的高压电源都经过热校准,能够在20 h内稳定工作。在使用外标校正的情况下,轨道阱的质量误差可控制在5×10-6以内。
2 轨道阱的应用
高性能的质谱仪器能够在诸多领域发挥重要作用,例如,高效液相色谱的保留时间、串联质谱信息与准确质量测量结合能够减少肽的候选物,有利于得到被测物的元素组成,这些能力可提供蛋白质翻译后修饰等信息。商品化的轨道阱质谱具有较好的离子传输效率,因此具有较高的灵敏度,加上前面提到的高质量准确度和高分辨率等优点,轨道阱被广泛应用于食品安全[31-33]、法庭科学[34-35]、临床医学[36]、脂质组学[37]、蛋白质组学[38-45]、代谢组学[46-50]等领域。例如,轨道阱质谱被用于蔬菜和水果中农药残留的检测[31-32];轨道阱质谱与纳升液相色谱联用,用于尿液中违禁药物的检测[36];Jang等[39]采用高分辨LTQ-Orbitrap完成了人血浆中葡萄球菌脂磷壁酸结合蛋白的鉴定;Marie等[40]采用碰撞诱导解离技术、高能量碰撞诱导解离以及电子转移解离等多种碎裂技术并结合Mascot和PEAKS DB软件进行搜索,成功完成了软体动物壳中低含量肽的分析和鉴定;轨道阱质谱与亲水相互作用色谱联用,应用于人体尿液代谢组学的研究,在人类尿液中检出近千种代谢产物[44];高效液相色谱与轨道阱质谱被用于何首乌中活性成分的研究,提供了一种对中药的低丰度代谢产物进行快速检测的技术手段[47]。
3 轨道阱与常压离子化技术联用的最新进展
近年来发展起来的常压质谱技术[51]能够对复杂基体样品进行直接分析,无需萃取、色谱分离等样品处理。由于未经处理的样品成分复杂,将这些常压离子化方法与高性能质量分析器耦合对准确分析被测物的化学组成至关重要。
Hu等[52]将轨道阱质谱与电喷雾解吸电离技术(desorption electrospray ionization, DESI)耦合,并用于肽和药物中有效成分的检测,分析时间小于1 s,分辨率达6万,使用VVK肽做内标,对克敏能药片的有效成分进行检测时,质量准确度高达1×10-6。Mcewen等[53]将大气压固体分析探针(atmospheric solid analysis probe, ASAP)与轨道阱联用,用于分析玉蜀黍黑粉菌(玉蜀黍黑穗病病原体)中麦角固醇的浓度;Zhang等[54]将低温等离子体探针(low temperature probe, LTP)与轨道阱联用,用于细菌样品中脂肪酸乙酯的直接检测,利用轨道阱的高质量准确度和串联质谱信息,对脂肪酸乙酯的种类进行鉴别,并结合主成分分析等数据处理方法对不同细菌进行区分,能够很容易区分革兰氏阳性和革兰氏阴性细菌;Edison等[55]将实时直接分析技术(direct analysis in real time, DART)与轨道阱联用,用于葡萄、苹果、桔子等水果表面杀虫剂的快速检测;Cooks等[56]将DESI与轨道阱联用,在正负离子模式下,分析了甜叶菊中主要成分二萜苷类化合物,通过精确质量测量和串联质谱信息对其进行确证,并在全扫描模式下,对其进行半定量测量。在定量分析方面,Vaclavik等[57]将DART与轨道阱联用,使用基体标物或同位素内标技术,对麦片中多种霉菌毒素进行准确定量分析,同位素稀释方法的回收率为100%~108%,重现性5.4%~6.9%;基于基体匹配校准,回收率为84%~118%,重现性RSD为7.9%~12.0%。
LTP曾被用于化学反应研究,例如苯的还原[58],将LTP与轨道阱联用将有利于反应产物和反应中间体的元素分析和结构确证;电喷雾萃取电离(extractive electrospray ionization, EESI)过程能够保持蛋白质的天然结构[59-60],将其与轨道阱质谱联用,并结合氢/氘交换质谱,可应用于蛋白质的四级结构定量研究。可以预见,常压离子化方法与高性能的轨道阱质谱联用将会在化学反应、反应机理研究及蛋白质四级结构定量等应用领域发挥重要作用,并成为质谱技术研究的新热点。
4 展望
轨道阱质谱具有较高的分辨率和较高的质量准确度,在静电场下工作,无需超低温环境,操作简单、易于维护,并可与液相色谱、毛细管电泳等高效分离技术联用,结合碰撞诱导解离、高能碰撞诱导解离以及电子转移解离等母离子碎裂技术,轨道阱质谱必将在蛋白质组学、代谢组学、脂质组学等领域发挥重要作用。
[1] 陈焕文, 李 明, 金钦汉. 质谱仪器及其发展 [J]. 大学化学, 2004, 19(3): 9-15.
