Bibliometric analysis of research relating to refractive cataract surgery over a 20-year period: from 2003 to 2022
Xiao-Yong Chen, Qian-Ru Wu, Min-Yue Xie, Di Zhang, Chun Zhang
1Department of Ophthalmology, Beijing Key Laboratory of Restoration of Damaged Ocular Nerve, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
2Beijing Tongren Eye Center, Beijing Tongren Hospital,Beijing Institute of Ophthalmology, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100730, China
Abstract
● KEYWORDS: bibliometric analysis; cataract surgery;refractive cataract surgery; corneal astigmatism
INTRODUCTION
Instead of blindness prevention, modern cataract surgery has entered the era of refractive surgery.Nowadays,patients undergoing cataract surgery not only expect vision improvement, but also spectacle independence.These high expectations increase the demand for surgeons to provide patients with better visual quality by minimizing postoperative refractive errors[1].Refractive cataract surgery includes precise preoperative measurement, individualized intraocular lens(IOL) power calculation, functional IOL selection, precise surgical techniques, and postoperative visual function analysis[2-4].
Accurate preoperative measurements for IOL formula calculations are the prerequisite for refractive cataract surgery[5].With the continuous innovation of measurement technology, we can make precise measurements such as the cornea curvature, the axial length, and the depth of the anterior chamber to obtain more accurate IOL power.For decades,we have only used topographic measuring equipment for corneal power.However, with the development of Placido disk technology and Scheimpflug photography[6-7], the impact of posterior corneal astigmatism has been realized.These technologies help a refractive surgeon assess anterior and posterior corneal power, pachymetry, and IOL power more accurately[8-9].Based on optical principles, biometers such as IOL master can measure various ocular parameters avoiding compressing and underestimation.Accurate preoperative measurements can help us obtain better optical results and can provide a variety of IOL calculation formulas, which optimize achieving the best refractive outcomes[10-13].
An individualized selection of functional IOLs can better meet the requirements of patients.In recent years, functional IOLs have found an increasingly wide utilization.Functional IOLs mainly include aspheric IOLs to correct high-order aberrations, Toric IOLs to correct corneal astigmatism, and multifocal IOLs.Among the high-order aberrations, spherical aberration has a great impact on visual quality[14].Aspherical IOLs reduce the inherent positive spherical aberration by reducing the curvature of the peripheral optical zone,thereby reducing the total spherical aberration of the eye and improving postoperative visual quality[15].Among all cataract patients, approximately 35% to 40% have cornea astigmatism above 1 D[16], which creates a great influence on postoperative visual quality[17].Toric IOLs are intended to correct preexisting regular corneal astigmatism ranging from 0.75 to 4.75 D,which provides patients with optimum distance vision[18].Multifocal lenses, by definition, separate light into different foci, and thus cause a dispersion of the energy of the light entering the eye[19].Multifocal IOLs implantation can provide a satisfactory solution for good vision at different distances.Compared with monofocal IOLs, multifocal IOLs can bring better vision and improve the quality of life[20].
The improvement of surgical technology has greatly improved the precision of the operation, reduced the occurrence of surgical complications, and laid a foundation for the development of refractive cataract surgery.In recent years, the development of micro incisions, together with advanced phacoemulsification tips and systems, cataract surgery complications, such as bleeding, iris prolapse, and anterior chamber instability,have been greatly reduced and the efficiency of surgery have been greatly improved[21-24].Corneal astigmatism can be corrected by the on-axis incision method in cataract surgery[25].With the development of surgeons’ techniques as well as corneal incision size, induced corneal astigmatism has been minimized[26], which reduces the occurrence of higher-order aberrations at the same time[27].A continuous curvilinear capsulotomy (CCC) reduces the occurrence of posterior capsule opacity, ensures the centering and stability of the IOL,and reduces the off-center and rotation of IOL, which ensures the optical effect of IOL[28].Femtosecond laser-assisted cataract surgery uses a femtosecond laser to create incisions and CCC,making cataract surgery more sophisticated[29].

Figure 1 The search strategy and screening procedure of publications about refractive cataract surgery in Web of Science database.
