吡咯烷类二肽基肽酶-Ⅳ抑制剂的最新研究进展
付文卓 吴英婷 张进禄
(首都医科大学医学实验与测试中心,北京100069)
胰高血糖素样肽1(glucagon like peptide,GLP-1)是一种肠促胰岛素,可以促进胰岛素分泌、调节血糖、保护胰岛β细胞,刺激其分化。但是活化的GLP-1在体内会迅速被二肽基肽酶降解而失去活性。吡咯烷类二肽基肽酶(dipeptidyl peptidase-Ⅳ,DPP-4)抑制剂是一种细胞表面的丝氨酸蛋白酶,主要作用是分解体内的蛋白质,能够特异地裂解GLP-1的N端末端第2位的脯氨酸或丙氨基残基[1-2]。
因此DPP-4抑制剂,可以通过抑制DPP-4活性,避免GLP-1快速失活,维持体内GLP-1浓度,进而促进2型糖尿病患者新的β细胞的生成,促进胰岛素分泌,达到降血糖的效果,阻止疾病恶化,是近年来治疗2型糖尿病的新方向[3]。
许多DPP-4抑制剂已经上市或者进入临床试验阶段,而且都显示了很好的治疗效果。大量DPP-4抑制剂的构效关系已经被报道[4],根据已知DPP-4抑制剂的结构特点和作用机制分为底物类似的DPP-4抑制剂和非底物类似的DPP-4抑制剂,通过结合方式可分为非共价键DPP-4抑制剂和共价键DPP-4抑制剂。对于目前已经报道的DPP-4抑制剂,均为杂环小分子化合物,本文就含有吡咯环烷结构的二肽基肽酶-Ⅳ抑制剂的作用机制和结构特点进行综述。
1 吡咯烷衍生物DPP-4抑制剂的作用机制
人类DPP-4是766个氨基酸跨膜糖蛋白,包括:胞质尾区(1~6位残基),跨膜区域(7~28位残基)和胞外区域(29~766位残基)[5]。几个重要的作用位点有S1口袋(由Tyr 631,Val 656,Trp 659,Tyr662,Tyr 666和Val711的侧链组成,疏水性较高,可以高特异性识别脯氨酸或其衍生物),N端识别区(谷氨酸残基Glu205/ Glu206和Tyr662的表面负电荷区域能与伯胺或仲胺配体形成氢键作用)。以脯氨酸为基本结构进行修饰,即含有吡咯环烷类DPP-4抑制剂,具有与DPP-4天然底物相似的结构,可以竞争性结合DPP-4活性部位。DPP-4的催化部位包括酶的S1口袋、N端识别区S2口袋和丝氨酸残基的共价作用[6]。所以吡咯环烷类DPP-4抑制剂的基本结构特点含有脯氨酸或类似结构,含有碱性的伯胺或仲胺。根据结合的方式,吡咯环烷类DPP-4抑制剂可分为共价和非共价2类。
2 共价键结合吡咯环烷类DPP-4抑制剂
