啤酒花的抑菌作用及其应用拓展
高智明
(新疆三宝乐农业科技开发有限公司,新疆乌鲁木齐830002)
啤酒花,学名Humulus lupulus L.,别名蛇麻草、陀得花(《本草纲目》上的名称)、唐草花(日本)、忽布(英文名称Hop的音译)等,是荨麻目大麻科葎草属多年生须根缠绕草本植物[1-2],生长区域集中在南北纬度 35~55°之间的地区[3-4],主要产地分布在德国、美国、英国、新西兰、捷克斯洛伐克、澳大利亚和中国等地。在植物学的分类上,大麻科是从桑科中分支出来的,因此,也有文献将其记载为桑科。尽管中文有葎草属和蛇麻属不同的名称记载,但其学名均为Humulus,因此并无歧义。啤酒花自从十二世纪在啤酒酿造中开始添加使用以来,至今它最主要的用途仍然是用于啤酒的酿造。由于啤酒花能够赋予啤酒特殊的苦味和独特的风味,并具有一定的防腐性能,因而被誉为“啤酒的灵魂”[5]。由于啤酒花有非常好的抑菌功能,最初将其添加到啤酒酿造中主要是为了延长啤酒的存放期。此外,除啤酒酿造之外,啤酒花还有很多其他方面的应用。本文就啤酒花的抑菌功能及其应用拓展做一概述。
1 啤酒花的抑菌作用
啤酒花所含的蛇麻酮、葎草酮、黄腐酚及其它黄酮类化学成分,对结核杆菌、金黄色葡萄球菌、枯草杆菌等有抑制作用,且由于蛇麻酮的脂溶性强,分布系数大,容易进入结核杆菌的蜡膜而起到特殊的亲和作用,产生抑制结核杆菌的功能,作用要强于葎草酮[6-8],已制成酒花素片、酒花素乳剂、啤酒花浸膏片等使用。表1为啤酒花中的主要抑菌成分及其作用。
大量研究表明,啤酒花成分对绝大多数革兰氏阳性菌具有很好的抑制作用,但对革兰氏阴性菌和酵母菌几乎没有活性,且对酵母菌还有一定的增殖作用。
2 啤酒花的拓展应用
2.1 啤酒花的药用
啤酒花和迷迭香、西洋薯草等一样,早在13世纪就有作为草药使用的记载。《本草纲目》所引的宋代《开宝本草》中的一种中药“陀得花”指的就是啤酒花[19],认为啤酒花性苦、微凉、有健胃、安神、化痰止咳、抗结核菌等功能。《食物中药与便方》中也记载[20]啤酒花对多种细菌有抑制作用,并有镇静及雌激素样作用。在民间,啤酒花多用于泡茶,有健胃、明目、解渴、降压、止咳、利尿、镇静等作用,药用部分为绿色的果穗。现代药理学对啤酒花的抗炎、抗肿瘤作用、抗氧化、抗病毒、降血糖、促进消化、雌性激素作用和镇静安神促进睡眠等功能的研究更为深入。啤酒花的药用作用见表2。
2.2 啤酒花在食品加工中的应用
啤酒花在面包工业中用以保存酵母和制造面包的添加剂,使面包具有防腐、持久保存和促进发酵的作用[51]。董海洲等采用经反复筛选的产香酵母等多种酵母搭配,并添加酒曲酵母、啤酒花发酵醪和乳酸球菌以及适当的化学膨松剂,对馒头的风味改善进行了系统研究,通过自然发酵,生产出具有香甜风味的馒头,显著改善了馒头的口感,这对推动我国馒头工业化生产的发展有一定的指导意义[52]。另外,啤酒花β-酸用于浓缩橙汁的贮存也非常有效果[53]。以3mg/kg的量添加啤酒花β-酸到60%DS的浓缩果汁中,与空白比较,可以抑制果汁中微生物的活性,相当长地延长转化糖和酸的形成时间。