Bibliometrics uses quantitative methods to evaluate academic productivity.Bibliometrics analyzes the quantity and quality of publications and describes the development of a certain field[30].Based on the statistical results, it can assist in clinical decision-making, formulating clinical guidelines,and research trends[31-32].The current study aims at presenting a comprehensive analysis of the current status of refractive cataract surgery research based on Web of Science data.Bibliometric methods are applied to reveal the research trend of refractive cataract surgery and explore its potential research hotspots.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Data Source and Research StrategyThe current study conducted a comprehensive literature search from 2003 to 2022 using the Science Citation Index-Expanded of Thomson Reuters’ Web of Science database, which has been considered the most appropriate database for performing bibliometric analysis.This study was performed in the Department of Ophthalmology, Peking University Third Hospital.All searches were conducted on January 18, 2023 to avoid bias due to the rapid database renewal, and a single author manually reviewed and categorized the publications.The following search strategies were used: (TI=cataract OR AK=cataract) AND TS=[surgery AND (astigmatism OR toric OR astigmatic OR surgical induced astigmatism OR wavefront OR curvature OR keratometry OR aberration OR topography OR refractive-surgery OR multifocal-intraocular-lenses OR corneal-relaxing-incisions OR myopia OR hyperopia OR ametropia OR microincisions OR presbyopia OR femtosecond OR femtocataract OR femtolaser)].Additionally, document types were limited to original articles and reviews in the core database.The search strategy and screening procedure were illustrated in Figure 1.

Figure 2 Contributions to the refractive cataract surgery research of different countries A: The total number of publications published each year and the number of publications of the top 3 countries were shown in the histogram.The fluctuation of relative research interest was shown in the line chart.B: Publications, citations (×0.05), and H-index (×5) of the top 20 countries.
Data Collection and Bibliometric AnalysisData from the included publications, such as titles, keywords, authors and institutions, publication countries, journals, the sum of citations, and H-index, were collected from the Web of Science database.Quantitatively and qualitatively of the publications were analyzed through Microsoft Excel 2019 (Redmond,USA), GraphPad Prism 6 (GraphPad Prism Software Inc.,CA, USA), VOSviewer (Leiden University, the Netherlands),and CiteSpace V5.5.R1 SE, 64bit (Drexel University,USA).Relative research interest (RRI), which represented the proportion of publications about a certain field in the publications of all fields, impact factor (IF) and H-index were extracted through Web of Science tools to the characteristics of the enrolled publications[33].Publication trends were predicted through a model: f(x)=ax3+bx2+cx+d, based on which the cumulative number of publications was calculated.VOSviewer was used to build a visualized network, using the Keyword Plus from WOS.Keywords were classified and colored into disparate clusters according to co-occurrence analysis and time-course.The line between words represented that the two words appeared in the same paper.The novelty of a certain keyword related to refractive cataract surgery was analyzed by average appearing year (AAY) through VOSviewer.Keywords with the strongest citation bursts were analyzed by CiteSpace.
RESULTS
Annual Number and Distribution of PublicationsA total of 2090 publications met the inclusion criteria.As it was shown in Figure 2A, from 2003 to 2023, the USA contributed the most publications (434, 20.8%), followed by China (345, 16.5%)and England (163, 7.80%).Over the past two decades, the total number of publications each year was increasing by year,and the number of articles published about refractive cataract surgery was the most in the year 2021.Since 2003, the United States had been publishing the most articles each year.Not until 2005 did China published the first article in this field, and no related papers were published in the following two years.Since 2014, the number of articles that Chinese researchers published in this field has increased at a surprising rate each year.And since 2015, China has risen to a rank of second in the number of publications.Global attention towards this field has gradually increased.RRI fluctuated between 0.003% to 0.006% before 2013, while went up to 0.007% and 0.009%from 2014 to 2022 (Figure 2A).
Distribution of Co-citations and H-indexAll publications related to refractive cataract surgery were cited 33 752 times since 2003 (23 530 citations without self-citations) and the average citing time for each paper was 16.15.Publications from the United States were cited more frequently than those from other countries (9552 citations and 8975 citations without self-citations), with the highest H-index of 48.Although China ranked second in the total number of publications, the papers were not cited that frequently (3237 citations and 2882 citations without self-citations), and the H-index ranked the sixth (H-index=29).England ranked second in total citations at 4442 citations (4236 citations without self-citations), with an H-index of 36 (Figure 2B).