这是研究最为广泛,最为深入的一类DPP-4抑制剂,基本结构包括:氰基吡咯环和含仲胺取代基[7]。诺华公司研发的1(NVP DPP-728)(IC50=22 nmol/ L),如图1,是第1个含有氰基吡咯环结构的DPP-4抑制剂,能够占据S1口袋,氰基能与受体产生共价作用。但是氰基容易与碱性氨基发生分子内环合,失去活性。所以对其进行结构修饰,降低分子内环合,大大提高了血浆半衰期[8]。
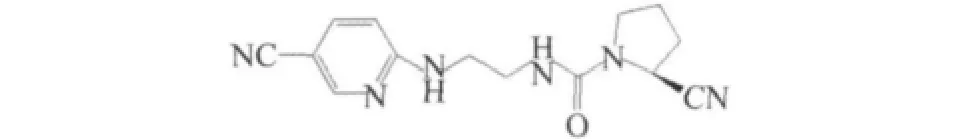
图1 NVP-DPP-728结构式Fig.1 NVP-DPP-728
1)N端修饰:诺华公司以NVP DPP-728为先导化合物,在氨基引入了大体积取代基,如金刚烷胺,得到维格他汀(vildagliptin)2(IC50=35 nmol/L),见图2,血浆半衰期明显延长为3 h,提高了口服生物药物的利用度(85%)[9]。
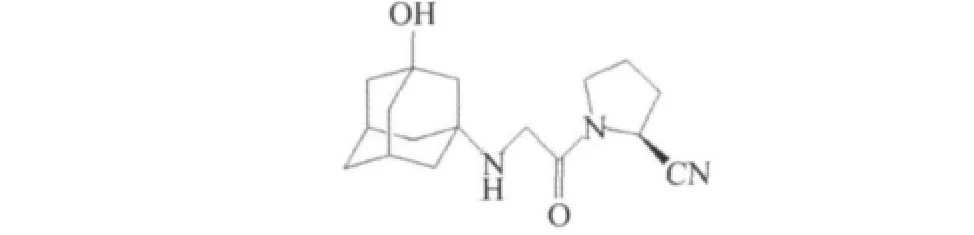
图2 维格列汀Fig.2 Vildagliptin
K-579(IC50=5 nmol/L),在氨基附近引入2个杂环结构,延长了作用时间,t1/2=0.144 h,可作为长效DPP-4抑制剂[10],见图3。类似机制的DPP-4抑制剂ASP4000(IC50=2.25 nmol/L),目前已进入临床前研究阶段[11],见图4。
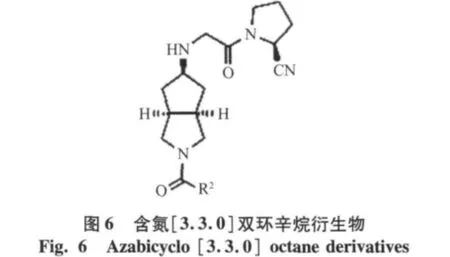
Cho T P等[13]在氨基端引入[3.3.0]双环辛烷,合成了一系列含有双环辛烷的衍生物,其中化合物(R1=OMe,R2=H)(IC50=0.008 μmol/L)并体现了对DPP-4较好的选择性[12],见图5。Cho T P等[13]以[3.3.0]双环辛烷衍生物为基础,继续合成了一系列[3.3.0]双环辛烷衍生物DPP-4抑制剂(IC50=0.009 μmol/L),见图6。其中取代基为N(CH3)2时,并体现了更好的DPP-4的选择性。目前已经进入到一期临床研究阶段。


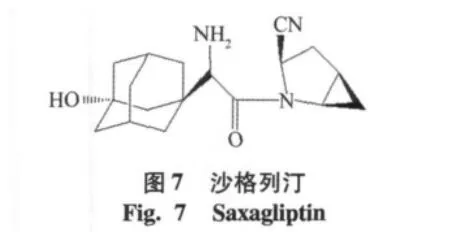
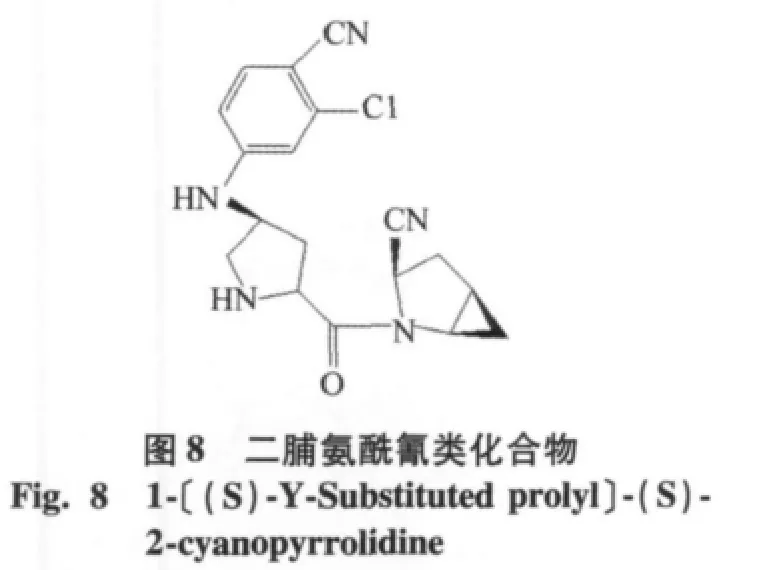
2)C端修饰:在氰基附近引入大体积基团也可以提高氰基吡咯烷类化合物的稳定性,如bristol-myers squibb公司在维格他汀结构的基础上,在氰基吡咯环上引入环丙基,沙格列汀(saxagliptin,IC50=3.37 nmol/l),增加了稳定性,2009年7月被美国FDA批准上市,生物口服利用度为75%,t1/2=2.1 h[14],见图7。另一个化合物二脯氨酰氰类化合物(IC50= 0.25 nmol/L),C端引入环丙烷基础上,在P2上以4位取代的脯氨酸基团取代,见图8。通过构效分析,引入5环的氨基酸可以提高氰基吡咯烷类DPP-4抑制剂的活性,要优于4环或者6环取代化合物。L-环氨基酸可以立体异构性地与酶的S2口袋结合[15]。
