嗜黏蛋白艾克曼菌在防治糖尿病中的作用研究进展
杨玥 吴晓康
摘要:腸道菌群与疾病的相关性成为近年来的研究热点,糖尿病的发病与慢性低度炎症及肠道菌群失调密切相关,干预肠道菌群失调成为目前预防及治疗糖尿病的研究热点。嗜黏蛋白艾克曼菌(Akkermansiamuciniphila,A.muciniphila)可通过改善肠道屏障功能、抑制机体慢性炎症、上调血糖调节相关激素如胰高血糖素样肽-1(GLP-1)水平等作用机制改善糖尿病相关症状,是预防及治疗糖尿病的潜在靶点。A.muciniphila丰度降低还是糖尿病早期诊断的标志。目前研究表明单独运用A.muciniphila后糖尿病患者机体炎症状态等相关症状明显改善,且已有研究显示人体对A.muciniphila有较好的安全性和耐受性。因此,A.muciniphila可作为一种潜在的新型益生菌治疗糖尿病。临床上用于治疗糖尿病的措施如二甲双胍、中医药及功能性饮食等的作用机制均发现与A.muciniphila丰度升高有关,其中中医药治疗糖尿病效果显著,具有多靶点、多途径、系统性等优势。研究发现A.muciniphila是中药干预糖尿病的潜在靶点,中药干预后,糖尿病相关指标改善与A.muciniphila丰度呈正相关。以上证据为研究中医药与肠道菌群相互作用从而治疗糖尿病的作用机制提供了新的思路。本文综述了嗜黏蛋白艾克曼菌在糖尿病防治中的作用及其与中医药防治糖尿病的相关性,以期为糖尿病预防及治疗提供新举措。
关键词:嗜黏蛋白艾克曼菌;糖尿病;中医药;作用机制
中图分类号: R587.1 文献标志码: A 文章编号:1000-503X(2023)01-0108-09
DOI:10.3881/j.issn.1000.503X.14497
Research Progress on the Role of Akkermansia Muciniphila in Prevention and Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus
YANG Yue1,WU Xiaokang2
1Xinjin District Peoples Hospital,Chengdu 611430,China
2Clinical Laboratory,The Second Affiliated Hospital of Xian Jiaotong University,Xian 710004,China
Corresponding author:WU Xiaokang Tel:029-87679358,E-mail:wxk111506@sohu.com
ABSTRACT:The correlation between intestinal flora and diseases has become a hot research topic in recent years.Since the incidence of diabetes is closely related to chronic low-grade inflammation and intestinal flora disorders,the intervention of intestinal flora imbalance has become a research focus in the prevention and treatment of diabetes mellitus.Akkermansia muciniphila(A.muciniphila) stands out among the intestinal flora as it can alleviate the diabetes-related symptoms by regulating glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) level,improving intestinal barrier function,and inhibiting chronic inflammation,which is a potential target for the prevention and treatment of diabetes.The reduction in the abundance of A.muciniphila is a marker for the early diagnosis of diabetes.The available studies have demonstrated that the administration with A.muciniphila alone can significantly attenuate inflammation and other related symptoms of diabetic patients.Moreover,A.muciniphila has good safety and can be tolerated by human body.Therefore,A.muciniphila has the potential to serve as a new species of probiotics for the treatment of diabetes.The clinical measures for treating diabetes,such as metformin,Chinese herbal medicines,and functional diet,have been confirmed to be associated with the increased abundance of A.muciniphila.Among them,Chinese herbal medicines can treat diabetes via multiple targets and pathways in a systemic manner.Studies have reported that A.muciniphila is a potential target of Chinese herbal