Priority conservation pattern and gaps of Guangxi sea area based on systematic conservation planning
LI Xiao,LIU Zhaoyang,WANG Xiaoli,WU Yue,ZUO Guocheng,TAO Yijun
1. National Marine Data and Information Services,Tianjin 300171,China;
2.National Center of ocean Standards And Metrology,Tianjin 300111,China
Abstract: The sea of Guangxi provides important habitat for the biodiversity maintenance of mangrove, coral reef , white dolphin and so on . Based on the data of mangroves, coral reefs, seagrass beds, beaches, wetlands, turtles, amphioxus, white dolphins and germplasm resources in Guangxi sea area,and used marxan software to build the priority protection pattern of Guangxi sea area and identify the protection vacancy. The results show that the priority reserves in Guangxi are concentrated in Sanniang Bay, Hepu and Weizhou Island, and some areas are not included in the existing protection system. Compared with the marine ecological red line in Guangxi,the protection gaps are mainly distributed in the coastal beach area, mangrove area and Weizhou Island Coral Reef area. Based on the theory of systematic protection planning, this paper studied the priority protection pattern of Guangxi sea area for the first time, and provided scientific suggestions for the protection planning and management of Guangxi sea area.
Keywords: system protection planning, priority protection pattern, marxan, protection vacancy,Guangxi sea area
Guangxi sea area has mangrove,coral reef,seagrass bed,coastal wetland and other special marine resources and important protected objects. It is one of the representative sea areas with high species diversity in the South China Sea. With the implementation of the national strategy of Guangxi Beibu Gulf Economic Zone and the rapid development of large-scale coastal industries, coastal urban agglomerations and transportation infrastructure,Guangxi's marine ecological protection is facing new challenges.At present,most of the protected areas off the coast of China are built based on the concept of"rescue",and only based on a single protected object,lacking systematic planning,and the protection effect is not significant. Optimizing the protection pattern of Guangxi sea area based on the integrity and connectivity of ecosystem, effectively identifying the current protection vacancy and carrying out multi-mode protection are very important for maintaining the biodiversity of Guangxi sea area.
Since the 21stcentury, the concept of Systematic Conservation Planning (SCP) has exerted a wide influence in the international academic circles,and has now developed into the mainstream conservation planning method in the field of conservation biology. The method emphasizes that ecological protection should not only pay attention to the target species themselves, but also consider the ecosystem and related ecological processes in which they are located; Attention should be paid not only to protected areas, but also to protected areas and their surroundings. The relationship between environment;Biodiversity conservation strategy should be carried out on multi-level and multi-scale such as species-habitat-reserve-reserve network, and conservation based on species habitat pattern and ecological process is more meaningful for biodiversity conservation(Margules CR, 2000, 2007; Song Xiaolong, 2010; Wang Zhiqiang, 2010). Because most nature reserves are built under the consciousness of rescue, lack of scientific evaluation before construction, and the site selection and management of nature reserves need to be optimized,the habitats of most species are isolated islands surrounded by human activities(Liu JG, 2003; Tang Xiaoping, 2005), there is an obvious gap in conservation, which is difficult to meet the current needs of biodiversity conservation (Yan Yan, 2010; Yu Hong,2006;Knight AT,2008).The habitat degradation and biodiversity loss caused by human activities have aggravated this "isolated island phenomenon" in the pattern of protected areas. The practice of nature conservation and management shows that if a single and isolated nature reserve can be connected to form a network of nature reserves by establishing an ecological corridor (Forman RT,1995; Xiaowen Li, 1999), can significantly improve the efficiency of biodiversity conservation.
