Histopathological assessment of the microscopic activity in inflammatory bowel diseases: What are we looking for?
Ondrej Fabian,Lukas Bajer
Abstract Advances in diagnostics of inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) and improved treatment strategies allowed the establishment of new therapeutic endpoints.Currently, it is desirable not only to cease clinical symptoms, but mainly to achieve endoscopic remission, a macroscopic normalization of the bowel mucosa.However, up to one-third of IBD patients in remission exhibit persisting microscopic activity of the disease. The evidence suggests a better predictive value of histology for the development of clinical complications such as clinical relapse, surgical intervention, need for therapy escalation, or development of colorectal cancer. The proper assessment of microscopic inflammatory activity thus became an important part of the overall histopathological evaluation of colonic biopsies and many histopathological scoring indices have been established. Nonetheless, a majority of them have not been validated and no scoring index became a part of the routine bioptic practice. This review summarizes a predictive value of microscopic disease activity assessment for the subsequent clinical course of IBD, describes the most commonly used scoring indices for Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, and comments on current limitations and unresolved issues.
Key Words: Crohn’s disease; Microscopy; Predictor; Score; Ulcerative colitis
INTRODUCTION
The first description of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) dates back to 1932, when Burrill Bernard Crohn published the article "Regional ileitis: A pathologic and clinical entity"[1]. In the following decades, our understanding of IBD has evolved. Currently, we perceive both Crohn's disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC) as systemic inflammatory conditions showing predilection to the gastrointestinal(GI) tract[2-4]. Despite persisting ominous etiology and poorly understood pathogenesis, substantial advances in diagnostics and therapy of IBD have been made, allowing new therapeutic endpoints to be laid out. At present, we strive not only to cease all clinical symptoms, but mainly to reach the endoscopic remission, defined as normalization of endoscopic mucosal appearance[5,6]. However,normal endoscopic finding does not necessarily reflect normal histology. Correlation between endoscopy and histology is poor and up to 1/3 of both CD and UC patients in endoscopic remission show signs of persisting histological activity[7-10]. There is increasing evidence that histological activity of the disease may be a better predictor of important clinical endpoints such as hospitalization rate, risk of clinical relapse, need for systemic corticosteroid use, or development of colorectal cancer when compared to sole endoscopy[11-16]. This is even more important for certain IBD subtypes such as IBD associated with primary sclerosing cholangitis, currently considered a distinct phenotype of IBD entailing a four times higher risk of a colorectal cancer development compared to conventional IBD[17,18]. The evaluation of the histological disease activity by reliable scoring indices thus represents an important part of the overall microscopic assessment. Nonetheless, a majority of them lack proper validation and none of them have been established in routine clinical practice. Endoscopy remains a gold standard for the assessment of luminal activity of the disease[5].
The aim of this review is to provide a summary of the most commonly used scoring indices for CD and UC, highlight clinical benefits of the microscopic disease activity assessment and comment on current limitations and unresolved issues from the pathologists’ perspective.
