氢化松脂体系汽液平衡测定与关联
杨和见, 任宝光, 陈小鹏, 王琳琳, 梁杰珍, 张众尧
氢化松脂体系汽液平衡测定与关联
杨和见1, 任宝光1, 陈小鹏2, 王琳琳2, 梁杰珍2, 张众尧2
(1. 梧州黄埔化工药业有限公司, 广西 梧州 543000;2. 广西大学化学化工学院, 广西石化资源加工及过程强化技术重点实验室, 广西 南宁 530004)
为了解决氢化松脂蒸馏分离问题,采用带有搅拌桨的改进Ellis平衡釜和气相色谱分析方法,测定了在常压和温度为169.2~176.2 ℃下氢化松脂体系汽液平衡数据;采用NRTL、Wilson和UNIQUAC模型对氢化松脂体系汽液平衡数据进行热力学关联;由相对挥发度判断了单萜烃和倍半萜烃分离难易程度。结果表明,氢化松脂体系汽液平衡数据经Herington积分法检验,所得实验数据符合热力学一致性;采用NRTL、Wilson和UNIQUAC模型计算时,气相摩尔分数的平均绝对偏差为0.012 1、最大偏差为0.037 3,温度的平均绝对偏差为1.5 ℃、最大偏差为2.8 ℃,即3种模型对氢化松脂体系汽液平衡计算都适用;单萜烃与倍半萜烃相对挥发度范围为1.924~2.146,因而单萜烃与倍半萜烃分离有一定难度。
氢化松脂;氢化松香;单萜烃;倍半萜烃;汽液平衡
1 前 言
氢化松脂由松脂直接催化加氢而得[1-3],其中氢化松香质量分数为50%~60%,氢化松节油质量分数为40%~50%。氢化松节油主要有单萜烃和倍半萜烃组分,其中单萜烃组分有蒎烷、-蒎烯、对伞花烃和对孟烷等,95.99 kPa压力下沸点为162~166 ℃;倍半萜烃主要有长叶烯和石竹烯等,94.12 kPa压力下沸点为254~256 ℃[4-5]。氢化松脂经连续蒸馏分离可得到氢化松香单萜烃轻组分和倍半萜烃重组分。为了解决氢化松脂蒸馏分离问题需要较完整的氢化松脂体系汽液平衡数据,但由于氢化松脂体系黏度较大、沸点高,所以氢化松脂体系汽液平衡测定有一定难度,导致氢化松脂体系汽液平衡数据十分匮乏。有关氢化松节油体系汽液平衡数据有如下一些报道,陈小鹏等[6]测定了常压和155.7~251.4 ℃下蒎烷、-蒎烯和长叶烯3个二元及1个三元体系汽液平衡数据;童张法等[7]测定了-蒎烯+对伞花烃和-蒎烯+对伞花烃2个二元体系分别在53.3和80.0 kPa下的汽液平衡数据;祝远姣等[8]、Huang等[9]、Yao等[10-11]、吴金芝等[12]、Sun等[13]测定了蒎烷、对伞花烃和长叶烯体系汽液平衡数据。本研究采用改进的Ellis平衡釜测定了氢化松香不同含量的氢化松脂体系在常压和169.2~176.2 ℃下汽液平衡数据,并对氢化松脂体系汽液平衡特性和分离难易程度进行了研究。

图1 改进的Ellis汽液两相双循环型平衡釜
1. liquid phase sampling tube 2,3. heating chamber 4. liquid phase thermometer 5. vapor phase thermometer 6. wooden case 7,8. reflux condenser 9. absolute pressure transmitter 10. U-tube manometer 11.vacuum pump 12. surge flask 13. vapor phase sampling tube 14. magnetic whisk
2 实验部分
2.1 试剂与材料
氢化松香(特级),广西梧州日成林产化工股份有限公司;蒎烷(单萜烃质量分数为98.50%)、蒎烯(单萜烃质量分数为95.85%),广西梧州松脂厂;长叶烯等倍半萜烃(单萜烃质量分数为96.21%),自制;四甲基氢氧化胺水溶液、甲醇、酚酞,均为市售分析纯。
2.2 实验装置