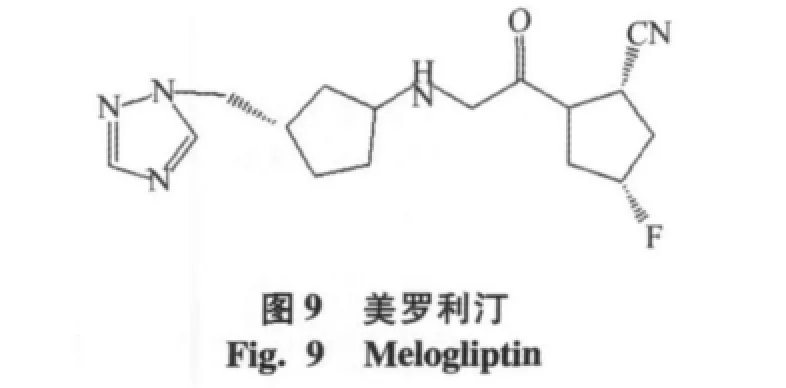
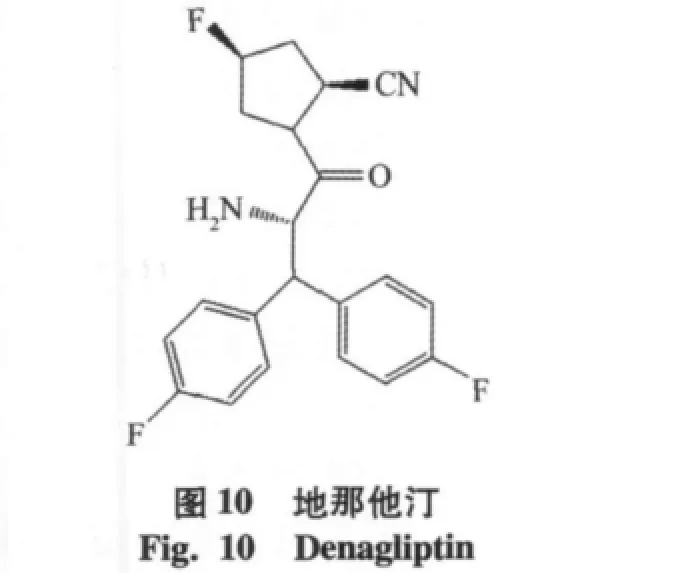
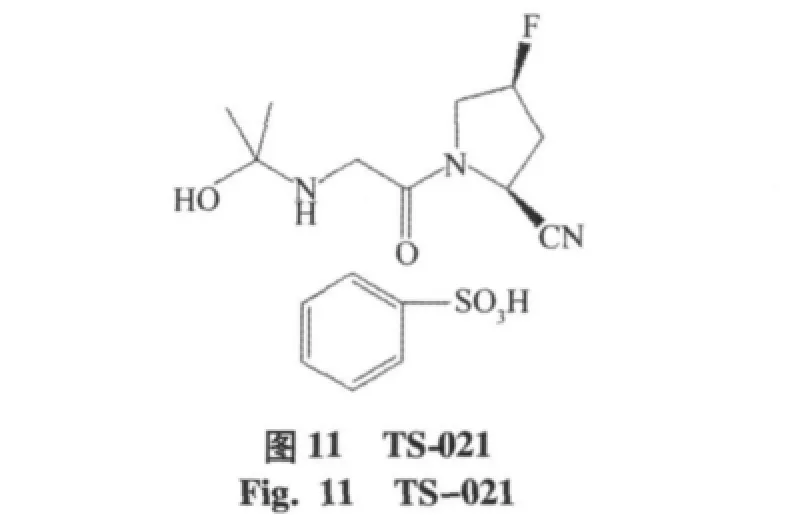
通过实验[22]表明在吡咯烷环C-4位单氟取代,可以提高稳定性,如Glenmark pharmaceuticals Ltd公司的化合物美罗利汀(melogliptin,IC50=1.61 nmol/ L),目前已经进入到临床Ⅱ期实验阶段[16]。Glaxosmithkline公司研发的地那列汀(denagliptin,IC50=22 nmol/ L),见图10,其中结构特征为氟取代吡咯烷环,在N端引入(S)-2-氨基-3,3-二-(4-氟苯基)丙酸,双氟苯取代基团可以与Phe357和Tyr547残基的芳环相互作用,已经进入到临床Ⅲ期实验阶段[17]。另外由Taisho公司研发的TS-021(IC50=5.0 nmol/L),目前处于临床Ⅰ期的实验阶段[18],见图11。
雅培公司研发的ABT-279引入乙炔基,见图12,表现了很好的活性和选择性〔Ki=1.0 nmol/L(DPP-4),>30 mol/L(DPP-8),>30 mol/L(DPP-9),>30 mol/L(DPP-7)〕,同时也具有很好的临床前药理安全性[CYP3A4,CYP2D6,CYP2C9(IC50>30 mol/L)]和毒理研究,给予鼠和狗4周每天大于1 000 mg/kg,均不见其产生明显的不良反应[19]。

3 非共价键结合吡咯环烷类DPP-4抑制剂
在上述氰基吡咯烷类化合物去掉亲电子基团氰基,可以直接减少环化的概率,提高稳定性。所以合理设计合成一系列无氰基的吡咯环类DPP-4抑制剂。由于缺少和丝氨酸的共价作用,所以活性中等。如苯基丙氨酸衍生物结构式(IC50=110 nmol/L),见图13[20]。
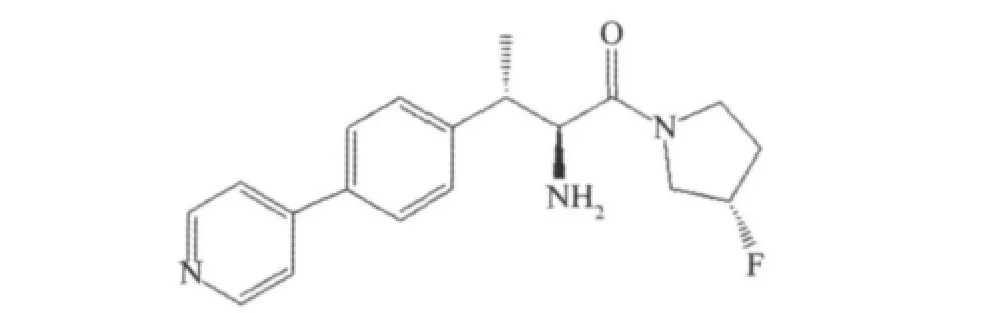
图13 苯基丙氨酸衍生物Fig.13 Phenylalanine based derivative
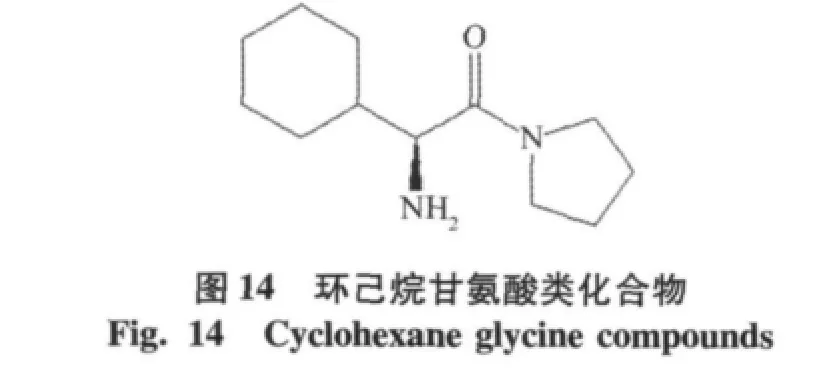