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF IBD HISTOPATHOLOGY
To better conceive microscopic features included in histopathological scoring indices, it seems convenient to briefly summarize a basic IBD pathology first. UC is characterized by a continuous inflammation affecting a rectum and progressing towards the proximal colon and terminal ileum. The inflammatory infiltrate is usually confined to the mucosa. Submucosa may be affected in case of severe colitis, but transmural inflammation is not a feature of UC. As far as CD is concerned, the inflammation displays a discontinuous pattern on both macroscopic and microscopic levels. Any part of the GI tract from the oral cavity to the anal region may be affected, while the terminal ileum is the most frequent site of the disease. The inflammation is typically transmural, infiltrating deeper layers of the bowel wall. In both IBD subtypes, the infiltrate is mainly mononuclear, with a predominance of lymphocytes and plasmacytes. The presence of neutrophils is a sign of the disease activity. In case of mildly active disease, they are scarce and confined to lamina propria. With an increasing degree of activity, they tend to infiltrate surface epithelium and colonic crypts (defined as cryptitis). Later on, the crypt walls are disrupted and neutrophils exudate into their lumina forming crypt abscesses. The most severe grade of activity is usually characterized by the presence of erosions and ulcerations. Erosions were traditionally defined as defects confined to the mucosa, whilst ulcerations penetrated deeper into the submucosa, but there is no strict adherence to this criterion in pathological practice. Currently, ulcerations are often recognized rather by the presence of granulation tissue and erosions by fibrinopurulent exudate covering the defect[4,19,20]. The inflammatory infiltrate is often accompanied by numerous eosinophils.However, their proper assessment remains challenging due to the lack of a clearly defined cut-off value for their pathological increase[21]. Their numbers also vary among bowel segments being more prevalent in the right-sided colon[22] and several studies document their substantial seasonal and geographic oscillation[23,24]. Other characteristic features of IBD are basal plasmacytosis and disrupted mucosal architecture. Basal plasmacytosis is defined as an increased number of plasmacytes between the base of the crypts and muscularis mucosae. It is a strong indicator of IBD and also one of the earliest signs of chronicity[25]. Disrupted mucosal architecture refers to any distortion of the physiological appearance of the crypts. Normally, colonic crypts are straight, parallel, and evenly spaced. In IBD, they show changes such as branching, angulation, dilatation, shortening, or dropout[26]. A hallmark of CD diagnosis is the presence of non-caseating epithelioid granulomas. Although a differential diagnosis of granulomatous colitis is broad, the presence of immune granuloma in IBD patients excludes the diagnosis of UC. Their incidence ranges from 15% to 85% according to various studies[26]. They are more closely tied to an ileocolic form of CD or CD with upper GI involvement[27] and seem to be almost twice as frequent in pediatric CD[28].
A PREDICTIVE VALUE OF MICROSCOPIC DISEASE ACTIVITY FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF CLINICAL COMPLICATIONS
According to a recent meta-analysis by Guptaet al[8] performed on 2677 UC patients in endoscopic remission, the presence of persisting microscopic activity is associated with an increased risk of clinical relapse [odds ratio (OR) 2.41; 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.91-3.04]. These findings are supported by another meta-analysis by Yoonet al[29], which showed similar results based on the analysis of 757 UC patients in endoscopic remission. In their cohort, an absence of histological activity of the disease was associated with a 63% lower risk of clinical relapse (risk ratio 0.37; 95%CI: 0.24-0.56). In the study by Heftiet al[30], the authors evaluated 561 UC patients with a median follow-up of 21.4 years since the onset of the disease. According to both univariate and multivariate analyses, a mean histological inflammatory activity showed to be a significant predictor of colectomy (P< 0.001). Azadet al[31] showed that the presence of mucosal neutrophils and eosinophils in clinically and endoscopically quiescent UC was associated with an increased risk of clinical relapse over 12 mo (P< 0.01). Last but not least, Bryantet al[12] performed a study on 91 UC patients assessing a prognostic value of endoscopic and histological remission for the prediction of corticosteroid use, hospitalization and colectomy in a median 6-year follow-up. In their analysis, a histological remission was a predictor of colectomy and development of an acute severe colitis, in contrast to endoscopy (OR 0.42, 95%CI: 0.2-0.9,P= 0.02; OR 0.21, 95%CI: 0.1-0.7,P= 0.02 respectively). These results suggest that persisting histological activity of the disease seems to be associated with an adverse clinical course in UC patients.
Studies documenting a prognostic value of histology in CD are still limited in number. However,Christensenet al[14] demonstrated that the absence of histologic activity in patients with ileal CD is associated with a lower risk of clinical relapse [hazard ratio (HR) 2.05; 95%CI: 1.07-3.94;P= 0.031],corticosteroid use (HR 2.44; 95 % CI 1.17 - 5.09;P= 0.018) and medical escalation (HR 2.17; 95%CI: 1.2-3.96;P= 0.011) in a 21-mo follow-up. In the study by Brennanet al[32], the absence of histological activity was associated with a lower percentage of disease flares at both 12 mo (2.4%vs25.5%,P= 0.03)and 24 mo (10.5%vs37.8%,P= 0.05) of follow-up, in contrast to endoscopy, where no significant difference between an endoscopically active and an inactive disease was found. On the other hand, the aforementioned meta-analysis by Guptaet al[8], which analyzed the predictive value of histology in 2677 UC patients, did not confirm the results, which were displayed by the group of 129 CD patients.