Under this background, the theory of system protection planning has been founded and developed, and has received wide attention from the international community. It puts forward nine basic principles (Chen Jingming, 2015), such as comprehensiveness,efficiency, connectivity, flexibility, complementarity, irreplaceability, representativeness,suitability and inclusiveness. Grasping these principles is also an important feature of system protection planning, which is different from other methods. Some domestic scholars have made exploratory research on terrestrial ecosystems, but there are few papers in the field of oceans. In 2019, Oxford University,York University and Greenpeace jointly wrote "30×30: Blueprint for Global Ocean Protection", using Marxan to push out hundreds of designs to protect the global high seas; Only in 2015, Chen Jingming (Chen Jingming,2015)applied this method to the research of Xiamen coastal marine biodiversity conservation pattern on a smaller scale; In this study,Guangxi sea area was taken as the research object, and the irreplaceable pattern of biodiversity was identified by using the theory and method of systematic protection planning, so as to provide scientific basis for the improvement of Guangxi sea area biodiversity protection system, and further enrich and expand the theoretical method and application value of systematic protection planning.
1 Research area
Guangxi's coastline is located at the southwest end of China's coastline, and the Beibu Gulf waters bordering it cover an area of about 129,300 square kilometers. There are six main rivers flowing into the sea,such as Nanliu River,Dafeng River,Qinjiang River,Maoling River, Fangchenggang River and Beilun River. The rivers in coastal areas have small runoff and large tidal range,and the coastal areas of Guangxi are mainly open coasts and bays.
Guangxi retains China's relatively primitive mangroves, coral reefs and seagrass beds,and the diversity of higher plant species in the coastal ecotone between land and sea is the richest in China, with more than 600 species per square kilometer. They build an ecological buffer zone and a species exchange corridor between the ocean and the mainland,which is an important stop zone in bird migration and an important guarantee for the offshore marine ecological environment.Guangxi Beibu Gulf is the main fishing ground in China,one of the representative sea areas with high species diversity in the South China Sea, the distribution area of germplasm resources of important economic species such as Pinctada martensii and Oyster near the river, and the habitat of dugong, Chinese white dolphin and finless porpoise.
2 Research methods
2.1 Data source and processing
The data used in this study mainly include the data of special species and habitats in Guangxi sea area, as shown in Tab. 1. Using GIS technology, the collected paper data is vectorized into spatial data,and the GIS database is established by combining the existing spatial data.
