(2,4-二甲氧基苯基)烯丙基丙二酸二乙酯异构体的GC/MS研究
王 敏,彭 奇
(中国科学院福建物质结构研究所,福建 福州 350002)
(2,4-二甲氧基苯基)烯丙基丙二酸二乙酯异构体的GC/MS研究
王 敏,彭 奇
(中国科学院福建物质结构研究所,福建 福州 350002)
为了研究钯催化的2,4-二甲氧基苯甲酸与烯丙基丙二酸二乙酯的脱羧Heck反应的产物结构,建立了(2,4-二甲氧基苯基)烯丙基丙二酸二乙酯同分异构体的分离与鉴定的气相色谱-离子阱质谱方法。首先通过脱羧Heck反应制得(2,4-二甲氧基苯基)烯丙基丙二酸二乙酯异构体混合物,然后利用GC/MS联用技术对混合物进行分析,得到各组分的EI和CI全扫描模式质谱信息。通过对照各组分的分子离子峰确定互为异构体的组分,再对异构体组分采用MS/MS模式获取各自的裂解碎片。通过分析异构体的不同的裂解碎片,讨论质谱裂解方式,从而确定异构体的结构。该方法省时、经济、高效,可为此类化合物的分析与鉴别提供参考。
气相色谱-质谱法;异构体的识别;Heck反应;丙二酸二乙酯;芳基烯烃
Heck反应是一类重要的卤代芳烃烯基化形成新的C—C键的合成反应,在过去的40多年中已经逐渐发展成为一种应用广泛的有机合成方法,在医药、天然产物、农药以及新型高分子材料的制备方面有着重要的应用价值[1-10]。Heck反应通常是卤代芳烃与含有α-吸电子基团的烯烃在钯催化下反应生成芳代烯烃。该反应生成主产物的同时,还常伴随着重排副反应,导致生成的产物为结构性质十分相近的异构体混合物,分离识别十分困难[11-12]。随着现代化仪器设备的快速发展,色质联用、质谱串联、核磁共振等技术的发展使得这类异构体的分离和识别变得相对容易[13-19]。
钯催化2,4-二甲氧基苯甲酸与烯丙基丙二酸二乙酯的脱羧Heck反应是制备芳代烯烃的新方法[20],但该反应生成的芳代烯烃同样存在多个同分异构体。这些同分异构体结构性质十分相近,分离提纯困难,结构难以确认。本研究采用气相色谱-离子阱质谱法研究该反应产物(2,4-二甲氧基苯基)烯丙基丙二酸二乙酯同分异构体的结构。
1 试验部分
1.1 主要仪器与试剂
CP3800-Saturn4000气相色谱-质谱联用仪:美国Varian公司产品,配有液体化学源(CI,色谱级甲醇为化学电离反应试剂)。
三氟醋酸钯、苯醌、1-金刚烷羧酸、2,4-二甲氧基苯甲酸、烯丙基丙二酸二乙酯:美国Sigma公司产品;乙酸乙酯:色谱纯,纯度99.9%,德国默克公司产品;N,N-二甲基甲酰胺、二甲基亚砜、二氧六环:分析纯,上海国药公司产品,重新蒸馏。