medicines intervening in diabetes.After the administration of Chinese herbal medicines,the improvement of diabetes-related indicators was positively correlated with the abundance of A.muciniphila.The above evidence provides a new idea for the research on the interaction between Chinese herbal medicines and intestinal flora in the treatment of diabetes.Therefore,this paper reviewed the role of A.muciniphila in diabetes and the correlation between the abundance of A.muciniphila and the administration of Chinese herbal medicines,aiming to provide new measures for the prevention and treatment of diabetes.
Key words:Akkermansia muciniphila;diabetes;traditional Chinese medicine;mechanism of action
Acta Acad Med Sin,2023,45(1):108-116
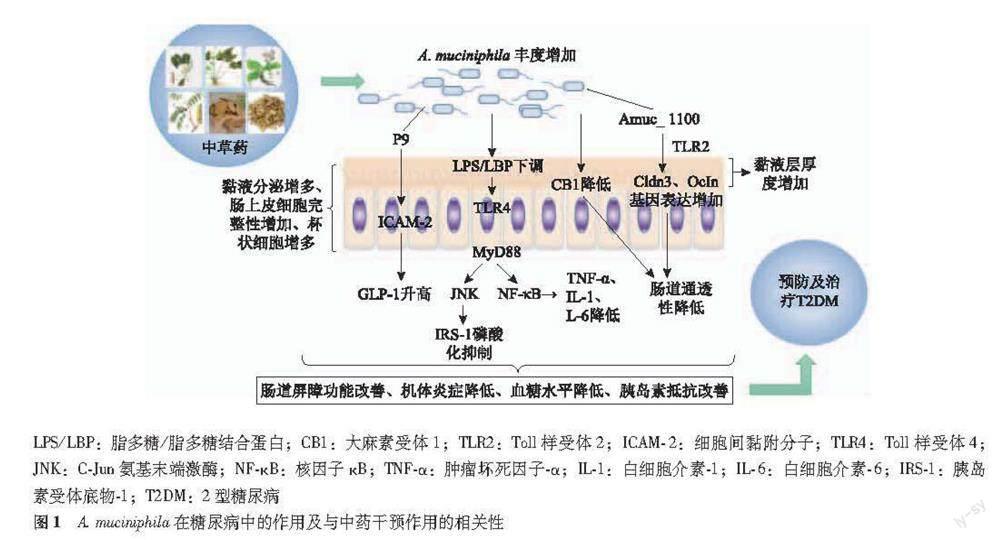
糖尿病是以胰島素抵抗和胰岛素分泌不足为主要特征的代谢性疾病。据国际糖尿病联盟最新报道,2019年全球糖尿病患病率预计为9.3%(4.63亿人),其中2型糖尿病(diabetes mellitus type 2,T2DM)占90%[1]。糖尿病患者与日俱增,对社会造成极大危害,它是成人十大死亡原因之一,占全球死亡人数的11.3%[2]。糖尿病的上升趋势可归因于城市化快速发展,不均衡饮食、久坐等因素的影响。因此,加强糖尿病的预防及探寻有效的治疗措施尤为重要。肠道菌群是与人类和谐共存的微生物,并在调节宿主的代谢、免疫等生理过程中发挥重要作用[3]。大量研究表明肠道菌群与T2DM的生理病理过程密切相关,如肠道菌群失调参与葡萄糖代谢、破坏肠道屏障功能、诱发机体慢性低度炎症、诱导短链脂肪酸及胆汁酸代谢紊乱等[4-6]。在42项关于人类T2DM和肠道菌群关系的研究中,较一致的报道了双歧杆菌属(Bifidobacterium)、拟杆菌属(Bacteroides)、粪杆菌属(Faecalibacterium)、艾克曼菌(Akkermansia.Muciniphila,A.muciniphila)和玫瑰菌(Roseburia)丰度与糖尿病呈负相关[7]。近年研究发现A.muciniphila可通过改善肠道屏障功能、抑制慢性炎症和调节机体代谢,改善糖尿病症状,是一种改善T2DM症状的潜在益生菌。事实上,许多目前用于治疗糖尿病的措施如膳食多酚、二甲双胍和中医药治疗糖尿病的作用机制均与A.muciniphila丰度增加密切相关[8-11]。此外,单独补充A.muciniphila可显著改善T2DM症状,甚至可抑制饮食诱导的肥胖等相关代谢症状[12-13]。中医药防治糖尿病具有多靶点、多途径、系统性等得天独厚的优势[14],大量动物和人类研究表明,中医药可通过调控肠道菌群失调改善糖尿病相关症状。最近研究表明中药活性成分及中药复方均可增加糖尿病患者A.muciniphila的丰度,且A.muciniphila丰度增加与血糖水平、葡萄糖耐量和胰岛素抵抗改善呈正相关,表明A.muciniphila是中医药治疗糖尿病的潜在靶点[15-19]。A.muciniphila不仅是预防及治疗糖尿病的潜在靶点,在T2DM病发前可以检测到A.muciniphila丰度降低,有助于T2DM早期诊断和干预[20-23]。A.muciniphila还有潜力作为预防及治疗糖尿病的新型益生菌,现已经实现了A.muciniphila作为下一代新型益生菌的重要步骤,发现通过巴氏杀菌不仅可提高其效果,还可以提高其稳定性和有效期,临床研究表明人体对A.muciniphila有较好的安全性和耐受性且A.muciniphila可改善人体多种代谢参数,A.muciniphila与宿主相互作用的机制也正在被阐明[20,24-27]。本文综述了A.muciniphila在糖尿病中的作用及与中药干预作用的相关性(图1)。
基因组测序表明,其许多基因编码黏蛋白降解酶[31]。A.muciniphila可产生60多种酶,包括糖苷酶、硫酸酯酶和唾液酸酶,它们降解寡糖链以适应富含黏液和内源性糖蛋白的生活环境[32]。Van Herreweghen等[33]研究了黏蛋白、A.muciniphila和肠道菌群之间的相互作用关系,结果显示黏蛋白是影响肠道菌群组成和代谢的重要调节剂,在受控的体外肠道菌群生态系统模型中添加黏蛋白可成功诱导肠道微生物群的组成和代谢变化,包括A.muciniphila、Ruminococcus、Clostridium clusterⅩⅣa菌群丰度增加。A.muciniphila不是严格的厌氧菌,而是对氧敏感的厌氧菌,这是它与其他厌氧菌竞争的优势[34]。因此A.muciniphila的定植并不严格依赖于饮食,具有独特的生存优势。A.muciniphila具有降解代谢黏蛋白产生乙酸和丙酸的特异性,可为其他肠道菌群生长提供营养[35],促进肠道菌群组成及结构的形成。同时A.muciniphila能促进黏蛋白的分泌。黏蛋白是A.muciniphila生长代谢的主要基质,由肠道上皮杯状细胞分泌,Kim等[36]研究表明A.muciniphila代谢产生的乙酸和丙酸可能是使分泌黏蛋白的杯状细胞成熟的关键因素。因此A.muciniphila在肠道菌群稳态和“宿主-肠道菌群”相互作用中所扮演的角色值得探索。
A.muciniphila与糖尿病的关系