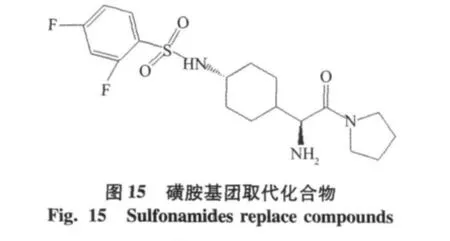
(s)-环己烷甘氨酸类化合物(IC50=320 nmol/ L)[21],不含氰基的吡咯环类抑制剂,后来多以环己烷甘氨酸类化合物为先导化合物,进行结构修饰,获得更优秀的DPP-4抑制剂。以磺胺基团修饰后磺胺基团取代化合物(IC50=88 nmol/L),活性和选择性都提高了[22],见图14。
Tsai T Y等[23]合成了一系列2-(吡咯烷-1-羰基)取代的酰胺类化合物,其中活性最好的是2-(吡咯烷-1-羰基)取代的酰胺类化合物(IC50=0.050 μmol/ L),通过 LC-MS该化合物在水中表现了很好的稳定性。

以氟取代的吡咯环替代环己烷甘氨酸类化合物的吡咯环,设计并合成了一系列衍生物,具有同等或者更好的母体化合物。苯基丙氨酸类衍生物二甲氨基取代苯基丙氨酸衍生物具有DPP-4抑制活性和选择性,见图17[24],由于该类化合物的亲脂性基团(联芳基团),其与hERG离子通道结合特性,所以在血浆中IC50值要增加到10倍以上。
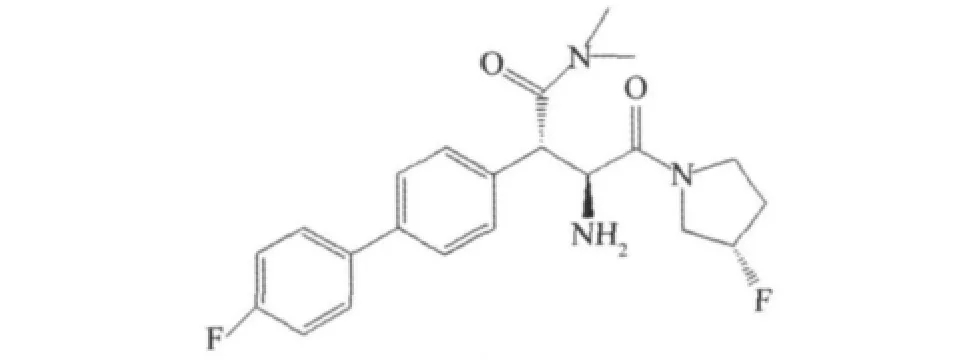
图17 二甲氨基取代苯基丙氨酸衍生物Fig.17 Dimethylamide substituted phenylalanine derivative
用其他杂环替代二甲氨基取代苯基丙氨酸衍生物中4位氟苯基,得到化合物二甲氨基取代苯基丙氨酸衍生物(IC50=4.3 nmol/L),与hERG的结合能力得到了提高(IC50=86 mol/L),但是因为可能存在经鼠和人的代谢后活化,所以并没有继续深入研究[25]。

图18 二甲氨基取代苯基丙氨酸衍生物Fig.18 Dimethylamide substituted phenylalanine derivative
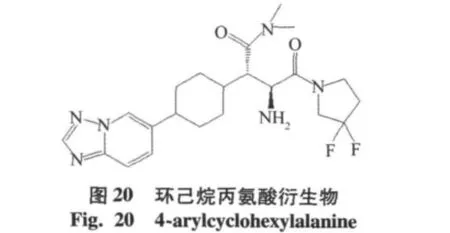
用环己基代替二甲氨基取代苯基丙氨酸衍生物中的苯基,得到的化合物4位氨苯基丙氨酸衍生物(IC50=0.016 μmol/L),具有很好的抑制活性,相对于DPP-8,DPP-9具有高度的选择性,和离子通道hERG结合性低(IC50>90 μmol/L),但是在啮齿类动物中的活性没有达到预期结果[26]。结合化合物二甲氨基取代苯基丙氨酸衍生物和4位氨苯基丙氨酸衍生物得到新的一系列4-芳环己基丙氨酸DPP-4抑制剂,如环己烷丙氨酸衍生物(IC50=0.0048 μmol/L),X-射线晶体,环己烷丙氨酸衍生物的杂环部分与DPP-4的Arg358活性部位以氢键结合[27]。
