血清小而密低密度脂蛋白与冠心病的相关性分析
樊鹏威
【摘要】 目的 研究血清小而密低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(sdLDL-C)与冠心病的关系,并分析其在冠心病诊断中的价值。方法 选择2017年12月—2018年12月期间到武汉市第七医院心内科接受治疗的192例冠心病患者以及180例健康体检者作为研究对象,分别采集2组对象清晨空腹12 h肘正中静脉血,将血液标本在离心机中以3 000 r/min速度离心5 min,分离出血清,再使用日立7600全自生化分析仪检测。检测血清小而密低密度脂蛋白、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇、超敏C反应蛋白、甘油三酯、总胆固醇等5项生化指标,對比2组检测结果。结果 冠心病患者sdLDL-C含量较正常人群明显增高,且低密度脂蛋白胆固醇、超敏C反应蛋白、甘油三酯、总胆固醇水平较健康体检者显著升高(P<0.05)。结论 sdLDL-C水平与冠心病有很强相关性,可提供风险预警,未来应继续深入研究以确定sd-LDL的有效阈值,对危险人群进行心血管风险评估,更加有效地筛查、诊断和治疗CHD高危人群。
【关键词】 冠心病; 动脉粥样硬化; 小而密低密度脂蛋白; 相关性
The relationship between serum small and dense LDL and coronary heart disease
Fan Pengwei.The Seventh Hospital of Wuhan City,Wuhan,Hubei 430065
【Abstract】 Objective To investigate the relationship between serum small and dense Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol(SDLDL-C)and coronary heart disease (chd),and to analyze the value of SDLDL-C in the diagnosis of chd. Methods We selected 192 patients with coronary heart disease and 180 healthy persons who were treated in the Department of Cardiology,the Seventh Hospital of Wuhan from December 2017 to December 2018 as the subjects of this study,compared the general data of the two groups,showing no significant difference(P>0.05),the two groups are comparable,the results can be analyzed.The blood samples were centrifuged at a speed of 3000 R/min for 5 min,then the serum was separated and detected by Hitachi 7600 automatic biochemical analyzer.Serum Small and dense Low-density Lipoprotein,Low-density Lipoprotein,high-sensitivity c-reactive protein,triglyceride and total cholesterol were measured and the data were analyzed statistically. Results The levels of sdldl-c in the coronary heart disease population were significantly higher than those in the normal population,and the levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol,high-sensitivity C-reactive protein,triglyceride and total cholesterol in the coronary heart disease population were significantly higher than those in the healthy people(P<0.05).Conclusion The level of SDLDL-C has a strong correlation with coronary heart disease(chd),which can provide early warning for the diagnosis of chd.In recent years,homogeneous enzymatic method has been used to detect the level of sd-LDL in clinical tests.Further studies will be carried out to determine the effective threshold of sd-LDL in the future,to assess the cardiovascular risk of CHD risk population,screening,diagnosis and treatment of Chd risk population are more effective.