T2DM的特征是在遗传背景、环境因素(如饮食习惯)和肠道菌群三者相互作用下诱导的胰岛素抵抗和血糖升高。越来越多的证据表明,肠道微生物群通过调节能量平衡、葡萄糖代谢和与肥胖相关的慢性炎症状态,在体内代谢平衡中起着决定性作用[37-38]。A.muciniphila是肠道菌群的核心菌群之一[39]。研究表明,A.muciniphila与人体健康有着紧密的联系,其丰度降低与T2DM、肥胖等代谢性疾病密切相关[22,40-41]。Hnninen等[42]研究发现糖尿病的高发病率与A.muciniphila缺乏有关,将A.muciniphila转移至小鼠肠道可降低小鼠糖尿病的发病率。众多动物和人类的研究表明,糖尿病患者肠道菌群中A.muciniphila菌群丰度降低[23,43]。一项研究表明,健康人肠道菌群中疣微菌门(Verrucomicrobia)丰富度较高,Verrucomicrobia是健康人的特征菌群,而A.muciniphila是这个门中唯一被鉴定的成员[39]。此外,Ahmad等[44]对T2DM患者肠道菌群特征进行分析发现,Verrucomicrobia在T2DM患者中较少甚至完全缺失,意味着A.muciniphila在T2DM中丰富度降低甚至完全缺失。Shih等[22]招募了79例患有T2DM和难治性糖尿病的患者,用线性判别分析效应大小和热图对肠道菌群操作分类单元进行了分析,结果在T2DM患者中发现了几种潜在的微生物标志物,其中包括A.muciniphila,还发现A.muciniphila的相对比例与糖化血红蛋白(HbA1c)呈显著负相关。
此外,研究表明目前预防和治疗糖尿病的措施与A.muciniphila丰度增加相关。例如,补充穿心莲内酯可通过增加小鼠A.muciniphila的丰度改善糖尿病小鼠的葡萄糖不耐受和胰岛素抵抗,甚至可预防db/db小鼠发生T2DM[11]。Régnier等[45]研究发现与对照组相比,补充大黄可以增加A.muciniphila丰度,预防高脂肪和高蔗糖饮食诱导小鼠肥胖和糖尿病的发生。单独补充A.muciniphila也可对机体产生有益作用。Plovier等[20]用A.muciniphila处理小鼠发现其可以降低高脂饮食(high-fat diet,HFD)喂养小鼠甘油三酯的浓度,纠正HFD诱发的高胆固醇血症,改善血脂异常、葡萄糖不耐受和胰岛素抵抗,巴氏杀菌后的A.muciniphila效力增加,上述作用更强。口服A.muciniphila的糖尿病大鼠显示肝糖原产生降低,脂多糖(lipopolysaccharide,LPS)水平降低,高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(high density liptein cholesterol,HDL-C)水平升高,肠道菌群的物种α多样性显著增加。大鼠体内群落丰富度和肠道菌群多样性的降低可以通过口服活的或巴氏杀菌的A.muciniphila得到适度恢复,这些结果表明A.muciniphila可以改善肝功能,降低糖/脂毒性,减轻氧化应激,抑制炎症,并使宿主的肠道菌群正常化,从而改善T2DM[41]。Yassour等[21]开展的一项队列研究结果显示,在T2DM病发作前可以检测到肠道菌群的变化,即A.muciniphila的丰度降低先于糖尿病发生。由此可见,A.muciniphila在糖尿病发生发展中发挥重要的作用,同时也是许多饮食、药物治疗糖尿病的中间媒介,而且A.muciniphila的单独补充也可改善糖尿病症状。A.muciniphila可能有助于T2DM早期诊断和干预,是未来治疗T2DM的一个潜在靶点。对促进A.muciniphila生长的药物及益生元的研究,可能为T2DM的预防和治疗提供新策略。但是A.muciniphila改善糖尿病症状的作用机制仍未被完全阐明,探究肠道菌群与宿主间相互作用的机制,也是未来研究的重点。
A.muciniphila改善糖尿病症状的作用机制
肠道菌群失调与糖尿病发病密切相关。以往研究表明,肠道菌群及其代谢产物参与宿主的代谢、机体的免疫调节、维持胃肠道稳态以及影响脑功能与宿主行为[46]。肠道菌群失调在糖尿病发生过程中的作用机制主要是破坏肠道屏障功能,导致机体慢性低度炎症、短链脂肪酸代谢紊乱及胆汁酸代谢失调,从而诱发机体胰岛素抵抗。A.muciniphila在糖尿病防治中发挥的有益作用与改善上述代谢紊乱过程密切相关,近年来发现的A.muciniphila改善糖尿病癥状的相关作用机制如下。
A.muciniphila与肠道屏障功能 肠道屏障主要由机械屏障、化学屏障、免疫及生物屏障构成,能有效阻止外来病原体、毒素和细菌的入侵。机械屏障结构基础为上皮细胞、细胞间紧密连接与菌膜,化学屏障则主要由肠黏膜上皮分泌的黏液构成,黏液层的厚度可调节肠道屏障的通透性。肠道屏障功能受损,肠道通透性增加是诱发T2DM患者代谢性炎症和胰岛素抵抗的关键因素。A.muciniphila定植于肠道黏液外层,可降解黏蛋白为肠上皮细胞及其他肠道菌群供能,还可促进黏蛋白分泌增加黏液层的厚度,维持肠道屏障完整性,降低肠道黏膜屏障的通透性[47]。Amuc_1100是A.muciniphila外膜蛋白最丰富的蛋白质之一,claudin 3、Ocld in是两种肠道紧密连接蛋白,A.muciniphila及Amuc_1100被证明可上调编码紧密连接蛋白的基因Cldn3(编码claudin 3)、Ocln(编码Ocld in)的表达,改善肠道屏障功能,此外,研究还表明Amuc_1100通过Toll样受体(Toll-like receptor,TLR)2信号转导参与A.muciniphila与宿主的相互作用,A.muciniphila的外膜蛋白Amuc_1100通过激活TLR2上调基因Cldn3、Ocln的表达,可见A.muciniphila可以调节包括occludin和claudin 3在内的紧密连接蛋白的表达。与对照组相比,用Amuc_1100处理HFD喂养小鼠,编码大麻素受体1 (Cannabinoid subtype 1,CB1)的Cnr1基因表达降低,说明小鼠CB1降低,而CB1的激活与肠道通透性增加有关,进一步说明A.muciniphila可调节肠道屏障的通透性[20]。