A predictive value of histology for the development of colorectal dysplasia and cancer is of no less importance. A meta-analysis by Floreset al[33] performed on 1443 UC patients found that even isolated histologic activity in otherwise endoscopically normal mucosa increased the risk of neoplasia (OR 2.6,95%CI: 1.49-4.46,P= 0.01). In the study by Guptaet al[16], the severity of histological inflammation correlated with the risk of progression to an advanced neoplasia (high-grade dysplasia, invasive cancer),with HR being 3.0 (95%CI: 1.4-6.3) for the mean inflammatory score, HR 3.4 (95%CI: 1.1-10.4) for the binary inflammatory score and HR 2.2 [inter-quartile range (IQR) 1.2-4.2] for the maximum inflammatory score. A case-control study of Rutteret al[34] included 68 patients with a colorectal neoplasia matched with 136 controls without a neoplasia revealed a highly significant correlation between the histological severity of inflammation and the risk of neoplasia development (OR 4.69, 95%CI: 2.10-10.48,P< 0.001). Paiet al[35] correlated 52 UC patients with colorectal cancer to 122 patients without cancer.Based on the retrospective re-evaluation of biopsies from the last five years, a mean histological disease activity assessed by two independent histological scores appeared to be a predictor of cancer development, in contrast to endoscopy (HR 7.53, 95%CI: 2.56-12.16,P< 0.001 and HR 5.89, 95%CI: 2.18-15.92,P< 0.001 respectively). In CD, the predictive value of histology for cancer development is still equivocal. However, in the study by Kirchgesneret al[36] assessing a cohort of 398 IBD patients including 237 patients with CD, mean histological disease severity was associated with the risk of cancer development (OR 1.69, 95%CI: 1.29-2.21,P< 0.001 per one-unit increase).
In summary, a vast majority of evidence suggests that cessation of microscopic inflammatory activity has a positive impact on the future clinical course of the disease, especially for patients suffering from UC. Assessment of the histological activity should therefore be an integral part of bioptic reports in all patients with IBD. However, the appropriate extent of the microscopic normalization is still not precisely established. In other words, we still lack a proper definition of histological remission. As a result, establishing it as a primary therapeutic endpoint in clinical practice or clinical trials still lacks validity[6,37,38].
HISTOPATHOLOGIC SCORING INDICES FOR UC
The first histopathological scoring index for UC and the first scoring index for IBD, in general, was established in the 1960s by Truelove and Richards[39]. Since then, up to thirty indices have been proposed according to Cochrane Collaboration review[40], although only a few of them have been fully validated. One of the most widely used remains the Geboes score (GS), established in 2000[41]. This score assesses seven histopathological features including architectural mucosal changes, chronic inflammatory infiltrate, neutrophils and eosinophils in lamina propria, intraepithelial neutrophils, crypt destruction, and mucosal defects. Each of the given variables is further subclassified according to its severity (Table 1). The overall microscopic inflammatory severity should be based on the worst score in the bioptic sample, not on the average grade counted from all samples. Although, such a score may appear overly complicated at the first glance (i.e., grading of the cryptitis severity as < 5%, < 50%, and >50% of the affected crypts in the sample), it showed surprisingly good interpersonal agreement in preliminary phases of the study, especially when evaluating the presence of disease activity and mucosal defects (Cohen's kappa coefficient κ was above 0.9). A weak agreement was reached for the assessment of an inactive chronic inflammation. The original purpose of the score was a classification scheme, intended to define specific thresholds of the inflammatory severity, such as the presence of the disease activity. In subsequent studies, the score was also used as a continuous scale, assessing treatment efficacy in clinical trials[42,43]. The score seems to have a decent predictive value, being a reliable predictor of a clinical relapse in patients in clinical and endoscopic remission[31,44]. However, it has not been completely validated. In 2017, the Geboes Simplified Score was proposed[45]. The score reduced grading of the inflammatory activity and included the presence of basal plasmacytosis(Table 2). The score shows better overall agreement compared to the original GS (κ 0.56vs0.4). With regards to individual grades, the best agreement was reached for the detection of the inflammatory activity (κ 0.7). However, the score has not yet been widely used.