【Key Words】 Coronary heart disease; Atherosclerosis; Small dense low density lipoprotein; Correlation
中图分类号:R541.4 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1672-1721(2023)19-0094-03
DOI:10.19435/j.1672-1721.2023.19.031
冠心病(CHD)是中老年人群中常见多发病,该病隐匿性强,需要在发病早期进行诊断治疗。有越来越多研究数据显示,小而密低密度脂蛋白(sdLDL-C)可以作为冠心病独立危险因素,其含量增多会导致冠状动脉发生粥样硬化,而动脉硬化与心血管疾病密切相关[1-2]。多项研究选用梯度凝胶电泳法和密度梯度超速离心法,将颗粒直径≤25.5 nm、密度为1.044~1.063 kg/L的LDL定义为小而密低密度脂蛋白。小而密低密度脂蛋白(sdLDL-C)联合其他传统血脂指标进行检测,有利于冠心病患者早期确诊并进行治疗,对于预后转归有积极的促进作用。本研究针对小而密低密度脂蛋白与冠心病的相关性进行分析,报告如下。
1 资料与方法
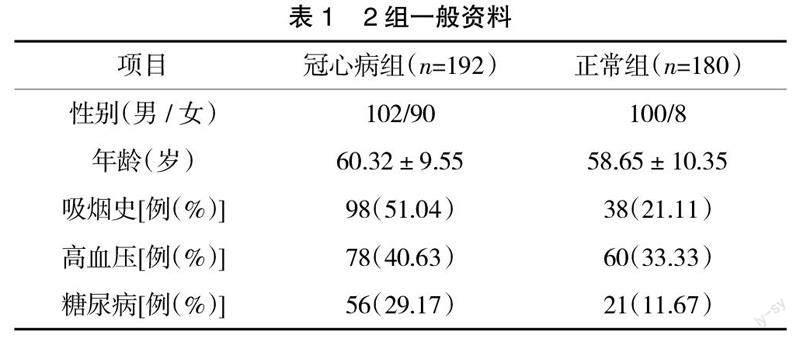
1.1 一般资料 选择2017年12月—2018年12月期间到武汉市第七医院心内科接受治疗的192例冠心病患者以及180例健康体检者作为研究对象,2组一般资料见表1。纳入标准:经标准Judkins法行冠状动脉造影检查后确诊;病历资料完整,并签署知情同意书。排除标准:患者在近6个月患有严重肝肾功能不全、血液系统疾病、恶性肿瘤、免疫缺陷疾病、各种感染性疾病等。
1.2 方法 分别采集2组对象清晨空腹12 h肘正中静脉血,标本采集后立即送往检验科,所有标本都应避免发生溶血、脂血。将血液标本在离心机中以3 000 r/min速度离心5 min,分离出血清,再使用日立7600全自生化分析仪检测。
1.3 观察指标 用生化仪检测血清小而密低密度脂蛋白、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-C)、超敏C反应蛋白(hs-CRP)、 甘油三酯(TG)、总胆固醇(TC)等5项生化指标。其中,sdLDL-C检测试剂盒由重庆中元提供,检测方法为过氧化物酶法,低密度脂蛋白胆固醇、甘油三酯、总胆固醇均采用氧化酶法测定,超敏C反应蛋白采用胶乳免疫比浊法测定,
1.4 统计学方法 使用SPSS 22.0统计学软件进行数据处理,计量资料以x±s表示,采用t检验,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
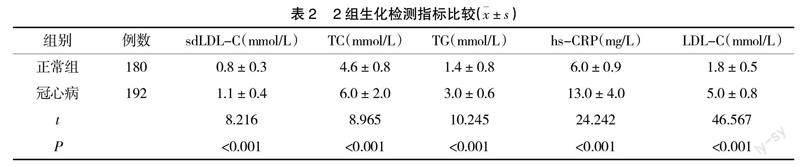
冠心病患者sdLDL-C含量较正常人群明显增高,低密度脂蛋白胆固醇、超敏C反应蛋白、甘油三酯、总胆固醇水平较健康体检者显著升高(P<0.05),见表2。
3 讨论
近年来,研究结果显示,低密度脂蛋白(LDL)水平升高可在一定程度上诱发冠心病。LDL是一种将胆固醇输送至外周组织的脂蛋白颗粒,主要由一系列大小、密度和化学成分不同的颗粒组成,临床上可根据其密度差异进行分类。随着国内外对低密度脂蛋白研究的深入,发现其亚组分中的sdLDL-C具有更强的致动脉粥样硬化作用;当体内TG水平显著升高时,在一定程度上可以支持LDL从大颗粒游离LDL向sdLDL-C转变。研究结果还证实,sdLDL-C与冠心病密切相关,也是近年来新发现的冠状动脉粥样硬化危险因素之一。血脂指标LDL-C、TG、TC直接反映冠心病患者脂代谢异常,而hs-CRP 是反映组织损伤及炎症程度的敏感指标,与冠心病患者的血管内皮损伤程度呈正相关[3]。本文研究结果显示,冠心病患者的血脂水平高于健康人,且血清sdLDL-C含量更高(P<0.05)。
降低LDL-C水平是目前减少CHD患者心血管事件风险的最重要手段,而sdLDL-C相对于LDL-C致动脉粥样硬化能力更强,与CHD更具相关性[4]。Austin等人最早在1990年发现,冠心病B型低密度脂蛋白(SD-LDL)的发病率是A型高密度脂蛋白(high-lift-LDL)的3倍。隨后,魁北克心血管中心于2005年的一项前瞻性研究也证实,LDL粒径≤25.5 nm的冠心病风险随着胆固醇浓度的增加而增加;而粒径>25.5 nm者,随着胆固醇浓度的增加,反而冠心病风险相对降低。随着对sdLDL-C研究的深入,显示其合成速度跟TG的浓度密切相关。TG明显上升时,LDL水平及合成变化不大,但TG越高,循环中极低密度脂蛋白(VLDL)与LDL之间的脂质变换越活跃,生成的sdLDL-C越多[5]。高TG患者会出现高sdLDL-C和低HDL,伴随着TG不断被水解,LDL颗粒被转化为不易被清除的sdLDL-C。
小而密低密度脂蛋白致动脉硬化存在以下几个方面的机制:sdLDL-C难以被肝脏代谢,需要较长时间才能在血液中清除;体积小、表面积大,容易穿透血管动脉壁[6];sdLDL-C还可增加LDL-C氧化应激反应,趋化巨噬细胞和(或)平滑肌细胞吞噬氧化修饰sdLDL-C,形成泡沫细胞[7-9],诱发免疫应答和炎症,形成动脉硬化。研究还表明,sdLDL-C颗粒表面极性分子数量减少,与动脉内膜上的蛋白聚糖亲和力较高,常黏附于血管壁,在进入血管内皮细胞后,可引起血管内皮细胞功能障碍[10],随之产生纤维蛋白原和纤溶酶原激活物抑制剂1(PAI-1),引发血栓形成[11],加剧动脉硬化的趋势。由此可知,sdLDL-C可作为CHD的独立预测指标[12],并且其对血管壁的损伤持久。