由于氢化松脂体系黏度大、沸点高,因而为了强化实验过程的传热、传质和混合效果,采用具有磁力搅拌、汽液双循环和平衡釜外缠电热丝保温的改进Ellis平衡釜进行氢化松脂体系汽液平衡测定,为了保障汽液平衡测定的温度稳定,把改进Ellis平衡釜装入一个保温良好的自制密闭木箱中,以防止热量的对流与辐射散失,该实验装置如图1所示。
2.3 实验方法
按照适当比例配制不同组成的氢化松香、蒎烷、-蒎烯和长叶烯溶液200 mL,加入改进的Ellis平衡釜内,启动磁力搅拌器,通过自动控温仪稳定控制加热、手动调压器调节保温电压。物料沸腾流出的蒸汽经冷凝后不断地回流至平衡釜,当汽相和液相精密温度计(精度为0.1 ℃)读数恒定2 h基本不变后,可认为汽液两相已经达到相平衡,从改进Ellis平衡釜取样口放出少量液体以置换并采集样品,然后同时取汽相冷凝液和液相样品,其中汽相样品直接进行气相色谱分析,而液相样品用质量分数为6% 的四甲基氢氧化铵甲醇溶液与2~3滴酚酞混合至粉红色再进行气相色谱分析[14~16]。
2.4 气相色谱分析
仪器:Agilent 7820型气相色谱仪,FID检测器,DB-5毛细管色谱柱(30 m×0.32 mm×0.25 μm)。
色谱条件:检测器和进样器温度250 ℃;载气为氮气,体积流量为48.0 mL×min-1,分流比为50:1,尾吹体积流量为24 mL×min-1;氢气体积流量为32 mL×min-1,空气体积流量为300 mL×min-1;灵敏度为8,液相样品进样量为0.4 μL,气相样品进样量为0.2 μL;柱温程序升温步骤为
液相样品:
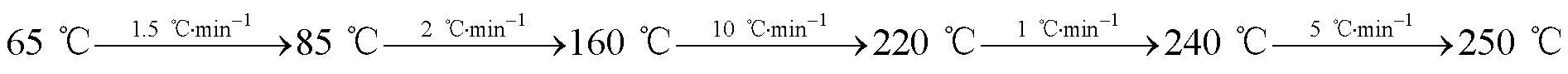
3 结果与讨论
3.1 氢化松脂体系汽液平衡测定
在实际生产中,氢化松脂中氢化松香的质量分数为50%~60%,其余为氢化松节油,氢化松节油主要成分为蒎烷等单萜烃,是轻组分,占氢化松节油质量分数为78%~96%;长叶烯等倍半萜烃是重组分,质量分数为4%~22%,而氢化松香是不挥发组分。在氢化松脂连续蒸馏过程中,氢化松香和氢化松节油摩尔分数随着蒸馏塔塔板数的变化而变化,因而调配不同摩尔分数的氢化松脂体系,用于测定常压(101 kPa)下该氢化松脂体系汽液平衡数据,实验结果如表1所示。

表1 氢化松脂体系汽液平衡实验值
- hydrogenated rosin mass fractionis a non-volatile component;- vapor-liquid equilibrium temperature;1and1represent the molar fractions of light monoterpenes in liquid phase and vapor phase, respectively. The mole fractions of sesquiterpenes in liquid and vapor phases are denoted by2and2, respectively. The remaining symbols are given in formula (1).
在常压下由式(1)关联氢化松脂体系汽液平衡关系。

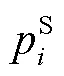
3.2 模型关联与预测
采用NRTL、Wilson和UNIQUAC模型对氢化松脂体系汽液平衡进行模拟计算,由表1实验数据拟合得到的模型能量参数如表2所示。表2中,12、21、12、21为二元交互作用参数,由表2模型能量参数及其模型进行相平衡数据预测,计算值与实验值偏差如表3所示。

表2 模型能量参数

表3 氢化松脂体系汽液平衡模拟计算值与实验值偏差表
∆1=1 exp-1 cal; ∆=exp-cal, the experimental values are shown in Table 1.