Robarts histopathology index (RHI)[46] was established in 2017 and was primarily intended to assess microscopic changes induced by the treatment. The construction process of the index was based on the original GS, from which the histopathological variables with reliable interobserver agreement and good correlation with grades of the inflammatory activity according to Visual Analogue Scale were used and served as a foundation for the final index. The definitive index consists of four histopathological features including chronic inflammatory infiltrate, neutrophils in lamina propria, neutrophils in the epithelium and mucosal defects. Each of the features is further subclassified according to its severity(range 0 to 3), giving the final index range from 0 to 33 points (Table 3). In contrast to GS, RHI exclusively assesses the histologic activity of the disease and excludes the features of chronicity. The agreement among the index grades is very good, with an intraclass correlation coefficient above 0.8. A predictive value of the index is still not fully elucidated. However, the aforementioned study by Paiet al[35] showed that a mean index score ≥ 8 during 5 years of observation predicted the development of colorectal cancer.
In the same year, a Nancy histological index (NHI) was proposed[47,48]. It uses five-grade scale based on the presence of chronic and active inflammatory infiltrate and mucosal defects (Table 4 and Figure 1). The final grade is determined by the worst histopathologic feature found in a biopsy sample.Despite the subjective nature of some features making the thresholds between several grades prone to possible higher interobserver variability (i.e., mildvsmoderate intensity of the chronic inflammatory infiltrate defining grades 0 and 1 respectively), the index shows very good overall interobserver agreement (κ above 0.8) and also a good reciprocal correlation with RHI [49]. The score is fully validated and widely used in clinical practice. With regards to its predictive value, in the study of D'Amicoet al[49] patients with histologic presence of the inflammation (NHI ≥ 1) had a higher risk of surgical intervention (14%vs0%,P= 0.01) and hospitalization (36%vs7.1%,P= 0.001) compared to patients in histological remission (NHI grade 0) during a 30-mo median follow-up.
HISTOPATHOLOGIC SCORING INDICES FOR CD
Scoring indices for CD are limited in number. The Cochrane collaboration review mentions 14 indices[50], but the only one used on the larger scale is the Global Histology Activity Score (GHAS)[51]. The score was established by D'Haenset alin 1998 with the purpose to assess early postoperative recurrence after ileocecal resection. It includes the following variables: the presence of architectural changes, degree of chronic, neutrophilic and eosinophilic inflammatory infiltration in lamina propria, presence of intraepithelial neutrophils, epithelial damage, mucosal defects, presence of granulomas, and a number ofaffected bowel segments (Table 5). Later on, the score became used separately for terminal ileum and large bowel as Ileal and Colonic GHAS[52]. However, the score is not validated and its utility is limited.Instead of being a continuous scale, it rather represents a sum of present variables, putting minute changes such as architectural distortion or increased mononuclear cells in lamina propria on the same level of importance, for instance mucosal defects. According to a recent multidisciplinary consensus panel[53], the score does not represent a reliable index for the assessment of the inflammatory severity in CD. Its eventual predictive value has not been evidenced.