一项研究评估了A.muciniphila来源的细胞外小泡(A.muciniphila-derived extracellular vesicle,AmEV)在调节肠道通透性中的作用,发现与T2DM患者相比,健康对照组的粪便样本中有更多的AmEV。此外,给予AmEV增强了糖尿病小鼠肠道屏障的紧密连接功能,减少了体重增加,改善了葡萄糖耐量。还研究了AmEV对人结肠上皮细胞Caco-2细胞的直接作用,发现AmEV通过激活AMP依赖蛋白激酶(AMP-activated protein kinase,AMPK)来调节Caco-2细胞紧密连接蛋白occludin表达,降低Caco-2细胞的屏障的通透性。AmEV以AMPK依赖的方式改善了HFD诱导的糖尿病小鼠的肠屏障完整性[48]。Reunanen等[34]的研究表明,A.muciniphila可显著提高肠上皮细胞Caco-2的单层细胞完整性。另一项研究给予糖尿病小鼠A.muciniphila后观察到葡萄糖不耐受改善和杯状细胞数量的增加,A.muciniphila的丰度和杯状细胞的数量之间呈正相关[49]。Plovier等[20]的研究也表明用A.muciniphila处理糖尿病小鼠,改善了葡萄糖不耐受,降低了胰岛素抵抗指数,且小鼠回肠中杯状细胞密度增加,黏液分泌增多。杯状细胞数量的增加可能是A.muciniphila给药后葡萄糖水平改善的基础[49]。肠上皮细胞是A.muciniphila调节肠道通透性和代谢功能的重要部位。以上研究表明A.muciniphila改善肠道屏障的作用机制为:(1)调节肠道紧密连接蛋白的表达,增强肠道紧密连接的功能:A.muciniphila产生AmEV是有效的AMPK激活剂,激活AMPK途径调节Caco-2细胞紧密连接蛋白occludin表达,增强肠道屏障紧密连接,降低肠道屏障通透性。(2)增加肠道黏液层的厚度:A.muciniphila可促进黏液分泌。(3)调节肠上皮细胞:A.muciniphila可显著提高肠上皮细胞Caco-2的单层细胞完整性,促进杯状细胞成熟。(4)调节与肠道屏障相关基因表达:A.muciniphila使编码紧密连接蛋白基因Cldn3(编码claudin 3)和Ocln(编码Ocld in)表达增加,编码CB1的基因Cnr1表达降低。
A.muciniphila与炎症 LPS又称为内毒素,是革兰阴性菌细胞壁成分,与脂多糖结合蛋白(lipopolysaccharide binding protein,LBP)形成复合物,识别免疫细胞表面的CD14/TLR4 受体后,激活核因子-κB(NF-κB)炎症信号通路,引发促炎因子如白细胞介素(interleukin,IL)-1、肿瘤坏死因子-α(tumor necrosis factor-α,TNF-α)、IL-6等的分泌,从而导致机体代谢性内毒素血症[50]。糖尿病患者肠道菌群特征是革兰阳性菌/革兰阴性菌比例失调,革兰阴性菌比例相对升高,因此LPS来源增多。糖尿病患者肠道通透性增加,释放更多LPS进入血液循环,代谢性内毒素血症在体内长期累积形成慢性低度炎症,诱发胰岛素抵抗[38,51]。代谢性内毒素血症的改善可能导致代谢表型的改善,如葡萄糖耐量和体重。因此,干预体内慢性炎症是治疗糖尿病的重要环节。
A.muciniphila对糖尿病炎症症状改善具有显著作用。Zhang等[41]研究表明糖尿病大鼠口服A.muciniphila与二甲双胍具有相同作用,降低了LPS和TNF-α的炎症标志物水平,且A.muciniphila可选择性地促进某些有益菌的生长并减轻全身炎症。有研究表明,小鼠补充A.muciniphila后慢性低度炎症减轻,肝脏和肌肉中LBP和瘦素(leptin)的血浆水平降低,LPS/LBP下游信号失活,例如C-Jun氨基末端激酶(c-Jun N-terminal kinase,JNK)减少,NF-κB抑制剂蛋白和NF-κB抑制剂因子A(IKBA)表达增加,血浆中抗炎因子α-生育酚、β-谷甾醇增加,胰岛素抵抗和葡萄糖耐量改善[13]。LPS触发的炎症级联反应途径中包括NF-κB和JNK激活[52]。其他几项研究也表明A.muciniphila通过抑制LPS 与NF-κB途径中TLR4和TLR2的结合,发挥抗炎作用[53-54]。一种重要的炎症标志物TNF-α的水平升高,在抑制胰岛素信号级联中胰岛素受体底物-1(insulin receptor substrate-1,IRS-1)和蛋白激酶B(Akt)底物的磷酸化中起作用,最终诱导胰岛素抵抗,而有研究发现A.muciniphila可以通过降低TNF-α水平改善机体胰岛素抵抗[55-56]。以上研究为A.muciniphila抑制炎症作用提供了潜在的机制:即A.muciniphila降低LBP水平的同时,还抑制了LPS/LBP下游信号如JNK和NF-κB的表达,表明A.muciniphila可诱导LPS炎症信号通路失活,改善代谢性内毒素血症和随后的局部炎症级联反应。A.muciniphila还可降低炎症因子TNF-α水平,干预胰岛素信号级联通路,改善胰岛素抵抗。
A.muciniphila对GLP-1的调节 胰高血糖素样肽(glucagon-like peptide,GLP)-1,是回腸内分泌细胞分泌的一种脑肠肽,目前主要作为T2DM药物作用的靶点。GLP-1是通过肠岛轴发挥降低血糖,抑制胰岛β细胞凋亡,刺激β细胞复制、新生和分化的作用[57]。A.muciniphila可调节GLP-1和GLP-2的内源性水平,而GLP-1和GLP-2是参与调节葡萄糖代谢和肠道屏障功能重要激素[58]。最新一项研究表明,口服A.muciniphila显著降低了HFD小鼠体重,改善了葡萄糖耐量,增加了胰岛素和β-氧化基因标志物的血清水平,且与血清中GLP-1浓度增高密切相关,A.muciniphila的16S rRNA基因计数与血清GLP-1浓度呈正相关,与葡萄糖不耐受水平呈负相关[59]。其作用机制为:A.muciniphila分泌一种84 kD的蛋白质,命名为P9(该蛋白质也存在于人类A.muciniphila中),P9与细胞间黏附分子(intercelluar adhesion molecule,ICAM) -2相互作用,从而产生级联信号诱导GLP-1分泌,P9对GLP-1的分泌具有特异性作用。此外还发现P9不仅可以诱导GLP-1分泌,还可以诱导IL-6分泌[59]。据报道,运动可诱导IL-6分泌增加,刺激肠L细胞和胰腺α细胞分泌GLP-1,从而促进胰岛素分泌,降低血糖[60]。且P9和IL-6共同促进GLP-1分泌具有累加效应。P9对葡萄糖稳态的影响在IL-6敲除小鼠中被完全消除,表明IL-6对于P9诱导GLP-1分泌及其对葡萄糖稳态的影响是必不可少的。A.muciniphila通过P9从肠道诱导IL-6的分泌,对机体代谢稳态具有有益的作用。以往研究表明,A.muciniphila可在人外周血诱导单核细胞高表达IL-6,改变肠道总GLP-1水平,从而降低胰岛素抵抗的风险[41,54]。这些结果表明A.muciniphila可以促进GLP-1的分泌,改善机体葡萄糖耐量及胰岛素抵抗,对机体葡萄糖稳态发挥有益作用。这可能是A.muciniphila抗糖尿病的潜在机制之一,P9和ICAM-2之间的相互作用可以作为代谢性疾病治疗的潜在靶点。