由表3可见,采用NRTL、Wilson和UNIQUAC模型进行氢化松脂体系汽液平衡模拟计算,计算值与实验值偏差都较小,因而3种模型对氢化松脂体系汽液平衡计算都适用,但UNIQUAC模型计算的温度偏差更小,最大温度偏差仅为1.6 ℃。
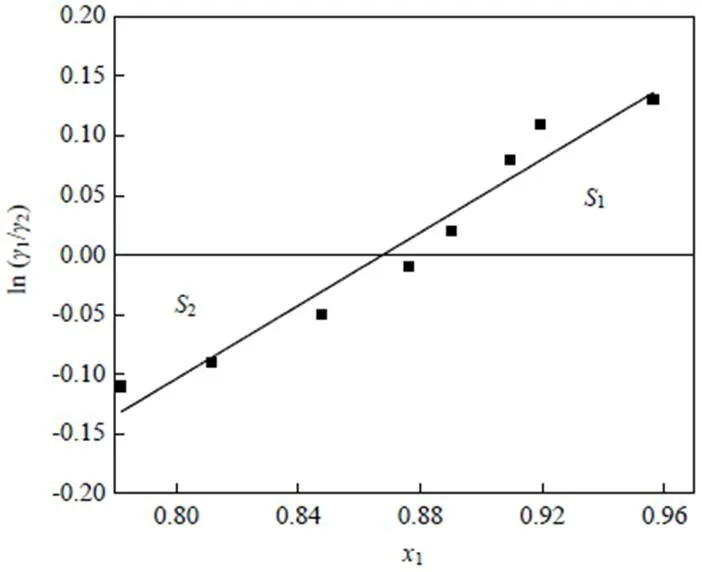
图2 氢化松脂体系汽液平衡数据热力学一致性检验积分图
3.3 热力学一致性检验
采用Herington积分法[17]对氢化松脂体系汽液平衡实验数据进行热力学一致性检验,如式(2)所示:
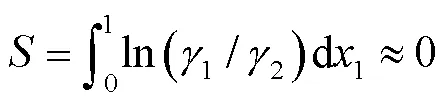
根据式(2),以ln(12)对1作图,结果如图2所示。
由图2可知,1=0.005 2,2=0.005 4,则实验误差为
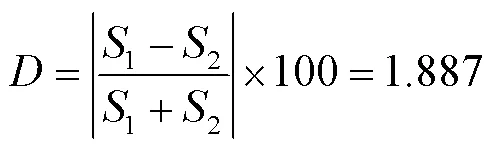

<10说明实验数据具有一定可靠性,因而实验测定的氢化松脂体系汽液平衡数据符合热力学一致性。
3.4 氢化松节油混合物负偏差性质
从表1可见,单萜烃(1)和倍半萜烃(2)的活度系数1、2多数小于1,表明氢化松节油混合物组分(1)、(2)都属负偏差性质;倍半萜烃组分(2)的活度系数2有3个实验点的值大于1,属正偏差,有5个实验值的活度系数2值小于1,属负偏差,但真实溶液的蒸汽压在全浓度范围都小于理想溶液,即

也就是说,单萜烃、倍半萜烃与氢化松香混合形成真实溶液后,分子间作用力增大,这是由于氢化松香所含氢化枞酸的羧基对氢化松节油组分的分子间作用力增大,使单萜烃和倍半萜烃不易挥发逸出,导致真实溶液蒸汽压小于理想溶液,因此氢化松节油混合物显现负偏差性质。
3.5 氢化松节油组分分离难度分析
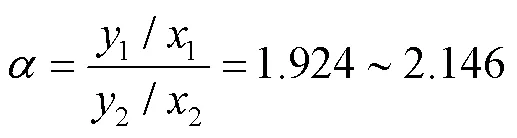
4 结 论
(1) 为了解决氢化松脂蒸馏分离问题,采用带有搅拌的改进Ellis平衡釜和气相色谱分析方法,实验测定了在常压和温度为169.2~176.2 ℃下氢化松香体系汽液平衡数据,经Herington积分法检验,所得实验数据符合热力学一致性。
(2) 采用NRTL、Wilson和UNIQUAC模型对所测氢化松脂体系汽液平衡进行热力学关联,气相摩尔分数的平均绝对偏差为0.012 1、最大偏差为0.037 3,温度的平均绝对偏差为1.5 ℃、最大偏差为2.8 ℃。因而3种模型对氢化松脂体系汽液平衡计算都适用。
(3) 氢化松脂体系汽液平衡温度相差仅为7.0 ℃,单萜烃与倍半萜烃相对挥发度范围为1.924~2.146,因而单萜烃与倍半萜烃分离有一定难度。
[1] HUANG Y Y, CHEN X P, DENG Y,. A novel nickel catalyst derived from layered double hydroxides (LDHs) supported on fluid catalytic cracking catalyst residue (FC3R) for rosin hydrogenation [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 269: 434-443.