Table 1 Original Geboes score
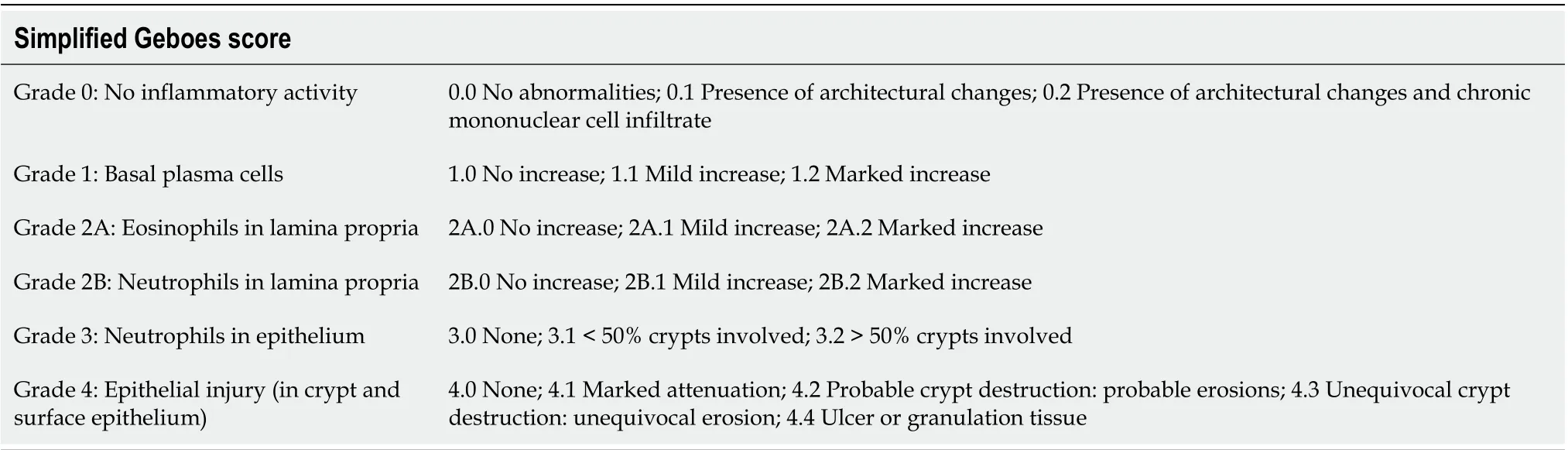
Table 2 Simplified Geboes score

Table 3 Robarts histopathology index
PRACTICAL ISSUES OF THE MICROSCOPIC ACTIVITY ASSESSMENT
The sole fact that we have been regularly confronted with new indices indirectly implies that we are still struggling to find the perfect one that would satisfy all our demands. A lot of unresolved issues persistthroughout the whole diagnostic process, reflecting both the proper biology of the disease and the limitations of given diagnostic modalities.

Table 4 Nancy histological index

Table 5 Global Histology Activity Score
Segmental and transmural character of the inflammation in CD
A correlation between endoscopic and histologic activity in CD is poor due to the segmental nature of the inflammation on both macroscopic and microscopic levels. Indeed, some degree of discrepancy between endoscopy and histology is desirable since the histology should not only confirm the endoscopic findings but represent an additional value by increasing the sensitivity of the inflammatory activity detection. On the other hand, a focal character of the disease may lead to a false underestimation of the histological activity. It is especially true in patients on therapy since treated IBD typically shows a focal and patchy character of the inflammation, even in UC[54].
In CD, a transmural character of the inflammation is one of the defining features, modifying the overall clinical severity of the disease and eventual development of complications. However, both histology and endoscopy provide information exclusively about the luminal activity of the disease.There is thus an increasing effort to establish a reliable scoring index of transmural severity of the disease. The well-known Lemann index[55] represents a clinical score, assessing the cumulative damage of the intestinal wall according to the presence of strictures, penetrating disease (fistulas or abdominal abscesses), previous surgical interventions, and perianal involvement. The majority of histopathological indices of transmural involvement are aimed at the assessment of resection margins of ileocecal resections. Later on, more complex indices were established, evaluating a full spectrum of transmural CD pathology including a degree of inflammatory intensity, fibrosis, smooth muscle changes, or neuronal hypertrophy[56-58]. However, such scores cannot be applied to endoscopic bioptic samples. In some instances, the sample is so superficial, that the basal portion of the mucosa is missing, precluding the assessment of important predictors such as basal plasmacytosis, which is also included in some scoring indices such as Simplified GS.
