Screening of Substrates of Protein Arginine Methyltransferase 1 in Glioma△
Shan Wang,Xiao-chao Tan,Bin Yang,Bin Yin,and Xiao-zhong Peng*
National Laboratory of Medical Molecular Biology,Institute of Basic Medical Sciences,Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences &Peking Union Medical College,Beijing 100005,China
SINCE the research on post-translational modification has become more and more crucial,the importance of arginine methylation of proteins has been recognized.Arginine methylation is involved in many biochemical and biological processes,such as signal transduction,cell proliferation,transcriptional regulation,and RNA splicing.1,2The protein arginine methyltransferase (PRMT) family is the main group of enzymes to methylate arginine residues.PRMTs catalyze the post-translational transfer of a methyl group from the donor S-adensoyl-L-methioinine to arginine residues.1In the mammalian cells,8 PRMT members have been identified so far to have enzymatic activity among 11 members of PRMT family.PRMT1 is the most important member and could contribute to as much as 85% of all the cellular PRMT activities.3It can catalyze the arginine residues to asymmetric dimethyl arginine (ADMA),which might play a role in many diseases,especially tumorgenesis.4For example,apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1,one of the important regulators in apoptosis signaling pathway,can be methylated by PRMT1 and implicated in the apoptosis of breast tumor.5Estrogen receptor α (ERα) is also one of the substrates of PRMT1.Methylated ERα can interact with Src/FAK and p85,and then activate Akt pathway to promote cell proliferation and inhibit apoptosis.6In all the brain tumors,glioma is the most common and malignant one.7The present study investigated the relationship between PRMT1 and proteins with ADMA in glioma,and screened the proteins binding with PRMT1,so as to lay the foundation for exploring the molecular mechanism of PRMT1 in glioma.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Tissue samples
Two human normal brain tissue samples were provided by Department of Anatomy,Peking Union Medical College.The study protocol was approved by Institutional Ethics Committee.
Glioma cell culture and RNAi transfection
The human glioma cell lines (T98G,U87MG,and A172)were obtained from American Type Culture Collection(ATCC) and all cultured according to the guidelines recommended by ATCC.The StealthTMRNAi Duplexes ofPRMT1were purchased from Invitrogen Life Technologies Inc.(Grand Island,NY,USA).The sequence of PRMT1-RNAi was 5’-GCCUGCAAGUGAAGCGGAAUGACUA-3’.The StealthTMRNAi Negtive Control Duplexes (RNAi-NC,Cat.NO.12935-300) were also synthesized by Invitrogen.Before transfection,glioma cells were seeded in DMEM containing 10% fetal bovine serum without antibiotics overnight.In the next day,according to the manufacturer’s protocol for LipofectaminTM2000-based transfections (Invitrogen),the cells were transfected with RNAi-PRMT1 or RNAi-NC,respectively.The final concentration was 100 nmol/L.
Western blot
Total protein of glioma cells or normal brain tissue samples were extracted with lysis buffer [50 mmol/L Tris-HCl (pH 8.0),1% NP-40,150 mmol/L NaCl,2 μg/mL leupeptin,2 μg/mL pepstain,2 μg/mL aprotinin,and 2 μg/mL PMSF].The protein lysate was separated by 12% or 8% sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDSPAGE) and transferred electrophoretically onto nitrocellulose membrane for 1 or 2 hours.After blocking with 5%skimmed milk for at least 1 hour,the membranes were incubated with specific primary antibodies for PRMT1 (Millipore,Billerica,MA,USA),ASYM24 (specifically to proteins containing ADMA,Millipore),or GAPDH (Abmart,Shanghai,China).Then the membranes were washed with Trisbuffered saline,further incubated with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG antibody or goat anti-mouse IgG antibody (Zhongshan Goldenbridge Biotechnology Co.,Beijing,China) for 1 hour,and visualized by enhanced chemiluminescence.
Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP)
U87MG,a representative glioma cell line,was harvested in ice-cold phosphate-buffered saline and lysed with lysis buffer,the same buffer as used in western blot.After centrifuging at 13 800×gfor 30 minutes,the cleared supernatants were pre-cleaned with protein G agarose(Roche Co.,Mannheim,Germany) for 1 hour at 4°C.The cleared lysates were incubated for 16 hours at 4°C with the antibodies for PRMT1 (Millipore,experimental group) and normal rabbit IgG (Zhongshan Goldenbridge Biotechnology Co.,negative control group).Protein G agarose was then added and incubated for 3 hours at 4°C.After washing with washing buffer [50 mmol/L Tris-HCl (pH 7.5),500 mmol/L NaCl,0.1% Nonidet 40,0.05% SDS]for four times,the Co-IP proteins were denatured and analyzed with SDSPAGE.
Silver-staining
The protein samples from Co-IP were separated using 10%SDS-PAGE,and the gel was then incubated with the stationary liquid (30% alcohol,10% acetic acid) for 20 minutes.After washing with washing buffer for 10 minutes,the gel was further incubated with sensitization buffer (0.05 g Na2S2O3,250 mL H2O) for 30 minutes.It was later incubated with silver staining buffer for 30 minutes and then color reagent (4 g Na2CO3,80 μL formaldehyde,200 mL H2O) for 6 minutes.
Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry(LC-MS/MS)
The stained protein bands after silver staining on the gel were carved,digested,and analyzed by mass spectrometry in the Center of Equipment Testing,Academy of Military Medical Sciences.Sequence analysis was performed with MASCOT (version 2.2,Matrix Sciences,Boston,MA,USA)using the non-redundant protein database from Mascot’s web site (http://www.matrixscience.com/cgi/search-from.pl?FORMVER=2&SEARCH=MIS).Then we utilized 2 methods to screen PRMT1’s binding proteins from the result of MASCOT.One was ions scores,in which a number greater than 38 indicates identity or extensive homology (P<0.05).The other was the same proteins,which existed in IP-PRMT1 group (Co-IP with PRMT1 antibody) and also in IP-IgG control group (Co-IP with rabbit IgG).Judging from the ions scores and eliminating the same proteins,we selected the final candidate proteins.
Bioinformation analysis
We put the sequences of final candidate proteins into MeMo web site,which focuses on predicting the protein methylation including arginine methylation or lysine methylation with an accuracy for prediction of arginine methylation reaching 86.7%.8MeMo’s web site is http://www.bioinfo.tsinghua.edu.cn/~tigerchen/memo.html.
RESULTS
PRMT1 expression and ADMA levels in glioma cells
After performing western blot in two normal brain tissues and three glioma cell lines,PRMT1 was found substantially up-regulated in glioma cells compared with normal brain tissues.Some ADMA levels were also higher in glioma cells,but a few ADMA levels were reduced (Fig.1)
Relationship between PRMT1 and proteins with ADMA
Western blot results showed that after suppression of PRMT1 expression with RNAi-PRMT1 transfection,a lot of ADMA levels were up-regulated to different degrees (Fig.2A),but others were not changed.Furthermore,Co-IP results revealed that there were some proteins binding to PRMT1 and being dimethylated at arginine site (Fig.2B).
Binding proteins of PRMT1 screened by LC-MS/MS
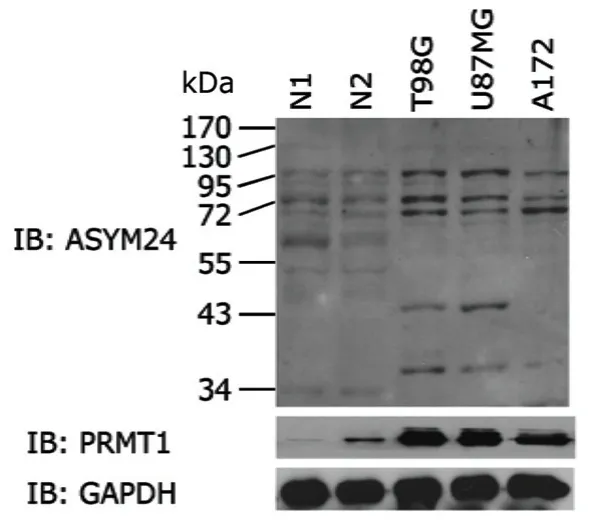
Figure 1.Western blot of PRMT1 expression and asymmetric dimethyl arginine (ADMA) levels (by ASYM24 antibody) in normal brain tissues (N1 and N2) and human glioma cell lines (T98G,U87MG,and A172).