Distribution of Publication Growth TrendsThe fitting curves demonstrate publication growth for refractive cataract surgery research.The cumulative number of publications in global, USA, China, and England were positively correlated with time (Figure 3).Publication trends for the following years could be estimated based on this model.We found that the growth of global publications increased slowly, which could also be found in several major countries, such as the United States and England (Figure 3A, 3B, 3D).Compared to other countries, China showed a faster publication growth in this field since 2015 (Figure 3C).
通过建设卫生厕所所产生的生活污水经过化粪池预处理后排入沿着村庄主路布置的排水管网,最终在排水一体化污水处理设施统一处理,处理达到一级B标准后排至沟渠。
Distribution of Journals Publishing ResearchMore than two-thirds of the papers were published in the top 20 journals (1396, 66.8%; Figure 4A).Journal of Cataract and Refractive Surgerypublished the most papers (333, 15.9%),followed byClinical Ophthalmology(104, 4.98%).European Journal of OphthalmologyandJournal of Refractive Surgery,with 96 (4.59%) and 81 (3.88%) publications respectively,ranked third and fourth.Other high-impact journals, such asOphthalmology, contributed 50 publications, and theAmerican Journal of Ophthalmology, published 48 articles over the past two decades.

Figure 3 The fitting curves of publications growth trends about refractive cataract surgery research A: Global; B: The United States; C: China;D: England.

Figure 4 Distribution of journals and institutions relating to refractive cataract surgery A: The top 20 journals distributed the most research in this field; B: The top 25 institutions distributed the most research in this field.
Distribution of Main Research InstitutionsThe University of London had the highest number of publications on refractive cataract surgery (75, 3.59%), followed by the University of California System (57, 2.72%).Within the top 25 institutions,there were five American institutions and nine European institutions.Of note, three Chinese institutions were listed in the top 20, of which Fudan University ranked sixth (44,2.11%), Sun Yat-Sen University ranked seventh (36, 1.72%),and Zhejiang University ranked thirteenth (31, 1.45%; Figure 4B).
Distribution of Authors and the High-Cited PapersThe top 15 authors contributed 348 publications, accounting for 16.7% of all literature.Dick HB from Ruhr University Bochum published the most the top ten authors, followed by Alio JL, from Universidad Miguel Hernandez De Elche (Table 1).Notably, among the top ten authors, 4 are from China.Lu Y from Fudan University, ranked third, with 34 publications over the past two decades, and Yao K, from Zhejiang University,ranked sixth with 20 works.Zhu XJ from Fudan University with 19 publications ranked eighth followed by Chen WR from Sun Yat-sen University with 17 papers.The top 10 highcited papers related to refractive cataract surgery were shown in Table 2.The most cited paper was from Thomas Olsen,published inActa Ophthalmologica Scandinavica, which was cited 386 times.