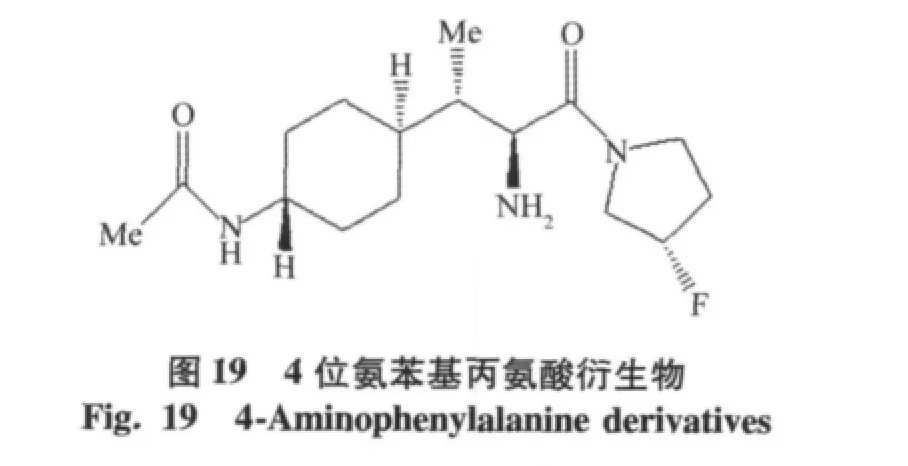
4-氨基环己烷氨基乙酸衍生的 DPP-4抑制剂(IC50=48 nmol/L),没有亲电子基团[28],活性得到显著提高,但是同时氟代吡咯氨基化合物对DPP-8,DPP-9也有很大的抑制作用DPP-8(IC50=993 nmol/ L),DPP-9(IC50=2 720 nmol/L),所以停止了进一步的研究,见图21。
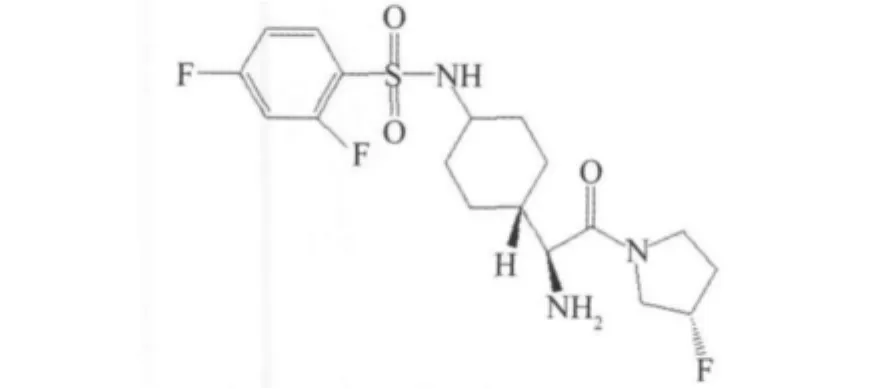
图21 氟代吡咯氨基化合物Fig.21 Fluoropyrrolidine amides
将图17中的苯基替代为其他杂环,通过构效关系研究合成了一系列新的恶唑环类DPP-4抑制剂,最优化的是〔IC50=0.019μmol/L(DPP-4),>100μmol/ L(DPP-8),>100 μmol/L(DPP-9)〕,并且体现了很好的选择性[29],见图22。通过X射线晶体衍射,二唑基衍生物的伯胺和β-甲基之间有同步性。图22中的结合方式不同于苯基丙氨酸类衍生物二甲氨基取代苯基丙氨酸衍生物,二甲氨基取代苯基丙氨酸衍生物,环已烷丙氨酸衍生物。恶唑环进入到另一个DPP-4键合口袋。但是二唑基衍生物口服半衰期很短,其中鼠的半衰期为 (t1/2=1.3 h),狗的半衰期为(t1/2=1.75 h),所以阻碍了进一步研究。

图22 二唑基衍生物Fig.22 Oxadiazole-based derivatives
多氟化的吡咯烷类衍生物已成为新的一类DPP-4抑制剂[30],代表性的化合物是四氟取代吡咯烷(Ki=81 nmol/L),表现了较强DPP-4抑制剂活性,见图23。
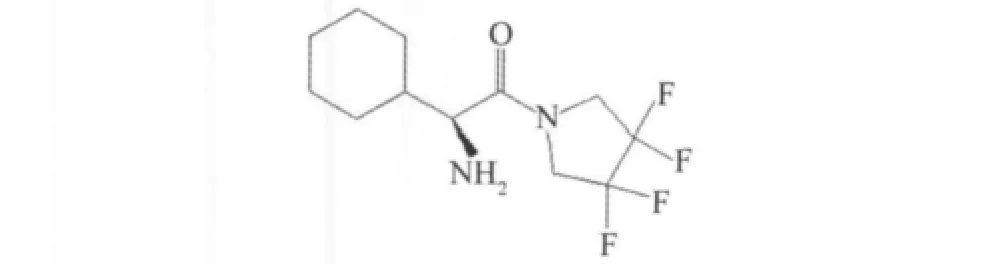
图23 氟代吡咯氮环丁烷Fig.23 Fluorinated pyrrolidine and azetidine amides
4 结语
2006年首个DPP-4抑制剂成功应用于临床后,DPP-4抑制剂就备受关注,目前已经有很多DPP-4抑制剂进入了临床实验阶段。其中吡咯烷类DPP-4抑制剂研究的最为广泛。通过晶体结构分析,研究了吡咯烷类DPP-4抑制剂的作用机制,通过构效关系研究,对吡咯烷类DPP-4抑制剂进行结构修饰,增加其稳定性的同时提高了DPP-4的抑制活性与选择性。期望在上述基础上,进一步研究,可以寻找到更高效,更安全的DPP-4抑制剂。