Figure 2.Detection of the relationship between PRMT1 and proteins containing ADMA.
Sliver staining visualized target proteins of PRMT1 (Fig.3A).After analysis of the carved bands by LC-MS/MS and MASCOT database,26 proteins were identified in the experimental group (Table 1).Based on the ions scores and after eliminating the same proteins,6 candidate proteins were selected from the 26 proteins.According to the analysis result of MeMo web site,SEC23-interacting protein(SEC23-IP) might have 1 arginine methylated site,ANKHD1-EIF4EBP3 protein and 1-phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate 5-kinase isoform 2 might have 11 sites each(Table 2).Because the bands of high molecular weight proteins were not clear in Figure 2B,we repeated western blot,changing the concentration of SDS-PAGE to 8% and prolonging the time of transferring to 2 hours.The results demonstrated that there were some high molecular weight proteins (95-170 kD),which could bind to PRMT1 and contained ADMA (Fig.3B).There was indeed a band around 130 kD,at a position similar to the one of carved band 1(Fig.3A).Judging from the results of LC-MS/MS and western blot,SEC23-IP was the most possible candidate protein of PRMT1,because the ions score of SEC23-IP is the highest (about 123) in the database,and the molecular weight of SEC23-IP is 111 kD,which is the closest to the carved band 1 in Figure 3A and the colorated band around 130 kD in Figure 3B.