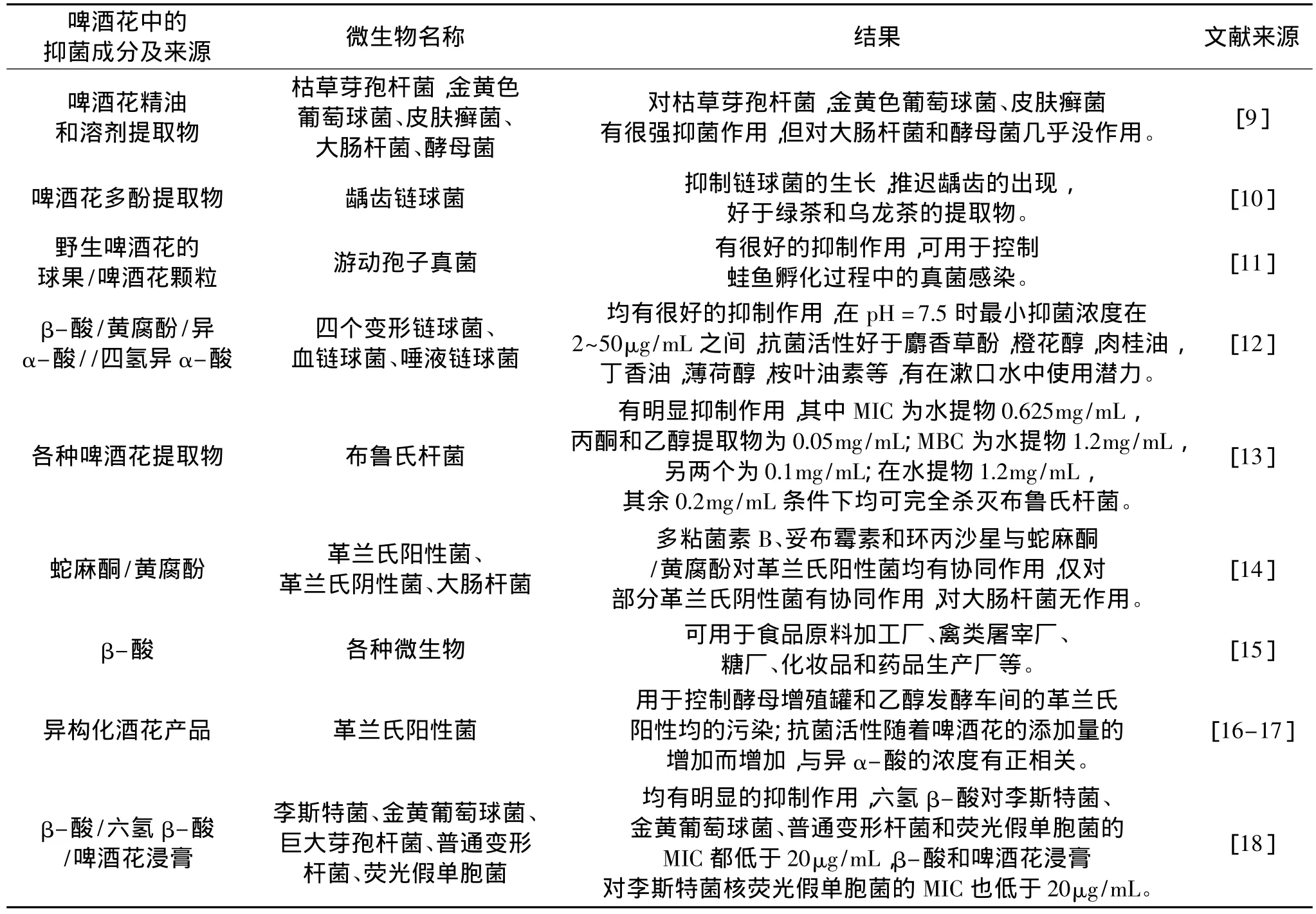
表1 啤酒花的主要抑菌成分及其作用Table 1 Main antibacterial ingredients derived from hops and their effect
2.3 啤酒花在制糖工业中的应用
啤酒花中的β-酸应用于制糖工业中可以明显地提高糖的产量[54-56]。1994年,啤酒花的产品首次被成功地应用到甜菜萃取的过程中,通过其抗菌作用可以控制微生物生长所造成的糖的损失和右旋糖苷的产生。这与啤酒花在传统的酿造工业中使用相比是一个崭新的应用领域。此后的十几年来啤酒花中的β-酸作为一种天然的抑菌助剂,为了控制嗜热菌或其它的革兰氏阳性微生物的生长,已经被使用于制糖工业中。因为在甜菜加工的过程中,萃取塔中通常会发酵产生乳酸,啤酒花中的β-酸在抑制NO2的形成和萃取塔中厌氧菌的感染方面表现出了非常好的效果,该化合物具有非常有效的抗菌作用,在较低浓度时有更高的活性,特别是对梭菌属的细菌有更强的作用(最小抑菌浓度为1μg/mL)。这些天然产品是对人体无害的,同时还可以在外界环境中被生物降解,商标品牌为“BetaStab”的啤酒花β-酸的碱性溶液已被用于制糖工业[57]。
2.4 啤酒花在酒精工业中的应用
酒精生产中,运用啤酒花所具有的明显的抑菌活性,可以抑制在生产过程中由于杂菌滋生而导致的产量降低的不利因素。抗生素通常在酒精工业中用于控制细菌的生长,但不利的是,它们通常也会影响酵母菌的活性和性能。啤酒花中的成分能够增强酵母的活性,并具有使其缓慢絮凝的作用,这样产生的结果更有利于酵母菌的生长并使发酵过程更快。在酵母菌的洗涤过程中,啤酒花的成分在低pH时将会产生一种协同的抗菌效果,在美国的乙醇生产厂和蒸馏酒厂使用后证明效果明显[58]。
3 展望
随着对啤酒花的深入研究和对天然来源的植物抗菌剂及植物活性成分研究的关注,基于其特殊的抑菌功能,目前在很多国家和地区,已将啤酒花开发成各种用途的洗发剂、染发剂或作为生发剂配方中的一个主要组成。此外,还有不少地区已将啤酒花及其提取物列入食品补充剂的行列,也有将其开发为具有治疗失眠作用的保健枕等。尽管目前啤酒花在我国目前还基本停留在啤酒酿造行业的使用中,相信在不久的将来,随着人们的关注,对啤酒花的开发利用一定会充满勃勃生机。

表2 啤酒花的药用Table 2 Pharmacological effects of hops
[1]谢宗万.全国中草药汇编(上册)[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,1996:770-771.
[2]卜慕华.我国栽培作物来源探讨[J].中国农业科学,1981(4):86-89.
[3]Verzele M,Keukeleire D D.Chemistry and analysis of hop and beer bitters[M].Elsevier Science Publishers BV,1991:1-3.