[1] Pratley R E,Salsali A.Inhibition of DPP-4:a new therapeutic approach for the treatment of type 2用diabetes[J].Curr Med Res Opin,2007,23(4):919-931.
[2] 倪卫惠.2型糖尿病的药物治疗进展[J].药物生物技术,2010,17(2):185-189.
[3] 李祎亮,王菊仙,吴春玫,等.二肽基肽酶Ⅳ抑制剂的研究进展[J].中国新药杂志,2008,17(20):1739-1745.
[4] Thornberry N A,Gallwitz B,.Mechanism of action of inhibitors of dipeptidyl peptidase-4(DPP-4)[J].Best Prac Res Clin Endocrinol Metabol,2009,23(4):479-486.
[5] Rasmussen H B,Branner S,Wiberg F C,et al.Crystal structure of human dipeptidyl peptidaseⅣ/CD26 in comp lex with a substrate analog[J].Nat Struct Biol,2003,10 (1):19-25.
[6] Wiedeman P E.DPPIV inhibition:promising therapy for the treatment of type 2 diabetes[J].Prog Med Chem,2007,45:63-109.
[7] Pan Y X,Ren A J,Zheng J,et al.Delayed cytoprotection induced by hypoxic preconditioning in cultured neonatal rat cardio-myocytes:role of GRP78[J].Life Sci,2007,81 (13):1042-1049.
[8] Hughes T E,Mone M D,Russell M E,et al.NVPDPP728(1-〔〔〔2-〔(5-cyanopyridine-2-yl)amino〕ethyl〕amino〕acetyl〕-2-cyano-(S)-pyrrolidine),a slow-binding inhibitor of dipeptidyl peptidaseⅣ[J].Biochemistry,1999,38(36):11597-11603.