由于sdLDL-C自身的特点,其比LDL-C更容易引起冠心病,并成为冠心病的独立预测因子。sdLDL-C可能指示冠心病的发生,并作为冠心病患者PCI后早期的预后评估指标,sdLDL-C可能从病理学角度反映斑块的严重程度。然而,淋巴液、UAP和AMI患者血清sdLDL-C水平的差异仍不确定,需要进一步研究。他汀类药物、依齐米布和PCSK9抑制剂可降低sdLDL-C水平,并已被证明能有效降低心血管疾病的风险。
综上所述,sdLDL-C水平与冠心病有很强相关性,可提供风险预警。未来还需继续深入研究以确定sd-LDL的有效阈值,对危险人群进行心血管风险评估,更加有效地筛查、诊断和治疗CHD高危人群。
参考文献
[1] 张岚,邵文琦,张爱伦,等.小而密低密度脂蛋白胆固醇方法学性能验证及与冠心病严重程度相关性分析[J].中华检验医学杂志,2017,40(6):425-430.
[2] HOOGEVEEN R C,GAUBATZ J W,SUN W,et al.Small dense lowdensity lipoprotein -cholesterol concentrations predict risk for coronary heart disease:the Atherosclerosis Risk In Communities(ARIC)study[J].Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol,2014,34(5):1069-1077.
[3] SNINSKY J J,ROWLAND C M,BACA A M,et al.Classifica-tion of LDL phenotypes by 4 methods of determining lipoprotein particle size[J].J Investig Med,2013,61(6):942-949.
[4] TAKIWAKI M,TOMODA F,KOIKE T,et al.Increased levels of small dense low -density lipoprotein cholesterol associated with hemorheological abnormalities in untreated,early-stage essential hypertensives[J].Hypertens Res,2014,37(11):1008-1013.
[5] 吴寿军,毛丽萍,陈雷阳,等.小而密低密度脂蛋白胆固醇在诊断心血管疾病及相关性的探究[J].浙江临床医学,2019,21(6):844-846.
[6] FAN J H,LIU Y Q,YIN S P,et al.Small dense LDL cholesterol is associated with metabolic syndrome traits independently of obesity and inflammation[J].Nutr Metab(Lond),2019,16(1):7-16.
[7] LI G,WU H K,WU X W,et al.Small dense low density lipoprotein-cholesterol and cholesterol ratios to predict arterial stiffness progression in normotensive subjects over a 5-year period[J].Lipids Health Dis,2018,17(1):27.
[8] SAKAI K,KOBA S,NAKAMURA Y,et al.Small dense low-density lipoprotein cholesterol is a promising biomarker for secondary prevention in older men with stable coronary artery disease[J].Geriatr Gerontol Int,2018,18(6):965-972.
[9] BORN J,CHAPMAN M J,KRAUSS R M,et al.Low-density lipoproteins cause atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease:pathophysiological,genetic,and therapeutic insights:a consensus statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel[J].European Heart Journal,2020,41(24):2313-2330.
[10] SUMINO H,NAKAJIMA K,MURAKAMI M.Possibility of new circulating atherosclerosis-related lipid markers measurement in medical and complete medical checkups:small dense low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and lipopro-teinlipase[J].RinshoByori,2016,64(3):298-307.
[11] 吳少南,张霜,王光磊.血清小而密低密度脂蛋白胆固醇表达水平与冠心病的关系分析[J].中国病案,2019,20(2):99-102.
[12] 王恺隽,李铁威,蔺亚晖,等.小而密低密度脂蛋白胆固醇与冠状动脉粥样硬化特征的相关性分析[J].临床检验杂志,2017,35(9):674-679.
(收稿日期:2023-04-08)