1.2 样品合成
在DMF、DMSO和二氧六环的混合溶液中,加入2,4-二甲氧基苯甲酸(0.25mmol,45.5 mg)、烯丙基丙二酸二乙酯(0.5mmol,100.1 mg)、三氟醋酸钯(0.025mmol,8.3mg)、1-金刚烷 羧 酸 (1mmol,180.3mg)、苯 醌 (0.3 mmol,32.5mg),120℃条件下反应1h[4]。反应液冷却后倒入水中,乙酸乙酯萃取,饱和食盐水洗涤,无水硫酸钠干燥后浓缩得到粗产物,再通过柱层析提纯(柱层析硅胶300~400目),用V(乙酸乙酯)∶V(正己烷)=1∶10的混合溶液洗脱,得到(2,4-二甲氧基苯基)烯丙基丙二酸二乙酯,产率为72%(异构体混合物),反应式示于图1。
1.3 实验方法
取1mg异构体混合物用乙酸乙酯定容于25mL容量瓶中,充分摇匀后进行分析。
通过多次优化程序升温条件,使各组分能达到较好分离,最终确定最佳的分离条件。
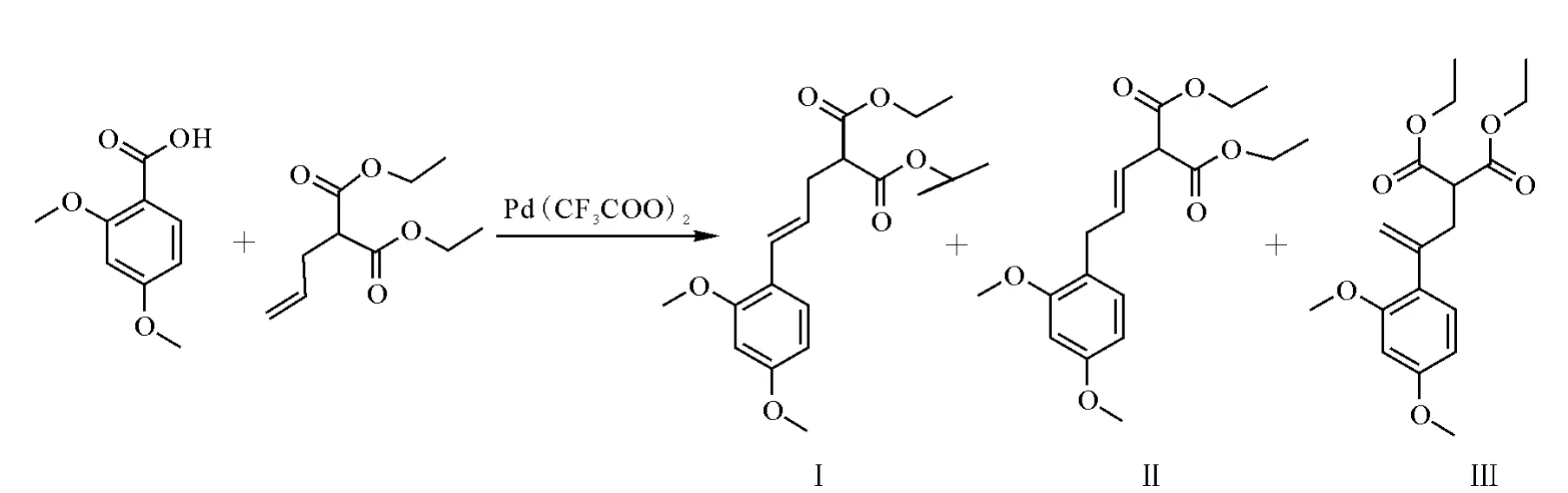
图1 (2,4-二甲氧基苯基)烯丙基丙二酸二乙酯的合成机理Fig.1 The synthesis mechanism of diethyl(3-(2,4-dimethoxyphenyl)allyl)malonate isomers
1.4 实验条件
1.4.1 色谱条件 色谱柱:VF-5ms石英毛细柱(30m×0.25mm×0.25μm);进样口温度:280℃;载气:He,纯度 99.999%,流速1.0 mL/min;程序升温:柱温100℃,保持1min,以20℃/min升至230℃,然后以2℃/min升至250 ℃,保持10min;进样量:1.0μL;分流比:30∶1。
1.4.2 质谱条件 电子轰击(EI)离子源;电子能量:70eV;离子阱温度:220℃;传输线温度:280℃;电子倍增器电压:1 300V;化学电离(PCI)源;电子能量:12eV;质量扫描范围:m/z 50~500。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 实验结果
在优化的分析条件下检测待测混合物,发现只有两种组分A和B,并且互为异构体,其总离子流图示于图2。分别对其做EI-MS、CI-MS扫描,获取各自的裂解碎片峰。为了进一步确定两种物质的结构,分别对化合物A和B做EI-MS/MS、CI-MS/MS扫描,结果分别示于图3~8。化合物A、B的质谱图中的主要碎片及其丰度列于表1。
2.2 结构讨论