A.muciniphila在中医药治疗糖尿病中的作用
中医药在中国已有数千年的历史,是中华民族的历史瑰宝。中医药治疗疾病具有得天独厚的优势,其特点为多靶点、多途径、系统性和整体调控[14]。近年来的研究表明,中医药通过调节肠道微生物来改善糖尿病,中医药对糖尿病的作用机制是以“细菌-黏膜免疫-炎症-糖尿病”为中心[61]。肠道菌群与中药之间存在双向作用的关系,中医药起药理作用的活性成分依赖于肠道菌群代谢吸收,同时中药活性成分又调节肠道菌群的组成及结构,大量动物和临床研究表明,许多中药如槲皮素[17]、黄芩[18]、小檗碱[19]等均可增加有益菌A.muciniphila的丰度,而且A.muciniphila在中药治疗糖尿病机制中发挥了有益作用。Régnier等[45]研究发现,喂养高脂肪和高蔗糖饮食的小鼠A.muciniphila的丰度降低,但在补充大黄后A.muciniphila的丰度大幅增加,大黄可能通过刺激A.muciniphila和Reg3γ之间的相互作用来防止病原菌的过度生长,从而预防高脂高糖诱导的疾病。另一项研究表明,补充大黄提取物诱导的A.muciniphila丰度增加,与代谢的改善有关[62]。厚朴酚是厚朴三物汤中的主要生物活性成分,厚朴酚处理糖尿病小鼠可改善小鼠脂质代谢紊乱、系统炎症和胰岛素抵抗,同时肠道菌群中A.muciniphila丰度显著增加,相关性分析结果显示A.muciniphila与体重、甘油三酯、LBP、IL-6呈负相关,这些结果提示厚朴酚可以通过增加肠道中A.muciniphila的丰度来改善糖尿病症状[63]。黄连解毒汤是中医治疗糖尿病的经典方剂,也可使糖尿病小鼠A.muciniphila丰度增加[64]。在金芪降糖片、半夏泻心汤等中药治疗糖尿病的其他多项实验研究中,A.muciniphila的丰度均有所增加[65-67]。A.muciniphila可抑制机体炎症反应,保持肠道屏障完整性,调节机体代谢的功能,并具有治疗糖尿病的潜力,与中医药改善糖尿病症状密切相关,是中医药治疗糖尿病的潜在靶点。
小結与展望
A.muciniphila是一种可治疗糖尿病的潜在益生菌,也是中医药治疗糖尿病的潜在靶点。糖尿病的发病机制与肠道屏障功能破坏、肠道菌群失调及其代谢产物密切相关。纠正肠道菌群失调成为治疗糖尿病的研究热点。A.muciniphila是一种特异性的黏液降解菌,是肠道菌群的核心菌群之一。近年来的研究表明,A.muciniphila在糖尿病患者中丰度明显降低甚至缺失,目前治疗T2DM的药物如二甲双胍和中药均可增加A.muciniphila的丰度,A.muciniphila丰度增加与糖尿病症状改善密切相关。此外,口服A.muciniphila也可改善糖尿病症状,A.muciniphila是一种治疗糖尿病新型的潜在益生菌。目前A.muciniphila治疗糖尿病的潜在机制有:(1)A.muciniphila可通过促进肠上皮细胞(如杯状细胞)生长、增加肠道黏液层的厚度、调节紧密连接蛋白及相关基因的表达改善肠道屏障功能;(2)A.muciniphila通过降低LPS与相关炎症因子的水平以及抑制LPS/LBP下游信号JNK和NF-KB炎症通路,改善机体炎症;(3)A.muciniphila分泌P9蛋白与ICAM-2结合促进GLP-1分泌,降低血糖,改善机体葡萄糖耐量及胰岛素抵抗。这些作用机制间相互作用的复杂性,以及各个分子通路上下游蛋白均需更多的实验研究予以验证。此外,A.muciniphila在免疫调节中的作用也是显著的,A.muciniphila通过调节免疫系统改善糖尿病症状的有关分子作用机制值得探索,以便探索潜在的治疗机制。
中医药干预肠道菌群治疗糖尿病的作用机制是目前众多研究学者探索的问题,A.muciniphila是中医药改善糖尿病症状的干预靶点,中医药与A.muciniphila的相互作用机制研究可为中药治疗糖尿病的作用机制提供新的线索。A.muciniphila丰度降低先于疾病发生,其丰度升高与糖尿病相关指标改善呈正相关,说明A.muciniphila不仅是预防和治疗糖尿病的潜在干预靶点,还可作为糖尿病早期诊断以及预后判断的潜在标志。总之,干预和调节A.muciniphila可作为糖尿病预防和治疗的新策略,也为未来的研究提供了新的研究方向。根据以上研究,A.muciniphila有潜力作为新型益生菌治疗糖尿病,其安全性问题、体外培养及制成生物制品技术问题是未来研究热点。中医药与A.muciniphila联合干预糖尿病患者是否具有累加效应仍待研究,他们之间相互作用机制也值得探索。目前关于A.muciniphila更多的实验集中于动物实验,缺乏相关人类试验的广泛研究,在未来需要更多的临床试验加以验证。
参 考 文 献
[1]Saeedi P,Petersohn I,Salpea P,et al.Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045:Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas,9 edition[J].Diabetes Res Clin Pract,2019,157:107843.DOI:10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843.