CHEN Huanwen, LI Ming, JIN Qinhan. Mass spectrometric instrumentation and the progress[J]. Chinese Journal of Collegial Chemistry, 2006, 19(3): 9-15 (in Chinese).
[2] OUYANG Z, TAKATS Z, COOKS R G, et al. Preparing protein microarrays by soft-landing of mass selected ions [J]. Nature, 2003, 301(5 638): 1 351-1 354.
[3] NIE Z X, LI G T, COOKS R G, et al. In situ SIMS analysis and reactions of surfaces prepared by soft landing of mass-selected cations and anions using an ion trap mass spectrometer [J]. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom, 2009, 20(6): 949-956.
[4] BANTSCHEFF M, LEMEER S, SAVITSKI M M, et al. Quantitative mass spectrometry in proteomics: Critical review update from 2007 to the present [J]. Anal Bioanal Chem, 2012, 404(4): 939-965.
[5] CAMERON L C. Mass spectrometry imaging: Fa-cts and perspectives from a non-mass spectrometrist point of view [J]. Methods, 2012, 57(4): 417-422.
[6] PERRY R H, COOKS R G, NOLL R J. Orbitrap mass spectrometry: Instrumentation, ion motion and applications [J]. Mass Spectrom Rev, 2008, 27(6): 661-699.
[7] HU Q Z, NOLL R J, COOKS R G, et al. The Or-bitrap: A new mass spectrometer [J]. J Mass Spectrom, 2005, 40(4): 430-443.
[8] MARSHALL A G, HENDRICKSON C L, JAC-KSON G S. Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry: A primer [J]. Mass Spectrom Rev, 1998, 17(1): 1-35.
[9] MCLUCKEY S A, WELLS J M. Mass analysis at the advent of the 21st century [J]. Chem Rev, 2001, 101: 571-606.
[10] WILLIAMS J D, FLANAGAN M, LOPEZ L, et al.Using accurate mass electrospray ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry with in-source cid to sequence peptide mixtures [J]. J Chromatogr A, 2003, 1020: 11-26.
[11] WELLS J M, GILL L A, OUYANG Z, et al. Factors affecting the mass measurement accuracy of quadrupole ion trap mass spectrometers. In Proceedings of the 46th ASMS Conference on Mass Spectrometry and Allied Topics, Orlando, 1998, 485.
[12] 何 坚, 杨芃原, 周 振, 等. 高分辨电喷雾离子源三级四极杆-飞行时间质谱仪的研制 [J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2003, 24(6): 50-52.
HE Jian, YANG Pengyuan, ZHOU Zhen, et al. The development of a high resolution ESI-QTOFMS coupled with three sect quadrupoles[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2003, 24(6): 50-52 (in Chinese).
[13] 江 游, 方 向, 黄泽建, 等. 大气压接口-单四极杆质谱仪的研制 [J]. 质谱学报, 2010, 31(6):337-341.
JIANG You, FANG Xiang, HUANG Zejian, et al. Development of atmospheric pressure interface-single quadrupole mass spectrometer[J]. Journal of Chinese Mass Spectrometry Society, 2010, 31(6): 337-341 (in Chinese).
[14] 李 明, 费 强, 金钦汉,等. 离子阱质谱仪小型化的最新研究进展 [J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2007, 28(6): 189-194.
LI Ming, FEI Qiang, JIN Qinhan, et al. The new progress of miniature ion trap [J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2007, 28(6): 189-194 (in Chinese).
[15] NIE Z X, CUI F P, CHU M L, et al. Calibration of frequency-scan quadrupole ion trap mass spectrometer for microparticles mass analysis [J]. Int J Mass Spectrom, 2008, 270: 8-15.
[16] KINGDON K H. A method for the neutralization of electron space charge by positive ionization at very low gas pressures [J]. Phys Rev, 1923, 21(4): 408-418.