据钯催化的碳氢活化偶联反应机理推测,2,4-二甲氧基苯甲酸与烯丙基丙二酸二乙酯的脱羧Heck反应产物可能为3种结构Ⅰ、П、Ш(示于图1)。结构I最为稳定,裂解方式比较简单,丢失丙二酸二乙酯得到的正离子碎片(m/z 177),由于2,4-二甲氧基苯乙烯的共轭作用十分稳定,因此给出的该碎片离子信号一定很强,这与化合物B的质谱图相吻合(示于图4,图6)。结构II中的双键由于丙二酸二乙酯的强烈吸电效应而容易断裂,应该会出现m/z 164和m/z 172两个碎片峰,化合物A与B质谱图中都没有这两个碎片峰,从而可以排除结构П的可能。结构Ш如果裂解丢失丙二酸二乙酯给出的正离子与苯环同位于双键的同侧并处于苯环的β位,结构不够稳定,信号应该比较弱,化合物A正是这样,m/z 177的碎片峰只能在CI源下才能找到,丰度只有15%,而丢失乙醇、一氧化碳、乙氧基而得到的碎片189成为结构十分稳定的1,3-丁二烯的共轭体系,因而离子信号最强(示于图3,图5)。CI源下MS/MS数据可以进一步证明上面的推测,化合物A丢失一分子水出现m/z 319,丢失一分子乙醇,一分子乙氧基成为m/z 245的碎片峰,m/z 245的碎片存在多共轭体系,结构比较稳定,丰度最大(示于图7);化合物B依然是m/z177的碎片峰最为稳定,丰度最大(示于图8)。
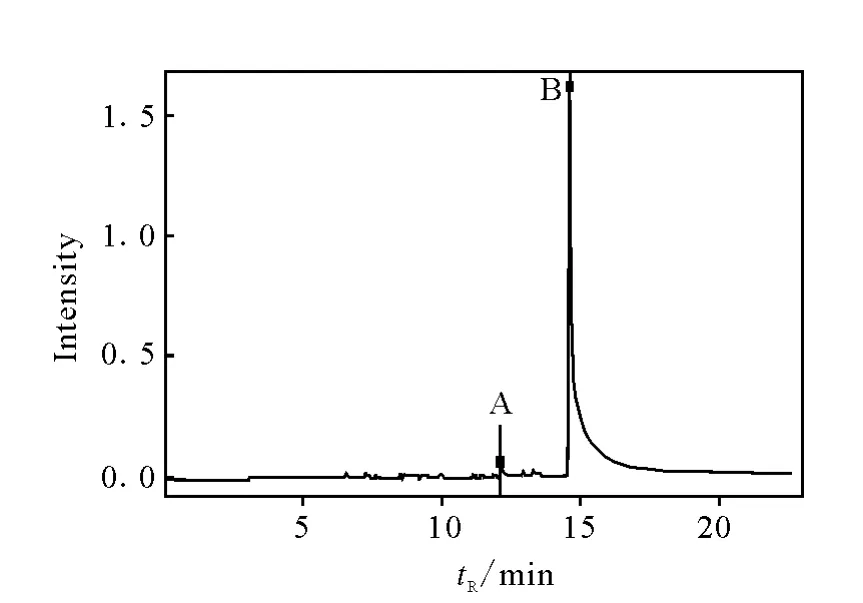
图2 异构体混合物的总离子流图Fig.2 TIC chromatograms of isomers

图3 化合物A的EI-MS质谱图Fig.3 EI-MS spectra of A

图4 化合物B的EI-MS质谱图Fig.4 EI-MS spectra of B

图5 化合物A的CI-MS质谱图Fig.5 CI-MS spectra of A

图6 化合物B的CI-MS质谱图Fig.6 CI-MS spectra of B

图7 化合物A的CI-MS/MS质谱图Fig.7 CI-MS/MS spectra of A

图8 化合物B的CI-MS/MS质谱图Fig.8 CI-MS/MS spectra of B
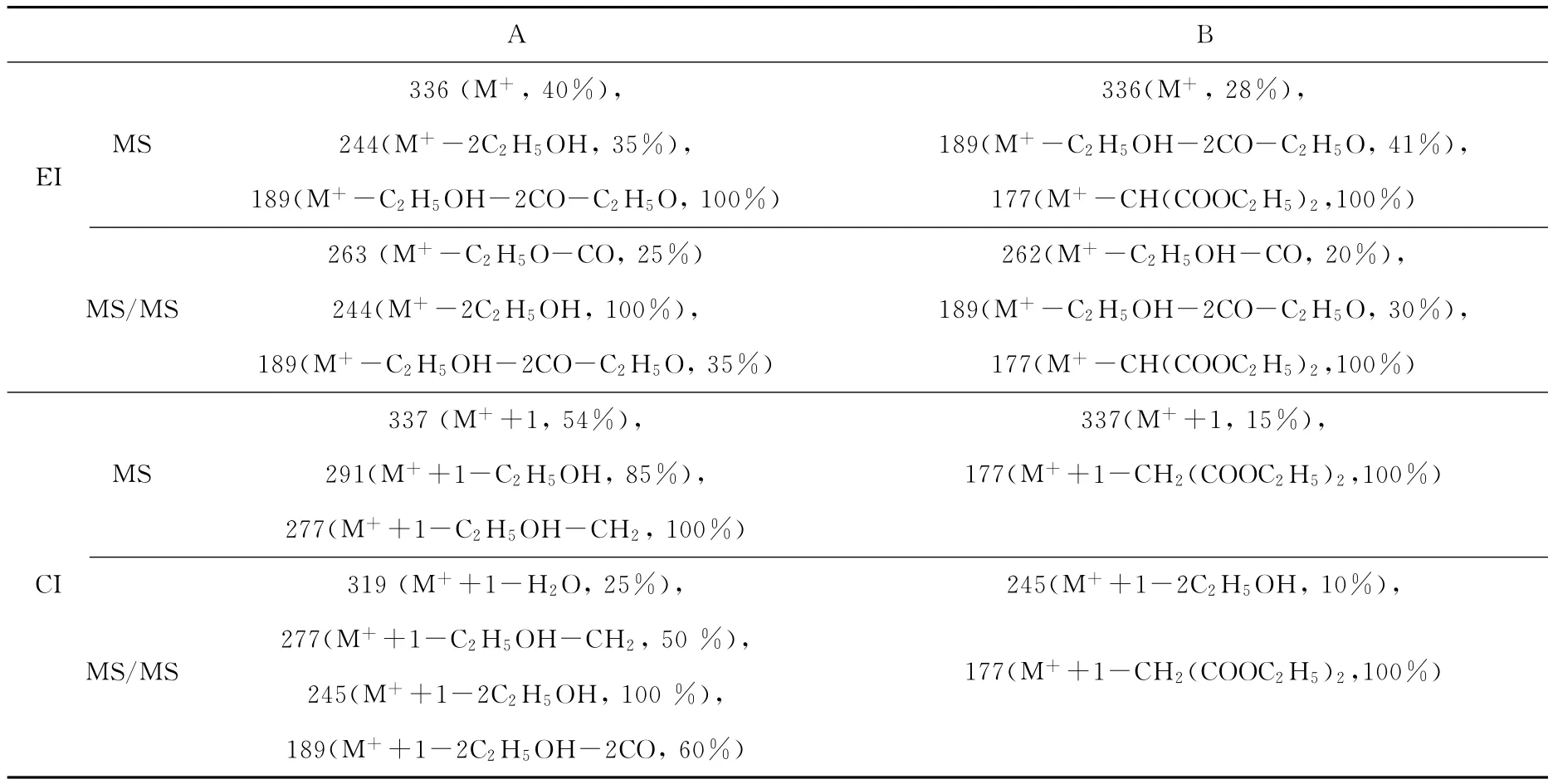
表1 化合物A和B的质谱图中的主要碎片及其丰度Table 1 Main fragments and their abundance of A and B
2.3 裂解机理分析