[4]路德维希·纳尔蔡斯.啤酒厂麦汁制备工艺技术[M].孙明波译.北京:中国轻工出版社,1991:85-90.
[5]Benitez J L,Forster A,Keukeleire D.Hops and hop products,manual of good practice[M].EBC and Verlag Hans Carl,1997,Chapter5:98-107.
[6]Mizobuchi S,Sato Y.A new flavanone with antifungal antifungal activity isolated from hops[J].Agriculture Biology Chemistry,1984,48(11):2771-2775.
[7]Suzuki K,Ljima K,Yamashita H.Isolation of a hop-sensitive variant of Lactobacillus lindneri and identification of genetic markers for beer spoilage ability of lactic acid bacteria[J].Appliedand EnvironmentalMicrobiology,2005,71(9):5089-5097.
[8]Sakamoto K,Konings W N.Beer spoilage bacteria and hop resistance[J].International Journal of Food Microbiology,2003,89(2/3):105-124.
[9]Langezaal C R,Chandra A,Scheffer J J.Antimicrobial screening of essential oils and extracts of some Humulus lupulus L.cultivars[J].Pharm Weekbl Sci,1992,14(6):353-356.
[10]Tagashira M,Uchiyama K,Yoshimura T,et al.Inhibition by hop bract polyphenols of cellular adherence and water-insoluble glucan synthesisofmutans Streptococci[J].Bioscience,Biotechnology and Biochemistry,1997,61(2):332-335.
[11]Barnes J M,Dupont T R,Barnes M E,et al.Initial investigations of hops as a salmonid egg fungicide[J].North American Journal of Aquaculture,2012,14(3):310-313.