[17] BROOKS P R, HERSCHBACH D R. Kingdon cage as a molecular beam detector [J]. Rev Sci Inst, 1964, 35(11): 1 528-1 533.
[18] LEWIS R R. Motion of ions in the Kingdon trap [J]. J Appl Phys, 1982, 53(6): 3 975-3 980.
[19] YANG L, CHURCH D A. Confinement of injected beam ions in a kingdon trap [J]. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect B, 1991, (B56/B57): 1 185-1 187.
[20] SEKIOKA T, TERASAWA M, AWAYA Y. Ion storage in Kingdon trap [J]. Radiat Eff Defects Solids, 1991, 117:253-259.
[21] KNIGHT K H. Storage of ions from laser-produced plasmas [J]. Appl Phys Lett, 1981, 38(4): 221-223.
[22] MCILRAITH A H. A charged particle oscillator [J]. Nature, 1996, 212(5 069): 1 422-1 424.
[23] BLUEMEL R. Dynamic kingdon trap [J]. Phys Rev A, 1995, 51(1): R30-R33.
[24] MAKAROV A A. Electrostatic axially harmonic orbital trapping: A high-performance technique of mass analysis [J]. Analy Chem, 2000, 72(6): 1 156-1 162.
[25] 李 明, 梁大鹏, 李红梅, 等. 傅立叶变换离子回旋共振质谱的最新进展和展望 [J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2011, 32(8): 1 195-1 120.
LI Ming, LIANG Dapeng, LI Hongmei, et al. New progress and prospect of Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2011, 32(8): 1 195-1 120 (in Chinese).
[26] 李 明, 费 强, 金钦汉, 等. 质谱检测技术及其一些最新进展 [J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2007, 28(8): 1 532-1 536.
LI Ming, FEI Qiang, JIN Qinhan, et al. Detection techniques for mass spectrometry and some new progresses[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2007, 28(8): 1 532-1 536 (in Chinese).
[27] 赛默飞世尔公司. 赛默飞世尔推新一代离子阱轨道阱质谱仪[EB/OL].[2012-03-08]. http://www.thermoscientific.com.
[28] HARDMAN M, MAKAROV A A. Interfacing the orbitrap mass analyzer to an electrospray ion source [J]. Anal Chem, 2003, 75(7): 1 699-1 705.
[29] MAKAROV A, DENISOV E, LANGE O, et al. Dynamic range of mass accuracy in LTQ orbitrap hybrid mass spectrometer [J]. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom, 2006, 17(7): 977-982.
[30] MAKAROV A, DENISOV E, KHOLOMEEV A,et al. Performance evaluation of a hybrid linear ion trap/orbitrap mass spectrometer [J]. Anal Chem, 2006, 78(7): 2 113-2 120.
[31] MOL H G J, ZOMER P, DE KONING M. Qu-alitative aspects and validation of a screening method for pesticides in vegetables and fruits based on liquid chromatography coupled to full scan high resolution (Orbitrap) mass spectrometry [J]. Anal Bioanal Chem, 2012, 403(10): 2 891-2 908.
[32] PADILLA-SANCHEZ J A, PLAZA-BOLANOS P, ROMERO-GONZALEZ R, et al. Innovative determination of polar organophosphonate pesticides based on high-resolution Orbitrap mass spectrometry [J]. J Mass Spectrom, 2012, 47(11): 1 458-1 465.
[33] YANG L, DING J F, MAXWELL P, et al. Determination of arsenobetaine in fish tissue by species specific isotope dilution LC-LTQ-Orbitrap-MS and standard addition LC-ICPMS [J]. Anal Chem, 2011, 83(9): 3 371-3 378.
[34] HE X, KOZAK M, NIMKAR S. Ultra-sensitive measurements of 11-nor-delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol-9-carboxylic acid in oral fluid by microflow liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry using a benchtop quadrupole/orbitrap mass spectrometer [J]. Anal Chem, 2012, 84(18): 7 643-7 647.
[35] THOMAS A, WALPURGIS K, KRUG O, et al.Determination of prohibited, small peptides in urine for sports drug testing by means of nano-liquid chromatography/benchtop quadrupole orbitrap tandem-mass spectrometry [J]. J Chromatogr A, 2012, 1 259: 251-257.