[2]Saeedi P,Salpea P,Karuranga S,et al.Mortality attributable to diabetes in 20-79 years old adults,2019 estimates:results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas,9 edition[J].Diabetes Res Clin Pract,2020,162:108086.DOI:10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108086.
[3]Kayama H,Okumura R,Takeda K.Interaction between the microbiota,epithelia,and immune cells in the intestine[J].Annu Rev Immunol,2020,38:23-48.DOI:10.1146/annurev-immunol-070119-115104.
[4]Patterson E,Ryan PM,Cryan JF,et al.Gut microbiota,obesity and diabetes[J].Postgrad Med J,2016,92(1087):286-300.DOI:10.1136/postgradmedj-2015-133285.
[5]Zhao L,Zhang F,Ding X,et al.Gut bacteria selectively promoted by dietary fibers alleviate type 2 diabetes[J].Science,2018,359(6380):1151-1156.DOI:10.1126/science.aao5774.
[6]Sircana A,Framarin L,Leone N,et al.Altered gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes:just a coincidence[J].Curr Diab Rep,2018,18(10):98.DOI:10.1007/s11892-018-1057-6.
[7]Gurung M,Li Z,You H,et al.Role of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes pathophysiology[J].E Bio Medicine,2020,51:102590.DOI:10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.11.051.
[8]Medina-Vera I,Sanchez-Tapia M,Noriega-López L,et al.A dietary intervention with functional foods reduces metabolic endotoxaemia and attenuates biochemical abnormalities by modifying faecal microbiota in people with type 2 diabetes[J].Diabetes Metab,2019,45(2):122-131.DOI:10.1016/j.diabet.2018.09.004.
[9]Anhê FF,Roy D,Pilon G,et al.A polyphenol-rich cranberry extract protects from diet-induced obesity,insulin resistance and intestinal inflammation in association with increased Akkermansia spp.population in the gut microbiota of mice[J].Gut,2015,64(6):872-883.DOI:10.1136/gutjnl-2014-307142.
[10]Vallianou NG,Stratigou T,Tsagarakis S.Metformin and gut microbiota:their interactions and their impact on diabetes[J].Hormones (Athens),2019,18(2):141-144.DOI:10.1007/s42000-019-00093-w.
[11]Su H,Mo J,Ni J,et al.Andrographolide exerts antihyperglycemic effect through strengthening intestinal barrier function and increasing microbial composition of Akkermansia muciniphila[J].Oxid Med Cell Longev,2020,2020:6538930.DOI:10.1155/2020/6538930.
[12]Derrien M,Belzer C,de Vos WM.Akkermansia muciniphila and its role in regulating host functions[J].Microb Pathog,2017,106:171-181.DOI:10.1016/j.micpath.2016.02.005.
[13]Zhao S,Liu W,Wang J,et al.Akkermansia muciniphila improves metabolic profiles by reducing inflammation in chow diet-fed mice[J].J Mol Endocrinol,2017,58(1):1-14.DOI:10.1530/JME-16-0054.
[14]Zhang HM,Liang FX,Chen R.Ancient records and modern research on the mechanisms of Chinese herbal medicines in the treatment of diabetes mellitus[J].Evid Based Complement Alternat Med,2015,2015:747982.DOI:10.1155/2015/747982.
[15]Li CN,Wang X,Lei L,et al.Berberine combined with stachyose induces better glycometabolism than berberine alone through modulating gut microbiota and fecal metabolomics in diabetic mice[J].Phytother Res,2020,34(5):1166-1174.DOI:10.1002/ptr.6588.
[16]Yue SJ,Wang WX,Yu JG,et al.Gut microbiota modulation with traditional Chinese medicine:A system biology-driven approach[J].Pharmacol Res,2019,148:104453.DOI:10.1016/j.phrs.2019.104453.
[17]Etxeberria U,Arias N,Boqué N,et al.Reshaping faecal gut microbiota composition by the intake of trans-resveratrol and quercetin in high-fat sucrose diet-fed rats[J].J Nutr Biochem,2015,26(6):651-660.DOI:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2015.01.002.
[18]Ju M,Liu Y,Li M,et al.Baicalin improves intestinal microecology and abnormal metabolism induced by high-fat diet[J].Eur J Pharmacol,2019,857:172457.DOI:10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172457.
[19]Zhang W,Xu JH,Yu T,et al.Effects of berberine and metformin on intestinal inflammation and gut microbiome composition in db/db mice[J].Biomed Pharmacother,2019,118:109131.DOI:10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109131.
[20]Plovier H,Everard A,Druart C,et al.A purified membrane protein from Akkermansia muciniphila or the pasteurized bacterium improves metabolism in obese and diabetic mice[J].Nat Med,2017,23(1):107-113.DOI:10.1038/nm.4236.
[21]Yassour M,Lim MY,Yun HS,et al.Sub-clinical detection of gut microbial biomarkers of obesity and type 2 diabetes[J].Genome Med,2016,8(1):17.DOI:10.1186/s13073-016-0271-6.
[22]Shih CT,Yeh YT,Lin CC,et al.Akkermansia muciniphilais negatively correlated with hemoglobin a1c in refractory diabetes[J].Microorganisms,2020,8(9):1360.DOI:10.3390/microorganisms8091360.