化合物A和B的EI-MS表明,发生裂解的方式根据偶联基团连接到烯烃双键不同的位置存在着较大差别。对于化合物A,2,4-二甲氧基苯基偶联到丙二酸二乙酯的β位,失去多个离子得到的碎片峰m/z 189成为结构十分稳定的1,3-丁二烯的共轭体系,丰度最大,裂解过程示于图9;对于化合物B,2,4-二甲氧基苯基偶联到丙二酸二乙酯的γ位,裂解方式比较简单,丢失丙二酸二乙酯得到的正离子碎片m/z 177,由于2,4-二甲氧基苯乙烯的共轭作用十分稳定,主要采用该种裂解方式,裂解过程示于图10。
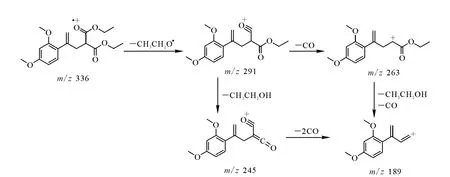
图9 化合物A的电子轰击质谱裂解机理Fig.9 EI-MS fragmentation mechanism of A

图10 化合物B的电子轰击质谱裂解机理Fig.10 EI-MS fragmentation mechanism of B
3 结 论
本研究通过气相色谱-质谱法分析了2,4-二甲氧基苯甲酸与烯丙基丙二酸二乙酯的脱羧Heck反应产物。该产物中含有两种组分且互为异构体,通过讨论这两种异构体的质谱裂解方式,确定了它们各自的结构。该方法具有快速简便,检测效率高,准确可靠等优点,适用于芳基烯烃同分异构体的检测,同时也为其它复杂样品中该类同分异构体的测定提供了可以借鉴的方法。
[1] OVERMAN L E.Application of intramolecular Heck reactions for forming congested quaternary carbon centers in complex molecule total synthesis[J].Pure Appl Chem,1994,66(7):1 423-1 430.
[2] CABRI W,CANDINAI I.Recent developments and new perspectives in the Heck reaction[J].Accounts of Chemical Research,1995,28(1):2-7.
[3] CRISP G T.Variations on a theme:recent developments on the mechanism of the Heck reaction and their implications for synthesis[J].Chem Soc Rev,1998,27(6):427-436.