[36] BERUBE M, ESPOURTEILLE F. Analysis of 25-hydroxyvitamin D in serum using automated online sample preparation technique with high resolution benchtop orbitrap mass spectrometer [J]. Clin Biochem, 2012, 45(13/14): 1 101-1 101.
[37] SCHUHMANN K, ALMEIDA R, BAUMERT M,et al. Shotgun lipidomics on a LTQ Orbitrap mass spectrometer by successive switching between acquisition polarity modes [J]. J Mass Spectrom, 2012, 47(1): 96-104.
[38] MUNTEL J, HECKER M, BECHER D. An exclusion list based label-free proteome quantification approach using an LTQ Orbitrap [J]. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom, 2012, 26(6): 701-709.
[39] JANG K S, BAIK J E, KANG S S, et al. Identification of staphylococcal lipoteichoic acid-binding proteins in human serum by high-resolution LTQ-Orbitrap mass spectrometry [J]. Mol Immunol, 2012, 50(3): 177-183.
[40] MARIE A, ALVES S, MARIE B, et al. Analysis of low complex region peptides derived from mollusk shell matrix proteins using CID, high-energy collisional dissociation, and electron transfer dissociation on an LTQ-orbitrap: Implications for peptide to spectrum match [J]. Proteomics, 2012, 12(19/20): 3 069-3 075.
[41] THEBERGE R, INFUSINI G, TONG W W, et al.Top-down analysis of small plasma proteins using an LTQ-Orbitrap. Potential for mass spectrometry-based clinical. assays for transthyretin and hemoglobin [J]. Int J Mass Spectrom, 2011, 300(2/3): 130-142.
[42] WYNNE C, EDWARDS N J, FENSELAU C. Phyloproteomic classification of unsequenced organisms by top-down identification of bacterial proteins using capLC-MS/MS on an Orbitrap [J]. Proteomics, 2010, 10(20): 3 631-3 643.
[43] PAPASOTIRIOU D G, JASKOLLA T W, MA-RKOUTSA S, et al. Peptide mass fingerprinting after less specific In-gel proteolysis using MALDI-LTQ-orbitrap and 4-chloro-alpha-cyanocinnamic acid [J]. J Proteome Res, 2010, 9(5): 2 619-2 629.
[44] MOHR J, SWART R, SAMONIG M, et al.High-efficiency nano- and micro-HPLC-High-resolution Orbitrap-MS platform for top-down proteomics [J]. Proteomics, 2010, 10(20): 3 598-3 609.
[45] ZHANG T, CREEK D J, BARRETT M P, et al.Evaluation of coupling reversed phase, aqueous normal phase, and hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography with orbitrap mass spectrometry for metabolomic studies of human urine [J]. Anal Chem, 2012, 84(4): 1 994-2 001.
[46] WEN B, HUANG J S, MOORE D. Screening and characterization of chemically reactive metabolites using polarity switching of hybrid linear trap quadrupole orbitrap fourier transform mass spectrometry [J]. Drug Metab Rev, 2011, 43: 130-131.
[47] RAO Y L, MCCOOEYE M, WINDUST A, et al.Mapping of selenium metabolic pathway in yeast by liquid chromatography-orbitrap mass spectrometry [J]. Anal Chem, 2010, 82(19): 8 121-8 130.
[48] XU W, ZHANG J, HUANG Z H, et al. Identification of new dianthrone glycosides from Polygonum multiflorum Thunb. using high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with LTQ-Orbitrap mass spectrometry detection: A strategy for the rapid detection of new low abundant metabolites from traditional Chinese medicines [J]. Anal Methods, 2012, 4(6): 1 806-1 812.
[49] ROUX A, XU Y, HEILIER J F, et al. Annotation of the human adult urinary metabolome and metabolite identification using ultra high performance liquid chromatography coupled to a linear quadrupole ion trap-orbitrap mass spectrometer[J]. Anal Chem, 2012, 84(15): 6 429-6 437.
[50] HEREBIAN D, LAMSHOFT M, MAYATEPE-KE, et al. Identification of NTBC metabolites in urine from patients with hereditary tyrosinemia type 1 using two different mass spectrometric platforms: Triple stage quadrupole and LTQ-Orbitrap[J]. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom, 2010, 24(6): 791-800.
[51] 陈焕文, 胡 滨, 张 燮. 复杂样品质谱分析技术的原理与应用 [J]. 分析化学, 2010, 38(8): 1 069-1 088.