[23]Dao MC,Everard A,Aron-Wisnewsky J,et al.Akkermansia muciniphila and improved metabolic health during a dietary intervention in obesity:relationship with gut microbiome richness and ecology[J].Gut,2016,65(3):426-436.DOI:10.1136/gutjnl-2014-308778.
[24]Dubourg G,Lagier JC,Armougom F,et al.High-level colonisation of the human gut by Verrucomicrobia following broad-spectrum antibiotic treatment[J].Int J Antimicrob Agents,2013,41(2):149-155.DOI:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2012.10.012.
[25]Zhang T,Li Q,Cheng L,et al.Akkermansia muciniphila is a promising probiotic[J].Microb Biotechnol,2019,12(6):1109-1125.DOI:10.1111/1751-7915.13410.
[26]Cani PD,de Vos WM.Next-generation beneficial microbes:the case of Akkermansia muciniphila[J].Front Microbiol,2017,8:1765.DOI:10.3389/fmicb.2017.01765.
[27]Depommier C,Everard A,Druart C,et al.Supplementation with Akkermansia muciniphila in overweight and obese human volunteers:a proof-of-concept exploratory study[J].Nat Med,2019,25(7):1096-1103.DOI:10.1038/s41591-019-0495-2.
[28]Derrien M,Collado MC,Ben-Amor K,et al.The Mucin degrader Akkermansia muciniphila is an abundant resident of the human intestinal tract[J].Appl Environ Microbiol,2008,74(5):1646-1648.DOI:10.1128/AEM.01226-07.
[29]Berry D,Stecher B,Schintlmeister A,et al.Host-compound foraging by intestinal microbiota revealed by single-cell stable isotope probing[J].Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2013,110(12):4720-4725.DOI:10.1073/pnas.1219247110.
[30]de Vos WM.Microbe profile:Akkermansia muciniphila:a conserved intestinal symbiont that acts as the gatekeeper of our mucosa[J].Microbiology (Reading),2017,163(5):646-648.DOI:10.1099/mic.0.000444.
[31]van Passel MWJ,Kant R,Zoetendal EG,et al.The genome of Akkermansia muciniphila,a dedicated intestinal mucin degrader,and its use in exploring intestinal metagenomes[J].PLoS One,2011,6(3):e16876.DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0016876.
[32]Zhou JC,Zhang XW.Akkermansia muciniphila:a promising target for the therapy of metabolic syndrome and related diseases[J].Chin J Nat Med,2019,17(11):835-841.DOI:10.1016/S1875-5364(19)30101-3.
[33]Van Herreweghen F,De Paepe K,Marzorati M,et al.Mucin as a functional niche is a more important driver of gut microbiota composition and functionality than supplementation of Akkermansia m uciniphila[J].Appl Environ Microbiol,2020,87(4):e02647-20.DOI:10.1128/AEM.02647-20.
[34]Reunanen J,Kainulainen V,Huuskonen L,et al.Akkermansia muciniphila adheres to enterocytes and strengthens the integrity of the epithelial cell layer[J].Appl Environ Microbiol,2015,81(11):3655-3662.DOI:10.1128/AEM.04050-14.
[35]Van Herreweghen F,De Paepe K,Roume H,et al.Mucin degradation niche as a driver of microbiome composition and Akkermansia muciniphila abundance in a dynamic gut model is donor independent[J].FEMS Microbiol Ecol,2018,94(12).DOI:10.1093/femsec/fiy186.
[36]Kim S,Shin YC,Kim TY,et al.Mucin degrader Akkermansia muciniphila accelerates intestinal stem cell-mediated epithelial development[J].Gut Microbes,2021,13(1):1-20.DOI:10.1080/19490976.2021.1892441.
[37]Cani PD,Jordan BF.Gut microbiota-mediated inflammation in obesity:a link with gastrointestinal cancer[J].Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol,2018,15(11):671-682.DOI:10.1038/s41575-018-0025-6.
[38]Rorato R,Borges BC,Uchoa ET,et al.LPS-induced low-grade inflammation increases hypothalamic JNK expression and causes central insulin resistance irrespective of body weight changes[J].Int J Mol Sci,2017,18(7):1431.DOI:10.3390/ijms18071431.
[39]Fujio-Vejar S,Vasquez Y,Morales P,et al.The gut microbiota of Healthy chilean subjects reveals a high abundance of the phylum verrucomicrobia[J].Front Microbiol,2017,8:1221.DOI:10.3389/fmicb.2017.01221.
[40]Qin J,Li Y,Cai Z,et al.A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes[J].Nature,2012,490(7418):55-60.DOI:10.1038/nature11450.
[41]Zhang L,Qin Q,Liu M,et al.Akkermansia muciniphila can reduce the damage of gluco/lipotoxicity,oxidative stress and inflammation,and normalize intestine microbiota in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats[J].Pathog Dis,2018,76(4):fty028.DOI:10.1093/femspd/fty028.
[42]Hnninen A,Toivonen R,Pysti S,et al.Akkermansia muciniphilainduces gut microbiota remodelling and controls islet autoimmunity in NOD mice[J].Gut,2018,67(8):1445-1453.DOI:10.1136/gutjnl-2017-314508.
[43]Wu F,Guo X,Zhang M,et al.An Akkermansia muciniphila subtype alleviates high-fat diet-induced metabolic disorders and inhibits the neurodegenerative process in mice[J].Anaerobe,2020,61:102138.DOI:10.1016/j.anaerobe.2019.102138.
[44]Ahmad A,Yang W,Chen G,et al.Analysis of gut microbiota of obese individuals with type 2 diabetes and healthy individuals[J].PLoS One,2019,14(12):e0226372.DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0226372.
[45]Régnier M,Rastelli M,Morissette A,et al.Rhubarb supplementation prevents diet-induced obesity and diabetes in association with increased in mice[J].Nutrients,2020,12(10):2932.DOI:10.3390/nu12102932.
[46]Lu YM,Xie JJ,Peng CG,et al.Enhancing clinical efficacy through the gut microbiota:a new field of traditional Chinese Medicine[J].Engineering,2019,5:40-49.DOI:10.1016/j.eng.2018.11.013.