2.2 Research methods and techniques
By selecting representative species, habitats or ecosystems and ecological processes as protection objects, the system protection planning method is driven by specific protection objectives,based on specific planning units,calculates the irreplaceable size of each planning unit by using spatial models, identifies important ecological function areas and biodiversity hotspots with low protection costs, and brings them into the nature reserve system.
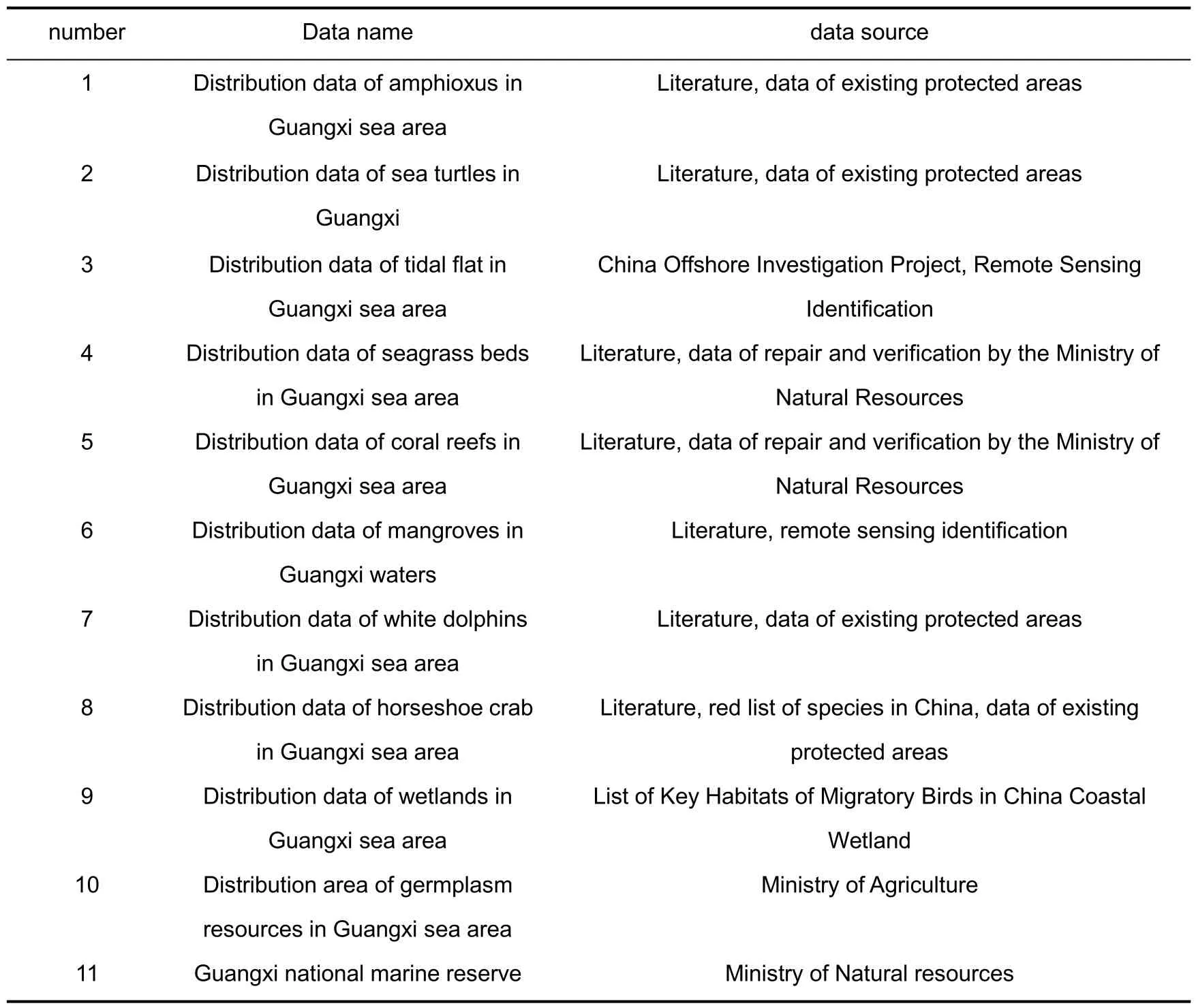
Tab.1 Source of Guangxi sea area research data
In this method,the priority protected area is identified by calculating the irreplaceable value. Irreplaceability is a core concept of system protection planning, and it is a representation of the importance of biodiversity obtained by comprehensively considering all relevant information of the area. If the irreplaceable value of a certain area is high, it means that the protection value of this area is high, and protecting this area can protect biodiversity well, so priority should be given to protection in practice. In addition, the system protection planning also considers connectivity. The purpose of the method is not only to determine the areas that need priority protection through analysis, but more importantly, to form an efficient ecological protection network by connecting the identified priority protection areas with the existing protection areas.
Based on the distribution of coral reefs, mangroves, seagrass beds, tidal flats,wetlands and other ecosystems in Guangxi waters, as well as the distribution of protected species such as horseshoe crab, amphioxus and white dolphin, taking into account the distance from the shoreline and other factors, this study set different protection targets for each protected object, using the theory and method of systematic protection planning widely used in the world at present, and using the Marxan spatial optimization model,based on the size of 0.1×0.1 The specific research route is shown in Fig.1.

Fig.1 Research route of priority protection pattern and protection vacancy analysis in Guangxi sea area based on systematic protection planning
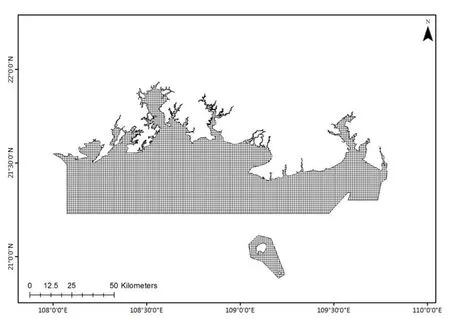
Fig.2 Guangxi sea area planning unit
2.3 System protection planning steps
The priority protection pattern is identified by using Marxan software, which is a space optimization software widely used in system protection planning at present. It is mainly based on the principle of Complementarity and simulated annealing algorithm(SAA),through iterative operation and repeated screening until the optimal planning unit is selected. At the same time, Marxan also realized the adjustment of spatial aggregation degree of planning structure through edge effect adjuster, so that the planning units of priority areas are relatively concentrated in space,which is more in line with the principle of establishing protected areas(Zuo Xiaoxiao,2019).