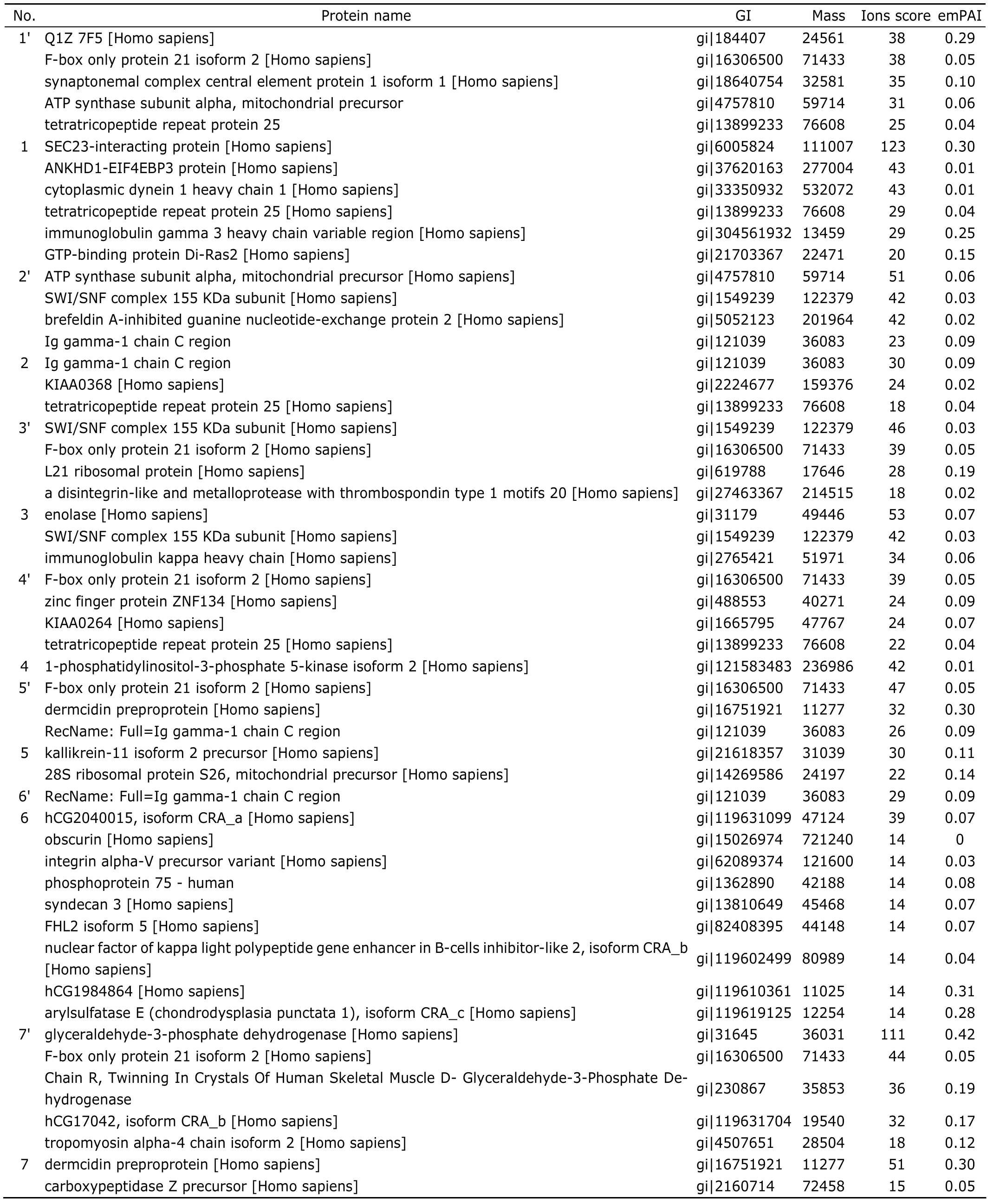
Table 1.The result of LC-MS/MS analysis for candidate proteins
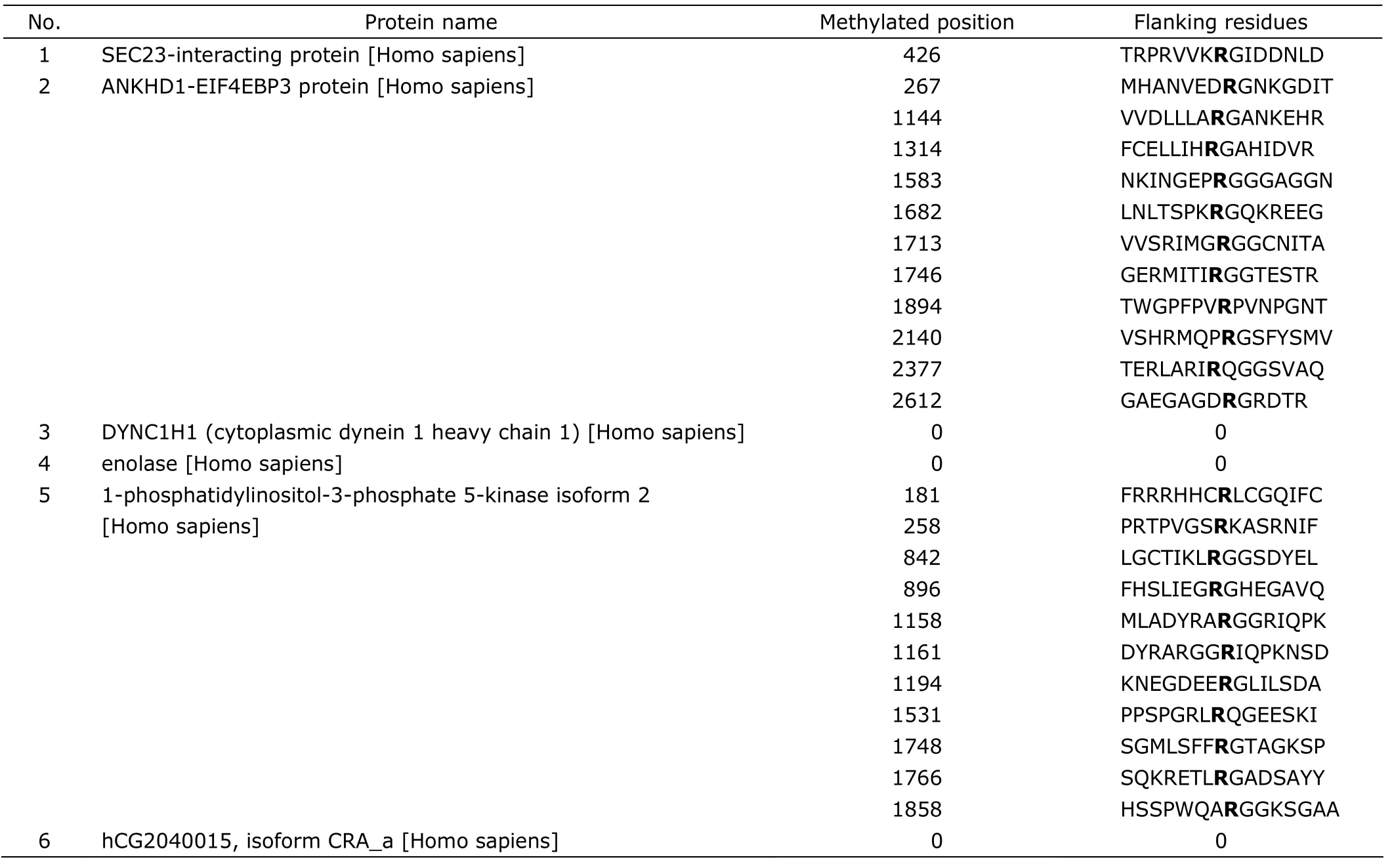
Table 2.The result of MeMo web site analysis for candidate proteins (individual ions score > 38,P<0.05)
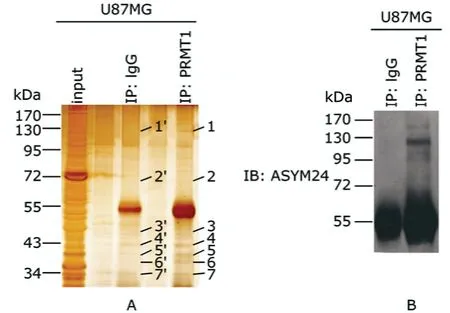
Figure 3.Screening for the putative target proteins of PRMT1.
DISCUSSION
PRMTs play a role in many cellular processes,such as DNA damage,signaling,and epigenetic gene expression,by methylating arginine residues of their substrates.1,2Proteomics analysis revealed more than 200 proteins that underwent arginine methylation.9,10Among the family members of PRMTs,PRMT1 is the most predominant methyltransferase in mammalian cells,and the role of PRMT1 in tumor genesis is gradually attracting attention.11It was reported that PRMT1 might influence the apoptosis of breast cancer cell and the proliferation of osteosarcoma cell,and might be a potential therapeutic target for many kinds of cancers.5,12
In the present study,the expression of PRMT1 and the levels of ADMA were found considerably changed in glioma cells,and the tendency of some ADMA levels was in accord with the expression of PRMT1.Additionally,ADMA levels declined after knock-down of PRMT1.The findings indicated that PRMT1 could regulate the levels of some ADMA in glioma.With Co-IP and LC-MS/MS,we screened 26 proteins that could combine with PRMT1,among which 6 had higher ions scores (>38) and only existed in the PRMT1 experimental group.Bioinformation analysis predicted that SEC23-IP,ANKHD1-EIF4EBP3 protein,and 1-phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate 5-kinase isoform 2 might have methylated aginines.Based on the ions score and molecular weight of candidate proteins,we supposed SEC23-IP was one of the most possible proteins,which could bind to PRMT1 and contain ADMA,in our database.As a member of the phosphatidic acid preferring-phospholipase A1 family,SEC23-IP is located in endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to play a crucial role in ER-Golgi transport.It takes part in the construction of the multimeric coat protein II complex and recognizes ER export signals on cargo proteins for inclusion in vesicles.13The result of the present study indicates that PRMT1 might bind to SEC23-IP and dimethylate its arginine,suggesting that PRMT1 might play roles in ER-Golgi transportviaarginine dimethylation of SEC23-IP.Previous studies reported significantly changed expression of SEC23-IP in some tumors,including gastric cancer and melanoma.14,15Yet few researches have been conducted on SEC23-IP in glioma so far.According to the findings of this research group,the relationship between SEC23-IP and PRMT1 might have an impact on the genesis of glioma.