[47]Roshanravan N,Mahdavi R,Alizadeh E,et al.The effects of sodium butyrate and inulin supplementation on angiotensin signaling pathway via promotion of abundance in type 2 diabetes;a randomized,double-blind,placebo-controlled trial[J].J Cardiovasc Thorac Res,2017,9(4):183-190.DOI:10.15171/jcvtr.2017.32.
[48]Chelakkot C,Choi Y,Kim DK,et al.Akkermansia muciniphila-derived extracellular vesicles influence gut permeability through the regulation of tight junctions[J].Exp Mol Med,2018,50(2):e450.DOI:10.1038/emm.2017.282.
[49]Shin NR,Lee JC,Lee HY,et al.An increase in the Akkermansia spp.population induced by metformin treatment improves glucose homeostasis in diet-induced obese mice[J].Gut,2014,63(5):727-735.DOI:10.1136/gutjnl-2012-303839.
[50]Ryu JK,Kim SJ,Rah SH,et al.Reconstruction of LPS transfer cascade reveals structural determinants within LBP,CD14,and TLR4-MD2 for efficient LPS recognition and transfer[J].Immunity,2017,46(1):38-50.DOI:10.1016/j.immuni.2016.11.007.
[51]Wisniewski PJ,Dowden RA,Campbell SC.Role of dietary lipids in modulating inflammation through the gut microbiota[J].Nutrients,2019,11(1):117.DOI:10.3390/nu11010117.
[52]Tsaousidou E,Paeger L,Belgardt BF,et al.Distinct roles for JNK and IKK activation in agouti-related peptide neurons in the development of obesity and insulin resistance[J].Cell Rep,2014,9(4):1495-1506.DOI:10.1016/j.celrep.2014.10.045.
[53]Kim KA,Lee IA,Gu W,et al.β-Sitosterol attenuates high-fat diet-induced intestinal inflammation in mice by inhibiting the binding of lipopolysaccharide to toll-like receptor 4 in the NF-κB pathway[J].Mol Nutr Food Res,2014,58(5):963-972.DOI:10.1002/mnfr.201300433.
[54]Ottman N,Reunanen J,Meijerink M,et al.Pili-like proteins of Akkermansia muciniphila modulate host immune responses and gut barrier function[J].PLoS One,2017,12(3):e0173004.DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0173004.
[55]Ibfelt T,Fischer CP,Plomgaard P,et al.The acute effects of low-dose TNF-α on glucose metabolism and β-cell function in humans[J].Mediators Inflamm,2014,2014:295478.DOI:10.1155/2014/295478.
[56]Smitka K,Mareová D.Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ:an update on pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory microenvironment[J].Prague Med Rep,2015,116(2):87-111.DOI:10.14712/23362936.2015.49.
[57]Holst JJ,Gribble F,Horowitz M,et al.Roles of the gut in glucose homeostasis[J].Diabetes Care,2016,39(6):884-892.DOI:10.2337/dc16-0351.
[58]Cani PD,Plovier H,van Hul M,et al.Endocannabinoids--at the crossroads between the gut microbiota and host metabolism[J].Nat Rev Endocrinol,2016,12(3):133-143.DOI:10.1038/nrendo.2015.211.
[59]Yoon HS,Cho CH,Yun MS,et al.Akkermansia muciniphila secretes a glucagon-like peptide-1-inducing protein that improves glucose homeostasis and ameliorates metabolic disease in mice[J].Nat Microbiol,2021,6(5):563-573.DOI:10.1038/s41564-021-00880-5.
[60]Kahles F,Meyer C,Mllmann J,et al.GLP-1 secretion is increased by inflammatory stimuli in an IL-6-dependent manner,leading to hyperinsulinemia and blood glucose lowering[J].Diabetes,2014,63(10):3221-3229.DOI:10.2337/db14-0100.
[61]Gao Z,Li Q,Wu X,et al.New insights into the mechanisms of Chinese herbal products on diabetes:a focus on the “bacteria-mucosal immunity-inflammation-diabetes” axis[J].J Immunol Res,2017,2017:1813086.DOI:10.1155/2017/1813086.
[62]Neyrinck AM,Etxeberria U,Taminiau B,et al.Rhubarb extract prevents hepatic inflammation induced by acute alcohol intake,an effect related to the modulation of the gut microbiota[J].Mol Nutr Food Res,2017,61(1):10.1002/mnfr. 201500899.DOI:10.1002/mnfr.201500899.
[63]Ding Y,Song Z,Li H,et al.Honokiol ameliorates high-fat-diet-induced obesity of different sexes of mice by modulating the composition of the gut microbiota[J].Front Immunol,2019,10:2800.DOI:10.3389/fimmu.2019.02800.
[64]Chen M,Liao Z,Lu B,et al.Huang-lian-jie-du-decoction ameliorates hyperglycemia and insulin resistant in association with gut microbiota modulation[J].Front Microbiol,2018,9:2380.DOI:10.3389/fmicb.2018.02380.
[65]Mei X,Zhang X,Wang Z,et al.Insulin sensitivity-enhancing activity of phlorizin is associated with lipopolysaccharide decrease and gut microbiota changes in obese and type 2 diabetes (db/db) mice[J].J Agric Food Chem,2016,64(40):7502-7511.DOI:10.1021/acs.jafc.6b03474.
[66]Cao Y,Yao G,Sheng Y,et al.Jinqi jiangtang tablet regulates gut microbiota and improve insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetes mice[J].J Diabetes Res,2019,2019:1872134.DOI:10.1155/2019/1872134.
[67]Du LJ,Pang B,Tan YM,et al.Banxia Xiexin Decoction ameliorates t-BHP-induced apoptosis in pancreatic beta cells by activating the PI3K/AKT/FOXO1 signaling pathway[J].J Diabetes Res,2020,2020:3695689.DOI:10.1155/2020/3695689.
(收稿日期:2021-09-03)