2.3.1 Planning unit setting
The system protection planning method is based on a certain size planning unit,which can be a grid hexagon or other environmental units. In this study, the grid size of 0.1×0.1 is analyzed,and 6 982 planning units are divided.
Identify the key elements (species,communities and habitats)that can represent the local biodiversity as protection objects. Because of the complexity of biodiversity and the limitation of existing data, it is difficult to obtain all biological information, so we must choose the protection objects that can best represent the local biodiversity. Based on the coarse-fine screening method and expert knowledge,the following 10 habitats and species(Tab.2)were selected as protection objects.
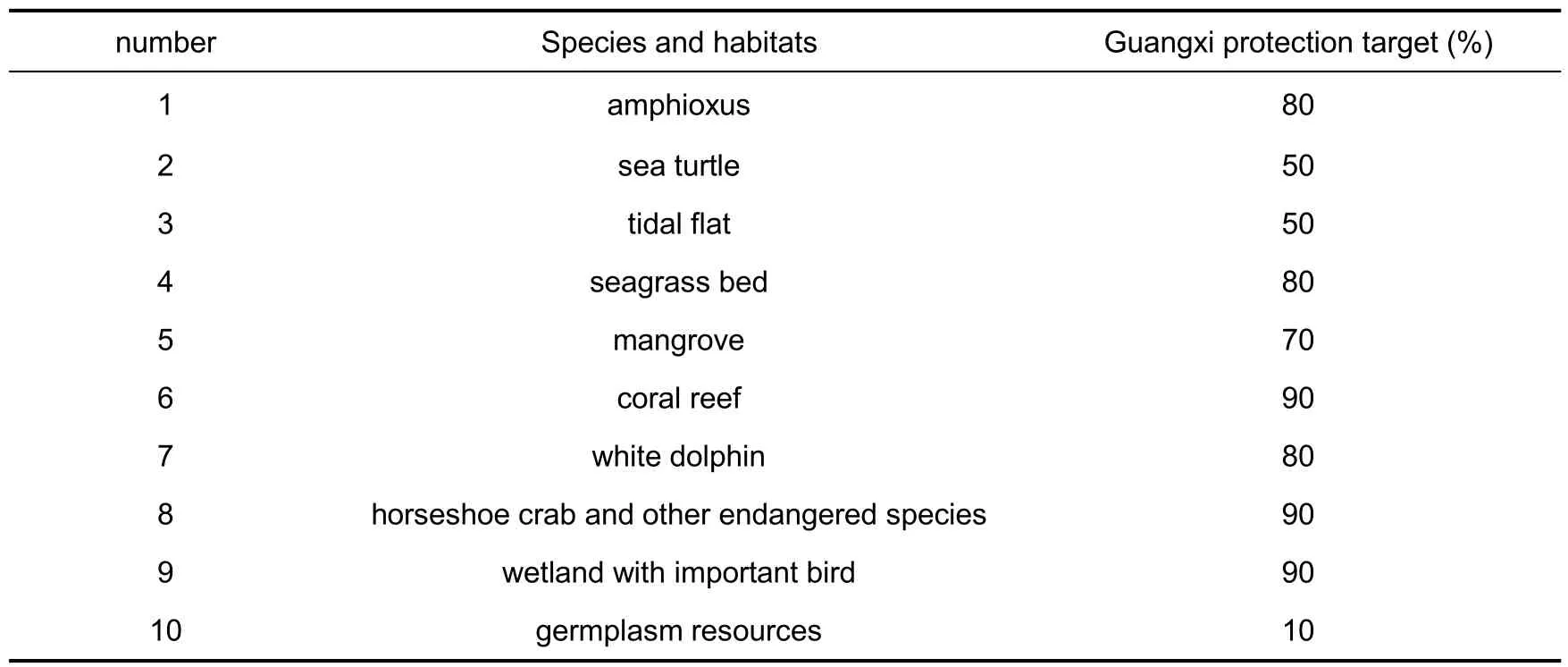
Tab.2 Protection objects and objectives of Guangxi sea area
2.3.2 Set protection goals
In the study of system protection planning,10%to 30%of the terrestrial ecosystem is usually set as the protection target. In the case of the Great Barrier Reef in Australia, the protection target of the Great Barrier Reef is set at 30%.The United Nations "Draft Global Biodiversity Framework after 2020" and other documents propose to protect 30% of the ocean. In this study, different protection targets are set for each protected object (Tab. 2).Because the distribution range of sea turtles comes from the description of the literature,the principle of drawing as large a picture as possible in GIS is adopted,so the distribution range of sea turtles is large. In this study, 50% of the protection targets are set for sea turtles. The tidal flats in Guangxi are widely distributed and concentrated in the coastal areas, so the protection cost is high. Therefore, a 50% protection target is set. The distribution of germplasm resources comes from the germplasm conservation zone on the website of the Ministry of Agriculture.In view of its relatively large area and low importance compared with other conservation targets,the conservation target of germplasm resources is set at 10%. Other protection targets, such as mangroves, seagrass, coral reefs, white dolphins, amphioxus, horseshoe crab, etc., are very important marine ecosystems and species in Guangxi waters. Taking into account the endangered degree, distribution area,current protection effect, etc., and consulting relevant experts, the protection targets have been appropriately raised and 70%-90%of them have been set.
2.3.3 Protection cost analysis
In the research of system protection planning, the analysis of protection cost is also called ecological integrity analysis or habitat suitability analysis. The higher the protection cost, the greater the man-made impact on the region, and the lower the suitability of its biodiversity.