Upper GI and small intestinal involvement

Figure 1 Microphotographs representing individual grades of Nancy Histopathological Index (hematoxylin and eosin, magnification 100×). A: Grade 0 with no increase in inflammatory cells; B: Grade 0 with mild increase in chronic inflammatory cells; C: Grade 1 with moderate increase in chronic inflammatory cells including more numerous eosinophils, but no neutrophils; D: Grade 2 with scarce neutrophils in lamina propria and epithelium; E: Grade 3 with numerous neutrophils including cryptitis and crypt abscess; F: Grade 4 with completely ulcerated colonic mucosa replaced by granulation tissue.
Both CD and UC are systemic inflammatory conditions capable of affecting any part of the GI tract. This is especially true for pediatric patients, in which the inflammation in the upper GI is more frequent. As defined by the revised Porto criteria for the diagnosis of IBD in children and adolescents[59], pediatric UC with upper GI involvement is even one of the atypical UC subtypes. However, grading of upper GI inflammatory severity is not a part of any available histological scoring index. In adult patients, a routine esophagogastroduodenoscopy is not even a part of the official recommendations for IBD diagnosis[2,3,59]. A subsequent clinical course may also be aggravated by the persisting inflammatory activity in a small bowel. However, an endoscopy can usually assess only its proximal and distal segments, frequently missing jejunum, and a large portion of the ileum. Key modalities for assessment the small bowel involvement are imaging techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging, computer tomography, ultrasonography or other radiologic procedures[60]. Some of them are also accompanied by respective scoring indices such as Simplified Magnetic Resonance Index of Activity for CD[61]. In recent years, scoring indices for capsule endoscopy were established, with Lewis Score[62] and Capsule Endoscopy Crohn Disease Activity Index[63] being among the most frequently used ones,recommended by both European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation (ECCO) and European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. Currently, there is no feasible way to sample biopsies during capsule endoscopy.
Number of bioptic samples
According to an official recommendation from the European Society of Pathology and ECCO[4,5], a diagnostic endoscopy should include at least two bioptic samples from at least five or six bowel segments including the terminal ileum and rectum. However, there is still no official recommendation for patients on treatment. Many gastroenterologists still prefer to perform an extensive sampling of severely affected regions and avoid normally appearing segments. This may falsely underestimate an overall histological inflammatory severity and negatively affect some scoring indices such as GHAS,which includes the number of affected regions into a final score.
Assessment of the disease activity in pediatric IBD
A Histopathological scoring index primarily designated for the pediatric population has not been established. Adult indices are used instead, but their feasibility for children is not self-evident. Studies aiming at the predictive value of histology in pediatric IBD are still limited in number. A few years ago,our group performed a retrospective analysis of 63 children with CD[64]. The microscopic severity of the inflammation at the time of diagnosis assessed by GHAS showed moderate correlation with endoscopic activity evaluated by Simple Endoscopic Score for Crohn's Disease (r= 0.48,P= 0.0001), no correlation with clinical activity of the disease, and had no predictive value for the development of defined complications [bowel stricture, intraabdominal or perianal abscess or fistula, initiation of antitumor necrosis factor (anti-TNF) therapy] during at least one year of follow-up. On the other hand,endoscopic activity appeared to be a predictor of the complications (HR 3.20, IQR 1.04-4.91,P= 0.037).With regards to pediatric UC, our recently conducted retrospective study[65] including 49 children with UC showed that microscopic activity of the inflammation assessed by NHI and GS had no predictive value for complications development (acute severe colitis, need of colectomy, initiation of anti-TNF therapy, initiation of systemic 5-aminosalicylic therapy and systemic corticosteroid use). By contrast,levels of fecal calprotectin (FCPT) and clinical activity of the disease assessed by Pediatric Ulcerative Colitis Activity Index (PUCAI) showed to be independent predictors of the systemic 5-aminosalicylic acid induction (FCPT: HR 2.42, IQR 1.042-5.631,P= 0.040; PUCAI: HR 2.98, IQR 1.011-8.787,P= 0.048)and systemic corticosteroid use (FCPT: HR 2.517, IQR 1.115-5.681,P= 0.026; PUCAI: HR 2.98, IQR 1.011-8.787,P= 0.048).