[9] Ahrén B,Landin-Olsson M,Jansson P A,et al.Inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 reduces glycemia,sustains insulin levels,and reduces glucagon levels in type 2 diabetes[J].J Clin Endocrinol Metab,2004,89(5):2078-2084.
[10]Takasaki K,Iwase M,Nakajima T,et al.K579,a slow binding inhibitor of dipeptidyl peptidaseⅣ,is a long-acting hypoglycemic agent[J].Eur J Pharm Acol,2004,486(3):335-342.
[11]Tanaka Amino K,Matsumoto K,Hatakeyama Y,et al.ASP4000,a novel,selective,dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor with antihyperglycemic activity[J].Eur J Pharm Acol,2008,590(1-3):444-449.
[12]Cho T P,Gang L Z,Long Y F,et al.Synthesis and biological evaluation of bicyclo[3.3.0]octane derivatives as dipeptidyl peptidase4 inhibitors for the treatment of type 2 diabetes[J].Bioorg Med Chem Lett,2010,20(12):3521-3525.
[13]ChoT P,Long Y F,Gang L Z,et al.Synthesis and biological evaluation of azabicyclo[3.3.0]octane derivatives as dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors for the treatment of type 2 diabetes[J].Bioorg Med Chem Lett,2010,20(12):3565-3568.