Figure 5 Analysis of keywords on refractive cataract surgery A: Mapping of the keywords on refractive cataract surgery; B: Distribution of keywords according to the average appearance time.
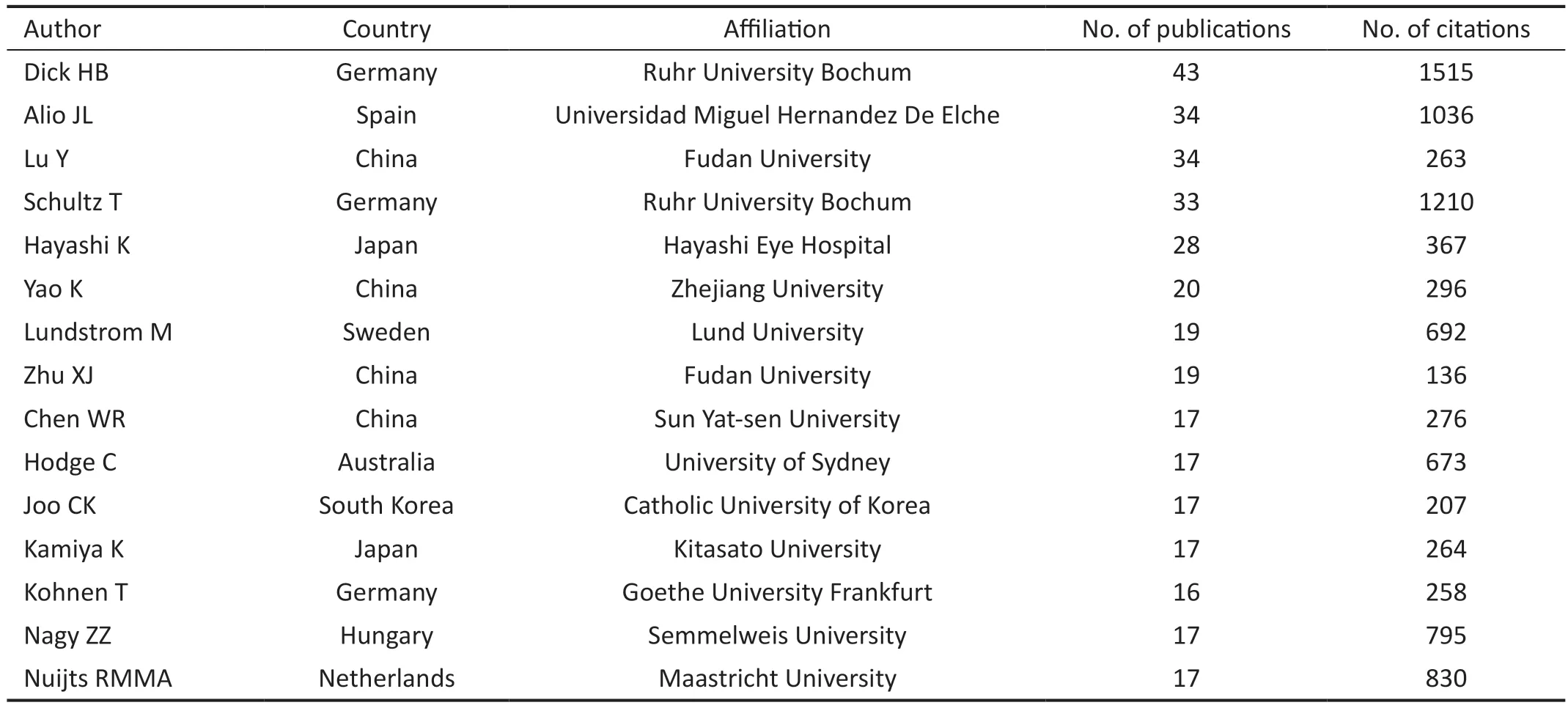
Table 1 Top 15 authors with the most publications in refractive cataract surgery
Analysis of Co-occurrence of Keywords on Refractive Cataract SurgeryAccording to VOSviewer, 139 keywords were classified into four clusters: corneal astigmatismrelated research, cataract surgery methods-related research,postoperative visual-quality relate to research, and postoperative complications-relate research (Figure 5A).Within the astigmatism-related research cluster, the keywords “corneal astigmatism” was mentioned 111 times, and the word“accuracy” appeared 118 times.Regarding the cataract surgery method-related research cluster, phacomulsification(339 times) and femtosecond laser (56 times) were frequently mentioned.In the postoperative visual-quality-related research cluster, keywords including “astigmatism” (140 times),“contrast sensitivity” (105 times) and performance (108 times)were frequently mentioned.In the postoperative complicationsrelate research clusters, keywords including refractive error(26 times) and children (55 times) were frequently mentioned.In addition, keywords were colored according to the AAY,representing the time when the keywords appeared (Figure 5B).Keywords shown in blue appeared earlier, such as children (2013.8) and contrast sensitivity (2013.6).Keywords shown in yellow appeared more recently, such as femtosecond laser (AAY of 2017.1) and posterior corneal astigmatism (AAY of 2019.3).
DISCUSSION
From the current study, it can be demonstrated that the United States and China ranked first and second respectively in the total number of publications in the research field related to refractive cataract surgery.The United States has contributed the most, which can be seen from the number of papers published, the frequency of citations, and the H-index.Since 2003, American scholars have got ahead of others in thenumber of publications.This may be related to the superior conditions and advanced equipment of basic medical research and clinical trials in the United States.As shown by the time curve, since 2005, we have observed a rapid increase in the number of cumulative publications related to refractive cataract surgery worldwide.Since 2003, the annual number of publications in the United States and the United Kingdom has shown steady growth, but the number of publications related to this field in China has revealed rapid growth.This may be related to the development of research conditions in China.In the past ten years, people’s requirements for visual quality have become higher.Patients not only require “seeing”, but also“seeing well”.They are hoping to improve their quality of life through cataract surgery.By 2020, the number of publications in this field in China exceed that of the United States for the first time, accounting for one-fifth of the global number of publications, indicating an important contribution of Chinese scholars in this field.