ARE WE ASKING THE RIGHT QUESTION?
Histological activity in IBD is defined by the presence of neutrophils. Hence, strictly speaking, the histological index of the disease activity should be based on the extent of neutrophilic infiltration, their localization (lamina propria, superficial epithelium, cryptitis, crypt abscesses), and the presence of mucosal defects. Grading of the microscopic disease activity thus seems to be apparently straightforward. However, such grading per se is of no use if it does not provide any additional value to other means of disease activity assessment such as endoscopy or non-invasive biomarkers. There is thus a fundamental question about whether histological appearance is predictive of subsequent clinical outcomes. As mentioned before, the bulk of evidence suggests that persisting microscopic activity of the disease harbors an increased risk of development of complications. However, disease activity is not the only microscopic variable associated with an adverse clinical course. Other microscopic features such as basal plasmacytosis or granulomas have proven prognostic value. According to Johnsonet al[66], the presence of granulomas was associated with increased serum levels of C-reactive protein, higher rates of stricturing and penetrating disease, higher rates of steroid, immunomodulators, biological therapy and narcotic use and higher healthcare utilization. With regards to basal plasmacytosis, the aforementioned meta-analysis by Guptaet al[8] demonstrated its predictive value for clinical recurrence in UC patients in endoscopic remission, as well. However, these features represent signs of chronicity rather than activity. Apart from that, there is still unresolved issue regarding the contribution of eosinophils,macrophages and other inflammatory cell types. Therefore, it seems to be more convenient to search for a suitable combination of microscopic features, providing the most accurate prediction for the subsequent clinical course of the disease, with a presence of neutrophils as a sign of the disease activity among the assessed variables. Apropos, the very presence of both chronic lymphoplasmacytic and active neutrophilic inflammatory infiltrate in one scoring index of disease activity may not properly reflect the biology of the process. In a majority of the scoring indices, the presence of isolated chronic inflammatory infiltrate is considered a lower grade of the inflammatory activity, aggravating with the increasing presence of neutrophils and eventually with the appearance of mucosal defects. But the lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate reflects rather chronicity of the process than its activity and these two variables don’t necessarily represent a continuum. Such a hypothesis was taken into consideration in the recently established scoring index called Inflammatory Bowel Disease-Distribution, Chronicity, Activity(IBD-DCA) score (Table 6)[67]. The score was proposed at Erlangen International Consensus Conference and consists of three parameters - Distribution (D), Chronicity (C) and, Activity (A), which are assessed in this order. Distribution determines the overall extent of the disease, independently of the presence or absence of the activity. Chronicity is represented by the disrupted mucosal architecture, presence of basal plasmacytosis and increased lymphoplasmacytic infiltration in lamina propria. Activity is marked by the presence of neutrophils. The score thus represents not only a scoring index of the histopathological inflammatory activity, but provides information about the overall microscopic severity of the disease. According to the recent evidence[68], it showed moderate inter-rater reliability for parameter D(median intraclass correlation coefficient 0.645), poor to moderate for parameter C (0.568), and moderate to good for parameter A (0.748) for UC and moderate to good for parameter D and A (0.655 and 0.644 respectively) and poor for parameter C (0.303) for CD. The intra-rater agreement was moderate to excellent for D and C parameters (0.894 and 0.798 respectively) and good to excellent for A (0.909)parameter for UC, whilst CD showed moderate to excellent agreement for parameter D (0.854), poor to excellent for parameter C (0.714) and good to excellent for parameter A (0.888). There is a moderate correlation with NHI and Simplified GS. The unique feature of the score is its versatility, which means that it can be used for both CD and UC, as well as for IBDU, which represents 5%-15% of both adult and pediatric IBD[69-71] and in some cases becomes a definite diagnosis. By this, the score questions the necessity of separate scoring indices for CD and UC. Both diseases share a similar pattern of inflammatory activity and the inferior utility of scoring indices for CD stems rather from the segmental and transmural nature of the disease that from inappropriate assessment of its histological activity. Such a hypothesis is also supported by several studies. In the aforementioned study of Kirchgesneret al[36]assessing a predictive value of histology for the development of colorectal cancer, the authors used NHI to evaluate microscopic disease severity for the whole IBD cohort. In both UC and CD, the grade of the NHI correlated with the risk of cancer development. In the study by Löwenberget al[72], the authors evaluated the ability of vedolizumab to induce endoscopic and histological remission in patients withCD and the microscopic disease activity in the study was assessed by RHI. Using UC scoring indices for CD patients is suggested also by the recent expert consensus panel[53].