CHEN Huanwen, HU Bing, ZHANG Xie. Fundamental principles and practical applications of ambient ionization mass spectrometry for direct analysis of complex samples[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2010, 38(8): 1 069-1 088 (in Chinese).
[52] HU Q Z, TALATY N, COOKS R G, et al. Desorption electrospray ionization using an orbitrap mass spectrometer: Exact mass measurements on drugs and peptides [J]. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom, 2006, 20(22): 3403-340.
[53] MCEWEN C, GUTTERIDGE S. Analysis of the inhibition of the ergosterol pathway in fungi using the atmospheric solids analysis probe (ASAP) method [J]. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom, 2007, 18(7): 1 274-1 278.
[54] ZHANG J I, COSTA A B, COOKS R G, et al. Direct detection of fatty acid ethyl esters using low temperature plasma (LTP) ambient ionization mass spectrometry for rapid bacterial differentiation [J]. Analyst, 2011, 136(15): 3 091-3 097.
[55] EDISON S E, LIN L A, GAMBLE B M, et al. Surface swabbing technique for the rapid screening for pesticides using ambient pressure desorption ionization with high-resolution mass spectrometry [J]. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom, 2011, 25(1): 127-139.
[56] JACKSON A U, TATA A, COOKS R G, et al. Direct analysis of stevia leaves for diterpene glycosides by desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry [J]. Analyst, 2009, 134(5): 867-874.
[57] VACLAVIK L, ZACHARIASOVA M, HRBEK V, et al. Analysis of multiple mycotoxins in cereals under ambient conditions using direct analysis in real time (DART ionization coupled to high resolution mass spectrometry [J]. Talanta, 2010, 82(5): 1 950-1 957.
[58] NA N, ZHANG X R,COOKS R G, et al. Birch reduction of benzene in a low-temperature plasma [J]. Angew Chem Int Edit, 2009, 48(11): 2 017-2 019.
[59] 李 明, 姜 杰, 李红梅, 等. 电喷雾萃取电离技术在蛋白质分析中的应用 [J]. 生物物理与生物化学进展, 2012, 39(2): 194-198.
LI Ming, JIANG Jie, LI Hongmei, et al. The application and perspective of extractive electrospray ionization on the protein analysis[J]. Progress in Biochemistry and Biophysics, 2012, 39(2): 194-198 (in Chinese).
[60] CHEN H W, YANG S P, LI M, et al. Sensitive detection of native proteins using extractive electrospray ionization mass spectrometry[J]. Angew Chem Int Edit, 2010, 49: 3 053-3 056.
ProgressonElectrostaticOrbitrapMassSpectrometer
LI Ming1, MA Jia-chen2, LI Hong-mei1, XIONG Xing-chuang1, JIANG You1,HUANG Ze-jian1, FANG Xiang1
(1.NationalInstituteofMetrology,Beijing100013,China;2.HarbinInstituteofTechnologyatWeihai,Weihai264209,China)
Electrostatic orbitrap is a newly developing mass analyzer in recent years. The information of ions in orbitrap can be obtained based on the different motion frequency of different ions in a specific electrostatic field. Orbitrap mass analyzer has the advantages of high mass resolution and high mass accuracy, therefore it has been widely used in chemistry, biology, medicine, et al. In this paper, the principle of electrostatic orbitrap mass spectrometer was introduced in detail; the applications of orbitrap in the fields of proteomics and metabolomics were briefly discussed; the recent progresses of coupling orbitrap with ambient ionization techniques were reviewed. Coupling orbitrap with ambient ionization techniques such as extractive electrospray ionization (EESI), low temperature probe (LTP) can potentially used for protein analysis, direct identification of product in the chemical synthesis, the study of mechanism of chemical reaction.
orbitrap; mass spectrometry; ambient ionization; proteomics; metabolomics
O 657.63
A
1004-2997(2013)05-0185-08
10.7538/zpxb.2013.34.03.0185
2012-10-08;
2012-12-31
国家自然科学基金(21005024);国家科技支撑计划(2009BAK59B03)项目资助
李 明(1979~),男(汉族),吉林人,博士,从事质谱学研究。E-mail: mingutah@hotmail.com
方 向(1963~),男(汉族),研究员,从事质谱仪器研发工作。E-mail: fangxiang@china.com