To determine the biological protection unit, it is necessary not only to meet the protection objectives,but also to consider the cost of selecting the planning unit.Due to the limitation of actual data,there is no direct data of protection cost in the study,so this study uses the shortest distance from the shoreline instead. It is considered that the closer the offshore line of a certain area is, the greater the cost of choosing this area as a protected area will be.
2.3.4 Optimizing the pattern and protecting vacancy identification
Based on the method of system protection planning,the above data are input into the Marxan space optimization model,and the irreplaceable value of planning unit is obtained.According to the size of irreplaceability, considering the information of existing protected areas and combining with expert knowledge,identify the priority protected areas.
In addition, the edge length adjustment (BLM) module is used to adjust the connectivity and aggregation of protection patterns in the process of pattern optimization.It is considered that the general pattern with high connectivity and aggregation is more conducive to the maintenance of biodiversity, and the relatively concentrated protection pattern is also conducive to the implementation and management of marine protection.However, too concentrated and contiguous protected areas will lead to the increase of protection cost. In order to weigh the aggregation degree of protection pattern and protection cost, a reasonable BLM value is obtained by sensitivity analysis. Finally, the irreplaceable area is selected as the priority protection area through the model. By comparing the priority protection pattern with the distribution pattern of existing protected areas,it is identified that it has irreplaceable protection value.
3 Results and analysis
3.1 Distribution of protected objects in Guangxi sea area
3.1.1 Amphioxus
Amphioxus has strict requirements for living environment, and likes to live in loose sandy land. The sea water should be salty, the water temperature should be appropriate,and the water flow and wind waves should be gentle,so it breeds very little,and its species are very precious.Amphioxus is an important transition type from lower animals to higher animals,and it is considered as the ancestor of chordates,a living fossil in the evolutionary history of animals, and a precious material for studying animal evolution.It has been listed as a national second-class protected animal in China. Guangxi amphioxus is mainly distributed in the sea area of Hepu County,Guangxi(Figure 3).