[2] HUANG Y Y, WANG L L, CHEN X P,. Intrinsic kinetics study of rosin hydrogenation on a nickel catalyst supported on spent equilibrium catalyst [J]. RSC Advances, 2017, 7(41): 25780-25788.
[3] CHEN X P, REN L, YASEEN M,. Synthesis, characterization and activity performance of nickel-loaded spent FCC catalyst for pine gum hydrogenation [J]. RSC Advances, 2019, 9(12): 6515-6525.
[4] 程芝. 天然树脂生产工艺学[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版, 1996: 52-54.
CHENG Z. Natural resin production technology [M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing, 1996: 52-54.
[5] 南京林产工业学院. 林产化学工业手册(上册) [M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 1980: 127-163.
Nanjing Forestry Industry College. Manual of forestry chemical industry (Volume I) [M].Beijing: China Forestry Press, 1980: 127 -163.
[6] 陈小鹏, 祝远姣, 王琳琳, 等. 蒎烷--蒎烯-长叶烯体系常压汽液平衡[J]. 广西大学学报(自然科学版), 2003, 28(3): 194-198.
CHEN X P, ZHU Y J, WANG L L,. Vapor-liquid equilibrium of pinene--pinene-longifolene system at atmospheric pressure [J]. Journal of Guangxi University(Natural Science Edition), 2003, 28(3): 194-198.
[7] 童张法, 王坤, 孙丽霞, 等.-蒎烯+对伞花烃和-蒎烯+对伞花烃体系减压汽液平衡数据的测定与关联[J]. 高校化学工程学报, 2011, 25(5): 734-739.
TONG Z F, WANG K, SUN L X,. Determination and correlation of vacuum vapor-liquid equilibrium data for-pinene+-cymene and-pinene+-cymene systems [J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Chinese Universities, 2011, 25(5): 734-739.
[8] 祝远姣, 陈小鹏, 王琳琳, 等. 蒎烷饱和蒸汽压的测定与关联[J]. 高校化学工程学报, 2003, 17(5): 564-568.
ZHU Y J, CHEN X P, WANG L L,. Determination and correlation of saturated vapor pressure of pinane [J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Chinese Universities, 2003, 17(5): 564-568.
[9] HUANG Y Y, LIANG J Z, WANG L L,. Vapor–liquid equilibria for binary and ternary systems with-caryophyllene, dipentene, and-pinene at 100.7 kPa [J]. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 2020, 65(8): 3770-3777.
[10] YAO G Y, WANG L L, CHEN X P,. Measurement and correlation of vapor–liquid equilibrium data for binary and ternary systems composed of (−)--caryophyllene,-cymene and 3-carene at 101.33 kPa [J]. The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 2019, 128: 215-224.
[11] 姚光艳, 王琳琳, 陈小鹏, 等.-石竹烯, 对伞花烃及3-蒈烯二元体系的超额焓[J]. 高校化学工程学报, 2018, 32(4): 779-784.
YAO G Y, WANG L L, CHEN X P.. Excess enthalpy of the binary system of-cymene and 3-carene [J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Chinese Universities, 2018, 32(4): 779-784.
[12] 吴金芝, 王琳琳, 陈小鹏, 等. 莰烯+(+)-3-蒈烯体系汽液平衡数据的测定与关联[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(6): 2092-2101.
WU J Z, WANG L L, CHEN X P,. Determination and correlation of vapor-liquid equilibrium data for camphene+(+)-3-carene system [J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(6): 2092-2101.