[12]Bhattacharya S,Virani S,Zavro M,et al.Inhibition of streptococcus mutans and other oral streptococci by hop(Humulus lupulus L.)constituents[J].Economic Botany,2003,57(1):118-125.
[13]Shapouri R,Rahnema M.Evaluation of antimicrobial effect of hops extracts on in abortus and B.melitensis[J].Jundishapur Journal of Microbiol,2011,4(2):51-58.
[14]Natarajana P,Kattab S,Andreic I,et al.Positive antibacterial coaction between hop(Humulus lupulus)constituents and selected antibiotics[J].Phytomedicine,2008,15(3):194-201.
[15]Wilson R J H,Smith R J,Haas G.Application for hop acids as anti-microbial agents[P].US7910140B2,2011.
[16]Maye J P.Method for inhibiting bacteria growth during ethanol fermentation[P].US13/046362,2011.
[17]Mudura E,Rotar A,Paucean A,et al.Antimicrobial effect of hop dosage in beer[J].Bulletin of University of Agricultural Sciences and Veterinary Medicine Cluj-Napoca.Agriculture,2011,68(2):543.
[18]刘玉梅.啤酒花的分析评价及六氢蛇麻酮类的合成与应用[D].无锡:江南大学,2007:80-82.
[19]李时珍.本草纲目[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,1972.
[20]叶桔泉.食物中药与便方[M].江苏:江苏科学出版社,1971.
[21]Kuhrts E.New COX-2 inhibitory composition comprising extract of hops containing an α-acid-useful for reducing inflammation and minimizing gastric erosion[P].WO2004062611-A2,2004-07-29.
[22]Yasukawa K,Takeuchi M,Takido M.Humulone,a bitter in the hop,inhibits tumor promotion by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate in two-stage carcinogenesis in mouse skin[J].Oncology,1995,52(2):156-158.
[23]Buckwold V E,Wilson R J,Nalca A,et al.Antiviral activity of hop constituents against a series of DNA and RNA viruses[J].Antiviral Res,2004,61(1):57-62.
[24]Shimura M,Hasumi A,Minato T.Isohumulones modulate blood lipid status through the activation of PPAR-alpha[J].Biochimica et Biophysica Acta,2005,1736(1):51-60.
[25]Chen W J,Lin J K.Mechanisms of cancer chemoprevention by hop bitter acids(beer aroma)through induction of apoptosis mediated by fas and caspase cascades[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2004,52(1):55-64.
[26]Bravo L,Cabo J,Fraile A,et al.Pharmacodynamic Study of the Lupulus’(Humulus lupulus L.)Tranquilizing Action[J].Boll Chim Farm,1974,13(5):310-315.
[27]Anto R J,Sukumaran K,Kuttan G,et al.Anticancer and antioxidant activity of synthetic chalcones and related compounds[J].Cancer Letters,1995,97(1):33-37.
[28]Pharmar V S,Bracke M E,Philippe J,et al.Anti-invasive activity of alkaloids and polyphenolic in vitro[J].Bioorganic Medicine and Chemistry,1997,5(8):1609-1619.
[29]Henderson M C,Miranda C L,Stevens J F,et al.In vitro inhibition of human P450 enzymes by prenylated flavonoids from hops,Humulus lupulus[J].Xenobiotica,2000,30(3):235-251.
[30]Miranda C L,Aponso L,Stevens J F,et al.Prenylated chalcones and flavanones as inducers of quinone reductase in mouse hepatoma(Hepa lclc7)cells[J].Cancer Letters,2000,149(1/2):21-39.
[31]Lust S,Vanhoecke B,Janssens A,et al.Xanthohumol kills B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells by an apoptotic mechanism[J].Molecular Nutrition & Food Research,2005,49(9):844-850.
[32]Honma Y,Tobe H,Makishima M,et al.Induction of differentiation of myelogenous leukemia cells by humulone,a bitter in the hop[J].Leukemia Res,1998,22(7):605-610.
[33]Saugspier M,Dorn C,Thasler W E,et al.Hop bitter acids exhibit anti-fibrogenic effects on hepatic stellate cells in vitro[J],Experimental and Molecular Pathology,2012,92(2):222-228.