[4] BELETSKAYA I P,CHEPRAKOV A V.The Heck reaction as a sharpening stone of palladium catalysis[J].Chem Rev,2000,100(8):3 009-3 066.
[5] DOUNAY A B,OVERMAN L E.The asymmetric intramolecular Heck reaction in natural product total synthesis[J].Chem Rev,2003,103(8):2 945-2 963.
[6] HONG B C,NIMJE R Y.Catalytic C-C bond formation in natural products synthesis.Highlights from the years 2000-2005[J].Curr Org Chem,2006,10(17):2 191-2 225.
[7] TIETZE L F,KINZEL T.Synthesis of natural products and analogs using multiple Pd-catalyzed transformations[J].Pure Appl Chem,2007,79(4):629-650.
[8] BENNASAR M L,ZULAICA E,SOLE D,et al.Total synthesis of the bridged indole alkaloid apparicine[J].J Org Chem,2009,74(21):8 359-8 368.
[9] MCCARTNEY D,GUIRY P J.The asymmetric Heck and related reactions[J].Chem Soc Rev,2011,40(10):5 122-5 150.
[10] WU X F,NEUMANN H,BELLER M.Palladium-catalyzed carbonylative coupling reactions between Ar-X and carbon nucleophiles[J].Chem Soc Rev,2011,40(10):4 986-5 009.
[11] KUHNERT N,LE-GRESLEY A.Synthesis and capsule formation of upper rim substituted tetraacrylamido calix[4]arenes[J].Org Biomol Chem,2005,3(11):2 175-2 182.