Table 6 Inflammatory Bowel Disease-Distribution, Chronicity, Activity score
STILL FAR FROM THE HISTOLOGICAL REMISSION
Although achieving deeper mucosal healing is presumably associated with improved clinical course, it is far from synonymous with histological remission. However, establishing its proper definition remains challenging. In previous studies, the definition varied from the absence of active inflammation to the complete normalization of bowel mucosa. A recent position paper from ECCO defines histological remission as a "return to normal". Cessation of the microscopic activity undoubtedly correlates with a lower percentage of future complications. But even a mucosa without a presence of neutrophils may display increased chronic lymphoplasmacytic infiltration or architectonic changes that may aggravate the clinical course of the disease. Returning to the meta-analysis by Guptaet al[8] once more, their analysis showed that disrupted mucosal architecture was one of the features independently predicting the disease recurrence (OR 2.22). On the other hand, strict adherence to the histological normalization of the mucosa in each patient in endoscopic and clinical remission could lead to an unreasonable burden of aggressive therapy including all possible side effects. More studies need to be performed until a proper degree of histological normalization with an appropriate cost-benefit ratio will be established. One way or another, a complex histopathological scoring index assessing not only a disease activity but rather an overall microscopical severity seems to be necessary before we finally reach a standardized definition of the histological remission in IBD.
CONCLUSION
A proper assessment of the histological disease activity in IBD represents an essential component of the overall disease severity evaluation and provides important data for the subsequent clinical management of the patients. Many histopathological scoring indices exists, especially for UC, and they seem to be useful tools for the proper objectivization of the microscopic activity. However, their broader validation,subsequent implementation in routine bioptic practice and establishing the universally accepted definition of the histological remission are necessary before we could recognize the absence of the microscopic activity as the primary therapeutic target in IBD.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We would like to thank Drab D for his contribution during the manuscript revision.
FOOTNOTES
Author contributions:Fabian O collected the data, performed the data analysis and wrote the paper; Bajer L participated in the data analysis and wrote the paper.
Supported byMinistry of Health of the Czech Republic, No. NV18-09-00493 and No. NU21J-06-00027.
Conflict-of-interest statement:All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Open-Access:This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial (CC BYNC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is noncommercial. See: https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/
Country/Territory of origin:Czech Republic
ORCID number:Ondrej Fabian 0000-0002-0393-2415; Lukas Bajer 0000-0002-3815-3120.
S-Editor:Gao CC
L-Editor:A
P-Editor:Gao CC
 World Journal of Gastroenterology2022年36期
World Journal of Gastroenterology2022年36期
- World Journal of Gastroenterology的其它文章
- Machine learning-based gray-level co-occurrence matrix signature for predicting lymph node metastasis in undifferentiated-type early gastric cancer
- Atherogenic index of plasma combined with waist circumference and body mass index to predict metabolic-associated fatty liver disease
- Deciphering the role of transforming growth factor-beta 1 as a diagnostic-prognostic-therapeutic candidate against hepatocellular carcinoma
- P2X7 receptor as the regulator of T-cell function in intestinal barrier disruption
- Liver-specific drug delivery platforms: Applications for the treatment of alcohol-associated liver disease
- Esophageal magnetic compression anastomosis in dogs