In conclusion,the tendency of ADMA levels was found in accordance with PRMT1 expression in glioma.Twenty-six candidate proteins binding with PRMT1 were identified by Co-IP and LC-MS/MS,among which 3 (i.e.SEC23-IP,ANKHD1-EIF4EBP3 protein,and 1-phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate 5-kinase isoform 2) had possible methylated aginine sites,as predicted by bioinformation analysis.Further studies on the relationship between PRMT1 and these proteins are needed to contribute to the exploration of the molecular mechanism of post-translational modification in glioma.
1.Wolf SS.The protein arginine methyltransferase family:an update about function,new perspectives and the physiological role in humans.Cell Mol Life Sci 2009;66:2109-21.
2.Bedford MT,Richard S.Arginine methylation an emerging regulator of protein function.Mol Cell 2005;18:263-72.
3.Tang J,Frankel A,Cook RJ,et al.PRMT1 is the predominant type I protein arginine methyltransferase in mammalian cells.J Biol Chem 2000;275:7723-30.
4.Nicholson TB,Chen T,Richard S.The physiological and pathophysiological role of PRMT1-mediated protein arginine methylation.Pharmacol Res 2009;60:466-74.
5.Cho JH,Lee MK,Yoon KW,et al.Arginine methylation-dependent regulation of ASK1 signaling by PRMT1.Cell Death Differ.2011 Nov 18.[cited 2012 Feb 16].Available from:http:// www.nature.com/cdd/journal/vaop/ncurrent/full/cdd2011168a.html
6.Le Romancer M,Treilleux I,Bouchekioua-Bouzaghou K,et al.Methylation,a key step for nongenomic estrogen signaling in breast tumors.Steroids 2010;75:560-4.
7.Furnari FB,Fenton T,Bachoo RM,et al.Malignant astrocytic glioma:genetics,biology,and paths to treatment.Genes Dev 2007,21:2683-710.
8.Chen H,Xue Y,Huang N,et al.MeMo:a web tool for prediction of protein methylation modifications.Nucleic Acids Res 2006;34:W249-53.
9.Boisvert FM.A proteomic analysis of arginine-methylated protein complexes.Mol Cell Proteomics 2003;2:1319-30.
10.Wu CC,MacCoss MJ,Mardones G,et al.Organellar proteomics reveals Golgi arginine dimethylation.Mol Biol Cell 2004;15:2907-19.
11.Pawlak MR,Scherer CA,Chen J,et al.Arginine N-methyltransferase 1 is required for early postimplantation mouse development,but cells deficient in the enzyme are viable.Mol Cell Biol 2000;20:4859-69.
12.Yoshimatsu M,Toyokawa G,Hayami S,et al.Dysregulation of PRMT1 and PRMT6,Type I arginine methyltransferases,is involved in various types of human cancers.Int J Cancer 2011;128:562-73.
13.Fortin S,Le Mercier M,Camby I,et al.Galectin-1 is implicated in the protein kinase C ε/vimentin-controlled trafficking of integrin-β1 in glioblastoma cells.Brain Pathol 2010;20:39-49.
14.Sun XJ,Sun KL,Zheng ZH,et al.Gene expression patterns in gastric cancer.Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi 2006;23:142-6.
15.Rose AE,Poliseno L,Wang J,et al.Integrative genomics identifies molecular alterations that challenge the linear model of melanoma progression.Cancer Res 2011;71:2561-71.
 Chinese Medical Sciences Journal2012年1期
Chinese Medical Sciences Journal2012年1期
- Chinese Medical Sciences Journal的其它文章
- Management of Pregnancy with Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Applicability of Community Periodontal Index Teeth and Random Half-mouth Examination to Gingival Bleeding Assessment in Untreated Adult Population in Beijing
- Personalized Management of Anastomotic Leak after Surgery for Esophageal Carcinoma
- Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography of Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada Disease:Novel Findings and New Insights into the Pathogenesis
- Radiofrequency Ablation of Hepatic Paragonimiasis:a Case Report
- Electrocorticography with Direct Cortical Stimulation for a Left Temporal Glioma with Intractable Epilepsy