[12] SHEN Y M,DU Y J,ZENG M F,et al.Heck reaction catalyzed by a recyclable palladium supported on shell powder[J].Appl Organomet Chem,2010,24(9):631-635.
[13] SCHMIT-QUILES F,NICOLE D,LAUER J C.Characterization of hydrogenated derivatives of methyl-and dimethyldicyclopentadiene isomers by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and carbon-13nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy[J].Analyst,1994,119(8):1 731-1 740.
[14] ROACH J A G,MOSSOBA M M,YURAWECZ M P,et al.Chromatographic separation and identification of conjugated linoleic acid isomers[J]. Anal Chim Acta,2002,465 (1/2):207-226.
[15] KAWAI Y,MIYOSHI M,MOON J-H,et al.Detection of cholesteryl ester hydroperoxide isomers using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry combined with thin-layer chromatography blotting[J].Analytical Biochemistry,2007,360(1):130-137.
[16] WU L M,HERNANDEZ-SOTO H,LIU D,et al.Tandem mass spectrometry and hydrogen/deuterium exchange studies of protonated species of 1,1'-bis(diphenylphosphino)-ferrocene oxidative impurity generated during a Heck reaction[J].Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom,2008,22(3):314-320.
[17] DESTAILLATS F,CRUZ-HERNANDEZ C,NAGY K,et al.Identification of monoacylglycerol regio-isomers by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J].Journal of Chromatography A,2010,1217(9):1 543-1 548.
[18] WU Z Y,ZENG Z D,MARRIOTT P J.Comparative qualitative analysis of nonylphenol isomers by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry combined with chemometric resolution[J].Journal of Chromatography A,2010,1217(49):7 759-7 766.
[19] DAI Y,FENG X J,LIU H S,et al.Synthesis of 2-naphthols via carbonylative Stille coupling reaction of 2-bromobenzyl bromides with tributylallylstannane followed by the Heck reaction[J].J Org Chem,2011,76(24):10 068-10 077.
[20] HU P,KAN J,SU W P,et al.Pd(O2CCF3)2/Benzoquinone:a versatile catalyst system for the decarboxylative olefination of arene carboxylic acids[J].Organic Letters,2009,11(11):2 341-2 344.
Study on Diethyl[3-(2,4-Dimethoxyphenyl)Allyl]Malonate Isomers by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry
WANG Min,PENG Qi
(Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Fuzhou350002,China)
A method applying gas chromatography-ion trap mass spectrometry(GC/MS)for the simultaneous analysis of diethyl[3-(2,4-dimethoxyphenyl)allyl]malonate isomers is described.The diethyl[3-(2,4-dimethoxyph-enyl)allyl]malonate mixture of isomers was prepared by the decarboxylative Heck reaction of 2,4-dimethoxybenzoic acid with diethyl 2-allylmalonate firstly,and then was analyzed by GC/MS in Electron ionization(EI)and Chemical ionization(CI)full-scan mode.Two components were isolated by gas chromatography,and identified as isomers from the determination of the molecular ions.Next,the isomers were analyzed by tandem mass spectrometry(MS/MS)mode.Through the analysis of different cleavage fragments of the isomers in MS/MS mode,mass spectrometric fragmentation pathways of the isomers were discussed.The structures of two isomers were determined on the base of different mass characteristic fragmentation pathways.This new meth-od of identifying isomers is a time-saving,economical and effective method,which could provide reference for analysis and identification of this kind of compounds.
gas chromatography-mass spectrometry(GC/MS);identification of isomers;Heck reaction;diethyl malonate;aryl olefin
O 657.63
A
1004-2997(2012)04-0219-06
2012-03-15;
2012-06-01
王 敏(1980~),女,山东济宁人,助理研究员,从事分析化学研究工作。E-mail:wangmin04@fjirsm.ac.cn
彭 奇(1962~),女,福建古田人,高级实验师,从事分析化学研究工作。E-mail:wpqjj@tom.com