[14]Fura A,Khanna A,Vyas V,et al.Pharmacokinetics of the dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor saxagliptin in rats,dogs,and monkeys and clinical projections[J].Drug Metab Dispos,2009,37(6):1164-1171.
[15]Zhao G,Taunk P C,Magnin D R,et al.Diprolyl nitriles as potent dipeptidyl peptidaseⅣinhibitors[J].Bioorg Med Chem Lett,2005,15(18):3992-3995.
[16]Gupta R,Walunj S S,Tokala R K,et al.Emerging drug candidates of dipeptidyl peptidaseⅣ(DPPⅣ)inhibitor class for the treatment of type 2 diabetes[J].Curr Drug Targets,2009,10(1):71-87.
[17]Kuhn B,Hennig M,Mattei P.Molecular recognition of ligands in dipeptidyl peptidaseⅣ[J].Curr Top Med Chem,2007,7(6):609-619.
[18]Fukushima H,Hiratate A,Takahashi M,et.al.Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of potent 4-fluoro-2-cyanopyrrolidine dipeptidyl peptidaseⅣ inhibitors[J].Bioorg Med Chem,2008,16(7):4093-4106.
[19]Pei Z H,Li X F,Longenecker K,et a l.Discovery,structure-activity relationship,and pharmacological evaluation of (5-substituted-pyrrolidinyl-2-carbonyl)-2-cyanopyrrolidines as potent dipeptidyl peptidaseⅣ inhibitors[J].J Med Chem,2006,49(12):3520-3535.
[20]Jinyou X,Lan W,Robert M,et al.Discovery of potent and selective phenylalanine based dipeptidyl peptidaseⅣinhibitors[J].Bioorg Med Chem Lett,2005,15:2533-2536.
[21]Pei Z,Li X,Longenecker K,et al.Discovery,structureactivity relationship,and pharmacological evaluation of(5-substituted-pyrrolidinyl-2-carbonyl)-2-cyanopyrrolidines as potent dipeptidyl peptidaseⅣinhibitors[J].J Med Chem,2006,49(12):3 520-3535.
[22]Parmee E R,He J,Mastracchio A,et al.4-Amino cyclohexylglycine analogues as potent dipeptidyl peptidaseⅣinhibitors[J].Bioorg Med Chem Lett,2004,14(1):43-46.
[23]Tsai T Y,Coumar M S,Hsu T,et al.Substituted pyrrolidine-2,4-dicarboxylic acid amides as potentdipeptidyl peptidaseⅣ inhibitors[J].Bioorg Med Chem Lett,2006,16 (12):3268-3272.
[24]Edmondson S D,Mastracchio A,Duffy J L,et.al.Discovery of potent and selective orally bioavailable b-substituted phenylalanine derived dipeptidyl peptidaseⅣ inhibitors[J].Bioorg Med Chem Lett,2005,15(12):3048-3052.
[25]Edmondson S D,Mastracchio A,Cox J M,et al.Aminopiperidine-fused imidazoles as dipeptidyl peptidase-Ⅳinhibitors[J].Bioorg Med Chem Lett,2009,19(15):4097-4101.
[26]Joseph D L,Kirk B A,Wang L,et al.4-Aminophenylalanine and 4-aminocyclohexylalanine derivatives as potent,selective,and orally bioavailable inhibitors of dipeptidyl peptidaseⅣ[J].Bioorg Med Chem Lett,2007,17(10):2879-2885.
[27]Kaelin D E,Smenton A L,Eiermann G J,et al.4-Arylcyclohexylalanine analogs as potent,selective,and orally active inhibitors of dipeptidyl peptidaseⅣ[J].Bioorg Med Chem Lett,2007,17(21):5806-5811.
[28]Caldwell C G,Chen P,He J,et al.Fluoropyrrolidine amides as dipeptidyl peptidaseⅣ inhibitors[J].Bioorg Med Chem Lett,2004,14(5):1265-1268.
[29]Xu J,Wei L,Mathvink R J,et.al.Discovery of potent,selective,and orally bioavailable oxadiazole-based dipeptidyl peptidaseⅣ inhibitors[J].Bioorg Med Chem Lett,2006,16(20):5373-5377.
[30]Hulin B,Cabral S,Lopaze M G,et al.New fluorinated pyrrolidine and azetidine amides as dipeptidyl peptidaseⅣinhibitors[J].Bioorg Med Chem Lett,2005,15(21):4770-4773.