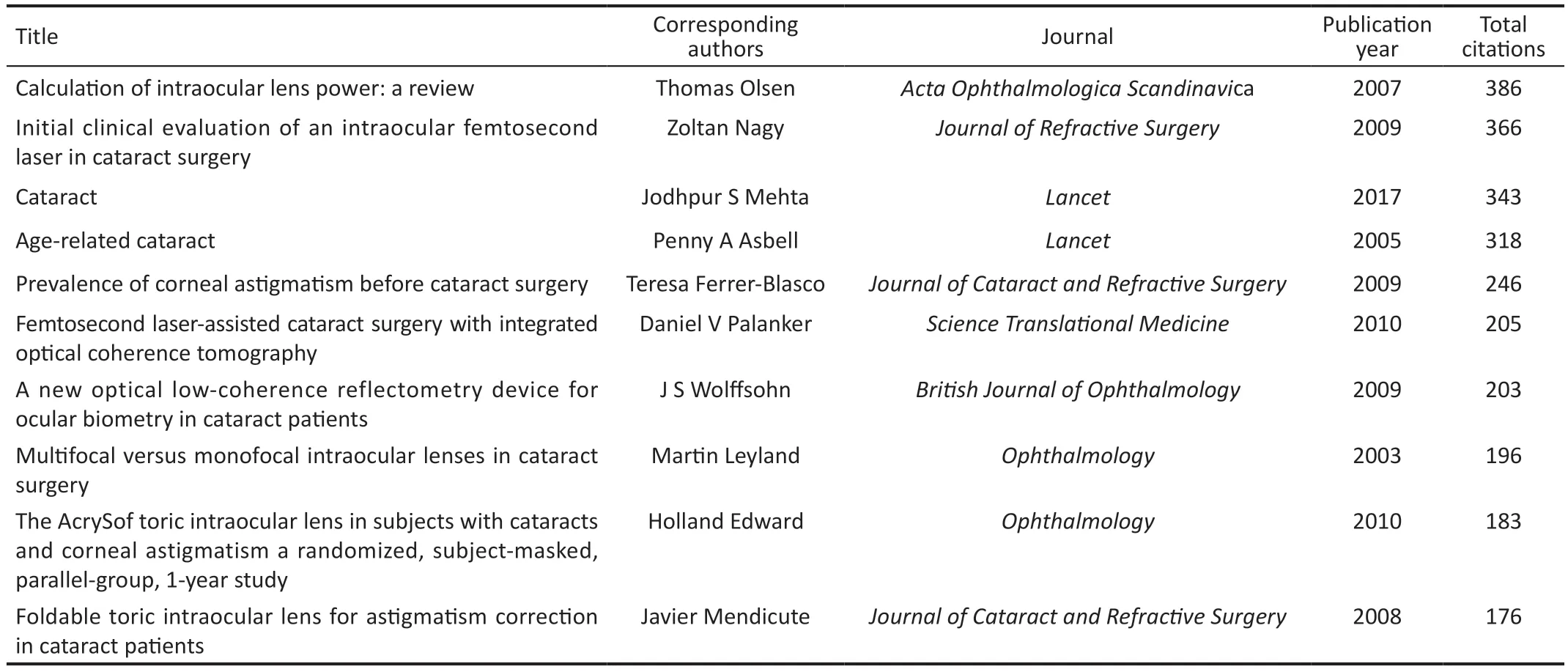
Table 2 Top 10 high-cited papers related to refractive cataract surgery
To note, China ranks second in the total number of publications but ranks sixth in both the sum of citations and the H-index.There may be several reasons for the contradiction between the quantity and quality of Chinese publications.First, China published the first article related to this field in 2005, but it was not until 2015 that the number of papers published related to this field began to increase with the years.Second, cataract is still the leading cause of reversible blindness in China[34-35].Although in cities, with high requirements for visual quality,cataract surgery has entered an era of refractive surgery instead of blindness prevention[36], in rural areas, cataract is still aimed to recover eyesight.Third, the lack of high-quality multi-center randomized clinical trials, and the uneven scientific research level in various institutions also result in this contradiction.Despite the rapid increase in the number of publications in this field in China, the quality of the papers still needs to be improved.