3.1.2 Sea turtle
According to the literature report, there are only 5 species (green turtle, hawksbill turtle, Pacific turtle, etc.) belonging to 5 genera in 2 families in China, and all of them are listed as the national second-class protected animals.At present,most of the turtle records are found in the South China Sea. According to the literature report and the existing ecological red line data,the distribution of turtles is drawn(Fig.3).

Fig.3 Distribution of protected objects in Guangxi sea area
3.1.3 Horseshoe crab
Limulus amebocyte lysate has high medicinal value, and its number has been decreasing for several years. Guangxi Province has listed it as a second-class protected animal. Limulus amebocyte lysate mainly lives on the shallow sandy seabed, likes the estuary with low salinity, and has the habit of going upstream. The sea area of Hepu County,Guangxi is the concentrated distribution area of Limulus amebocyte lysate(Fig.3).
3.1.4 White dolphin
Chinese white dolphin, the most endangered marine life in the world, is listed in the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora, and it is also the only national first-class protected animal among marine whales and dolphins in China, known as the "giant panda at sea". White dolphins mostly live in shallow seas,gathering in bays close to beaches,and are mainly distributed in Qinzhou and Hepu waters in Guangxi(Fig.3).
3.1.5 Seagrass
Seagrass is another important marine ecosystem besides mangroves and coral reefs.A large area of contiguous seagrass is called seagrass bed, which is the habitat for many large marine organisms and even mammals,and has ecological significance(Han Qiuying,2007). Seagrass beds are suitable for distribution in temperate, tropical coastal or coastal estuary waters. The intertidal zone to subtidal zone along Tieshan Port, Yingluo Port and Pearl Harbor in Guangxi is the main distribution area of seagrass beds, with an area of about 737 hectares(Fig.3).
3.1.6 Mangrove
Mangrove is a special plant community that grows in the intertidal zone of tropical and subtropical coasts. It is mainly distributed in estuaries of rivers and bays along the coastline, and has obvious effects on wind and waves protection, seawall protection and coast protection, and at the same time, it has certain purification effect and anti-pollution ability for pollution caused by modern industrialization (Liang Shichu, 1999). There are 8046 hectares of mangroves along the coast of Guangxi, which are distributed in the muddy intertidal zone at the confluence of bays and estuaries with obvious beach surface(Fig.3).
3.1.7 Coral reef
Coral reef ecosystem is a special ecosystem supported by the sediment formed by reef-building coral communities.It provides a complex ecological environment and has the largest number of species in the ocean. Its richness is close to that of tropical rain forests on land, and it is called "submarine rain forest" and biodiversity preservation bank. Coral reefs are suitable for growing in the sea water at 25~30℃ with abundant sunshine, and generally adhere to a solid foundation. Guangxi coral reef ecosystem is mainly distributed in Weizhou Island,Xieyang Island and Fangchenggang sea area(Fig.3).
3.1.8 Tidal flat
Tidal flat is one of the wetland ecosystems with rich biodiversity,high productivity and great value, which is closely related to the protection of biodiversity. See Fig. 3 for the distribution of tidal flats in Guangxi.
3.1.9 Wetland with important bird
Wetland has complex and diverse habitat types and ecological environment, and is an important habitat for the survival and breeding of marine life and birds. The important bird distribution wetland data mainly comes from the list of important bird wetlands,mainly distributed in Fangchenggang,Guangxi and Beihai waters(Fig.3).
3.1.10 Germplasm resources
The distribution of germplasm resources mainly comes from the germplasm conservation zone range issued by the Ministry of Agriculture, with a large distribution range(Fig.3).
3.2 Analysis of irreplaceable protection of marine ecosystem in Guangxi
Irreplaceability is an important representation of biodiversity obtained by comprehensively considering all relevant information in a region, which can well express the importance of a planning unit. If the irreplaceability value of a planning unit is high, it means that the planning unit contains abundant biological information or important endangered biological information, and protecting the planning unit can effectively protect the regional biodiversity. Under the specific protection target, the simulated annealing algorithm of space model Marxan is used to calculate it repeatedly.