[34]刘莎,刘玉梅.啤酒花多酚提取物的抗氧化活性研究[J].酿酒科技,2010(10):19-22.
[35]刘莎,姜春耕,刘玉梅.啤酒花多酚超声提取工艺及清除的活性研究[J].中国酿造,2010(11):59-62.
[36]赵素华,司琴图亚.黑加仑、榅桲、无花果、桑椹和啤酒花苦味酸及制品抗氧化作用研究[J].食品科学,2002,23(2):35-37.
[37]Gerhauser C.Broad spectrum antiinfective potential of xanthohumol from hop(Humulus lupulus L.)in comparison with activities of other hop constituents and xanthohumol metabolites[J].Molecular Nutrition & Food Research,2005,49(9):827-831.
[38]Stevens J F,Ivancic M,Hsu V L,et al.Prenylflavonoids from humulus lupulus[J].Phytochemistry,1997,44(8):1575-1585.
[39]Miranda C L,Stevens J F,Helmrich A,et al.Antiproliferative and cytotoxic effects of prenylated flavonoids from hops(Humulus lupulus)in human cancer cell lines[J].Food and Chemical Toxicology,1999,37(4):271-285.
[40]汪江碧,罗蓉,田雪松,等.啤酒花对去卵巢肥胖大鼠的影晌[J].中药材,2004,27(2):1105-107.
[41]Miligan S R,Kalita J C,Pocock V,et al.The endocrine actitives of 8-prenyl naringenin andrelated hopnavonoids[J].Journal of Clin Endocrinol Metab,2000,85(12):4912.
[42]应雀森,潘勤,张娟.啤酒花的化学成分、药理作用与临床应用[J].国外医药:植物药分册,2008,23(4):139-142.
[43]Bourges S.Hop extracts and their use in preparation of a medicament having oestrogenic properties,patent:FR 2 823 672 A1.
[44]Kondo K.Beer and health:Preventive effects of beer components on lifestyle-related diseases[J].BioFactors,2004,22:303-310.
[45]Yajima H,Ikeshima E,Shiraki M,et al.Bitter acids derived from hops,activate both peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α and γ and reduce insulin resistance[J].Journal of Biological Chemistry,2004,279(32):33456-33462.
[46]Shindo S,Tomatsu M,Nakda T,et al.Inhibition of aldose reductase activity by extracts from hops[J].Journal of the Institute of Brewing,2002,108(3):344-347.
[47]张肇富 .啤酒花具有药用价值[J].酿酒科技,2000(1):94.
[48]宋振玉.中草药现代研究[M].北京:北京医科大学出版社,1997.
[49]Anton P.The physiological effects of hops[J].Hopfenrund Schau International,2001/2002:1-2.
[50]苏德利.啤酒花在兽医临床上的应用[J].吉林畜牧兽医,1994,16(6):31-32.
[51]Green M R,Richards M,Tasker M C.Use of hop components in foods[P].WO 03/090555 A1.
[52]董海州,许志祥,刘传富.改善馒头风味品质的最佳生产工艺[J].食品与发酵工业,2003,29(4):95-98.
[53]Hein W,Pollach G,Roesner G.Studies of microbiological activities during thick juice storage[J].Zuckerindustrie,2002,127(4):243-257.
[54]Hein W,Pollach G.New findings with the use of hop products in the sugar industry[J].Zuckerindustrie,1997,122(12):940-949.
[55]Pollach G,Hein W,Leitner A,et al.Detection and control of strictly anaerobic,spore-forming bacteria in sugarbeet tower extractors[J].Zuckerindustrie,2002,127(7):530-537.
[56]Pollach G,Hein W,Beddie D.Application of hop beta-acids and rosin acids in the sugar industry[J].Zuckerindustrie,2002,127(12):921-930.
[57]Beddie D,Isles N,Wirth T,et al.Successful application points to control bacterial infections throughout sugar factories using beta acids/betaStab®10A[C].Poster-Presentation on the Occasion of the SPRI Conference in Atlanta Georgia USA,2004:4-7.
[58]Rückle L,Senn T.Hop acids can efficiently replace antibiotics in ethanol production[J].International Sugar Journal,2006,108(1287):139-147.