Journal of Cataract and Refractive Surgeryhas published 333 papers in this field, far ahead of other journals.Highscoring journals in the field of ophthalmology include theBritish Journal of Ophthalmology, theAmerican Journal of Ophthalmology,and theOphthalmology.Although most of the journals are ophthalmic research journals, theJournal of Cataract and Refractive Surgeryis dedicated to the area of cataract and refractive surgery[37].Therefore, this indicates that future developments in this field may appear in this journal.
Among the top 20 institutions in the field of refractive cataract surgery, there were five American institutions.This partly explains why the United States has always contributed the most scientific achievements in this field.However, the institution that publishes the most articles in this field (the University of London) belongs to England.It is worth noting that China has three institutions among the top 20 institutions, indicating that Chinese research institutions play an important role in this field.China’s large population is conducive to large-sample clinical trials, making the data more authentic and complete,and more conducive to make a breakthrough in this field.
As for the authors, Dick HB from Germany, Alio JL from Spain, Lu Y from China, Schultz T from Germany, and Hayashi K from Japan, ranked top 5 in the number of the publications related to refractive cataract surgery.Studies[38-40]mainly focus on femtosecond cataract surgery, including dry eye after femtosecond laser-assisted cataract surgery and posterior capsule opacification after femtosecond cataract surgery.The published articles are also ranked first in the sum of citations, indicating that femtosecond cataract surgery is a hot area of refractive cataract surgery.Oliveiraet al[41]and Alioet al[42]mainly studies visual quality after functional IOL implantation.Hayashiet al[43-45]focuses on the influence of corneal astigmatism on refractive cataract surgery, including changes in corneal astigmatism caused by different incision positions and lengths of the incisions, and the influence of age on corneal astigmatism after cataract surgery.Menget al[46]and Zhuet al[47]is committed to studying the factors that affect visual quality after a cataract combined with high myopia, such as the application of multifocal IOLs in high myopia eyes, and proposed dome-shaped macula may be a protective factor for visual function after cataract surgery in highly myopic eye.The academic achievements of these researchers play a unique and indispensable role in this field, which will widely influence future development and continue to guide future research and clinical treatment in this field.
In the current study, we list the top ten most cited papers relating to refractive cataract surgery.The more citations, the more academic impact higher the publication has in this area.The paper entitled “Calculation of intraocular lens power:a review” has been cited 386 times since its publication,which was mainly about the principles and practices in the calculation of IOL power.This paper also emphasizes the importance of accuracy in the estimation of corneal power[48].The second paper on the list is an article from Nagyet al[49],which was the first evaluating the lens fragmentation and anterior capsulotomy with femtosecond cataract surgery and found that higher precision of capsulorhexis and reduced phacoemulsification power during the surgery.A review named “Age-related cataract” published inLancetranked third and was cited 318 times.This review demonstrated the epidemiology, etiology, risk factors, surgical management, and complications of cataracts and conducted a systematic review of cataract-related papers.
As shown in the current study, the trend of research hotspots transferred mainly from the basic surgical techniques to new technologies and pay more attention to the postoperative visual outcome.Femtosecond laser-assisted cataract surgery as a new cataract surgery method has become to be the latest hotspot.Nagyet al[49]reported the first case of femtosecond laserassisted cataract surgery.Compared with traditional cataract surgery, femtosecond laser-assisted cataract surgery improves the stability of capsulotomy and IOL implantation and reduces postoperative astigmatism[50].The femtosecond laser is mainly used for anterior lens capsulotomy, laser nucleus fragmentation,and astigmatism management.The femtosecond laser can accurately determine the diameter of the capsulorhexis, and create CCC, which can make a more centered and more circular opening, thereby avoiding the complications related to capsulorhexis to the greatest extent[51-52].By segmenting the nucleus, femtosecond laser-assisted cataract surgery can reduce thermal or ultrasound energy and in turn protect the corneal endothelium[53].Pajicet al[54]found that femtosecond laser-assisted cataract surgery could provide a reproducible capsulotomy and highly effective lens nucleus technology,which could bring good postoperative visual acuity and surgical safety.Femtosecond laser-assisted keratotomies can precisely align the incision with the astigmatism axis and flatten the steepest meridian of corneal astigmatism effectively.Robertset al[55]reported that femtosecond laser-assisted keratotomies achieved a higher correction index and a smaller difference vector, and less postoperative cylinder.