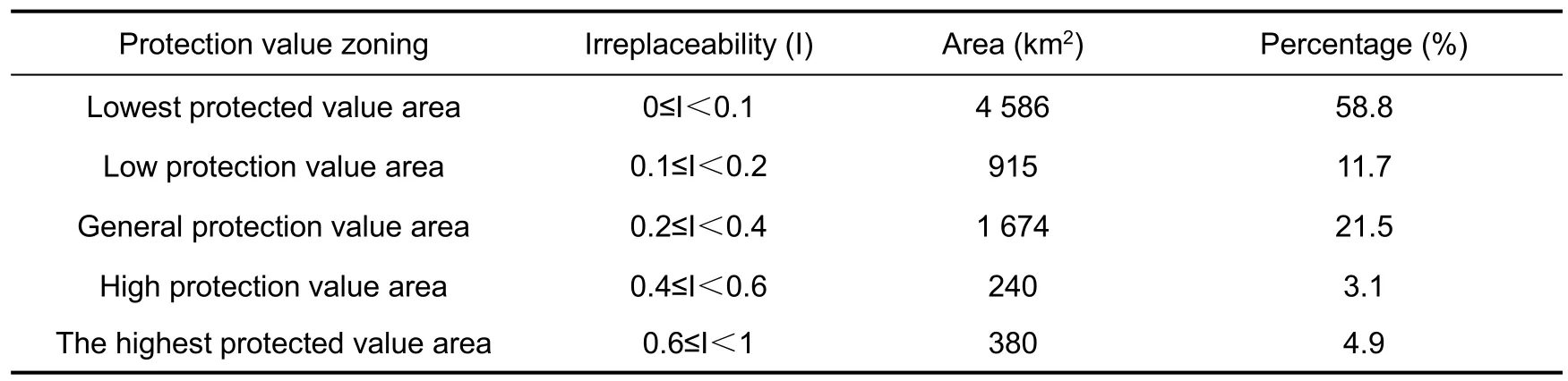
The irreplaceability of ecosystem protection in the study area can be divided into five grades(Fig.4).High protected value areas,i.e.irreplaceable(i)the highest(0.6 ≤i<1)and high(0.4 ≤i < 0.6).These cells are concentrated distribution areas of protected objects, so protected areas should be set up for priority protection, with a total area of 620 km2,accounting for 8.0% of the total area of the study area; The general protected value area(0.2 ≤I < 0.4) covers an area of 1 674 km2, accounting for 21.5% of the total area of the study area.These areas are protected areas,but the protected objects are relatively single.Low-value protected areas and the lowest-value protected areas account for 11.7% and 58.8%respectively(Tab.3).
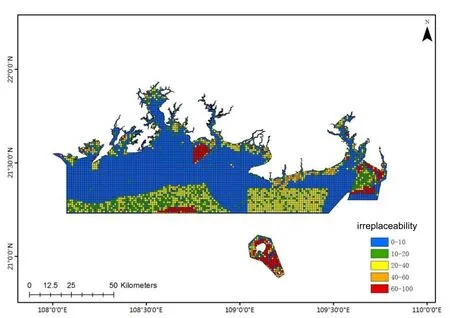
Fig.4 Different levels of priority protection planning units based on irreplaceable values in Guangxi sea area
Tab.3 Irreplaceable grades of marine ecosystem protection in Guangxi
Under the premise of controlling the protection cost, the Marxan software selected 862 cells that need to be protected, which are basically consistent with the cells with high irreplaceability value. The area of priority protection is about 1 061 km2, accounting for about 13.6% of the total planned area, thus achieving the protection targets set for most protected objects(Fig.5).