[13] SUN L X, LIAO D K, YANG Z Y,. Measurement and correlation of (vapor+liquid) equilibrium data for {-pinene+-cymene+(S)-(−)-limonene} ternary system at atmospheric pressure [J]. The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 2013, 58: 416-421.
[14] WANG S F, CHEN X P, LIANG J Z,. Vapor–liquid equilibrium of-pinene, longifolene, and abietic acid of pine oleoresin: HS-GC measurements and model correlation [J]. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 2022, 67(5): 1125-1139.
[15] QIN Y M, CHEN X P, WANG L L,. Experimental determination and computational prediction of dehydroabietic acid solubility in (−)--pinene+(−)--caryophyllene+-cymene system [J]. Molecules, 2022, 27(4): 1220.
[16] 侯文彪, 江文夺, 吴嘉超, 等. 松脂气液平衡特性及其 N2/CO2循环活气法蒸馏过程分析[J]. 林产化学与工业, 2021, 41(5): 93-99.
HOU W B, JIANG W D, WU J C,. Vapor-liquid equilibrium (VLE) characteristics of pine oleoresin and its N2/CO2cycle distillation process analysis [J]. Biomass Chemical Engineering, 2021, 41(5): 93-99.
[17] PRAUSNITZ J M, ANDERSON T F, GRENS E A,. Computer calculation for multicomponent VLE and LLE [M]. New Jersey: Prentice Hall, 1980: 67-103.
Determination and correlation of vapor-liquid equilibrium of the hydrogenated pine resin system
YANG Hejian1, REN Baoguang1, CHEN Xiaopeng2, WANG Linlin2,LIANG Jiezhen2, ZHANG Zhongyao2
(1. Wuzhou Huangpu Chemical Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Wuzhou 543000, China;2. School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Guangxi Key Laboratory of Petrochemical Resource Processing and Process Intensification Technology, Guangxi University, Nanning 530004, China)
In order to solve the problem of distillation separation of hydrogenated pine resin, the vapor-liquid equilibrium data of the hydrogenated pine resin system were measured at atmospheric pressure and temperatures from 169.2 to 176.2 ℃ using a modified Ellis equilibrium kettle with stirring and a gas chromatographic analysis method. NRTL, Wilson and UNIQUAC models were used to correlate the vapor-liquid equilibrium data thermodynamically. Separation difficulty of monoterpene and sesquiterpene hydrocarbons was judged by relative volatility. The results show that the vapor-liquid equilibrium data of the hydrogenated pine resin system obtained by the Herington integration method are consistent with the thermodynamics. When calculated using the NRTL, Wilson and UNIQUAC models, the mean absolute deviation of the gas-phase mole fraction was 0.012 1 with a maximum deviation of 0.037 3, and the mean absolute deviation of the temperature was 1.5 ℃ with a maximum deviation of 2.8 ℃, which indicates that the three models are applicable to the hydrogenated pine resin system. The relative volatility of monoterpene hydrocarbons and sesquiterpene hydrocarbons ranged from 1.924 to 2.146, thus it is difficult to separate monoterpene hydrocarbons from sesquiterpene hydrocarbons.
hydrogenated pine resin; hydrogenated rosin; monoterpene hydrocarbons; sesquiterpene hydrocarbons; vapor-liquid equilibrium
O642.42
A
10.3969/j.issn.1003-9015.2023.05.019
1003-9015(2023)05-0858-05
2022-09-13;
2022-11-21。
国家自然科学基金(31960294, 21878056);广西石化资源加工及过程强化技术重点实验室课题基金(2019Z002)。
杨和见(1972- ),男,广东揭阳人,梧州黄埔化工药业有限公司工程师,学士。
陈小鹏,E-mail:lilm@gxu.edu.cn
杨和见, 任宝光, 陈小鹏, 王琳琳, 梁杰珍, 张众尧. 氢化松脂体系汽液平衡测定与关联 [J]. 高校化学工程学报, 2023, 37(5): 858-862.
:YANG Hejian, REN Baoguang, CHEN Xiaopeng, WANG Linlin, LIANG Jiezhen, ZHANG Zhongyao. Determination and correlation of vapor-liquid equilibrium ofthe hydrogenated pine resin system [J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Chinese Universities, 2023, 37(5): 858-862.