Besides cataract surgery method, corneal astigmatism,postoperative visual acuity and postoperative complications methods are the research focus in this field.Astigmatism can have a great impact on visual function.There are several ways to correct astigmatism during cataract surgery: Toric IOL implantation, corneal incisions on the steep axis of astigmatism, or manual peripheral corneal relaxing incisions,etc[56].Intraoperative astigmatism management improves surgical outcomes and brings better visual quality.The emergence of functional IOLs promotes the development of refractive cataract surgery.Aside from Toric IOLs, functional IOLs also include an aspheric IOL and a multifocal IOL.
With the application of a multifocal IOL, better-uncorrected distance visual acuity and spectacle independence attract more attention.However, complications may affect the patient’s quality of life and level of satisfaction, such as glare,halo, or starbursts[57].Now studies have been focusing on improving visual quality after multifocal IOL implantation,such as aberration-correcting, measurement of kappa angle,and avoiding IOL tilt[58-60].However, despite advances in preoperative measurement technology, refractive errors still may occur for a variety of reasons, such as high myopic,congenital cataracts, post-corneal refractive surgery,etc[61].To reduce the postoperative refractive error, pre-enhancement measurements should be applied.As technology has advanced,we can measure the axial length, intraocular wavefront aberrometry, and IOL power by optical biometers such as IOL master or swept-source optical coherence tomography technology[11-12,62].In addition, the corneal power can not only be assessed by a keratometer but can also be by Placido disk-based device or Ray Tracing device[63-65].Also, advance IOL power calculations such as Barrett Universal II, Barrett True-K, Olsen Formular, and Emmetropia Verifying Optical(EVO) Formula perform better refractive outcomes[66-67].The development of preoperative measurements will help achieve the better visual outcomes, avoid refractive errors.
A number of articles and reviews about cataract surgery have been published these years, but none of the publications carried out bibliometric analysis.Publications on refractive cataract surgery are extracted from the Web of Science database and the data analysis is comprehensive and objective.And to the best of our knowledge, this study was the first that provided a comprehensive analysis on the publications of refractive cataract surgery and predicted the future hot spots.Nonetheless, there are some limitations.We selected the publications in recent 20y; however, the database is updated frequently, and the latest publications are not included.And we only enrolled publications written in English, so some important research published in other languages is inevitably overlooked.
The current study demonstrates global trends in research related to refractive cataract surgery.According to the bibliometric analysis, the authors and institutions contribution,publication countries, journals, the sum of citations, and H-index, and the keywords of the latest hotspot were shown.It is worth noting that China has risen to a rank of second in the number of publications.And China has three authors among the top 15 authors and three institutions among the top 20 institutions, indicating that Chinese research institutions play an important role in this field.This study also shows that corneal astigmatism, cataract surgery method, postoperative visual-quality and postoperative complications relate researches has become the emerging hotspots, which can give a direction in the future researches.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Authors’ contributions:ChenXY contributed to the ideas and design of the study.Wu QR and Zhang D collected data.Xie MY helped in the statistical analysis.Wu QR drafted the manuscript.Chen XY and Zhang C reviewed and revised the manuscript.All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Foundations:Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.82201145); the Hygiene and Health Development Scientific Research Fostering Plan of Haidian District Beijing (No.HDCXZHKC2021212).
Conflicts of Interest: Chen XY,None;Wu QR,None;Xie MY,None;Zhang D,None;Zhang C,None.
 International Journal of Ophthalmology2023年10期
International Journal of Ophthalmology2023年10期
- International Journal of Ophthalmology的其它文章
- A novel approach for 25-gauge transconjunctival sutureless vitrectomy to evaluate vitreous substitutes in rabbits
- Visual resolution under photopic and mesopic conditions in patients with Sjögren's syndrome
- Effects of obstructive sleep apnea on retinal microvasculature
- Three-dimensional bioprinting in ophthalmic care
- Agreement of intraocular pressure measurement with Corvis ST, non-contact tonometer, and Goldmann applanation tonometer in children with ocular hypertension and related factors
- A combined treatment for patients with dry eye and associated laryngopharyngeal reflux: a real-life approach