Fig.5 Priority protection planning unit based on optimal solution
3.3 Analysis of Guangxi sea area protection vacancy
Spatial superposition of the existing national marine protected areas and marine ecological protection red lines and the results of priority protection planning will result in Guangxi sea area protection vacancy(Fig.6).The existing national marine reserves mainly include Hepu Dugong Nature Reserve, Qinzhou Maoweihai Marine Park, Weizhou Island Coral Reef Marine Park, Beilun Estuary Nature Reserve and Shankou Mangrove Nature Reserve. The marine reserves are scattered, with a relatively small area, and most of the planned priority areas have not been included in the scope of the reserves,so they cannot form an effective protection network, especially for coastal beaches and mangrove ecosystems, and the rare and endangered species distribution areas far offshore are relatively weak.The red line of marine protection is relatively contiguous and covers a large area, covering most of the planning priority areas, forming a good protection pattern,especially in the protection of rare and endangered species distribution areas far offshore,but the protection of coastal beaches and mangroves is still weak. On the whole, the protection vacancies are mainly distributed in coastal tidal flats,mangroves and coral reefs in Weizhou Island. These areas are close to the shore, and there is a serious conflict between development and protection.

Fig.6 Gap of Guangxi sea area protection(Part I:Existing protected areas;below:the red line of marine ecological protection)
4 Conclusion and discussion
Based on the theory of systematic protection planning, this study studied the priority protection pattern of Guangxi sea area for the first time,and provided scientific suggestions for the protection planning and management of Guangxi sea area.
(a) Guangxi sea area is rich in biodiversity resources. In this study, when selecting protected objects, the relevant data were processed to extract the habitat types and protected species with more regional characteristics. In addition, when setting the protection targets, the importance and distribution range of protected objects were comprehensively considered,and different protection targets were set for different types of protected objects.
(b)It is a great innovation to apply the theory of systematic protection planning to the domestic marine field in this study.Compared with land,the consideration factors are more comprehensive (wetlands, birds, mammals, etc. are mostly selected as protection objects in land, while marine ecosystems are more diverse, and more protection objects need to be considered), which provides an intuitive reference for the formulation of protection strategies.
(c) According to the results of this study, the priority protected areas in Guangxi waters are concentrated in Sanniang Bay, Hepu and Weizhou Island, but the existing protected areas can't effectively cover the key areas of biodiversity conservation. It is suggested to build and expand nature reserves in areas where biodiversity conservation is vacant, such as adding Sanniang Bay in Qinzhou and Weizhou Island to improve conservation efficiency.At the same time, it is also possible to establish connections and buffer zones between conservation priority areas,or ecological corridor conservation areas,to form a network of conservation areas,so as to effectively protect biodiversity resources.
However,due to the limitation of data, this paper still has some shortcomings, which will be improved from the following aspects in the future:
(1)Improve the geographic information database of protected objects.The layer data of protecting habitats and species produced in this paper have different research years and limited accuracy, and many data are qualitative descriptions. GIS can only draw a rough distribution area, reflecting the real level of protected objects in the research area, which still has some defects.
(2) Optimize the measurement of protection cost. Generally, the distance between land and residential areas, roads, etc. is chosen to determine the cost of protection. This paper refers to the distance between land and shoreline as the measurement factor of protection cost. In the next step, factors such as the nature of development and utilization in different sea areas will be taken into consideration to make the determination of protection cost more reasonable.
(3) Collect data of provincial, municipal and county-level protected areas. Due to the limitation of data, this study mainly selected the national protected areas, but did not consider the provincial, municipal and county-level protected areas. In the next step,relevant data will be collected to support the research of protection vacancies, so that the research results of protection vacancies will be more scientific and instructive.
The research of system protection planning method has been mature abroad,but the research in China has just started, and it mainly focuses on terrestrial ecosystems.Therefore, the research prospect of this method in domestic marine ecosystems is very broad, and with the development of marine spatial planning, evaluation of resources and environment carrying capacity and suitability, and selection and designation of protected areas,this method will be applied creatively in China.
 Marine Science Bulletin2023年1期
Marine Science Bulletin2023年1期
- Marine Science Bulletin的其它文章
- Characteristics of storm surge disasters along Fujian coast in recent 10 years
- Leveraging open source software and programming best practices for sustainable web applications in support of marine data sharing-BCO-DMO case
- Methods and empirical research on Chinese sea area resource assets value accounting
- Design and development of international buoy data operational processing system
- Isolation and purification of diketopiperazines with antialgal activity from marine macroalgae
- Data analysis of HF surface wave radar in Zhoushan sea area
